Preface
The delivery of many potentially therapeutic and diagnostic compounds to specific areas of the brain is restricted by brain barriers, the most well known of which are the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) barrier. Recent studies have shown numerous additional roles of these barriers, including an involvement in neurodevelopment, control of cerebral blood flow, and, when barrier integrity is impaired, a contribution to the pathology of many common CNS disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and stroke. Thus, many key areas of neuroscientific investigation are shared with the ‘brain barriers sciences’. However, despite this overlap there has been little crosstalk. This lack of crosstalk is of more than academic interest as our emerging understanding of the neurovascular unit (NVU), composed of local neuronal circuits, glia, pericytes and the endothelium, illustrates how the brain dynamically modulates its blood flow, metabolism, and electrophysiological regulation. A key insight is that the barriers are an essential part of the NVU and as such are influenced by all cellular elements of this unit.
Introduction
There is a commonly held notion that the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a simple anatomical structure that restricts the traffic of molecules in and out of the CNS, but otherwise is not very relevant to neuroscience. This view is flawed; however, as brain barrier sciences and neuroscience are inextricably linked in many areas of neurophysiology and neuropathology.
The BBB is one of a number of blood-CNS interfaces, which also include the blood-CSF barrier, the blood-retinal barrier, the blood-nerve barrier and the blood-labyrinth barrier, all of which are important for the physiological functions of the CNS (Figure 1). Among these interfaces, the BBB occupies by far the largest surface area. A wide range of neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease1–3, Parkinson’s disease4, multiple sclerosis5, 6, trauma7, 8, brain tumours9, 10, stroke11–14 and epilepsy15 are associated with perturbations in the normal BBB that contribute to their pathology (Table 1, references for Table 1 are in supplementary material S3). Furthermore, the cells that constitute the BBB play a part in the control of cerebral blood flow16, 17 and neuronal development18. Thus, it is important to recognize that the BBB has many other roles and is not simply a control point for molecular trafficking in and out of the brain.
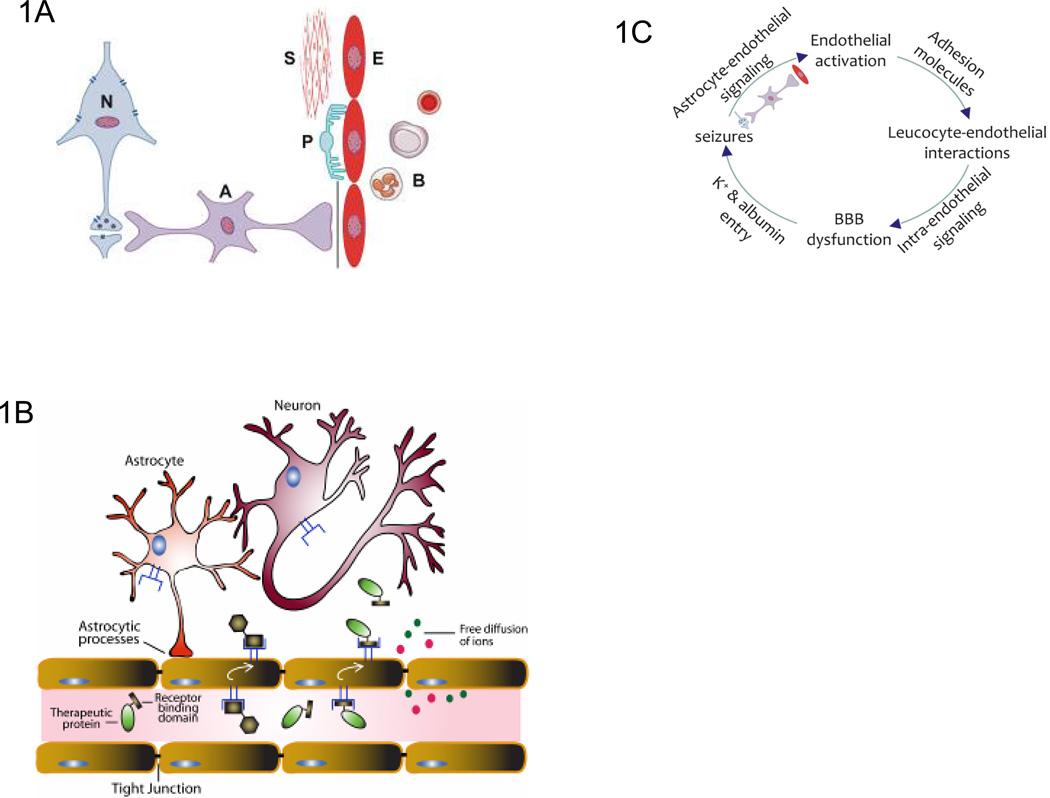
Figure 1. The extended Neurovascular Unit (NVU).
a. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an essential part of the neurovascular unit (NVU). A classical view of the NVU incorporates neurons, glial cells such as astrocytes and microglial cells closely juxtaposed with vascular endothelial cells, pericytes and smooth muscle cells. Blood cells, particularly PMN cells, lymphocytes and monocytes, also interact with the BBB endothelium and are therefore an integral part of this unit. The interactions between these cellular components and inter- and intra-cellular signaling regulate NVU function to maintain homeostasis, or to respond to inflammation and disease.
b. Receptor-mediated transcytosis of proteins at the BBB. Transcytosis is a receptor-mediated transport mechanism by which proteins that are targeted to the CNS bind extracellular receptors in vascular lumen, transport across the BBB endothelial cells, and are released in brain parenchyma. The presence of specific receptors (i.e. the insulin receptor) on the surface of BBB endothelial cells has allowed targeting and transport of some therapeutic proteins to the CNS44, 128.
c. Pathological signaling in the extended NVU. The proposed sequence order is based on data available from the epilepsy field144 and requires further exploration in the context of other brain diseases, including stroke and AD. The cycle starts with altered expression of vascular cell adhesion molecules and interactions of leucocytes with the endothelium, initiating intra-endothelial signals that alter BBB function and lead to neural tissue dysfunction as a consequence of K+ and albumin entry into the brain interstitium. Astrocytes detect the altered neuronal activity and transmit signals back to the BBB thereby facilitating interactions with leucocytes and turning the sequence into a vicious circle that maintains and exacerbates the pathological state. The activated endothelium may, as an integral part of the extended NVU, disturb neuron–astrocyte interactions, thereby adding an additional layer of pathological signaling to the process. Astrocytes emerge from this cascade as a primary target for interventions that aim to interrupt the proposed cycle.
Table 1.
Diseases that affect the BBB or diseases impacted by the BBB.
|
Disease or Process |
BBB Protein Affected – or mechanism |
|---|---|
|
Neurodegenerative diseases Alzheimer disease |
RAGE - receptor for advanced glycation end products – influx of Abeta 163 |
| LRP-1: multi-ligand lipoprotein receptor – efflux of Abeta 163 | |
| P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) is reduced at blood-brain barrier and seems to play a critical role in clearing Abeta from brain 164–166 | |
| Changes in ABCG2 is related to cerebral amyloid angiopathy and controls blood-brain barrier transfer of Abeta 167 | |
| Parkinson disease | Polymorphism in P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene association?; ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B, member 1 (ABCB1) gene encoding the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) 168, 169 |
| Cerebrovascular diseases | |
| tPA and reperfusion induced hemorrhage | MMPs released by neutrophils and possibly endothelial cells degrade tight junction (TJ) proteins and BM – increase risk of hemorrhage 170–173 |
| VEGF – blood brain barrier breakdown | Occludin and claudin-5 : down regulation of mRNA and protein 174 |
| Familial Cerebral Cavernous Malformations | CCM1/KRIT1, CCM2 or CCM3/PDCD10 localized in endothelial cells and perhaps astrocyte end feet- venous malformations with bleeding 175, 176 |
| Ischemic brain edema | BBB breakdown due to MMP9 release by neutrophils which degrades occludin, claudins, JAM, basement membrane (BM) 177–179 SUR1-regulated NC(Ca-ATP) channel mediates ischemic cerebral edema 180 |
| Acute mountain sickness and high altitude cerebral edema | Vasogenic edema 181 |
| Epilepsy and seizures | |
| Epilepsy and Exercise Induced Dystonia | GLUT1 mutations in brain endothelial cells (BEC) 182–184 |
| Resistance to pharmacotherapy in some patients with epilepsy | multidrug efflux pumps from the ATP Binding Cassette (ABC) superfamily (P-glycoprotein) at the BBB 185, 186 |
| Alexander Disease – large brain, seizures, retardation | GFAP mutations – blood brain barrier abnormalities 187 |
| Leukoencephalopathy with epilepsy | ClC-2 is a broadly expressed plasma membrane chloride channel – epilepsy, white matter degeneration, retinal degeneration in mice 188 |
| Infections | |
| HIV entry into brain | HIV activation of STAT and rho kinase down regulate claudin-5, ZO-1, and ZO-2 in endothelial cells which may increase HIV entry 189–191 |
| Susceptibility to certain types of brain infections – e.g., malaria and CNS listeria moncytogenes | MDR1A (ABCB1) deficiency at BBB-susceptibility to cerebral malaria; opc gene in Meningococcus produces protein that binds HBMECs via α 5 β 1 integrin receptors via fibronectin 192–194 |
| CNS infections in general | Pathogens co-op BBB cellular machinery to enter the brain 165 |
| NeuroAIDS in HIV | BBB efflux systems keep out antivirals from brain, fostering neuroAIDS 195 |
| Malaria | Effect protein expression and permeability of human endothelial cells selectively from brain 196 |
| Neuroinflammation and brain tumors | |
| White blood cell oxidative stress causes adhesion to endothelium and transmigration across BBB | White blood cell (selectins, VLA-4, CD44,a4b7 integrin) and brain endothelial (selectin ligands, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, CD44) proteins mediate migration across BBB 197–199 |
| CD8+ cytotoxic T cell mediated BBB breakdown and edema | Perforin release degrades tight junction proteins 200 |
| Brain Edema – tumor, inflammation, others | Aquaporins (astrocyte end feet) 201, 202 |
| Brain Edema – role of steroids; prednisone and dexamethasone decrease BBB leakage in acute MS plaques, tumors, and other pathologies | Steroids act on Glucocorticoid response elements (GRE) on promoter of tight junction genes (occludin, claudins, cadherin) to increase TJ proteins and increase BBB tightness 203–205 |
| BBB break down in Multiple Sclerosis: Monocyte- endothelial interactions induce tPA in endothelial cells | tPA induction of ERK1/2 in endothelial cells mediates monocyte transmigration across BBB and control breakdown of occludin 206 |
| BBB break down in MS: role of IL17 and IL22 | T(H)17 lymphocytes release IL17 and IL22 that act on receptors on BEC that results in degradation of TJ proteins and opening of the BBB 207, 208 |
| Prevent leukocyte trafficking across the BBB – decreased Multiple Sclerosis relapses | Monoclonal antibody to alpha4 integrin (Natalizumab) – adhesion molecule on leukocytes necessary to attach to and cross the BBB in EAE 209–211 |
| Inflammatory Pain – Cytokines mediate BBB breakdown | Down regulation of Occludin and claudin-5 212 |
| Metabolic and psychiatric diseases | |
| Brain Edema – associated with diabetic ketoacidosis and cerebral ischemia | Na-K-Cl cotransporter and Na/H exchanger at BBB 213–218 |
| Adrenoleukodystrophy – abnormal white matter in brain with a wide range of neurological findings; retinal degeneration | ABCD1 gene mutation – ATP binding cassette disorder; ATP-binding cassette (ABC) superfamily 219, 220 |
| Obesity - leptin released from adipose tissue and binds to leptin receptor to modulate food intake | Deficient BBB transporter protein function - reduced leptin transport across the BBB 221–223 |
| Imerslund-Gräsbeck syndrome- familial B12 malabsorption – dementia and white matter abnormalities | Amnionless (AMN) mutations- possible B12 transport into brain 224 |
| Canavans Disease – large brain, seizures, retardation, white matter degeneration, other signs | Mutations in aspartoacetylase lead to accumulation of N-acetylaspartate (NAA) 225 |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis | Loss of the GUSB transporter with maturation underlies difficulty in treatment 226 |
| Depression | Polymorphisms in the drug transporter gene ABCB1 predict antidepressant treatment response in depression 227 |
| Hepatic encephalopathy | Affects potassium homeostasis in astrocyte and produces swelling and disrupts control of extracellular potassium 228–230 |
The common wisdom has been that the BBB consists of endothelial cells and is either open or closed depending on the status of tight junction proteins that create a restrictive, fixed barrier. We now know that the BBB is, in fact, quite dynamic, with a wide permeability range that is controlled by intra- and intercellular signaling events among endothelial cells, astrocytes and neurons in the BBB and other cells that are in contact with the BBB, as well as by paracellular changes at the BBB. A further key conceptual advance has been the discovery that the BBB is an integral part of the NVU (see below)19 (Figure 1A).
The complex regulation of barrier properties is far from understood. Gaining better insight into the physiological and pathophysiological processes that alter intra- and intercellular junction protein distribution and function is important for understanding how the barrier can be fixed when it does not function properly and how it can be manipulated for therapeutic purposes. Suffice it to say, herein lies the opportunity for interdisciplinary approaches to expand our knowledge and improve strategies for treatments of neurological disorders.
Many factors have contributed to the lack of interaction between neuroscientists and brain barriers scientists, including the complexities of each field and the numerous gaps in our understanding of the BBB. This, in turn, has resulted in relatively little emphasis on brain barrier sciences as an interdisciplinary topic or educational objective, both of which would facilitate such communication. However, recent advances have increasingly emphasized the common ground between the two fields of study and the urgency for crosstalk. The present review provides a vision for future study that integrates both disciplines, highlighting areas of relevance and convergence.
A meeting of minds
In an effort to bring the two fields of neuroscience and brain barrier science closer, an international panel of experts was assembled in March 2009 to discuss current areas of overlapping interests where the expertise and observations of one group might advance the research progress of the other. Leaders in the fields of neuroscience and brain barriers science identified five topic areas as central to advancing the treatment of CNS disorders; these included molecular physiology of the brain and brain barriers; intercellular communication within the NVU; transport biology in the brain and brain barriers; neurodevelopment and the brain barriers; and imaging the structure, function and dynamics of the brain and brain barriers.
Within each topic, four main questions were addressed: What are the key scientific opportunities in the neuroscience field that may be applied to the brain barriers field and vice versa?; What is the status of the science in the topic area, including key scientific advances made in the respective fields over the past four years and are they relevant to the other field?; What are the barriers to progress in the topic area?; and What are the highest-priority recommendations for developing and advancing knowledge in the topic area, including the key resources and approaches needed?
For each of the five key topic areas, an international panel of experts, co-chaired by internationally renowned neuroscientists and brain barriers scientists drafted reports answering the four primary questions as well as addressing the key question “What is the single most important issue that would advance research in each topic area?” The draft reports were discussed among approximately 150 neuroscientists and brain barrier scientists at the 2009 Annual Blood-Brain Barrier Consortium Meeting, at Salishan Resort, Gleneden Beach, Oregon, USA (see supplementary information S1 and S2 (box)). The co-chairs and working groups incorporated into their final reports the discussion and input from the combined group of scientists (see supplementary information S4 for the final reports from each of the five topic areas (box)).
Physiology of the NVU
The NVU consists of an endothelial cell monolayer (connected by tight junctions and resting on the basal lamina), integral neighboring cells (including pericytes and smooth muscle cells) and astrocytic endfeet covering >98% of the vascular wall and occasional neuronal terminals. The astrocytes also extend processes that surround synapses and can thereby link neuronal activity and the oxygen and nutrient supply. Finally, components of the NVU include the circulating blood cells such as polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells, lymphocytes and monocytes that adhere and roll along the vascular lumen and perform surveillance of neural signaling and cellular activity20 (Figure 1A).
The endothelial cells of the NVU are highly polarized, with different integral membrane proteins at the luminal and abluminal surfaces. These include various receptors, enzymes and transporters that support the functions of this cellular barrier within the NVU. For example, the endothelial barrier performs vectorial transport of solutes, including ions, nutrients and drugs, at the blood--brain interface. It also engages in highly specialized interactions with blood cells through specific luminal receptors and with elements of the basal lamina and underlying cells (e.g., astrocytic endfeet and neuron terminals) at the abluminal surface through specific abluminal plasma membrane proteins. Furthermore, astrocytes and pericytes possess their own complement of transporters, channels, receptors and signalling mechanisms with which they coordinate the role of the NVU in supporting nervous system function.
The tripartite synapse and the NVU
A major notion that has emerged from neuroscience over the past few years is the concept of the ‘tripartite synapse’, which has compelled neuroscientists to consider the influence of glia in synaptic function21, 22. In the cerebral microcirculation, tripartite synapses composed of pre and postsynaptic endings, together with their related glia, are structurally and functionally related to the brain’s capillary bed and together (Figure 1A) form the NVU. The role of the NVU interface in the context of the tripartite synapse is just beginning to be understood. The cellular components include the endothelium (forming the barrier proper at the capillary level), astrocytic endfeet, pericytes and circulating immune cells, adjoined at some distance by nerve endings and vascular smooth muscle cells found at the arterial level19, 23 (Figure 1A and B). Note, immune cells indeed sneak into the NVU and are defined further in this manuscript as part of the extended NVU.
The NVU, together with the basal lamina and extracellular matrix components, engages in complex signaling processes (fast and slow; active and trophic). Documented examples include the propagation of Ca2+ waves through the NVU24, neuro-metabolic coupling25, neuro-hemodynamic coupling, neuro-angiogenic coupling and neuro-trophic coupling26, 27 and cell adhesion-based signaling networks28. These NVU signaling processes are also linked to membrane transport29–33, regulation of cellular permeability (specific, selective or via paracellular pathways)32, 34, 35 and intracellular metabolic cascades25, 36, 37.
Dynamic regulation of brain barrier permeability by the NVU
Cells of the NVU form a complex and fine-tuned transport machine that balances the influx of nutrients and the efflux of wastes, toxins, and drugs to maintain CNS homeostasis38. Numerous factors regulate the barrier permeability of the NVU, including modulation of membrane transporters and transcytotic vesicles and modulation of transcellular permeability34 (Figure 1B).
The importance of investigating NVU transport proteins is underscored by the recent finding that 10–15% of all proteins in the NVU are transporters39. In 2003 it was estimated that only about 50% of brain barrier transporter proteins had been identified39, 40. Since then, several new transporters have been detected and localized in the brain endothelium and the choroid plexus (which forms the blood—CSF barrier). The identity and cellular location of multiple — generally efflux — transporters that are present in the NVU and that function possibly in drug transport are shown in Figure 2 (cell-type specific differences in expression are not shown here). New neuroscience discoveries include structural and mechanistic insights into coupled transporters (e.g. GABA and norepinephrine transporters (GAT/NET)), excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs)41 and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters42. Improved understanding of the physiological and biophysical mechanisms underlying transport function43–46 should be applicable to both general brain function and dysfunction in disease.
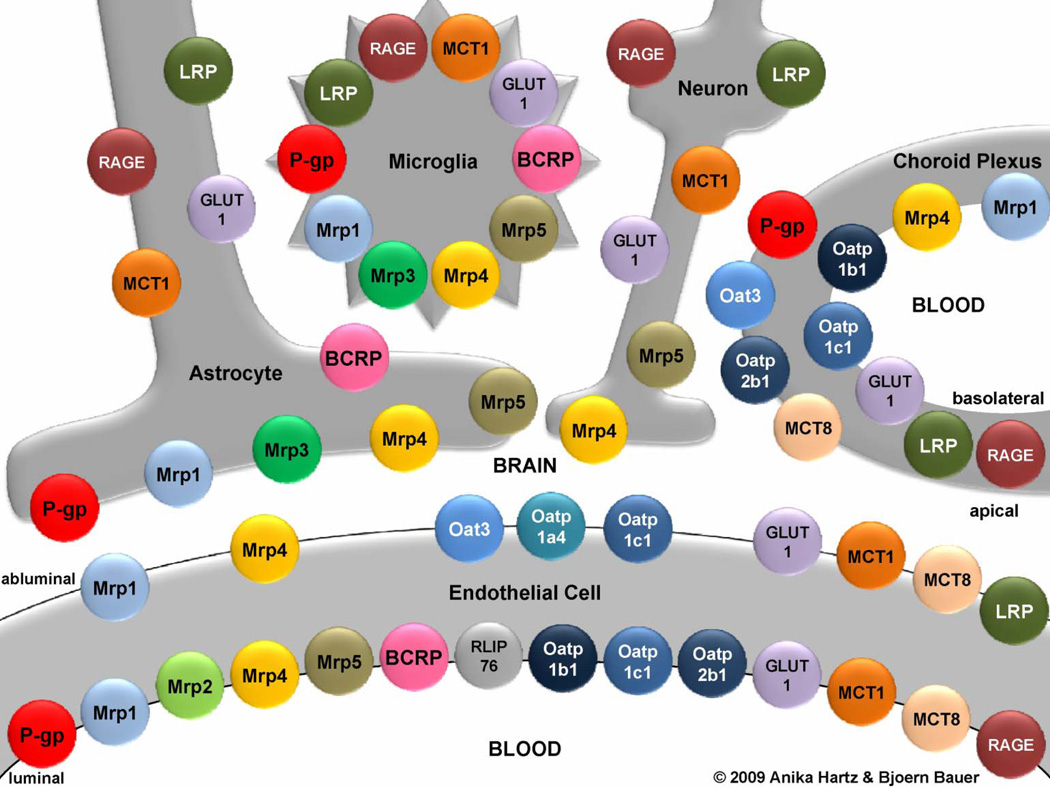
Figure 2. Primary transporters in the neurovascular unit.
The spatial and cellular relationships of the transporters are shown. Only proteins detected at the protein level are depicted. For a more complete listing of carrier-mediated transport systems at the blood-brain interface see Ohtsuki and Terasaki38. The following acronyms are used: BCRP, breast cancer resistance protein; GLUT1, glucose transporter-1; LRP, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein; MCT, monocarboxylic acid transporter; Mrp, multidrug resistance protein; Oat, organic anion transporter; Oatp, organic anion transporting protein; P-gp, P-glycoprotein; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products; RLIP76, Ral-binding protein-1. Modified, with permissions, from Refs. 80 and 161.
Ion transporter proteins in cells of the NVU play an important role in maintaining fluid balance in the brain and our understanding of their role in water and electrolyte movement among cells of the NVU has recently been expanded. These studies largely focused on whole brain and/or hypoxia in neurons and astrocytes, and led to the discoveries of a family of HCO3− transporters, the electrogenic and electroneutral Na+/HCO3− transporters (NBCe and NBCn, respectively) and Na+-driven Cl−/HCO3− exchangers (NDCBE)47–49. Expression levels of these transporters varies with brain region and cell type, with prominent expression of both NBC and NDCBE transporters reported for neurons and choroid plexus and little or no expression in astrocytes. Little is known about expression and function of the NBC and NDCBE transporters in cells of the cerebrovasculature.
Recent studies have provided important new insights regarding the role of aquaporins AQP4 in astrocytic endfeet50 distribution of water within the brain51–55 and have shown that abnormal fluid dynamics or AQP malfunctions may have pathological consequences56. Several aquaporins are found in brain including AQP1, 3, 4, 5, 8, and 9, with AQP1, 4 and 9 most heavily studied. While AQP9 is found in the astrocyte cell body, AQP4 is abundant in perivascular astrocyte endfeet and also where the astrocyte is in close apposition to neurons. Choroid plexus exhibits AQP1 and 4. Endothelial cells of the NVU appear to have minor amounts of AQP4 at best. Pathways by which water moves through the endothelial cells of the NVU are largely understudied. A relatively recent finding is that that CO2 and NH3 conductances are regulated by AQP1 and AQP457. This has created a paradigm shift in the way we think about how metabolically relevant gases move through the NVU, i.e. that diffusion of the gases across plasma membrane is not by simple diffusion but rather, by facilitated diffusion via the aquaporins.
It has long been accepted that the NVU functions as a selective barrier to various substances passing between blood and brain, but these new discoveries have lead to a more developed understanding of the NVU which recognizes the NVU as a functionally complex blood–brain interface with multiple, interacting roles.
The NVU as a barrier to xenobiotics
One of the most important roles of the NVU is to limit xenobiotics, including CNS drugs, from entering the brain. This barrier function is mainly achieved by two components in the brain capillary endothelium: ATP-driven membrane transporters known as ‘efflux transporters’ and tight junctions that ‘seal’ spaces between endothelial cells.
Signaling pathways that regulate efflux transporters
Transporter-mediated export of xenobiotics can affect the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a large number of therapeutics and poses a challenge for the ability to deliver drugs into the CNS. Direct transporter inhibition has been pursued as one strategy, but it leaves little control over the extent and duration of the inhibition. Accordingly, transporter inhibitors are currently not in clinical use. Recent efforts have therefore focused on targeting the intracellular signaling pathways and molecular switches that control efflux transporter regulation, for several reasons. First, modulating these pathways and switches would allow fine-tuning of transporter activity so that transporters can be turned off for controlled periods, thus providing a time window to deliver drugs58. Second, such strategies could be used to up-regulate expression and activity of efflux transporters in the NVU in order to minimize brain side effects associated with the treatment of a disease in the periphery (e.g., “chemobrain” in cancer patients)59. Third, efflux transporters are affected by — and likely contribute to — disease pathology of CNS disorders that are accompanied by inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotransmitter release, including cancer, epilepsy, and Alzheimer’s disease60–62. Thus, understanding the signaling pathways that regulate efflux transporter expression and activity is likely to be useful for improving CNS drug delivery, protecting the brain during systemic treatment, and preventing pathogenesis or slowing the progression of several CNS diseases.
For example, three major pathways have been identified that regulate P-glycoprotein (P-gp), a major efflux transporter at the blood-brain barrier that limits brain penetration of therapeutic drugs63. One pathway is triggered by the inflammatory mediator tumor necrosis factor- α (TNF-α), which signals through TNF-R1 resulting in release of endothelin-1 (ET-1), which in turn signals through the ETB receptor resulting in signaling through nitric oxide (NO) synthase and protein kinase C (PKC) βI to alter P-gp expression and function58, 64–66. Indeed, activating PKC βI reduced P-gp activity and enhanced delivery of small molecule therapeutics into the brain58. A second pathway involves the neurotransmitter glutamate, which signals through the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and the prostaglandin E2 receptor EP1 to up-regulate P-gp expression and activity67–70. Inhibiting this pathway prevents seizure-induced P-gp up-regulation and improves brain penetration of anti-epileptic drugs and reduces epileptic seizures71. The third pathway involves activation of xenobiotic-nuclear receptors such as the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), the pregnane xenobiotic receptor (PXR) and the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR)72–78 to regulate transporter expression. For example, in a recent study, activation of PXR has been used to restore brain endothelial P-gp in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model, which resulted in enhanced amyloid- β clearance from the brain60. In addition, several of the signaling pathways have common elements (e.g. TNF-α, NF-κB, COX-2) that may be potential therapeutic targets.
Thus, findings from studies using physiological and pathophysiological modulators, pharmacologic inhibitors and activators of efflux transporters may be useful for improving the delivery of drugs into the brain, protecting the brain from harmful xenobiotics and alleviating CNS disorders79, 80. In addition to studying brain barrier transporters, understanding the molecular regulation of tight junctions may provide therapeutic opportunities in diseases where endothelial barrier integrity is disrupted81.
Role of tight junctions in NVU function
In the brain capillary endothelium, tight junctions that seal the spaces between neighboring endothelial cells represent a passive barrier that restricts paracellular diffusion of water soluble solutes, including drugs, from blood to brain. The role of tight junctions and their key constituent proteins, claudins and occludins, in the regulation of barrier function is beginning to be elucidated. However, it is not yet known how these and other proteins interact to create the highly effective and precisely regulated tight junction. For example, although genetic ablation of claudin 5 has shown that this tight junction protein is necessary to limit movement of small molecules into the brain82, other studies have shown that claudin 5 is expressed in all endothelial cells, not just those in the NVU. Conversely, occludin is brain endothelial cell-specific but is not required for barrier function83. Thus the molecular basis for the tightness of the cerebrovascular endothelium compared to endothelia in most other tissues remains unknown.
NVU and the control of cerebral blood flow
Communication between neurons and glial cells — especially astrocytes84 — in response to electrical and synaptic activity can influence cerebral blood flow. This occurs under conditions of physiological levels of neuronal activity85, strong or pathological stimuli86 and spontaneous activation87. Astrocytic calcium signals propagate to astrocytic endfoot extensions that are in contact with blood vessels and also extend to neighboring endfeet88, thereby triggering the release of vasoactive messengers89–91, thus altering local cerebral blood flow. Neuroimaging techniques such as functional MRI use these changes in cerebral blood flow as an indicator of CNS activity.
A key finding is that astrocytic endfeet release vasodilatory as well as vasoconstrictive messengers and this depends on the availability of oxygen: if oxygen availability is low, vasodilators prevail while if oxygen availability is high vasoconstrictors predominate92. Vasoactive messengers released by astrocytes include arachidonic acid, prostaglandin members of the epoxy-eicosa-trienoic acid family, and NO as vasodilators, and ET and OH-eicosa-tetraenoic acid products as vasoconstrictors17. As astrocytes make extensive contacts with smooth muscle cells at the arteriolar level93, vasotropic actions of astrocytic calcium signals may also affect smooth muscle cells directly or indirectly via brain endothelial cells (which in turn secrete vasoactive substances such as NO)89.
The observation that calcium signals in astrocytic endfeet located at the blood-brain interface suggests that these signals may influence endothelial cells at less than 0.1 µm distance and thus could cause dynamic alterations in BBB function25. Clearly the astrocyte is a major communication link between the multiple parts of the NVU.
Neurodevelopment of the brain barriers
Research on vascular and neuronal development has been converging over the past decade, for example in the study of angiogenesis in fetal brain. There are at least two major reasons for this: first, there is evidence for shared molecules and coordinated cellular mechanisms during the development of these systems94, 95; and second, there is evidence that neurogenesis and angiogenesis are co-regulated in embryonic and adult brains94, 96, 97.
The CNS vasculature develops by angioblastic invasion of the head region that occurs in early phases of embryogenesis and this vasculogenic process establishes the extracerebral vascular plexus that eventually covers the entire surface of the neural tube98–100. After the primary vascular plexus is formed, further vascularization of the CNS is exclusively achieved by angiogenesis from the perineural vascular complex. Driven by metabolic demands of the expanding neuroectoderm, capillary sprouts invade from the extracerebral vascular plexus toward the periventricular zone101. Once formed, the nascent brain vasculature is further stabilized by the recruitment of mural cells and the formation of the extracellular matrix, and is fine-tuned by microenvironmental cues from the neighboring cells102, 103. Through this process of maturation all the components of brain vascular network acquire the phenotype that allows them to form a fully differentiated NVU.
It has been known for decades that there is a functional NVU well before the middle of the 150-day gestation of sheep104–106 and the existence of tight junctions during brain development has also been noted in various other species, including humans, as summarized elsewhere107. Over the past five years, unequivocal evidence has been published of both structural and functional barriers in the developing brain. In fact, studies using small molecular weight markers have shown that functionally effective tight junctions are present as soon as blood vessels begin to penetrate the early CNS parenchyma and as soon as epithelial cells of the choroid plexuses begin to differentiate108, 109.
These tight junctions provide the basis for selectivity of barrier interfaces. Efflux transporters (e.g. P-glycoprotein, breast cancer resistance protein, multidrug resistance proteins), which can reduce the accumulation of drugs and toxins in the brain, are expressed in cerebral endothelial and choroid plexus epithelial cells early in development110–112. A recent study reported that pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis113. Specifically, the data indicated that pericyte-endothelial cell interactions regulate some properties of the BBB during development, and disruption of these interactions may lead to BBB dysfunction and thus, to neuroinflammation as part of the response to CNS injury and disease113.
The functional role of the brain barriers during development is to provide the brain with a specialized internal environment. As shown in Figure 3, one major barrier difference is that the neuroependyma lining the cerebral ventricles constitutes a barrier during early development but not at later times, when it has become the adult ependyma. The molecular properties114 and specific functions of the brain barriers alter as the brain matures to reflect its changing role, influenced by the surrounding neural environment and its intrinsic developmentally regulated properties. In addition, the vasculature interacts with the neural environment – this includes shared molecular processes that influence the growth and maturation of the brain at specific stages of its development94. Several key studies have identified important CNS parenchymal cell-derived molecular signals, including angiotensinogen and Wnt, that seem to regulate the formation and function of the cerebrovasculature and thereby the NVU18, 27, 94, 104, 115. In addition to being essential for angiogenesis, Wnt/βcatenin signaling appears to be essential for expression of cerebral endothelial cell specific transporters such as slc2a1 (glut-1), slc7a1 (CAT1), and slc7a5 (TA1), but not tight junction molecules including occludin and ZO-1 or pan-endothelial molecules including PECAM and VE-cadherin27. The finding that Wnt regulates CNS-specific angiogenesis and induces specific NVU properties such as gene expression and restricted permeability27, 94 suggests that CNS angiogenesis and brain barrier formation are linked by Wnt regulation and mutual interactions. The similarity of some immune and neural molecular mechanisms during development might also have implications for vascular development of CNS barriers, but this has so far remained unexplored. Combining vascular and neuronal developmental approaches to tackle questions related to brain barrier development promises to unravel the poorly understood mechanisms of barrier development, as has recently been reviewed94.
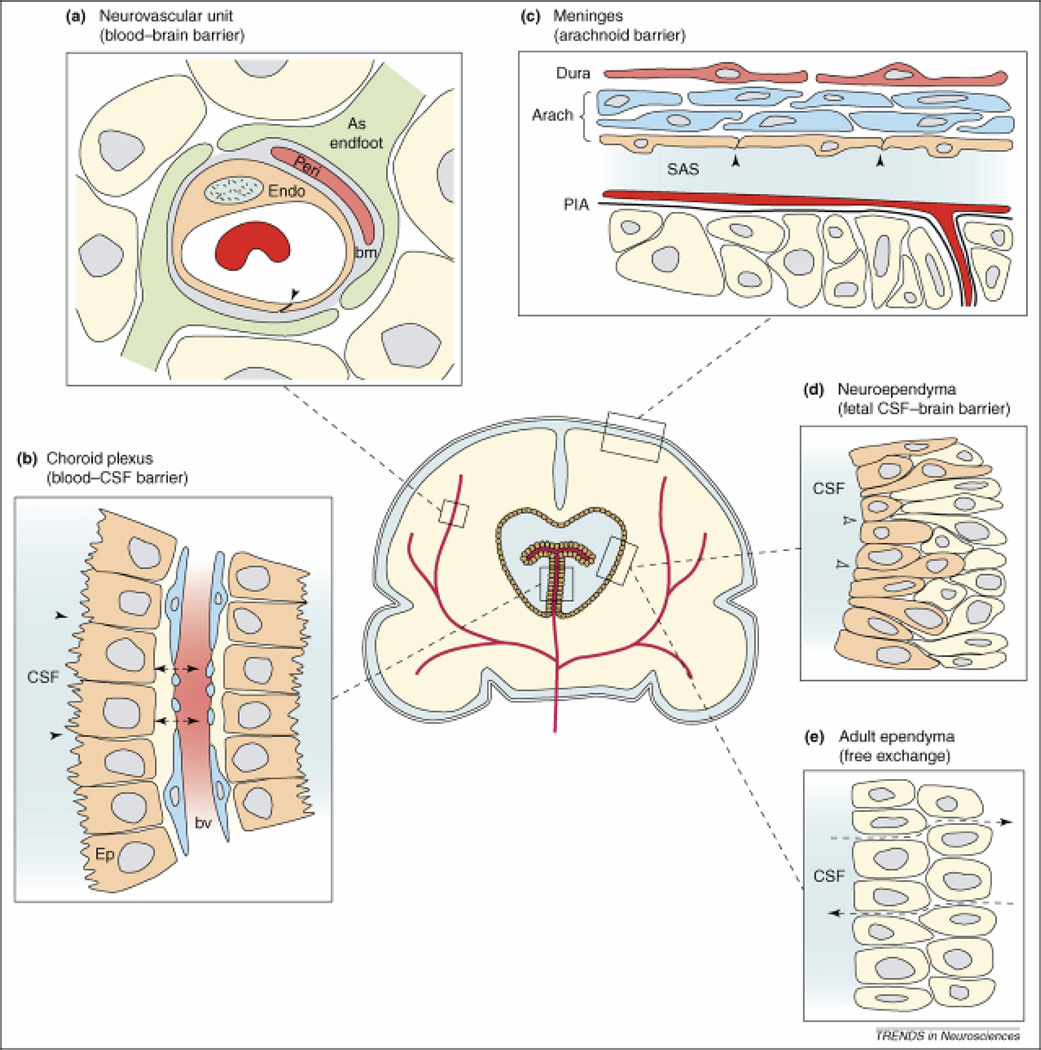
Figure 3. Barrier interfaces.
The neurovascular unit (a), blood-CSF barrier (b), and arachnoidal barrier (c) are common between developing and adult brain, whereas fetal neuroependyma (d) differs from adult ependyma (e). (a) Endothelial cells (Endo) have luminal tight junctions (arrowhead) forming the physical barrier of the interendothelial cleft. Outside the endothelial cell is a basement membrane (bm) which also surrounds the pericytes (Peri). Around all these structures are the astrocyctic endfeet processes from nearby astrocytes (As Endfoot). (b) The endothelial cells of choroid plexus blood vessels are fenestrated and form a non-restrictive barrier (arrowheads) between the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood vessel (BV). The epithelial cells (Ep) have apical tight junctions (small arrows) that restrict intercellular passage of molecules. (c) In the meninges, the blood vessels of the dura are fenestrated and provide little barrier function (not shown); however, the outer cells of the arachnoid membrane (Arach) have tight junctions (arrowheads) and this cell layer forms the physical barrier between the CSF-filled subarachnoid space (SAS) and overlying structures. The blood vessels between the arachnoid and the pial surface (PIA) have tight junctions (not shown). (d) In early development the neuroependymal cells are connected to each other by strap-junctions (small arrows) that are believed to form the physical barrier restricting the passage of larger molecules such as proteins but not smaller molecules such as sucrose. (e) The mature adult ventricular ependyma does not restrict the exchange of molecules. Reproduced, with permissions, from Ref. 162.
The blood-CSF barrier seems to be especially important during development as the choroid plexuses are functional, possess protein specific transport mechanisms and restrict paracellular passage at a time in development when the brain parenchyma has low levels of vascularization108, 116, 117.
The NVU in disease
The NVU is usually considered in the context of its role in preventing CNS access of drugs and proteins with neurotherapeutic potential. The NVU is also affected in many CNS conditions and plays a role in their pathology. Brain abscess, trauma, MS, diabetic ketoacidosis and stroke can all alter brain endothelial cell and NVU function, with consequent edema that may be life threatening. NVU abnormalities themselves can result in distinct disease entities, as highlighted in Table 1. These disorders range from acute mountain sickness causing vasogenic edema118–120, and hepatic encephalopathy causing astrocyte swelling in the NVU121, 122 to malaria impacting the cerebral endothelium123–125.
The complexity of the cellular interactions in the NVU offer numerous potential targets for treatment. For example, one of the newest treatments for MS is a monoclonal antibody that binds the alpha 4 integrin receptor found on leukocytes and that prevents adhesion of the leukocytes to brain endothelial cells126. This reduces the effects of the leukocytes that lead to the demyelination and brain injury seen in acute MS plaques. In addition, molecules found on the luminal side of brain endothelial cells are now recognized as receptors or ligands for proteins associated with various infectious microorganisms that have a predisposition to invade the brain, i.e. malaria (see Table 1). Furthermore, the large number of transporters and receptors on the luminal and abluminal membranes of brain endothelial cells and astrocyte endfeet provide numerous potential therapeutic targets for treatment of CNS diseases127. One example is co-opting insulin receptors for transport of drugs across the NVU128, a possibility that is now being examined129, 130.
Cerebral vascular abnormalities have been reported in brains from both AD and PD patients131 and human genetics studies have linked vascular phenotypes to amyloid precursor protein (APP)132. Specifically, mutations in APP of the Dutch-type lead to cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) in both humans and transgenic mouse models133. CAA induces intracranial hemorrhages, with cognitive decline and seizures, which may also contribute to the pathology and symptoms of AD. ApoE4-positive patients, who carry the most common late-onset genetic risk factor for AD, also have a higher rate of CAA134. Recent advances have also described an influx and efflux mechanism for amyloid-beta, via receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP-1), and more recently P-gp, respectively20, 60. These membrane proteins might be targets for modulating movement of amyloid-beta out of the brain of AD patients to slow or reverse plaque formation. Although barrier-specific genes have not been implicated in directly inducing CNS disease, there are genes associated with barrier function that have been linked to disease135–143.
Recent data from the epilepsy field indicate a prominent role of interactions of leucocytes, in particular PMN cells, with brain endothelium in the initiation of seizure activity144. This is a key observation that not only points to the importance of the BBB in initiating pathology but also stresses the need to consider the blood cells (leucocytes in this case) as members of the family of NVU cells. We therefore propose to use the term ‘extended NVU’ (Figure 1A) to underscore the importance of blood cells and inflammatory signals as key players in disturbed NVU and barrier function. We further anticipate that astrocytes may play an active role to maintain disturbed NVU function, by feeding back pathological signals from the disturbed NVU to the BBB (Figure 1C). Indeed, astrocytes as well as microglial cells are physiological sensors of brain function and pathology145. The work by Appel146 in which neuroprotective signals may cause microglia to become protective in axonal injury models and in PD and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (in contrast to the majority of literature in which microglia are damaging) further emphasize the need for greater communication between neuroscientists and brain barrier scientists.
Imaging Brain Barrier function
At the microscopic level, new imaging techniques, including confocal- and time-lapse microscopy, which allow simultaneous tagging and visualization of multiple molecular targets, molecular imaging of brain cells in vitro and brain tissues in vivo have made tremendous advances in recent years147. Although imaging techniques at the atomic level and “label-less” techniques such as Raman spectroscopy148 have much improved resolution, they can only be used to detect one or a few molecular species simultaneously. With imaging mass spectroscopy (IMS) tissue sections can be directly analyzed for the spatial distribution of multiple molecular markers149, a powerful method for ex vivo imaging (bio)markers that define particular regions, or following ‘biomarker’ responses to disease, pharmacological treatment, electrical stimulation, etc.149.
Further, the field of bioimaging relying on confocal, multiphoton and spinning disk confocal microscopy have been enhanced through the use of fluorescent murine transgenic reporter systems, mostly using green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a reporter. These have gained in popularity and have made great contributions to in vivo tracking exogenously-added cells (i.e. tumor cells, immune cells, and progenitor cells) and as proxy reporters for endogenous genes (i.e. transgenic mice)150–152. These approaches have enhanced greatly our understanding of the trafficking of inflammatory cells across the BBB in models of ischemic brain injury and autoimmune demyelination, among others153. In addition, the recent introduction of optogenetic approaches154 will allow investigators to examine discrete neuronal signaling events in the context of the NVU, providing a degree of in vivo analytical power previously achievable only using in vivo systems. Since brain vasculature is functionally implicated in many brain diseases (Table 1), molecular changes in the NVU could be exploited as image-able biomarkers for early diagnosis or monitoring of the disease using targeted molecular imaging agents155; the added advantage of such biomarkers is their accessibility from the systemic circulation.
At a macroscopic level, analysis of drug delivery to the CNS will be advanced by imaging technologies. For example, studies in animals using positron emission tomography (PET) indicate that it is possible to assess endothelial P-glycoprotein function and its role in the uptake and binding of drugs in the intact CNS by using suitable P-gp modulators that are labeled with a positron emitting isotopes156 (Figure 4). In functional MRI, signal intensity changes are detected as changes in local blood flow and oxygenation, presumably linked to changes in neural activity. The opportunity exists to apply this technology (as well as other methods for imaging cerebral perfusion i.e. dynamic MR) with nanoparticle-based brain mapping methods to advance our understanding of neuro-glio-vascular coupling and BBB pathophysiology157. As no single method can cover the several orders of magnitude in temporal and spatial resolutions and at the same time capture cellular and vascular events, one of the key opportunities to be harnessed in the future is a combination and integration of data and knowledge obtained through multi-modal imaging, such as MRI and PET.
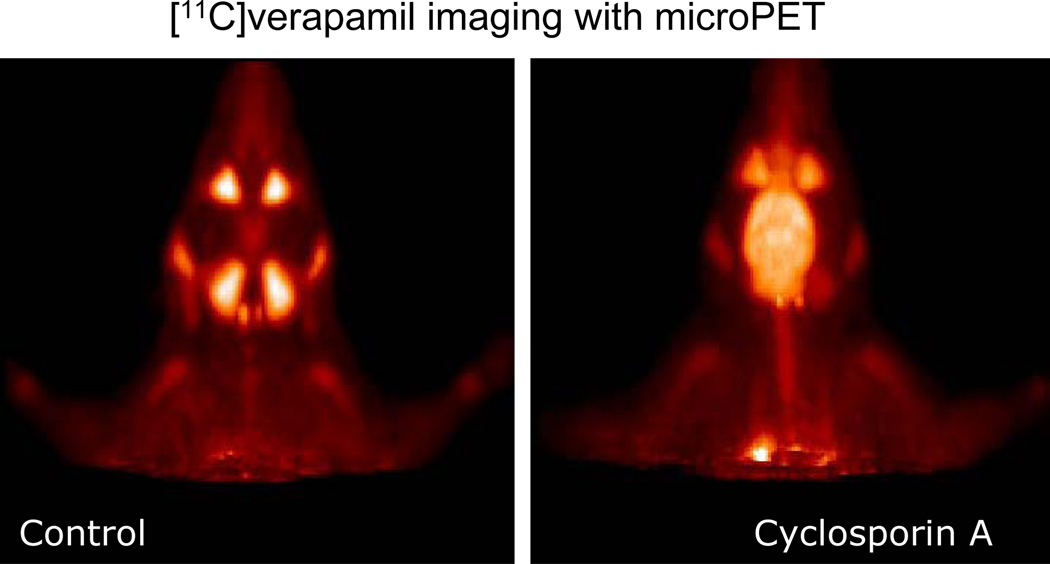
Figure 4. Micro PET images of the head biodistribution of calcium channel blocker.
Micro PET images of the head of a Wistar rat, showing the biodistribution of the calcium channel blocker, [11C] verapamil injected systemically, either alone (Control) or after pre-treatment of the animal with the Pgp inhibitor Cyclosporin A. [11C] verapamil, a substrate for the blood-brain barrier efflux transporter P-glycoprotein, gains access to the brain only after Pgp inhibition by Cyclosporin A. Images are courtesy of Dr. P. Elsinga, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
Barriers to Progress
The most important barrier to progress in our understanding of the role of brain barriers in brain functioning is the lack of communication between neuroscience and brain barrier science. This lack of communication contributes to the omission of the brain barriers sciences in interdisciplinary education programs, thus perpetuating the gap between the fields. If the relationships among neurons, astrocytes and cells of the NVU are to be fully appreciated, it is essential for researchers in both fields to expand their knowledge of the cellular and molecular mechanisms at play in all cells of the NVU, not just those of the endothelial cell (currently studied by brain barrier scientists) or neurons and astrocytes (currently studied by neuroscientists). This should include, for example, attention to all classes of membrane proteins involved in transport across the barriers and among cells of the NVU, such as ion transporters and channels, nutrient transporters, drug transporters, and to proteins that are involved in transport mechanisms (including receptor-mediated endocytosis) and to the receptors and transduction pathways signaling to these proteins.
Because the endothelial cells are thin and tightly embedded within the brain parenchyma, they are not easily isolated for routine biochemical, molecular or cellular analysis. This has posed significant technical difficulties that have delayed progress in the study of blood-brain interfaces. This interface is a highly interactive structure, in which endothelial cells engage with multiple neighboring cells including pericytes, astrocytes, neurons and blood cells such as leukocytes. Brain endothelial cells are very flat cells, with a thickness of less than 0.5 µm outside the nuclear region, comparable in size to dendritic spines. The major technical difficulty here is the fact that the numerous cellular partners at the barrier interface interact with each other in a very thin compartment that has a thickness in the order of the size of dendritic spines. As such, it is very inaccessible. In addition, barrier function can only be studied in vivo because blood cells and blood flow are now considered as essential elements for its normal function. The presence of an intact circulation is a technical difficulty for microscopic imaging studies because of the presence of mechanical vascular pulsations. We propose to apply highly specialized microscope imaging techniques based on two-photon excitation that have been employed to study dendritic functions and dynamics for investigating the functional interaction s at the BBB interface.
Finally, there are misconceptions that need to be overcome, particularly with regard to the status of the NVU during development. A perception persists for some researchers in the field of brain barrier physiology, and therefore in the wider area of neurobiology, that the barrier systems are immature in the developing brain in both their structure and function. This misunderstanding of barrier function during neural development represents an impediment to a full understanding of the biological processes involved in barrier development and the contribution of barrier functions to neural development. The emphasis that is currently placed on understanding the role of the NVU in neuronal development, and recent evidence that vascular and neuronal development have common mechanisms, make a fruitful merger of fields possible. Similarly, there are misconceptions that the blood-brain interface is either open or closed in brain tumors158, i.e. opened as in systemic tissues or closed as in normal brain. In truth, cerebral microvessels coursing through most malignant brain tumors have intermediate paracellular permeability so that some drugs and proteins can move from blood into tumor158. However, recent evidence has shown that enhanced delivery of antitumor agents by further opening the blood-brain interface may improve survival in malignant brain tumor patients159. One key obstacle is the lack of efficacious yet non-invasive methods. Modeling animal models of the BBB in human diseases such as stroke is difficult since our clinical knowledge in patients over time is so limited. Improved models may open up new avenues to define opportunities and time windows for therapeutic interventions.
Conclusions and future directions
In order to further the science in both fields, it is important that understanding what constitutes the functional blood-CNS interface under various physiological and pathophysiological conditions is paramount for developing appropriate therapies to address different disease states. New and improved animal models, including transgenic rodents, will be beneficial in achieving this aim. The use of zebrafish as an easily accessible comparative model for mechanistic in vivo studies should be further explored160. Investigations on the contribution of blood cells and inflammatory signals as part of the NVU are needed. Although blood cells and inflammatory signals are generally not considered part of the NVU proper, they must be considered part of the extended NVU and are important mediators of CNS pathophysiology and need further investigation. Furthermore, animal models will be useful with application of advanced microscopy tools for real time and spatial resolution of cellular interactions, signaling events and metabolism.
Transporters, receptors and their signaling pathways in the NVU are important targets for improving CNS drug delivery and brain protection, and in preventing CNS disease. Advancing knowledge of transporter function, expression, localization and regulation in the brain vasculature and CNS tissues will surely aid progress.
Further consideration of the role of the NVU in research into nervous system development will likely continue to lend insight into both developmental neuroscience and the barriers sciences. There is also a need for improved animal models that are appropriate for studies investigating the links between barrier versus neural development. Furthermore, neuroscientists should consider the possible contributions of the NVU to the interpretation of their neuroscience data, including analysis of genetically engineered mouse models, drug efficacy studies, etc. Acceptance of the recent evidence in support of barrier function in the developing brain, along with the advent of an increased research focus on the development of brain barriers will help to overcome impediments to progress in these fields.
The simultaneous and remarkable advancements in neuroscience and brain-barriers research over the past decade have followed relatively independent tracks. Because of the mutual interests in understanding the mechanisms underlying neural function and disease and in delivering therapeutics through the blood-brain interface, it is now becoming clear that these dual tracks must become one. A careful analysis of common interests as reviewed here indicates that many underlying biological principles and technical approaches in neuroscience apply to the brain barriers and vice versa. Further progress in both fields will be advanced by continued and greater cross-talk and collaboration among the respective scientists and clinicians in the brain barriers and neuroscience fields.
Supplementary Material
References
- 1.Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer disease: mechanistic understanding predicts novel therapies. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:627–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-8-200404200-00047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zlokovic BV. Neurovascular mechanisms of Alzheimer's neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:202–208. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2005.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Iadecola C. The overlap between neurodegenerative and vascular factors in the pathogenesis of dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;120:287–296. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0718-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kortekaas R, et al. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in parkinsonian midbrain in vivo. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:176–179. doi: 10.1002/ana.20369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gold R, Linington C, Lassmann H. Understanding pathogenesis and therapy of multiple sclerosis via animal models: 70 years of merits and culprits in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis research. Brain. 2006;129:1953–1971. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hemmer B, Cepok S, Zhou D, Sommer N. Multiple sclerosis -- a coordinated immune attack across the blood brain barrier. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2004;1:141–150. doi: 10.2174/1567202043480152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shlosberg D, Benifla M, Kaufer D, Friedman A. Blood-brain barrier breakdown as a therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:393–403. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2010.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barzo P, Marmarou A, Fatouros P, Hayasaki K, Corwin F. Contribution of vasogenic and cellular edema to traumatic brain swelling measured by diffusion-weighted imaging. J Neurosurg. 1997;87:900–907. doi: 10.3171/jns.1997.87.6.0900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jain RK, et al. Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:610–622. doi: 10.1038/nrn2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Papadopoulos MC, et al. Occludin expression in microvessels of neoplastic and non-neoplastic human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2001;27:384–395. doi: 10.1046/j.0305-1846.2001.00341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C. The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron. 2010;67:181–198. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.07.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Belayev L, Busto R, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD. Quantitative evaluation of blood-brain barrier permeability following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res. 1996;739:88–96. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(96)00815-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Benchenane K, Lopez-Atalaya JP, Fernandez-Monreal M, Touzani O, Vivien D. Equivocal roles of tissue-type plasminogen activator in stroke-induced injury. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:155–160. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2003.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kuroiwa T, Ting P, Martinez H, Klatzo I. The biphasic opening of the blood-brain barrier to proteins following temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;68:122–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00688633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Navarro Mora G, et al. Does pilocarpine-induced epilepsy in adult rats require status epilepticus? PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e5759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Takano T, et al. Astrocyte-mediated control of cerebral blood flow. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:260–267. doi: 10.1038/nn1623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Iadecola C, Nedergaard M. Glial regulation of the cerebral microvasculature. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1369–1376. doi: 10.1038/nn2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stenman JM, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling regulates organ-specific assembly and differentiation of CNS vasculature. Science. 2008;322:1247–1250. doi: 10.1126/science.1164594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. doi: 10.1038/nrn1824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Neuwelt E, et al. Strategies to advance translational research into brain barriers. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:84–96. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70326-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Perea G, Navarrete M, Araque A. Tripartite synapses: astrocytes process and control synaptic information. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32:421–431. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2009.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG. Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:208–215. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(98)01349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Grotta JC, Jacobs TP, Koroshetz WJ, Moskowitz MA. Stroke program review group: an interim report. Stroke. 2008;39:1364–1370. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.510776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Barres BA. The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron. 2008;60:430–440. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Leybaert L. Neurobarrier coupling in the brain: a partner of neurovascular and neurometabolic coupling? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25:2–16. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lok J, et al. Cell-cell signaling in the neurovascular unit. Neurochem Res. 2007;32:2032–2045. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Daneman R, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is required for CNS, but not non-CNS, angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:641–646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805165106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.McCarty JH. Cell adhesion and signaling networks in brain neurovascular units. Curr Opin Hematol. 2009;16:209–214. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e32832a07eb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.MacAulay N, Zeuthen T. Water transport between CNS compartments: contributions of aquaporins and cotransporters. Neuroscience. 2010;168:941–956. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miller DS. Regulation of P-glycoprotein and other ABC drug transporters at the blood-brain barrier. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010;31:246–254. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2010.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kimelberg HK, Nedergaard M. Functions of astrocytes and their potential as therapeutic targets. Neurotherapeutics. 2010;7:338–353. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2010.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zlokovic BV. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron. 2008;57:178–201. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pedersen SF, O'Donnell ME, Anderson SE, Cala PM. Physiology and pathophysiology of Na+/H+ exchange and Na+ -K+ -2Cl- cotransport in the heart, brain, and blood. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006;291:R1–R25. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00782.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Persidsky Y, Ramirez SH, Haorah J, Kanmogne GD. Blood-brain barrier: structural components and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006;1:223–236. doi: 10.1007/s11481-006-9025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jin R, Yang G, Li G. Molecular insights and therapeutic targets for blood-brain barrier disruption in ischemic stroke: critical role of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue-type plasminogen activator. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;38:376–385. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bell RD, et al. Pericytes control key neurovascular functions and neuronal phenotype in the adult brain and during brain aging. Neuron. 2010;68:409–427. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Madri JA. Modeling the neurovascular niche: implications for recovery from CNS injury. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;60(Suppl 4):95–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ohtsuki S, Terasaki T. Contribution of carrier-mediated transport systems to the blood-brain barrier as a supporting and protecting interface for the brain; importance for CNS drug discovery and development. Pharm Res. 2007;24:1745–1758. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Enerson BE, Drewes LR. The rat blood-brain barrier transcriptome. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 2006;26:959–973. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pardridge WM. Molecular biology of the blood-brain barrier. Methods Mol Med. 2003;89:385–399. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-419-0:385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Torres GE, Amara SG. Glutamate and monoamine transporters: new visions of form and function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007;17:304–312. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Locher KP. Review. Structure and mechanism of ATP-binding cassette transporters. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009;364:239–245. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Melzer N, Torres-Salazar D, Fahlke C. A dynamic switch between inhibitory and excitatory currents in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:19214–19218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508837103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bunch L, Erichsen MN, Jensen AA. Excitatory amino acid transporters as potential drug targets. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009;13:719–731. doi: 10.1517/14728220902926127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bridges RJ, Esslinger CS. The excitatory amino acid transporters: pharmacological insights on substrate and inhibitor specificity of the EAAT subtypes. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;107:271–285. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gonzalez MI, Robinson MB. Neurotransmitter transporters: why dance with so many partners? Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4:30–35. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2003.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chen LM, Haddad GG, Boron WF. Effects of chronic continuous hypoxia on the expression of SLC4A8 (NDCBE) in neonatal versus adult mouse brain. Brain Res. 2008;1238:85–92. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.08.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bevensee MO, Boron WF. Effects of acute hypoxia on intracellular-pH regulation in astrocytes cultured from rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2008;1193:143–152. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chen LM, et al. Expression and localization of Na-driven Cl-HCO(3)(-) exchanger (SLC4A8) in rodent CNS. Neuroscience. 2008;153:162–174. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Amiry-Moghaddam M, et al. An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:2106–2111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0437946100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Benfenati V, Ferroni S. Water transport between CNS compartments: functional and molecular interactions between aquaporins and ion channels. Neuroscience. 2010;168:926–940. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Speake T, Freeman LJ, Brown PD. Expression of aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 water channels in rat choroid plexus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1609:80–86. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(02)00658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gunnarson E, Zelenina M, Aperia A. Regulation of brain aquaporins. Neuroscience. 2004;129:947–955. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.King LS, Kozono D, Agre P. From structure to disease: the evolving tale of aquaporin biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:687–698. doi: 10.1038/nrm1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Badaut J, Lasbennes F, Magistretti PJ, Regli L. Aquaporins in brain: distribution, physiology, and pathophysiology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22:367–378. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200204000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Francesca B, Rezzani R. Aquaporin and blood brain barrier. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010;8:92–96. doi: 10.2174/157015910791233132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Musa-Aziz R, Chen LM, Pelletier MF, Boron WF. Relative CO2/NH3 selectivities of AQP1, AQP4, AQP5, AmtB, and RhAG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:5406–5411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813231106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rigor RR, Hawkins BT, Miller DS. Activation of PKC isoform beta(I) at the blood-brain barrier rapidly decreases P-glycoprotein activity and enhances drug delivery to the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30:1373–1383. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Raffa RB, Tallarida RJ. Effects on the visual system might contribute to some of the cognitive deficits of cancer chemotherapy-induced 'chemo-fog'. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010;35:249–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01086.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hartz AM, Miller DS, Bauer B. Restoring blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein reduces brain amyloid-beta in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Pharmacol. 2010;77:715–723. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.061754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Loscher W, Potschka H. Drug resistance in brain diseases and the role of drug efflux transporters. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:591–602. doi: 10.1038/nrn1728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Fletcher JI, Haber M, Henderson MJ, Norris MD. ABC transporters in cancer: more than just drug efflux pumps. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:147–156. doi: 10.1038/nrc2789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Schinkel AH. P-Glycoprotein, a gatekeeper in the blood-brain barrier. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1999;36:179–194. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(98)00085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bauer B, Hartz AM, Miller DS. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and endothelin-1 increase P-glycoprotein expression and transport activity at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;71:667–675. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.029512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hartz AM, Bauer B, Fricker G, Miller DS. Rapid regulation of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier by endothelin-1. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:387–394. doi: 10.1124/mol.104.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Hartz AM, Bauer B, Fricker G, Miller DS. Rapid modulation of P-glycoprotein-mediated transport at the blood-brain barrier by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lipopolysaccharide. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;69:462–470. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.017954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bankstahl JP, Hoffmann K, Bethmann K, Loscher W. Glutamate is critically involved in seizure-induced overexpression of P-glycoprotein in the brain. Neuropharmacology. 2008;54:1006–1016. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bauer B, et al. Seizure-induced up-regulation of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier through glutamate and cyclooxygenase-2 signaling. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;73:1444–1453. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.041210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Pekcec A, et al. Targeting prostaglandin E2 EP1 receptors prevents seizure-associated P-glycoprotein up-regulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;330:939–497. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.152520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zibell G, et al. Prevention of seizure-induced up-regulation of endothelial P-glycoprotein by COX-2 inhibition. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:849–855. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Schlichtiger J, et al. Celecoxib treatment restores pharmacosensitivity in a rat model of pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;160:1062–1071. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00765.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Bauer B, et al. In vivo activation of human pregnane X receptor tightens the blood-brain barrier to methadone through P-glycoprotein up-regulation. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70:1212–1219. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.023796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wang X, Sykes DB, Miller DS. Constitutive androstane receptor-mediated up-regulation of ATP-driven xenobiotic efflux transporters at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol. 2010;78:376–383. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.063685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Wang X, Hawkins BT, Miller DS. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated up-regulation of ATP-driven xenobiotic efflux transporters at the blood-brain barrier. FASEB J. 2010 doi: 10.1096/fj.10-169227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bauer B, Hartz AM, Fricker G, Miller DS. Pregnane X receptor up-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression and transport function at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:413–419. doi: 10.1124/mol.66.3.. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dauchy S, et al. ABC transporters, cytochromes P450 and their main transcription factors: expression at the human blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem. 2008;107:1518–1528. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Narang VS, et al. Dexamethasone increases expression and activity of multidrug resistance transporters at the rat blood-brain barrier. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;295:C440–C450. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00491.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ott M, Fricker G, Bauer B. Pregnane X receptor (PXR) regulates P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier: functional similarities between pig and human PXR. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;329:141–149. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.149690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Miller DS, Bauer B, Hartz AM. Modulation of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier: opportunities to improve central nervous system pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60:196–209. doi: 10.1124/pr.107.07109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Hartz AM, Bauer B. Regulation of ABC transporters at the blood-brain barrier: new targets for CNS therapy. Mol Interv. 2010;10:293–304. doi: 10.1124/mi.10.5.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57:173–185. doi: 10.1124/pr.57.2.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Nitta T, et al. Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. Journal of Cell Biology. 2003;161:653–660. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200302070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Saitou M, et al. Complex phenotype of mice lacking occludin, a component of tight junction strands. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2000;11:4131–4142. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.12.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Volterra A, Meldolesi J. Astrocytes, from brain glue to communication elements: the revolution continues. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:626–640. doi: 10.1038/nrn1722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Wang X, et al. Astrocytic Ca2+ signaling evoked by sensory stimulation in vivo. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:816–823. doi: 10.1038/nn1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ding S, et al. Enhanced astrocytic Ca2+ signals contribute to neuronal excitotoxicity after status epilepticus. J Neurosci. 2007;27:10674–10684. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2001-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Takata N, Hirase H. Cortical layer 1 and layer 2/3 astrocytes exhibit distinct calcium dynamics in vivo. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e2525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Mulligan SJ, MacVicar BA. Calcium transients in astrocyte endfeet cause cerebrovascular constrictions. Nature. 2004;431:195–199. doi: 10.1038/nature02827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Zonta M, et al. Neuron-to-astrocyte signaling is central to the dynamic control of brain microcirculation. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:43–50. doi: 10.1038/nn980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Koehler RC, Roman RJ, Harder DR. Astrocytes and the regulation of cerebral blood flow. Trends Neurosci. 2009 doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Haydon PG, Carmignoto G. Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:1009–1031. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00049.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gordon GR, Choi HB, Rungta RL, Ellis-Davies GC, MacVicar BA. Brain metabolism dictates the polarity of astrocyte control over arterioles. Nature. 2008;456:745–749. doi: 10.1038/nature07525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Simard M, Arcuino G, Takano T, Liu QS, Nedergaard M. Signaling at the gliovascular interface. J Neurosci. 2003;23:9254–9262. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-27-09254.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Tam SJ, Watts RJ. Connecting vascular and nervous system development: angiogenesis and the blood-brain barrier. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010;33:379–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-152829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Carmeliet P, Tessier-Lavigne M. Common mechanisms of nerve and blood vessel wiring. Nature. 2005;436:193–200. doi: 10.1038/nature03875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Stubbs D, et al. Neurovascular congruence during cerebral cortical development. Cereb Cortex. 2009;(19 Suppl 1):i32–i41. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Javaherian A, Kriegstein A. A stem cell niche for intermediate progenitor cells of the embryonic cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2009;(19 Suppl 1):i70–i77. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Risau W, Wolburg H. Development of the blood-brain barrier. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13:174–178. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90043-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Harrigan MR. Angiogenic factors in the central nervous system. Neurosurgery. 2003;53:639–660. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000079575.09923.59. discussion 660-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature. 1997;386:671–674. doi: 10.1038/386671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Stone J, et al. Development of retinal vasculature is mediated by hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression by neuroglia. J Neurosci. 1995;15:4738–4747. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-07-04738.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Jain RK. Molecular regulation of vessel maturation. Nat Med. 2003;9:685–693. doi: 10.1038/nm0603-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Greenberg DA, Jin K. From angiogenesis to neuropathology. Nature. 2005;438:954–959. doi: 10.1038/nature04481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Dziegielewska KM, et al. Plasma proteins in fetal sheep brain: blood-brain barrier and intracerebral distribution. J Physiol. 1981;318:239–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Dziegielewska KM, et al. Studies of the development of brain barrier systems to lipid insoluble molecules in fetal sheep. J Physiol. 1979;292:207–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Evans CA, Reynolds JM, Reynolds ML, Saunders NR, Segal MB. The development of a blood-brain barrier mechanism in foetal sheep. J Physiol. 1974;238:371–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Mollgard K, Saunders NR. The development of the human blood-brain and blood-CSF barriers. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1986;12:337–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1986.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Johansson PA, Dziegielewska KM, Liddelow SA, Saunders NR. The blood-CSF barrier explained: when development is not immaturity. Bioessays. 2008;30:237–248. doi: 10.1002/bies.20718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Ek CJ, Dziegielewska KM, Stolp H, Saunders NR. Functional effectiveness of the blood-brain barrier to small water-soluble molecules in developing and adult opossum (Monodelphis domestica) J Comp Neurol. 2006;496:13–26. doi: 10.1002/cne.20885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Gazzin S, et al. Differential expression of the multidrug resistance-related proteins ABCb1 and ABCc1 between blood-brain interfaces. J Comp Neurol. 2008;510:497–507. doi: 10.1002/cne.21808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Kalabis GM, Petropoulos S, Gibb W, Matthews SG. Breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp1/Abcg2) in mouse placenta and yolk sac: ontogeny and its regulation by progesterone. Placenta. 2007;28:1073–1081. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2007.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Ek CJ, et al. Efflux mechanisms at the developing brain barriers: ABC-transporters in the fetal and postnatal rat. Toxicol Lett. 2010;197:51–59. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.04.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Daneman R, Zhou L, Kebede AA, Barres BA. Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature. 2010;468:562–566. doi: 10.1038/nature09513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Daneman R, et al. The mouse blood-brain barrier transcriptome: a new resource for understanding the development and function of brain endothelial cells. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e13741. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Wosik K, et al. Angiotensin II controls occludin function and is required for blood brain barrier maintenance: relevance to multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci. 2007;27:9032–9042. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2088-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Liddelow SA, et al. Cellular transfer of macromolecules across the developing choroid plexus of Monodelphis domestica. Eur J Neurosci. 2009;29:253–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Liddelow SA, et al. Modification of protein transfer across blood/cerebrospinal fluid barrier in response to altered plasma protein composition during development. Eur J Neurosci. 2010 doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Krasney JA. A neurogenic basis for acute altitude illness. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1994;26:195–208. doi: 10.1249/00005768-199402000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Severinghaus JW. Hypothetical roles of angiogenesis, osmotic swelling, and ischemia in high-altitude cerebral edema. J Appl Physiol. 1995;79:375–379. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1995.79.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Wilson MH, Newman S, Imray CH. The cerebral effects of ascent to high altitudes. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:175–191. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Laursen H. Cerebral vessels and glial cells in liver disease. A morphometric and electron microscopic investigation. Acta Neurol Scand. 1982;65:381–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb03097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Martinez A. Electron microscopy in human hepatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1968;11:82–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00692797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Tripathi AK, Sha W, Shulaev V, Stins MF, Sullivan DJ., Jr Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes induce NF-kappaB regulated inflammatory pathways in human cerebral endothelium. Blood. 2009;114:4243–4252. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-226415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Tripathi AK, Sullivan DJ, Stins MF. Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes increase intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression on brain endothelium through NF-kappaB. Infect Immun. 2006;74:3262–3270. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01625-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Tripathi AK, Sullivan DJ, Stins MF. Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes decrease the integrity of human blood-brain barrier endothelial cell monolayers. J Infect Dis. 2007;195:942–950. doi: 10.1086/512083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Engelhardt B, Kappos L. Natalizumab: targeting alpha4-integrins in multiple sclerosis. Neurodegener Dis. 2008;5:16–22. doi: 10.1159/000109933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Spencer BJ, Verma IM. Targeted delivery of proteins across the blood-brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:7594–7599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702170104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Hoffman AS. The origins and evolution of "controlled" drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2008;132:153–163. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Pardridge WM. Biopharmaceutical drug targeting to the brain. J Drug Target. 2010;18:157–167. doi: 10.3109/10611860903548354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Vastag B. Biotechnology: Crossing the barrier. Nature. 2010;466:916–918. doi: 10.1038/466916a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Farkas E, De Jong GI, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Luiten PG. Pathological features of cerebral cortical capillaries are doubled in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2000;100:395–402. doi: 10.1007/s004010000195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Levy E, et al. Mutation of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid gene in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage, Dutch type. Science. 1990;248:1124–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.2111584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Herzig MC, et al. Abeta is targeted to the vasculature in a mouse model of hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:954–960. doi: 10.1038/nn1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Premkumar DR, Cohen DL, Hedera P, Friedland RP, Kalaria RN. Apolipoprotein E-epsilon4 alleles in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and cerebrovascular pathology associated with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1996;148:2083–2095. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Westerlund M, et al. Association of a polymorphism in the ABCB1 gene with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009;15:422–424. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Weber YG, et al. GLUT1 mutations are a cause of paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesias and induce hemolytic anemia by a cation leak. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:2157–2168. doi: 10.1172/JCI34438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Suls A, et al. Paroxysmal exercise-induced dyskinesia and epilepsy is due to mutations in SLC2A1, encoding the glucose transporter GLUT1. Brain. 2008;131:1831–1844. doi: 10.1093/brain/awn113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Newmeyer A, Cecil KM, Schapiro M, Clark JF, Degrauw TJ. Incidence of brain creatine transporter deficiency in males with developmental delay referred for brain magnetic resonance imaging. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2005;26:276–282. doi: 10.1097/00004703-200508000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Klepper J. Glucose transporter deficiency syndrome (GLUT1DS) and the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. 2008;(49 Suppl 8):46–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Kim WS, Weickert CS, Garner B. Role of ATP-binding cassette transporters in brain lipid transport and neurological disease. J Neurochem. 2008;104:1145–1166. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Drozdzik M, et al. Polymorphism in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene: a possible link between environmental and genetic factors in Parkinson's disease. Pharmacogenetics. 2003;13:259–263. doi: 10.1097/01.fpc.0000054087.48725.d9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Dean M. The genetics of ATP-binding cassette transporters. Methods Enzymol. 2005;400:409–429. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)00024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Blanz J, et al. Leukoencephalopathy upon disruption of the chloride channel ClC-2. J Neurosci. 2007;27:6581–6589. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0338-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Fabene PF, et al. A role for leukocyte-endothelial adhesion mechanisms in epilepsy. Nat Med. 2008;14:1377–1383. doi: 10.1038/nm.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Kreutzberg GW. Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:312–318. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(96)10049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Appel SH, Beers DR, Henkel JS. T cell-microglial dialogue in Parkinson's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: are we listening? Trends Immunol. 2010;31:7–17. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2009.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Raj A, van den Bogaard P, Rifkin SA, van Oudenaarden A, Tyagi S. Imaging individual mRNA molecules using multiple singly labeled probes. Nat Methods. 2008;5:877–879. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Freudiger CW, et al. Label-free biomedical imaging with high sensitivity by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Science. 2008;322:1857–1861. doi: 10.1126/science.1165758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Seeley EH, Caprioli RM. Molecular imaging of proteins in tissues by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:18126–18131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801374105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Todman MG, Han SK, Herbison AE. Profiling neurotransmitter receptor expression in mouse gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons using green fluorescent protein-promoter transgenics and microarrays. Neuroscience. 2005;132:703–712. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Turney SG, Lichtman JW. Chapter 11: Imaging fluorescent mice in vivo using confocal microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 2008;89:309–327. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(08)00611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Zhuo L, et al. Live astrocytes visualized by green fluorescent protein in transgenic mice. Dev Biol. 1997;187:36–42. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Priller J, et al. Targeting gene-modified hematopoietic cells to the central nervous system: use of green fluorescent protein uncovers microglial engraftment. Nat Med. 2001;7:1356–1361. doi: 10.1038/nm1201-1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Miesenbock G. The optogenetic catechism. Science. 2009;326:395–399. doi: 10.1126/science.1174520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Iqbal U, et al. Molecular imaging of glioblastoma multiforme using anti-insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 single-domain antibodies. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:1606–1616. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Elsinga PH, Hendrikse NH, Bart J, van Waarde A, Vaalburg W. Positron emission tomography studies on binding of central nervous system drugs and P-glycoprotein function in the rodent brain. Mol Imaging Biol. 2005;7:37–44. doi: 10.1007/s11307-005-0951-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Weinstein JS, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging and potential therapeutic applications in neurooncology and central nervous system inflammatory pathologies, a review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30:15–35. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Muldoon LL, et al. Chemotherapy delivery issues in central nervous system malignancy: a reality check. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2295–2305. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.09.9861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Angelov L, et al. Blood-brain barrier disruption and intra-arterial methotrexate-based therapy for newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma: a multi-institutional experience. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3503–3509. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.3789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Eliceiri BP, Gonzalez AM, Baird A. Zebrafish model of the blood-brain barrier: morphological and permeability studies. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;686:371–378. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-938-3_18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Hartz AM, Bauer B. ABC Transporters in the CNS - An Inventory. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12:423–440. doi: 10.2174/138920111795164020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Saunders NR, Ek CJ, Habgood MD, Dziegielewska KM. Barriers in the brain: a renaissance? Trends Neurosci. 2008;31:279–286. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Bates KA, et al. Clearance mechanisms of Alzheimer's amyloid-beta peptide: implications for therapeutic design and diagnostic tests. Mol Psychiatry. 2008;16:16. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Vogelgesang S, et al. Deposition of Alzheimer's beta-amyloid is inversely correlated with P-glycoprotein expression in the brains of elderly non-demented humans. Pharmacogenetics. 2002;12:535–541. doi: 10.1097/00008571-200210000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Cirrito JR, et al. P-glycoprotein deficiency at the blood-brain barrier increases amyloid-beta deposition in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:3285–3290. doi: 10.1172/JCI25247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Hartz AM, Miller DS, Bauer B. Restoring blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein reduces brain amyloid-beta in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Pharmacol. 2010;77:715–723. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.061754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Xiong H, et al. ABCG2 is upregulated in Alzheimer's brain with cerebral amyloid angiopathy and may act as a gatekeeper at the blood-brain barrier for Abeta(1–40) peptides. J Neurosci. 2009;29:5463–5475. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5103-08.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Drozdzik M, et al. Polymorphism in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene: a possible link between environmental and genetic factors in Parkinson's disease. Pharmacogenetics. 2003;13:259–263. doi: 10.1097/01.fpc.0000054087.48725.d9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Westerlund M, et al. Association of a polymorphism in the ABCB1 gene with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009;15:422–424. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Lu A, et al. Reperfusion activates metalloproteinases that contribute to neurovascular injury. Exp Neurol. 2008;210:549–559. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinases and their multiple roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:205–216. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70016-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Wang X, Rosell A, Lo EH. Targeting extracellular matrix proteolysis for hemorrhagic complications of tPA stroke therapy. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008;7:235–242. doi: 10.2174/187152708784936635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Xue M, Yong VW. Matrix metalloproteinases in intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurol Res. 2008;30:775–782. doi: 10.1179/174313208X341102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Argaw AT, Gurfein BT, Zhang Y, Zameer A, John GR. VEGF-mediated disruption of endothelial CLN-5 promotes blood-brain barrier breakdown. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(6):1977–1982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808698106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Guzeloglu-Kayisli O, et al. KRIT1/cerebral cavernous malformation 1 protein localizes to vascular endothelium, astrocytes, and pyramidal cells of the adult human cerebral cortex. Neurosurgery. 2004;54:943–949. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000114512.59624.a5. discussion 949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Pagenstecher A, Stahl S, Sure U, Felbor U. A two-hit mechanism causes cerebral cavernous malformations: complete inactivation of CCM1, CCM2 or CCM3 in affected endothelial cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:911–918. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Candelario-Jalil E, Yang Y, Rosenberg GA. Diverse roles of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation and cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2009;158:983–994. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Gidday JM, et al. Leukocyte-derived matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates blood-brain barrier breakdown and is proinflammatory after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289:H558–H568. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01275.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Strbian D, et al. The blood-brain barrier is continuously open for several weeks following transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2008;153:175–181. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Simard JM, et al. Newly expressed SUR1-regulated NCCa-ATP channel mediates cerebral edema after ischemic stroke. Nat Med. 2006;12:433–440. doi: 10.1038/nm1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Wilson MH, Newman S, Imray CH. The cerebral effects of ascent to high altitudes. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:175–191. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Klepper J. Glucose transporter deficiency syndrome (GLUT1DS) and the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. 2008;(49 Suppl 8):46–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Suls A, et al. Paroxysmal exercise-induced dyskinesia and epilepsy is due to mutations in SLC2A1, encoding the glucose transporter GLUT1. Brain. 2008;131:1831–1844. doi: 10.1093/brain/awn113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Weber YG, et al. GLUT1 mutations are a cause of paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesias and induce hemolytic anemia by a cation leak. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:2157–2168. doi: 10.1172/JCI34438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Hughes JR. One of the hottest topics in epileptology: ABC proteins. Their inhibition may be the future for patients with intractable seizures. Neurol Res. 2008;30:920–925. doi: 10.1179/174313208X319116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Miller DS, Bauer B, Hartz AM. Modulation of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier: opportunities to improve central nervous system pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60:196–209. doi: 10.1124/pr.107.07109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Mignot C, et al. Alexander disease: putative mechanisms of an astrocytic encephalopathy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004;61:369–385. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3143-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Blanz J, et al. Leukoencephalopathy upon disruption of the chloride channel ClC-2. J Neurosci. 2007;27:6581–6589. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0338-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Chaudhuri A, Yang B, Gendelman HE, Persidsky Y, Kanmogne GD. STAT1 signaling modulates HIV-1-induced inflammatory responses and leukocyte transmigration across the blood-brain barrier. Blood. 2008;111:2062–2072. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-091207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Huang W, Eum SY, Andras IE, Hennig B, Toborek M. PPARalpha and PPARgamma attenuate HIV-induced dysregulation of tight junction proteins by modulations of matrix metalloproteinase and proteasome activities. Faseb J. 2009;23:1596–1606. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-121624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Yamamoto M, et al. Phosphorylation of claudin-5 and occludin by rho kinase in brain endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 2008;172:521–533. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.de Lagerie SB, et al. MDR1A (ABCB1)-deficient CF-1 mutant mice are susceptible to cerebral malaria induced by Plasmodium berghei ANKA. J Parasitol. 2008;94:1139–1142. doi: 10.1645/GE-1493.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Unkmeir A, et al. Fibronectin mediates Opc-dependent internalization of Neisseria meningitidis in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 2002;46:933–946. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Wang L, Lin M. A novel cell wall-anchored peptidoglycan hydrolase (autolysin), IspC, essential for Listeria monocytogenes virulence: genetic and proteomic analysis. Microbiology. 2008;154:1900–1913. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/015172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Banks WA. Physiology and pathology of the blood-brain barrier: implications for microbial pathogenesis, drug delivery and neurodegenerative disorders. Journal of Neurovirology. 1999;5:538–555. doi: 10.3109/13550289909021284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Tripathi AK, Sullivan DJ, Stins MF. Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes decrease the integrity of human blood-brain barrier endothelial cell monolayers. J Infect Dis. 2007;195:942–950. doi: 10.1086/512083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Haorah J, et al. Oxidative stress activates protein tyrosine kinase and matrix metalloproteinases leading to blood-brain barrier dysfunction. J Neurochem. 2007;101:566–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Man S, Ubogu EE, Ransohoff RM. Inflammatory cell migration into the central nervous system: a few new twists on an old tale. Brain Pathol. 2007;17:243–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Zlokovic BV. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron. 2008;57:178–201. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Suidan GL, McDole JR, Chen Y, Pirko I, Johnson AJ. Induction of blood brain barrier tight junction protein alterations by CD8 T cells. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e3037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Verkman AS. Mammalian aquaporins: diverse physiological roles and potential clinical significance. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008;10:e13. doi: 10.1017/S1462399408000690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Yang B, Zador Z, Verkman AS. Glial cell aquaporin-4 overexpression in transgenic mice accelerates cytotoxic brain swelling. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:15280–15286. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801425200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Blecharz KG, Drenckhahn D, Forster CY. Glucocorticoids increase VE-cadherin expression and cause cytoskeletal rearrangements in murine brain endothelial cEND cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008;28:1139–1149. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Felinski EA, Cox AE, Phillips BE, Antonetti DA. Glucocorticoids induce transactivation of tight junction genes occludin and claudin-5 in retinal endothelial cells via a novel cis-element. Exp Eye Res. 2008;86:867–878. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2008.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Harke N, Leers J, Kietz S, Drenckhahn D, Forster C. Glucocorticoids regulate the human occludin gene through a single imperfect palindromic glucocorticoid response element. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;295:39–47. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Reijerkerk A, et al. Tissue-type plasminogen activator is a regulator of monocyte diapedesis through the brain endothelial barrier. J Immunol. 2008;181:3567–3574. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.5.3567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Kebir H, et al. Human TH17 lymphocytes promote blood-brain barrier disruption and central nervous system inflammation. Nat Med. 2007;13:1173–1175. doi: 10.1038/nm1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Morgan L, et al. Inflammation and dephosphorylation of the tight junction protein occludin in an experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Neuroscience. 2007;147:664–673. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.04.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Goodin DS, Cohen BA, O'Connor P, Kappos L, Stevens JC. Assessment: the use of natalizumab (Tysabri) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (an evidence-based review): report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2008;71:766–773. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000320512.21919.d2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Lutterotti A, Martin R. Getting specific: monoclonal antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:538–547. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Martin C, et al. FGF2 plays a key role in embryonic cerebrospinal fluid trophic properties over chick embryo neuroepithelial stem cells. Dev Biol. 2006;297:402–416. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Brooks TA, et al. Biphasic cytoarchitecture and functional changes in the BBB induced by chronic inflammatory pain. Brain Res. 2006;1120:172–182. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.08.085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Foroutan S, Brillault J, Forbush B, O'Donnell ME. Moderate-to-severe ischemic conditions increase activity and phosphorylation of the cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na+-K+-Cl- cotransporter. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;289:C1492–C1501. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00257.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Lam TI, Anderson SE, Glaser N, O'Donnell ME. Bumetanide reduces cerebral edema formation in rats with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes. 2005;54:510–516. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.2.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Lam TI, O'Donnell ME. BBB Na/H exchange: plasma membrane distribution of NHE1 and NHE2 isoforms and stimulation by arginine vasopressin. FASEB J. 2008;22:734.3. [Google Scholar]
- 216.O'Donnell ME, Duong V, Suvatne J, Foroutan S, Johnson DM. Arginine vasopressin stimulation of cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na-K-Cl cotransporter activity is V1 receptor and [Ca] dependent. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;289:C283–C292. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00001.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.O'Donnell ME, Lam TI, Tran L, Anderson SE. The role of the blood-brain barrier Na-K-2Cl cotransporter in stroke. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004;559:67–75. doi: 10.1007/0-387-23752-6_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Yuen N, Anderson SE, Glaser N, Tancredi DJ, O'Donnell ME. Cerebral blood flow and cerebral edema in rats with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes. 2008;57:2588–2594. doi: 10.2337/db07-1410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Dean M. The genetics of ATP-binding cassette transporters. Methods Enzymol. 2005;400:409–429. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)00024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Kim WS, Weickert CS, Garner B. Role of ATP-binding cassette transporters in brain lipid transport and neurological disease. J Neurochem. 2008;104:1145–1166. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Banks WA. The blood-brain barrier as a cause of obesity. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14:1606–1614. doi: 10.2174/138161208784705496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Jequier E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;967:379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Pan W, et al. Astrocyte leptin receptor (ObR) and leptin transport in adult-onset obese mice. Endocrinology. 2008;149:2798–2806. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Luder AS, Tanner SM, de la Chapelle A, Walter JH. Amnionless (AMN) mutations in Imerslund-Grasbeck syndrome may be associated with disturbed vitamin B(12) transport into the CNS. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2008;7:7. doi: 10.1007/s10545-007-0760-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Gordon N. Canavan disease: a review of recent developments. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2001;5:65–69. doi: 10.1053/ejpn.2001.0467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Urayama A, Grubb JH, Sly WS, Banks WA. Developmentally regulated mannose 6- phosphate receptor-mediated transport of a lysosomal enzyme across the blood-brain barrier. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2004;101:12658–12663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405042101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Uhr M, et al. Polymorphisms in the drug transporter gene ABCB1 predict antidepressant treatment response in depression. Neuron. 2008;57:203–209. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Tanigami H, et al. Effect of glutamine synthetase inhibition on astrocyte swelling and altered astroglial protein expression during hyperammonemia in rats. Neuroscience. 2005;131:437–449. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.10.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Sugimoto H, Koehler RC, Wilson DA, Brusilow SW, Traystman RJ. Methionine sulfoximine, a glutamine synthetase inhibitor, attenuates increased extracellular potassium activity during acute hyperammonemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:44–49. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199701000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Strauss GI, Knudsen GM, Kondrup J, Moller K, Larsen FS. Cerebral metabolism of ammonia and amino acids in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:1109–1119. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.29310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.