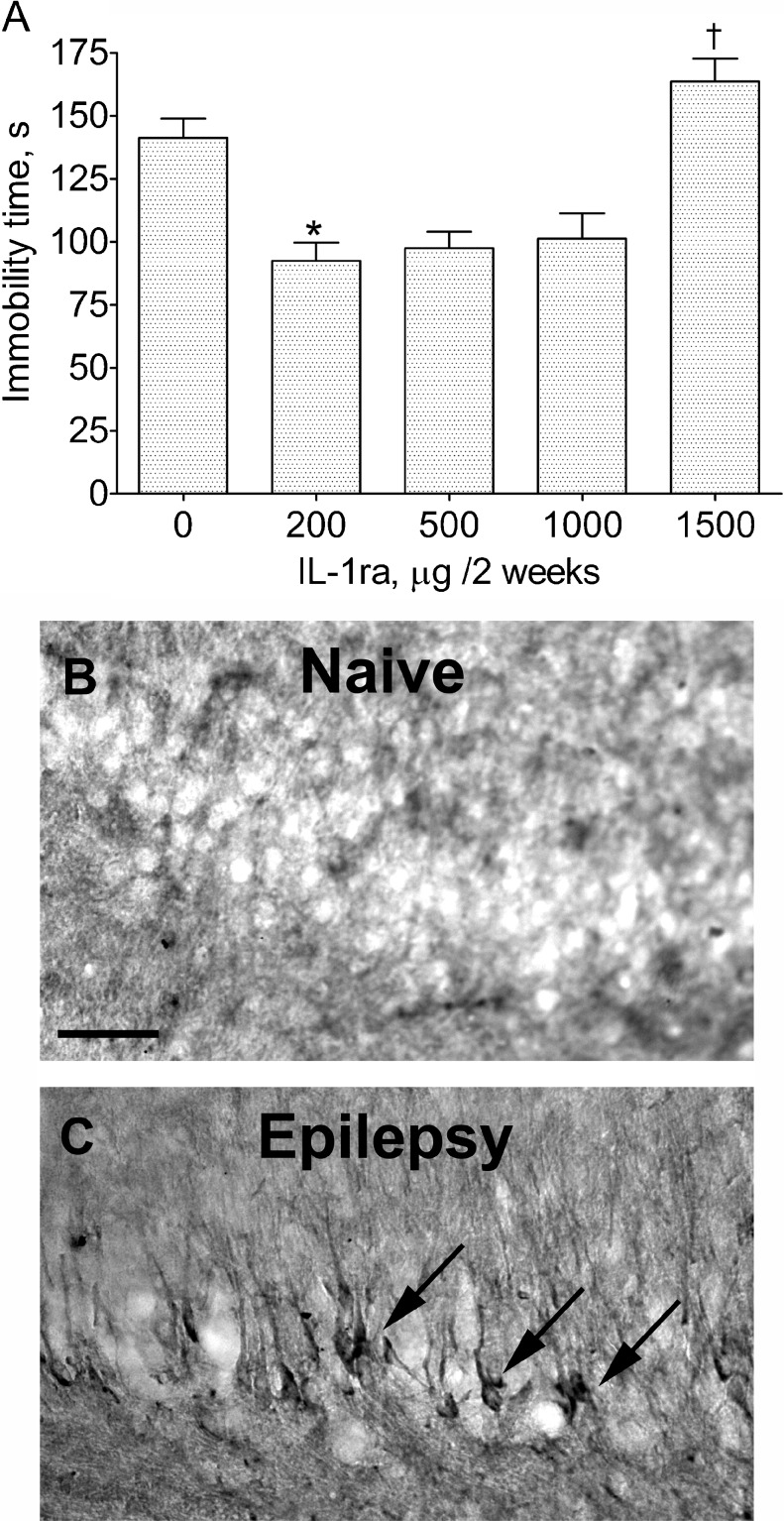
Fig. 1.
(a) Effects of various doses of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) in post-status epilepticus (SE) rats on the immobility time in the forced swim test (FST). The effects of 200, 500, and 1000 μg were statistically similar. At 1500 μg IL-1ra treatment worsened the performance of the animals in the FST. Each group included 4 animals. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 vs “0 μg”; †p < 0.05 vs “200 μg” (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Mann–Whitney U post hoc test). (b, c) Immunohistochemical staining of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in the CA3 area of the hippocampus of a naïve rat (b) and a rat 2 months after SE and documented spontaneous seizures (c). Note the appearance of IL-1β-positive cells in the post-SE rat. Scale bar = 40 μM