Abstract
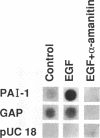
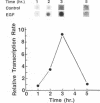
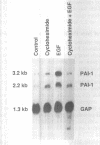
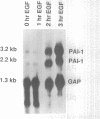
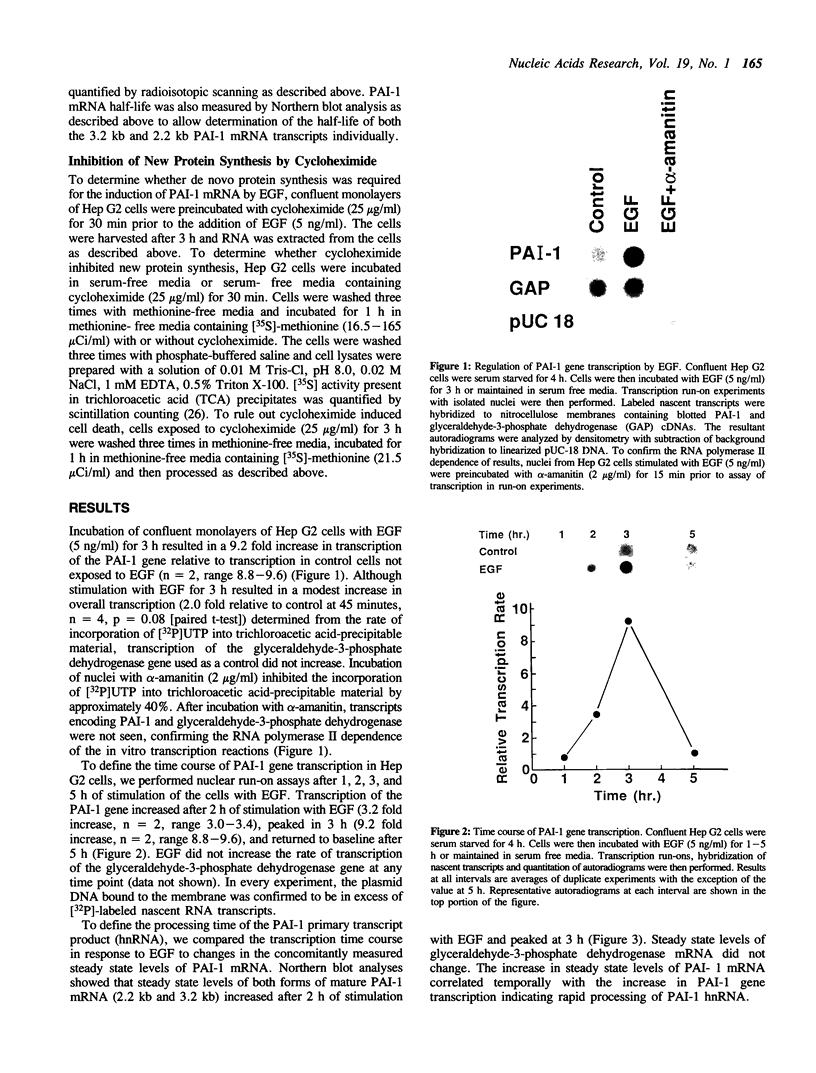
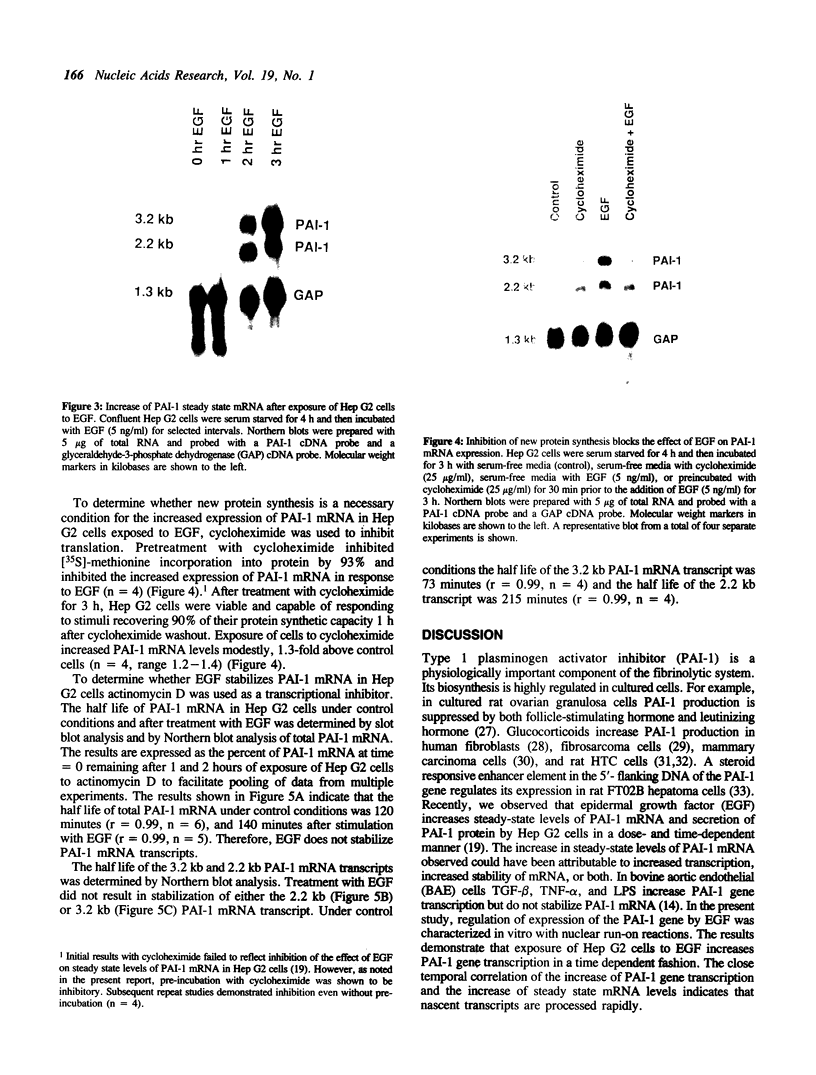
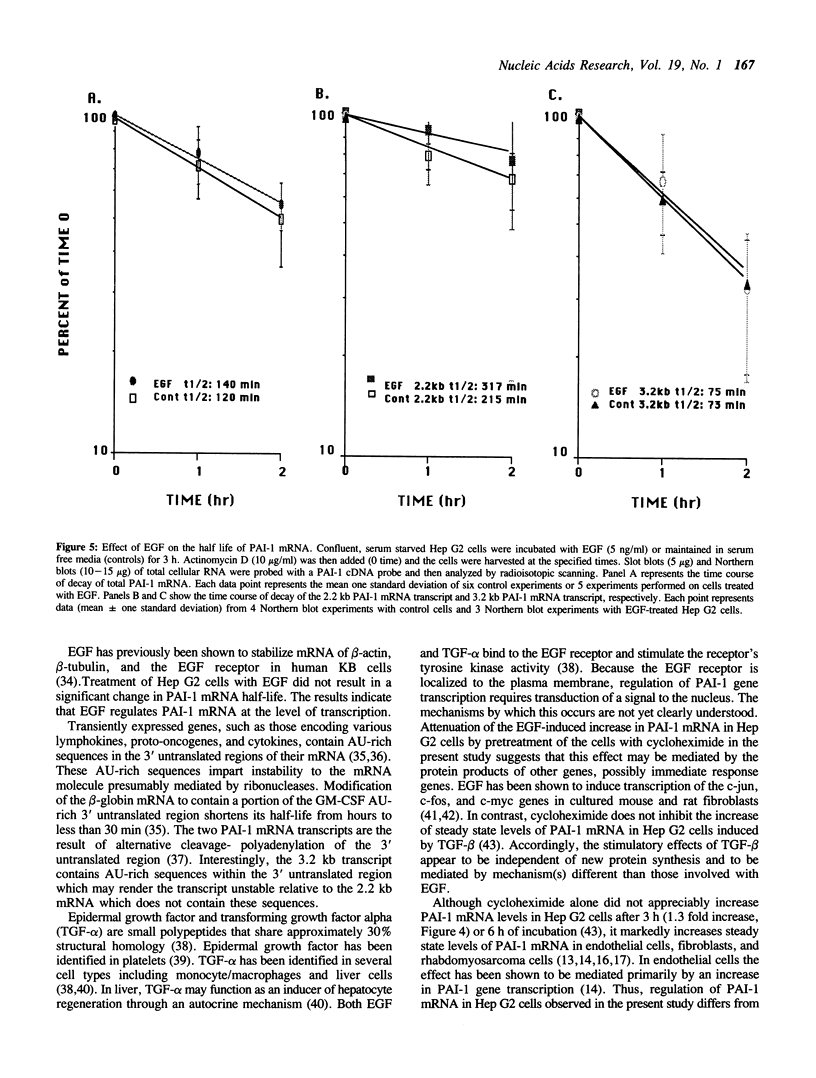
Secretion of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) by cultured cells is increased after exposure to specific cytokines and growth factors. We have shown previously that incubation of Hep G2 cells with epidermal growth factor (EGF) results in a marked increase in steady state levels of PAI-1 mRNA (Lucore, C.L., et al. (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263, 15845-15848). The present study was undertaken to determine whether the regulation of expression of PAI-1 mRNA by EGF is mediated at the level of transcription and/or by post-transcriptional mechanisms. The rate of transcription of the PAI-1 gene measured by nuclear run-on assays was found to be increased within 2 h after stimulation of the cells with EGF (5 ng/ml) (3.2 fold increase relative to control, n = 2, range 3.0-3.4). It reached a maximum in 3 h, (9.2 fold increase relative to control, n = 2, range 8.8-9.6) and returned to baseline in 5 h. Exposure of the cells to EGF did not increase the rate of transcription of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. The half life of PAI-1 mRNA in Hep G2 cells was 120 min as determined by RNA blot analysis after exposure of the cells to actinomycin D to inhibit transcription. Stimulation of the cells with EGF did not result in significant change in the half life of PAI-1 mRNA. The results demonstrate that exposure of Hep G2 cells to EGF increases PAI-1 gene transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen P. A., Pyke C., Riccio A., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Lund L. R., Blasi F., Danø K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 biosynthesis and mRNA level are increased by dexamethasone in human fibrosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):3021–3025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.3021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boström K., Borén J., Wettesten M., Sjöberg A., Bondjers G., Wiklund O., Carlsson P., Olofsson S. O. Studies on the assembly of apo B-100-containing lipoproteins in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4434–4442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Merlie J. P. Transcriptional regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes during muscle development. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11452–11455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Belin D., Failly-Crépin C., Vassalli J. D. Glucocorticoid modulation of plasminogen activators and of one of their inhibitors in the human mammary carcinoma cell line MDA-MB-231. Cancer Res. 1987 Jan 15;47(2):364–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Paramo J. A., Collen D. Generation in plasma of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in response to endotoxin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):818–824. doi: 10.1172/JCI111777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley D. J., Conanan L. B., Maynard J. R. Human fibroblasts produce inhibitor directed against plasminogen activator when treated with glucocorticoids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:609–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutry A. F., Kinniburgh A. J., Krabak M. J., Hui S. W., Wenner C. E. Induction of c-fos and c-myc proto-oncogene expression by epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha is calcium-independent. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19700–19705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwikel B. J., Barouski-Miller P. A., Coleman P. L., Gelehrter T. D. Dexamethasone induction of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator in HTC hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6847–6851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R. Transforming growth factor alpha. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):593–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichek D., Quertermous T. Thrombin regulation of mRNA levels of tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):222–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillmann W. H., Barrieux A., Neeley W. E., Contreras P. Influence of thyroid hormone on the in vitro translational activity of specific mRNAs in the rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7738–7745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebretsen L. F., Kierulf P., Brandtzaeg P. Extreme plasminogen activator inhibitor and endotoxin values in patients with meningococcal disease. Thromb Res. 1986 Jun 1;42(5):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. A., Ginsberg M. H., Loskutoff D. J. Detection and partial characterization of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1465–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI111559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Lucore C. L., Hopkins W. E., Billadello J. J., Sobel B. E. Potential attenuation of fibrinolysis by growth factors released from platelets and their pharmacologic implications. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Jun 15;63(20):1505–1511. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinno Y., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. A novel effect of EGF on mRNA stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4957–4966. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluft C., Verheijen J. H., Jie A. F., Rijken D. C., Preston F. E., Sue-Ling H. M., Jespersen J., Aasen A. O. The postoperative fibrinolytic shutdown: a rapidly reverting acute phase pattern for the fast-acting inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator after trauma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Nov;45(7):605–610. doi: 10.3109/00365518509155267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen B. S., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Plasminogen activator inhibitor is associated with the extracellular matrix of cultured bovine smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1082–1089. doi: 10.1172/JCI113164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Gudinchet A., Bachmann F. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and plasminogen activator inhibitor 2 in various disease states. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Feb 25;59(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Saksela O., Andreasen P. A., Keski-Oja J. Enhanced production and extracellular deposition of the endothelial-type plasminogen activator inhibitor in cultured human lung fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2403–2410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Roegner K., Erickson L. A., Schleef R. R., Huttenlocher A., Coleman P. L., Gelehrter T. D. The dexamethasone-induced inhibitor of plasminogen activator in hepatoma cells is antigenically-related to an inhibitor produced by bovine aortic endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Feb 28;55(1):8–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Sawdey M., Mimuro J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1989;9:87–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucore C. L., Fujii S., Wun T. C., Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Regulation of the expression of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in Hep G2 cells by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15845–15848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucore C. L., Sobel B. E. Interactions of tissue-type plasminogen activator with plasma inhibitors and their pharmacologic implications. Circulation. 1988 Mar;77(3):660–669. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.77.3.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Riccio A., Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Laiho M., Saksela O., Blasi F., Danø K. Transforming growth factor-beta is a strong and fast acting positive regulator of the level of type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor mRNA in WI-38 human lung fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Skouv J., Nielsen L. S., Stacey S. N., Danø K., Andreasen P. A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 protein, mRNA and gene transcription are increased by phorbol esters in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15688–15693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J. E., Fausto N. Transforming growth factor alpha may be a physiological regulator of liver regeneration by means of an autocrine mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1558–1562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Loskutoff D. J. Binding of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor to the extracellular matrix of cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5058–5063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Bjersing L., Hsueh A. J., Loskutoff D. J. Cultured granulosa cells produce two plasminogen activators and an antiactivator, each regulated differently by gonadotropins. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1666–1668. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Sawdey M., Lawrence D., Millan J. L., Loskutoff D. J. Cloning and sequence of a cDNA coding for the human beta-migrating endothelial-cell-type plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6776–6780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Orth D. N. Human plasma epidermal growth factor/beta-urogastrone is associated with blood platelets. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):249–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI110964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quantin B., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates transcription of the c-jun proto-oncogene in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):538–539. doi: 10.1038/334538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccio A., Lund L. R., Sartorio R., Lania A., Andreasen P. A., Danø K., Blasi F. The regulatory region of the human plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2805–2824. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M., Podor T. J., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Induction by transforming growth factor-beta, lipopolysaccharide, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10396–10401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Bevilacqua M. P., Sawdey M., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Loskutoff D. J. Cytokine activation of vascular endothelium. Effects on tissue-type plasminogen activator and type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5797–5803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., Princen H. M., Kooistra T., van Hinsbergh V. W. Inhibition of plasminogen activators by conditioned medium of human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line Hep G2. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jun;105(6):751–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator (antiactivator) synthesized by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14914–14921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zonneveld A. J., Curriden S. A., Loskutoff D. J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene: functional analysis and glucocorticoid regulation of its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5525–5529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]