Abstract
Translation initiation on EMCV RNA occurs via binding of ribosomes to an internal sequence within the 5' noncoding region. To investigate the organization of the internal ribosome entry site (IRES) we have determined the translational efficiencies of a series of deletion mutants within the 5' noncoding region of EMCV RNA. Three functional regions have been distinguished: a sequence between nts 315-484 and the upper parts of the double-helical structural domains III (nts 488-647) and IV (nts 701-763). The first one greatly enhances translation, but is not absolutely necessary for internal initiation. The other two regions are indispensable to this process. A sequence within domain IV determines inhibition of in vitro translation of mRNAs with 5'-terminal dependent initiation. It is proposed to interact with a translational factor(s) common to the internal and 5'-terminal dependent initiation.
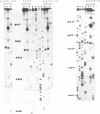
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barta A., Steiner G., Brosius J., Noller H. F., Kuechler E. Identification of a site on 23S ribosomal RNA located at the peptidyl transferase center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3607–3611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Baudin F., Mougel M., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Probing the structure of RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9109–9128. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasev A. V., Miroshnichenko N. A., Ugarova T. Iu. Ispol'zovanie beskletochnoi beloksinteziruiuiushchei sistemy iz kletok astsitnoi kartsinomy Krebs-2 dlia transliatsii RNK virusov rastenii. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1989 Jan-Feb;23(1):119–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazachkov YuA, Chernovskaya T. V., Siyanova EYu, Svitkin YuV, Ugarova TYu, Agol V. I. Leader polypeptides encoded in the 5'-region of the encephalomyocarditis virus genome. FEBS Lett. 1982 May 17;141(2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Sonenberg N. Translational efficiency of poliovirus mRNA: mapping inhibitory cis-acting elements within the 5' noncoding region. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2219–2227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2219-2227.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Chernov B. K., Dmitrieva T. M., Agol V. I. Conservation of the secondary structure elements of the 5'-untranslated region of cardio- and aphthovirus RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5701–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelness G. S., Williams D. L. Secondary structure analysis of apolipoprotein II mRNA using enzymatic probes and reverse transcriptase. Evaluation of primer extension for high resolution structure mapping of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8637–8646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Park I. W., Evans C. L., Jaynes J. M., Palmenberg A. C. Effects of cDNA hybridization on translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2033–2037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2033-2037.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Racaniello V. R., Dunn G., Cooper J., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. New model for the secondary structure of the 5' non-coding RNA of poliovirus is supported by biochemical and genetic data that also show that RNA secondary structure is important in neurovirulence. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Andino R., Baltimore D. An RNA sequence of hundreds of nucleotides at the 5' end of poliovirus RNA is involved in allowing viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2291–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2291-2299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Translation in mammalian cells of a gene linked to the poliovirus 5' noncoding region. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):445–448. doi: 10.1126/science.2839901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugarova T. Iu. Pervichnaia struktura mRNK i transliatsionnaia strategiia éukariot. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1987 Jul-Aug;21(4):888–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Angel R. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Fernández-Tomás C., Silverstein S. J., Racaniello V. R. Cell proteins bind to multiple sites within the 5' untranslated region of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8299–8303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]