Abstract
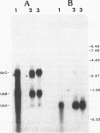
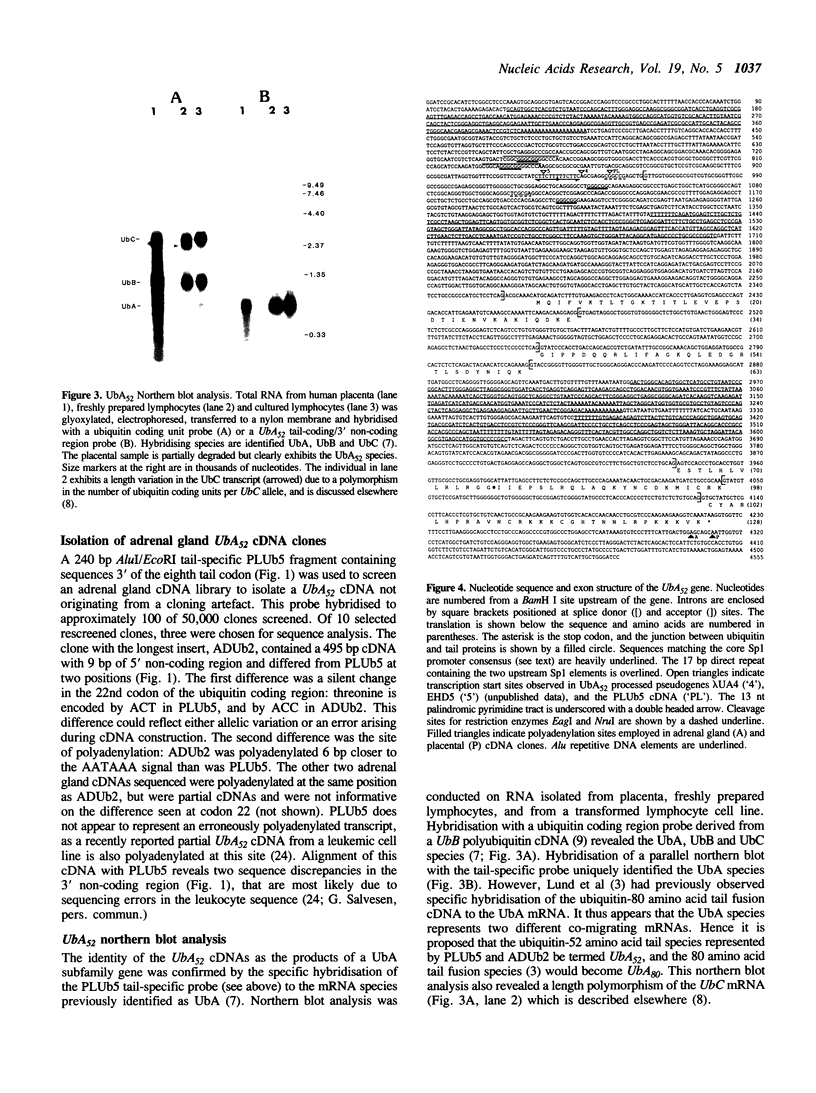
Complementary DNA clones encoding ubiquitin fused to a 52 amino acid tail protein were isolated from human placental and adrenal gland cDNA libraries. The deduced human 52 amino acid tail protein is very similar to the homologous protein from other species, including the conservation of the putative metal-binding, nucleic acid-binding domain observed in these proteins. Northern blot analysis with a tail-specific probe indicated that the previously identified UbA mRNA species most likely represents comigrating transcripts of the 52 amino acid tail (UbA52) and 80 amino acid tail (UbA80) ubiquitin fusion genes. The UbA52 gene was isolated from a human genomic library and consists of five exons distributed over 3400 base pairs. One intron is in the 5' non-coding region, two interrupt the single ubiquitin coding unit, and the fourth intron is within the tail coding region. Several members of the Alu family of repetitive DNA are associated with the gene. The UbA52 promoter has several features in common with mammalian ribosomal protein genes, including its location in a CpG-rich island, initiation of transcription within a polypyrimidine tract, the lack of a consensus TATA motif, and the presence of Sp1 binding sites, observations that are consistent with the recent identification of the ubiquitin-free tail proteins as ribosomal proteins. Thus, in spite of its unusual feature of being translationally fused to ubiquitin, the 52 amino acid tail ribosomal protein is expressed from a structurally typical ribosomal protein gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R. T., Board P. G. An improved method for mapping recombinant lambda phage clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1198–1198. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Board P. G. Nucleotide sequence of a human ubiquitin Ub B processed pseudogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4352–4352. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Board P. G. The human ubiquitin gene family: structure of a gene and pseudogenes from the Ub B subfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):443–463. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Board P. G. Unequal crossover generates variation in ubiquitin coding unit number at the human UbC polyubiquitin locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):534–542. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U., Schlesinger M. J. The chicken ubiquitin gene contains a heat shock promoter and expresses an unstable mRNA in heat-shocked cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4602–4610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J., Morishima J. K., Devarayalu S., Gelinas R. E. Regulatory elements in the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the human alpha 1(I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8869–8873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F. High-sensitivity S1 mapping with single-stranded [32P]DNA probes synthesized from bacteriophage M13mp templates. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callis J., Raasch J. A., Vierstra R. D. Ubiquitin extension proteins of Arabidopsis thaliana. Structure, localization, and expression of their promoters in transgenic tobacco. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12486–12493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowland J. B., Wiborg O., Vuust J. Human ubiquitin genes: one member of the UbB gene subfamily is a tetrameric non-processed pseudogene. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80728-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorda R., Ennis H. L. Structure of two developmentally regulated Dictyostelium discoideum ubiquitin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2097–2103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. W., Jones D., Candido E. P. UbiA, the major polyubiquitin locus in Caenorhabditis elegans, has unusual structural features and is constitutively expressed. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):268–277. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Perry R. P. A characterization of the elements comprising the promoter of the mouse ribosomal protein gene RPS16. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5323–5337. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley C., Fried M. The mouse rpL7a gene is typical of other ribosomal protein genes in it's 5' region but differs in being located in a tight cluster of CpG-rich islands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5353–5357. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya Y., Kato K., Hayashizaki Y., Himeno S., Tarui S., Matsubara K. Revision of consensus sequence of human Alu repeats--a review. Gene. 1987;53(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. S., Simon J. A., Lis J. T. Structure and expression of ubiquitin genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4727–4735. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Moats-Staats B. M., Simmons J. G., Hoyt E., D'Ercole A. J., Martin F., Van Wyk J. J. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding human ubiquitin reveals that ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7609–7613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H. Control of ribosomal protein gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monia B. P., Ecker D. J., Jonnalagadda S., Marsh J., Gotlib L., Butt T. R., Crooke S. T. Gene synthesis, expression, and processing of human ubiquitin carboxyl extension proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4093–4103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Taubenberger A., Westphal M., Jaeger E., Noegel A., Gerisch G. Complete cDNA sequence of a Dictyostelium ubiquitin with a carboxy-terminal tail and identification of the protein using an anti-peptide antibody. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 14;229(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin genes: a family of natural gene fusions. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1429–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman K. L., Rechsteiner M. Identification of the long ubiquitin extension as ribosomal protein S27a. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):438–440. doi: 10.1038/338438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G., Lloyd C., Farley D. cDNA encoding a human homolog of yeast ubiquitin 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5485–5485. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Bond U. Ubiquitin genes. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1987;4:77–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H. The human growth hormone gene family: nucleotide sequences show recent divergence and predict a new polypeptide hormone. DNA. 1982;1(3):239–249. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T., Gallatin W. M., Siegelman M., Smith H. T., Fried V. A., Weissman I. L. Expression cloning of a lymphocyte homing receptor cDNA: ubiquitin is the reactive species. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):845–850. doi: 10.1126/science.3003914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindle J., Ajioka J., Eisen H., Sanwal B., Jacquemot C., Browder Z., Buck G. The genomic organization and transcription of the ubiquitin genes of Trypanosoma cruzi. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1121–1127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiborg O., Pedersen M. S., Wind A., Berglund L. E., Marcker K. A., Vuust J. The human ubiquitin multigene family: some genes contain multiple directly repeated ubiquitin coding sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):755–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]