Abstract
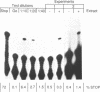
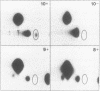
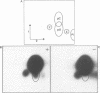
Human apolipoprotein (apo) B mRNA is edited in a tissue specific reaction, to convert glutamine codon 2153 (CAA) to a stop translation codon. The RNA editing product templates and hybridises as uridine, but the chemical nature of this reaction and the physical identity of the product are unknown. After editing in vitro of [32P] labelled RNA, we are able to demonstrate the production of uridine from cytidine; [alpha 32P] cytidine triphosphate incorporated into RNA gave rise to [32P] uridine monophosphate after editing in vitro, hydrolysis with nuclease P1 and thin layer chromatography using two separation systems. By cleaving the RNA into ribonuclease T1 fragments, we show that uridine is produced only at the authentic editing site and is produced in quantities that parallel an independent primer extension assay for editing. We conclude that apo B mRNA editing specifically creates a uridine from a cytidine. These observations are inconsistent with the incorporation of a uridine nucleotide by any polymerase, which would replace the alpha-phosphate and so rule out a model of endonucleolytic excision and repair as the mechanism for the production of uridine. Although transamination and transglycosylation remain to be formally excluded as reaction mechanisms our results argue strongly in favour of the apo B mRNA editing enzyme as a site-specific cytidine deaminase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H. An unwinding activity that covalently modifies its double-stranded RNA substrate. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1089–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Van den Burg J., Brakenhoff J. P., Sloof P., Van Boom J. H., Tromp M. C. Major transcript of the frameshifted coxII gene from trypanosome mitochondria contains four nucleotides that are not encoded in the DNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):819–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum B., Bakalara N., Simpson L. A model for RNA editing in kinetoplastid mitochondria: "guide" RNA molecules transcribed from maxicircle DNA provide the edited information. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90735-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boström K., Lauer S. J., Poksay K. S., Garcia Z., Taylor J. M., Innerarity T. L. Apolipoprotein B48 RNA editing in chimeric apolipoprotein EB mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15701–15708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Habib G., Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Lee B. R., Weng S. A., Silberman S. R., Cai S. J., Deslypere J. P., Rosseneu M. Apolipoprotein B-48 is the product of a messenger RNA with an organ-specific in-frame stop codon. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):363–366. doi: 10.1126/science.3659919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese R., Kammen H. O., Spengler S. J., Ames B. N. Biosynthesis of pseudouridine in transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1103–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese R., Landsberg R., Haar R. A., Umbarger H. E., Ames B. N. Pleiotropy of hisT mutants blocked in pseudouridine synthesis in tRNA: leucine and isoleucine-valine operons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1857–1861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covello P. S., Gray M. W. RNA editing in plant mitochondria. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):662–666. doi: 10.1038/341662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A. M., Montero-Puerner Y., Lee B. J., Hatfield D. Selenocysteine inserting tRNAs are likely generated by tRNA editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6727–6727. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. M., Wynne J. K., Wallis S. C., Scott J. An in vitro system for the editing of apolipoprotein B mRNA. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. S., Trewyn R. W. Inosine biosynthesis in transfer RNA by an enzymatic insertion of hypoxanthine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2407–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Abraham J. M., Stuart K. Extensive editing of the cytochrome c oxidase III transcript in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto J. M., Lamattina L., Bonnard G., Weil J. H., Grienenberger J. M. RNA editing in wheat mitochondria results in the conservation of protein sequences. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):660–662. doi: 10.1038/341660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto J. M., Weil J. H., Grienenberger J. M. Editing of the wheat coxIII transcript: evidence for twelve C to U and one U to C conversions and for sequence similarities around editing sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3771–3776. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Diamond A., Dudock B. Opal suppressor serine tRNAs from bovine liver form phosphoseryl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiesel R., Wissinger B., Schuster W., Brennicke A. RNA editing in plant mitochondria. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1632–1634. doi: 10.1126/science.2480644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith G., Desgrès J., Pochart P., Heyman T., Kuo K. C., Gehrke C. W. Eukaryotic tRNAs(Pro): primary structure of the anticodon loop; presence of 5-carbamoylmethyluridine or inosine as the first nucleoside of the anticodon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90095-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman I. R. DNA ligase: structure, mechanism, and function. Science. 1974 Nov 29;186(4166):790–797. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4166.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Nishikawa K., Nemoto F., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Miyazawa T., Yokoyama S. Codon and amino-acid specificities of a transfer RNA are both converted by a single post-transcriptional modification. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):179–181. doi: 10.1038/336179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Yokoyama S., Horie N., Matsuda A., Ueda T., Yamaizumi Z., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Miyazawa T. A novel lysine-substituted nucleoside in the first position of the anticodon of minor isoleucine tRNA from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9261–9267. doi: 10.1351/pac198961030573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S. Minor components in transfer RNA: their characterization, location, and function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1972;12:49–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Nishimura S. Isolation and characterization of a guanine insertion enzyme, a specific tRNA transglycosylase, from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3061–3066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Noguchi S., Kasai H., Shindo-Okada N., Ohgi T., Goto T., Nishimura S. Novel mechanism of post-transcriptional modification of tRNA. Insertion of bases of Q precursors into tRNA by a specific tRNA transglycosylase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3067–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick L., Furneaux H., Hurwitz J. Purification of wheat germ RNA ligase. II. Mechanism of action of wheat germ RNA ligase. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6694–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Edwards Y. H., Knott T. J., Scott J. A novel form of tissue-specific RNA processing produces apolipoprotein-B48 in intestine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster W., Hiesel R., Wissinger B., Brennicke A. RNA editing in the cytochrome b locus of the higher plant Oenothera berteriana includes a U-to-C transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2428–2431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Greer C. L., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Enzymatic mechanism of an RNA ligase from wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8374–8383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weill D., Heyman T. Nucleotide sequence of two proline tRNA (AGG and CGG) genes from chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6134–6134. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Maizels N. RNA editing: guided but not templated? Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):917–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90053-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]