Abstract
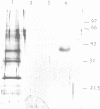
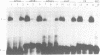
The transcription factors LF-A1 and LF-B1 are required for the cell-specific expression of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene in hepatocytes. We report here the purification and preliminary characterization of LF-A1. This protein, purified to homogeneity from calf liver nuclei by site-specific DNA affinity chromatography and reverse-phase HPLC, has a molecular mass of 40 kDa. Binding sites of LF-A1 are present in the promoter regions of several genes expressed in the liver (alpha 1-antitrypsin, apolipoproteins A1, B1, A4 and pyruvate kinase). Interestingly, the binding site of LF-A1 is bipartite and consists of two short sequence motifs (consensus: TGGACT/CT/C and TGGCCC) separated by a variable 'spacer' region. Insertion or deletion of 1-4 nucleotides in the 'spacer' region of the site in the alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter does not abolish DNA binding.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumhueter S., Mendel D. B., Conley P. B., Kuo C. J., Turk C., Graves M. K., Edwards C. A., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):372–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao Y. S., Ding X. H., Dai P. H., Wu T. J., Pan T. C., Hao Q. L., Yamin T. T. Identification of an enhancer-like element in the 5' flanking region of the rat apolipoprotein A-I gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7061–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control of the mouse prealbumin (transthyretin) gene: both promoter sequences and a distinct enhancer are cell specific. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4697–4708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Ciliberto G., Hardon E., Paonessa G., Palla F., Lundberg L., Cortese R. Cis- and trans-acting elements responsible for the cell-specific expression of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2759–2766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Walker D. W., Paik Y. K., Boguski M. S., Freeman M., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Structure and expression of the human apolipoprotein A-IV gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7973–7981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad I. A., Ordovas J. M., Fitzpatrick T., Karathanasis S. K. Linkage, evolution, and expression of the rat apolipoprotein A-I, C-III, and A-IV genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13268–13277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardon E. M., Frain M., Paonessa G., Cortese R. Two distinct factors interact with the promoter regions of several liver-specific genes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jose-Estanyol M., Danan J. L. A liver-specific factor and nuclear factor I bind to the rat alpha-fetoprotein promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10865–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardassis D., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Ramji D. P., Cortese R., Zannis V. I., Cladaras C. Characterization of the promoter elements required for hepatic and intestinal transcription of the human apoB gene: definition of the DNA-binding site of a tissue-specific transcriptional factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2653–2659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Schaffner W. Octamer transcription factors and the cell type-specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1444–1449. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fast P., McBride W., Staudt L. M. A human protein specific for the immunoglobulin octamer DNA motif contains a functional homeobox domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Schibler U. A glycosylated liver-specific transcription factor stimulates transcription of the albumin gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1179–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucero M. A., Sanchez D., Ochoa A. R., Brunel F., Cohen G. N., Baralle F. E., Zakin M. M. Interaction of DNA-binding proteins with the tissue-specific human apolipoprotein-AII enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2283–2300. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa A., Brunel F., Mendelzon D., Cohen G. N., Zakin M. M. Different liver nuclear proteins binds to similar DNA sequences in the 5' flanking regions of three hepatic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):119–133. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Morrone G., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene: transcriptional regulation during development and acute phase induction. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1905–1912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paonessa G., Gounari F., Frank R., Cortese R. Purification of a NF1-like DNA-binding protein from rat liver and cloning of the corresponding cDNA. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3115–3123. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangan V. S., Das G. C. Purification and biochemical characterization of hepatocyte nuclear factor 2 involved in liver-specific transcription of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8874–8879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. Chicken liver TGGCA protein purified by preparative mobility shift electrophoresis (PMSE) shows a 36.8 to 29.8 kd microheterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9707–9726. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Kugler W., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. Hepatocyte-specific promoter element HP1 of the Xenopus albumin gene interacts with transcriptional factors of mammalian hepatocytes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Inagami S., Lovegren E., Chalkley R. DNA denatures upon drying after ethanol precipitation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8739–8754. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Puzenat N., Kahn A., Raymondjean M. Analysis by cell-free transcription of the liver-specific pyruvate kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4409–4415. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B. Enhancers and transcription factors in the control of gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):17–35. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]