Abstract
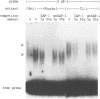
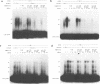
Interleukin-1, a mediator of inflammation, or tumor promoting phorbol esters induce transcription of stromelysin, a metalloproteinase that degrades extracellular matrix molecules and that is overexpressed in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Sequences required for induction of transcription of the human stromelysin promoter are contained on a 46 base pair fragment. This fragment contains a sequence with a high degree of similarity to the binding site for the transcription factor activator protein-1 (AP-1) and indeed, the AP-1 sequence of this fragment is necessary but not sufficient for the maximal response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (phorbol) or interleukin-1. Maximal induction requires functional cooperation between the AP-1 sequence and a neighboring upstream regulatory sequence (URS) of the stromelysin promoter which is also necessary but not sufficient. We demonstrate that both the AP-1 sequence and the URS bind phorbol or interleukin-1 induced nuclear proteins. Cooperation of the AP-1 sequence with another sequence present in the stromelysin promoter may be a general mechanism whereby the AP-1 element, which is found in many promoters, achieves a maximal and specific response to various stimuli.
Full text
PDF

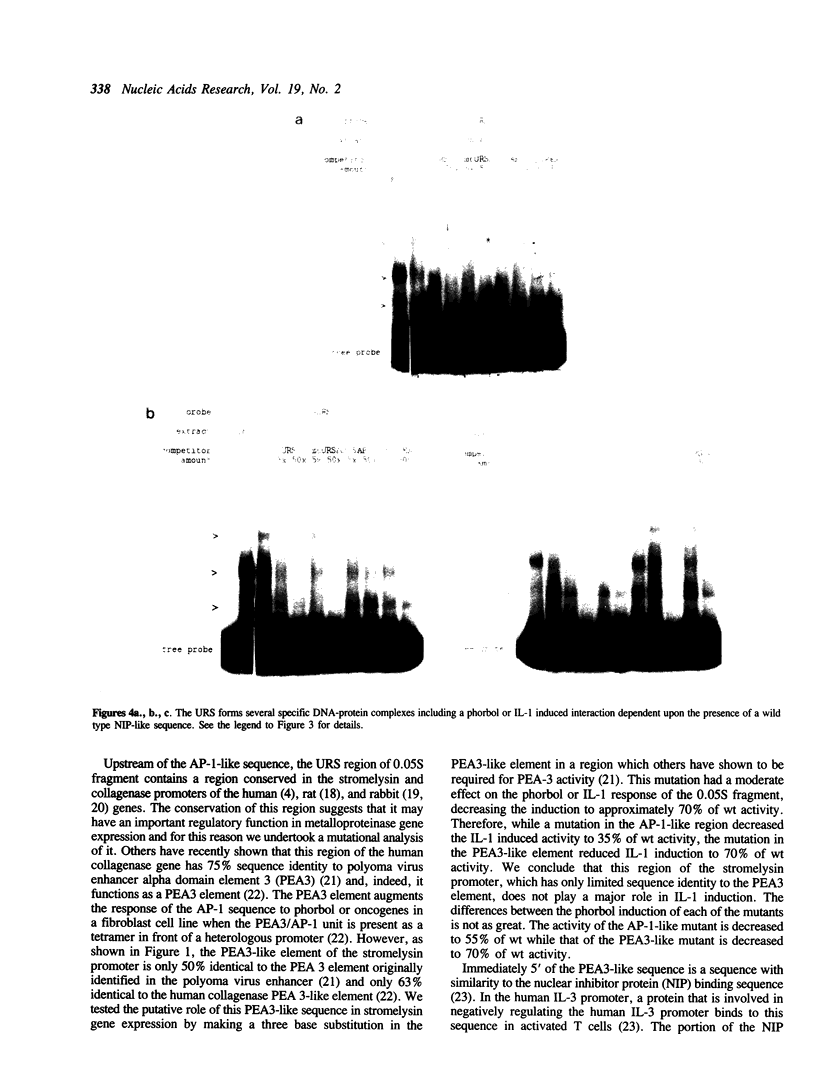
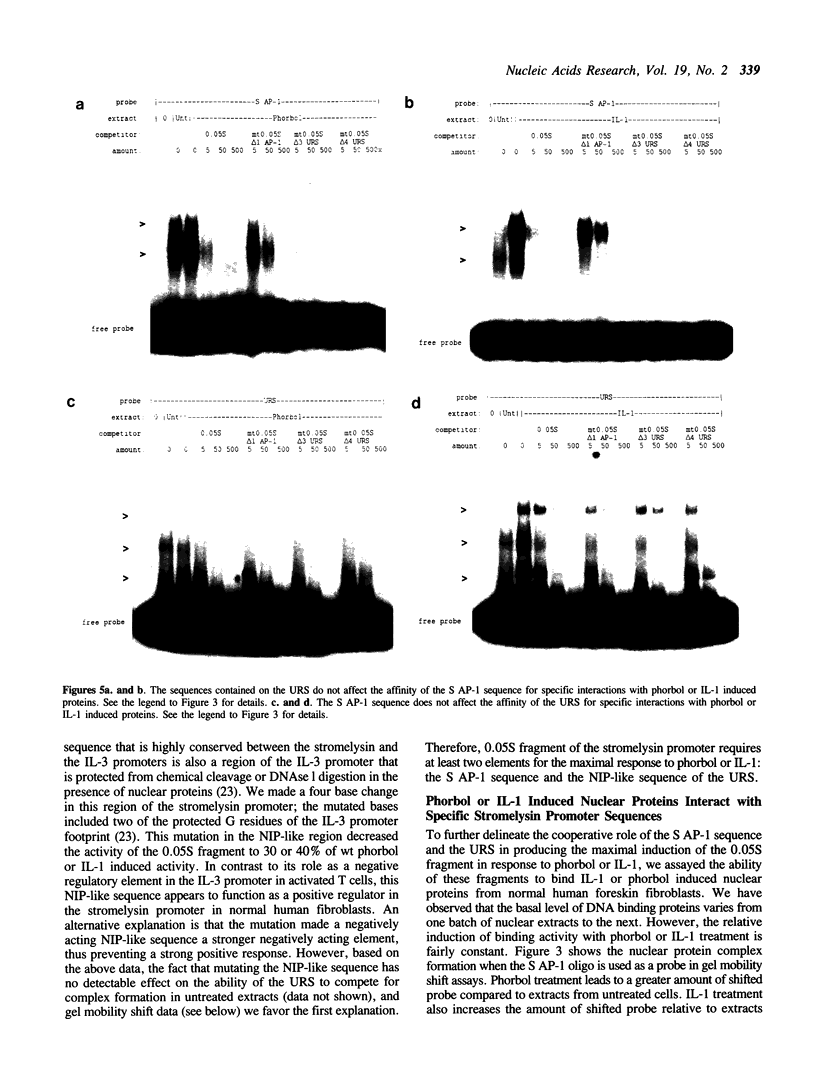


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fini M. E., Plucinska I. M., Mayer A. S., Gross R. H., Brinckerhoff C. E. A gene for rabbit synovial cell collagenase: member of a family of metalloproteinases that degrade the connective tissue matrix. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6156–6165. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Ruley H. E. Transcription from the stromelysin promoter is induced by interleukin-1 and repressed by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16300–16304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Andrews N. C., Murphy H. S., Kreissman S. G., Nathan D. G. Positive and negative elements regulate human interleukin 3 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Leroy P., Ruhlmann C., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Isolation of the oncogene and epidermal growth factor-induced transin gene: complex control in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1679–1686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muegge K., Williams T. M., Kant J., Karin M., Chiu R., Schmidt A., Siebenlist U., Young H. A., Durum S. K. Interleukin-1 costimulatory activity on the interleukin-2 promoter via AP-1. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):249–251. doi: 10.1126/science.2799385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinones S., Saus J., Otani Y., Harris E. D., Jr, Kurkinen M. Transcriptional regulation of human stromelysin. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8339–8344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan W. A., Jr, Franza B. R., Jr, Gilman M. Z. Two distinct cellular phosphoproteins bind to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirum K. L., Brinckerhoff C. E. Cloning of the genes for human stromelysin and stromelysin 2: differential expression in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 31;28(22):8691–8698. doi: 10.1021/bi00448a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Flores P., Gutman A., Wasylyk B. PEA3 is a nuclear target for transcription activation by non-nuclear oncogenes. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3371–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]