Abstract
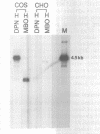
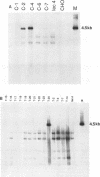
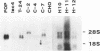
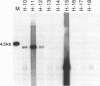
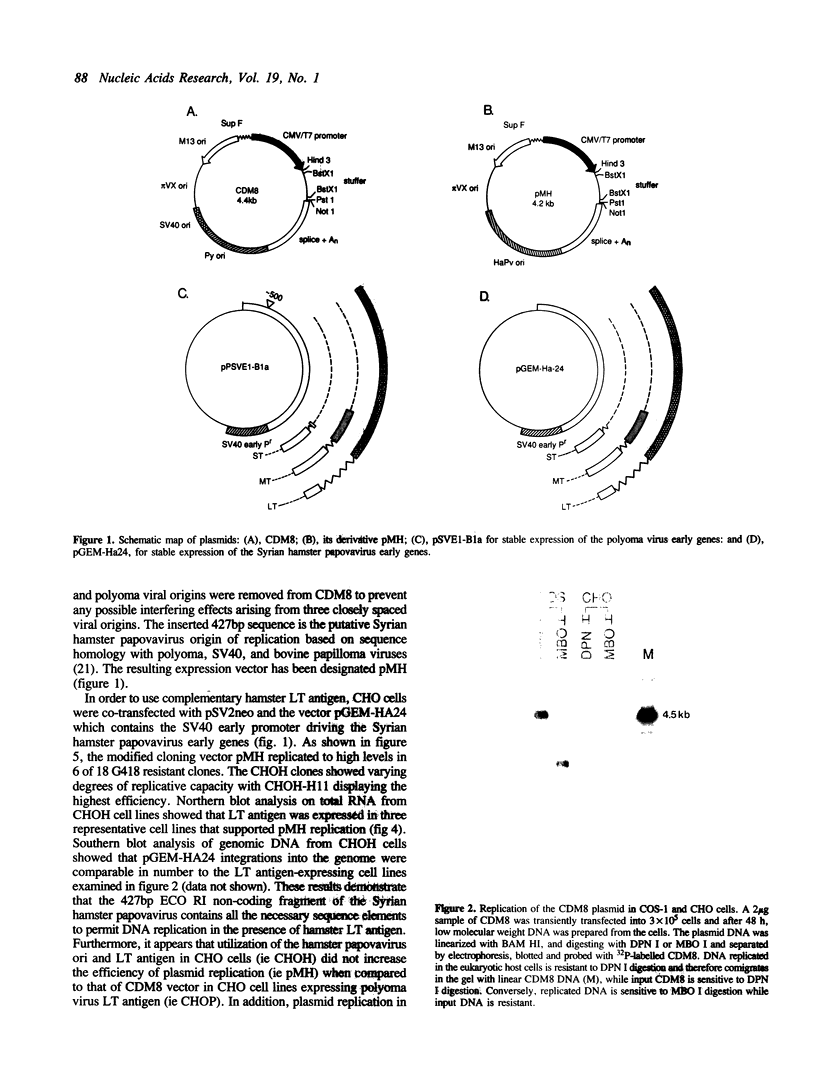
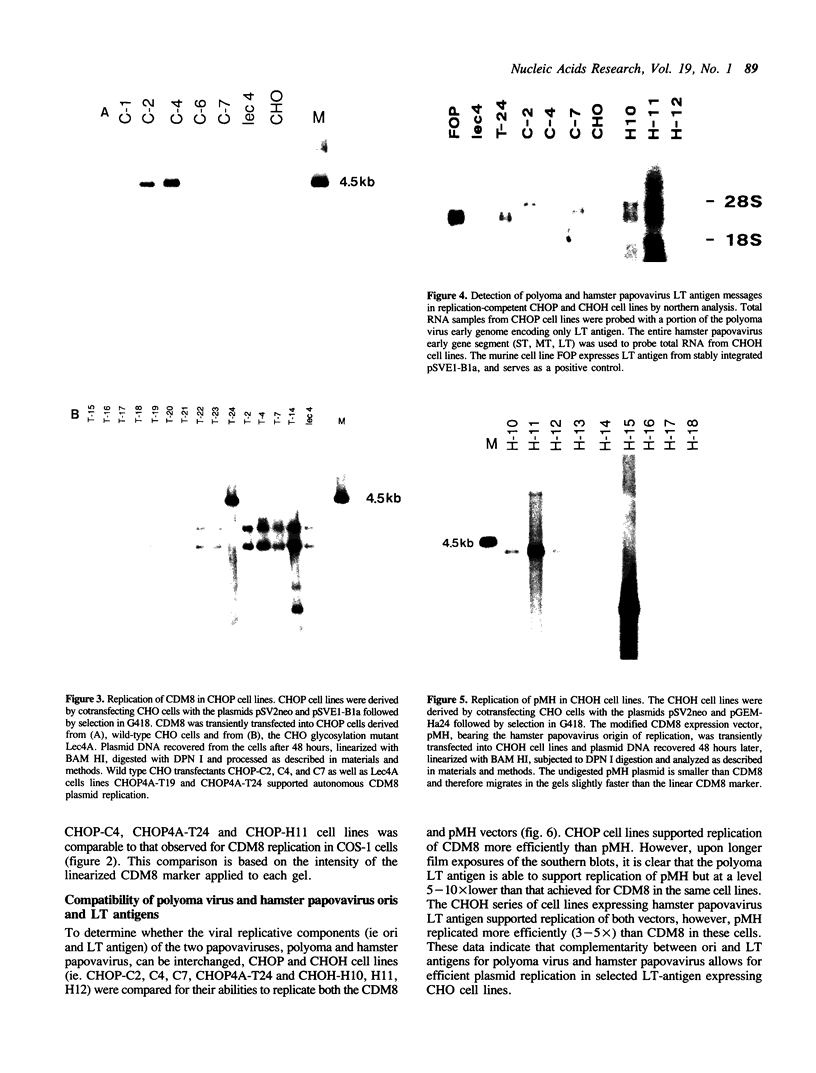
Eukaryotic expression vectors have been used successfully in viral LT-expressing cell lines (ie. COS) to clone cDNAs encoding proteins that can be detected through their bio-activity or reactivity with specific antibodies. Since Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO) have been used extensively for the isolation and characterization of somatic cell mutants, we felt it would be an advantage to develop an expression cloning system in CHO cells. We have modified the eukaryotic expression vector CDM8 by replacing the polyoma and SV40 origins of replication with the 427bp non-coding region of the Syrian hamster papovavirus. Wild-type CHO cells and the CHO glycosylation-mutant Lec4A were transfected with plasmids bearing the early genes of either polyoma virus or hamster papovavirus in order to establish stable, LT antigen-expressing cell lines designated CHOP or CHOH, respectively. CHOP cell lines expressing polyoma LT antigen supported efficient replication of CDM8, but replicated pMH poorly. Conversely, CHOH cells expressing the hamster papovavirus LT antigen supported replication of pMH, and at a lower efficiency, CDM8. Replication of CDM8 and pMH vectors were equally efficient in selected CHOP and CHOH cell lines, respectively and comparable to that of CDM8 replication in COS-1 cells. A bacterial beta-galactosidase fusion gene inserted into the multiple cloning site of a CDM8 derivative was efficiently expressed when transiently transfected into CHOP and CHOH cells but not CHO cells since only the former supports autonomous plasmid replication. These results show that expression-cloning in CHO cells expressing either polyoma virus or hamster papovavirus LT antigens is possible using either the CDM8 or the pMH vectors, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basilico C., Matsuya Y., Green H. The interaction of polyoma virus with mouse-hamster somatic hybrid cells. Virology. 1970 Jun;41(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaney W., Sundaram S., Friedman N., Stanley P. The Lec4A CHO glycosylation mutant arises from miscompartmentalization of a Golgi glycosyltransferase. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2089–2096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogen B. Virus-specific early RNA in 3T6 cells infected by a tsA mutant of polyoma virus. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings R. D., Kornfeld S. Characterization of the structural determinants required for the high affinity interaction of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides with immobilized Phaseolus vulgaris leukoagglutinating and erythroagglutinating lectins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11230–11234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F., Wong G. G. Expression cloning of the murine erythropoietin receptor. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas V., Bastien C., Scherneck S., Feunteun J. A new member of the polyomavirus family: the hamster papovavirus. Complete nucleotide sequence and transformation properties. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1279–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03773.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst L. K., Rajan V. P., Larsen R. D., Ruff M. M., Lowe J. B. Stable expression of blood group H determinants and GDP-L-fucose: beta-D-galactoside 2-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase in mouse cells after transfection with human DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3436–3447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joziasse D. H., Shaper J. H., Van den Eijnden D. H., Van Tunen A. J., Shaper N. L. Bovine alpha 1----3-galactosyltransferase: isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone. Identification of homologous sequences in human genomic DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14290–14297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Stanley P. Transfection of a human gene that corrects the Lec1 glycosylation defect: evidence for transfer of the structural gene for N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5713–5717. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Bella F., Ozer H. L. Differential replication of SV40 and polyoma DNAs in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Virus Res. 1985 Jun;2(4):329–344. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen R. D., Rajan V. P., Ruff M. M., Kukowska-Latallo J., Cummings R. D., Lowe J. B. Isolation of a cDNA encoding a murine UDPgalactose:beta-D-galactosyl- 1,4-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminide alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferase: expression cloning by gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Naujokas M. A., Hassell J. A. Isolation of large T antigen-producing mouse cell lines capable of supporting replication of polyomavirus-plasmid recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2406–2412. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Eki T., Yamada M., Prives C., Hurwitz J. Species-specific in vitro synthesis of DNA containing the polyoma virus origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Role of DNA polymerase alpha and DNA primase in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Colley K. J. Glycosyltransferases. Structure, localization, and control of cell type-specific glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17615–17618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherneck S., Delmas V., Vogel F., Feunteun J. Induction of lymphomas by the hamster papovavirus correlates with massive replication of nonrandomly deleted extrachromosomal viral genomes. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3992–3998. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3992-3998.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper N. L., Shaper J. H., Meuth J. L., Fox J. L., Chang H., Kirsch I. R., Hollis G. F. Bovine galactosyltransferase: identification of a clone by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1573–1577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch L. On the nature of hereditable variation in cultured somatic cells. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. Carbohydrate heterogeneity of vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein allows localization of the defect in a glycosylation mutant of CHO cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Nov;219(1):128–139. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. Glycosylation mutants of animal cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:525–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.002521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Functional cloning of ICAM-2, a cell adhesion ligand for LFA-1 homologous to ICAM-1. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):61–64. doi: 10.1038/339061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stengelin S., Stamenkovic I., Seed B. Isolation of cDNAs for two distinct human Fc receptors by ligand affinity cloning. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L., Siminovitch L., Buchwald M. Persistence of freely replicating SV40 recombinant molecules carrying a selectable marker in permissive simian cells. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J., Lee E. U., McEntee K., Lai P. H., Paulson J. C. Primary structure of beta-galactoside alpha 2,6-sialyltransferase. Conversion of membrane-bound enzyme to soluble forms by cleavage of the NH2-terminal signal anchor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17735–17743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Dean F., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. In vitro replication of duplex circular DNA containing the simian virus 40 DNA origin site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5710–5714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto F., Clausen H., White T., Marken J., Hakomori S. Molecular genetic basis of the histo-blood group ABO system. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):229–233. doi: 10.1038/345229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]