Abstract
A chemically prolific strain of Aspergillus was isolated from a soil sample collected near Waikiki Beach, Honolulu, Hawaii. The fungus produced several secondary metabolites that were purified and placed in our natural products library, which was later screened for substances capable of inhibiting biofilm formation by Candida albicans. It was determined that one of the secondary metabolites from the Hawaiian fungal isolate, a new complex prenylated indole alkaloid named waikialoid A (1), inhibited biofilm formation with an IC50 value of 1.4 μM. Another structurally unrelated, presumably polyketide metabolite, waikialide A (15), also inhibited C. albicans biofilm formation, but was much less potent (IC50 value of 32.4 μM). Microscopy studies revealed that compound 1 also inhibited C. albicans hyphal morphogenesis. While metabolite 1 appears ineffective at disrupting preformed biofilms, the accumulated data indicate that the new compound may exert its activity against C. ablicans during the early stages of surface colonization involving cell adherence, hyphal development, and/or biofilm assembly. Unlike some other stephacidin/notoamide compounds, metabolite 1 was not cytotoxic to fungi or human cells (up to 200 μM), which makes this an intriguing model compound for studying the adjunctive use of biofilm inhibitors in combination with standard antifungal antibiotics.
During the period of February 2009 to October 2011, our research group prepared extracts from just over two thousand fungal isolates originating from three environmentally disparate regions: Alaska, Hawaii, and Oklahoma. Many of the fungal extracts were subsequently screened by LC-ESIMS leading us to classify a selection of the isolates as ‘metabolically talented’1 or ‘chemically productive’2 in reference to their capacities to generate multiple secondary metabolites (for our purposes, we define secondary metabolites as compounds with masses of ~300–1,200 Da that elute from C18 with ~25–85% methanol). From our perspective, extracts containing natural products that fulfill these simple criteria represent potentially valuable sources of drug-like substance and our group is actively engaged in building a modest library of compounds meeting these benchmarks. The functions of the pure compound library are two-fold: first, it provides a unique chemical resource for bioactive compound discovery that complements our extensive collection of >4,000 microbial-derived crude extracts; and second, it serves as an improved tool for vetting new in-house bioassays prior to screening against crude extracts and fractions.
One of the new biological screens we recently introduced to our lab was designed to identify compounds that inhibit biofilm formation by the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Candida spp. are widely recognized as the single most common source of opportunistic mycoses throughout the world 3–6 with an estimated annual financial burden topping $1 billion in the United States alone.7 Infections caused by Candida spp. are encountered with growing frequency among several patient populations including infants, the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, diabetics, patients receiving oncological treatments, and others.7 An important feature linked to the propensity of many Candida spp. to cause serious infections is their capabilities of generating biofilms. Candida biofilms demonstrate remarkable versatility in their abilities to grow on a variety of surfaces including human tissues and implanted devices.8, 9 Biofilms are thought to play key roles in enhancing morbidity and mortality associated with Candida infections since biofilm matrices severely reduce the penetrance of antifungal therapeutics into cells.8 Moreover, Candida biofilms serve as favorable substrates that harbor other pathogens and encourage the expansive growth of polymicrobial (mixed bacterial and fungal) communities.10, 11 Candida biofilms have recently been linked to the emergence of highly drug-resistant persister cell populations, which are purported to be major contributors to infection relapses following the cessation of standard courses of antifungal therapeutics.12, 13
In this report, we focus on the preparation of purified natural products from a metabolically-talented Aspergillus sp. The fungus was isolated from a soil sample collected in the summer of 2009 near Waikiki Beach, Honolulu, Hawaii. Compounds from the fungus were deposited in our secondary-metabolite library and later screened in our biofilm inhibition assay. As a result of the library screening, several bioactive compounds emerged that inhibited C. albicans biofilm-formation. One of the especially noteworthy inhibitors we encountered was obtained from a Hawaiian Aspergillus sp. isolate. The compound was found to be a new complex prenylated indole alkaloid that we have named waikialoid A (1). To the best of our knowledge, metabolite 1 is among the most potent inhibitors of fungal biofilm formation reported to date.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Structure Characterization of Secondary Metabolites from the Hawaiian Aspergillus sp. Isolate
LC-ESIMS examination of the organic extract from the Hawaiian Aspergillus sp. isolate demonstrated that this fungal strain was capable of generating many putative secondary metabolites with masses between ~400–900 Da. Prior to scale-up fermentation, further tests were performed on this fungus to compare the effects of different fermentation conditions and growth-medium additives (i.e., the chemical epigenetic modifier14 suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid at 400, 800, and 1,000 μM1, as well as 3.5% NaCl) on secondary metabolite production. These experiments provided a revealing set of LC-ESIMS profiles (Supporting Information, Figure S1) confirming that the Hawaiian fungal isolate was capable of generating a diverse assemblage of natural products. Scale-up liquid-state and static cultures of the fungus provided sufficient material that enabled us to purify and promptly dereplicate (by HRESIMS, specific rotation, and 1H and 13C NMR) several components including notoamide B (2),15 sclerotiamide (3),16 notoamide F (4),17 notoamide R (5),18 stephacidin A (6),19 CJ-17665 (also known as avrainvillamide) (7),20 circumdatin C (8),21 circumdatin F (9),22 two diketopiperazines (10 and 11),23 flavacol (12),24, 25 and 3-isobutyl-6-(1-hydroxyl-2-methylpropyl)-2(1H)-pyrazinone (13)24 (Supporting Information, Scheme S1). Four additional metabolites were also purified (1, 14–16) that could not be dereplicated, which led us to thoroughly investigate and characterize their respective structures.
HRESIMS of purified 1 yielded an adduct ion that was consistent with a molecular formula of C52H54N6O7. This necessitated that compound 1 possessed 29 degrees of unsaturation. Inspection of the 1H NMR spectrum of 1 provided a series of proton resonances that were consistent with other compounds in the stephacidin/notoamide family of prenylated indole alkaloid natural products; however, the molecular formula we proposed for 1 was approximately twice the size expected for the majority of metabolites in this series. These data alerted us to a previous report by Cian-Cutrone et al. describing stephacidin B (17),19 which had been shown to be an unusual asymmetric dimerization product of CJ-17665 (7) (Supporting Information, Scheme S1).26 Although a large proportion of the proton and carbon resonance for 1 matched those reported for 17, the loss of one oxygen atom in the molecular formula of 1 necessitated that the two compounds were different.
Examination of the 1H NMR resonances for the new metabolite (Table 1) revealed that 17 contained a single amide proton (δH 7.76, NH-25)26 and a signal for the N-hydroxylamine hydroxyl group (δH 10.74, OH-62),26 whereas 1 possessed two different downfield exchangeable proton singlets (δH 7.58 and 7.44) (Table 1). This led us to scrutinize the oxidation state of the N-9 and N-39 nitrogen atoms in 1 since reduction of either the nitrone or N-hydroxylamine, respectively, in 17 could have contributed to the loss of one oxygen atom with the concomitant introduction of a new exchangeable amine proton. Examination of the 1H-13C HSQC and 1H-13C HMBC results for 1 (Table 1) provided strong evidence that the N-9 nitrone remained intact, while N-39 was reduced from an N-hydroxylamine to an amine. Although other subtle changes in the chemical shifts of carbon atoms near the presumed indole amine provided further evidence in support of this hypothesis, additional data were required to resolve the structure of 1.
Table 1.
1H (500 MHz), 13C (100 MHz), and 1H-13C NMR data for 1 and 15 (CDCl3)
| waikialoid A (1) | waikialoid B (15) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| position | δC, type | δH, mult. (J in Hz) | HMBC (H→C) | δCa, type | δH, mult. (J in Hz) | HMBC(H→C) |
| 1a | 44.2, CH2 | 3.29, td (7.2, 11.6) | C-2,3,4 | 43.8, CH2 | 3.19, m | |
| 1b | 3.47, m | 3.41, m | ||||
| 2 | 24.8, CH2 | 2.00, m | C-1,3 | 24.6, CH2 | 1.98, m | C-26,37 |
| 2.22, m | C-4,7,26 | |||||
| 3a | 29.4, CH2 | 1.83, m | C-1,2,4,5,26 | 29.1, CH2 | 1.81, m | C-4,26 |
| 3b | 2.76, td (6.5, 12.8) | 2.75, m | C-4,6,26 | |||
| 4 | 65.8, qC | 65.5, qC | ||||
| 5 | 28.6, CH2 | 2.16, m | C-4,6,7,26 | 28.7, CH2 | 2.12, m | C-5,26 |
| 2.20, m | C-4,26 | |||||
| 6 | 43.6, CH | 3.00, m | C-4,5,7,23,27,28 | 43.0, CH | 2.74, m | C-22,23,27,28 |
| 7 | 38.1, qC | 38.0, qC | ||||
| 8 | 151.3, qC | 148.5, qC | ||||
| 10 | 140.0, qC | 140.9, qC | ||||
| 11 | 113.0, qC | 112.6, qC | ||||
| 12 | 116.7, CH | 7.56, d (10.5) | C-10,13,14,16 | 116.9, CH | 7.34, d (10.3) | C-14,16 |
| 13 | 131.7, CH | 5.52, d (10.5) | C-11,14 | 131.8, CH | 5.54, d (10.2) | C-11,14 |
| 14 | 76.4, qC | 76.3, qC | ||||
| 16 | 153.6, qC | 154.6, qC | ||||
| 17 | 115.0, CH | 6.44, d (8.3) | C-11,16,19 | 115.4, CH | 6.98, d (8.4) | C-10,16,20 |
| 18 | 120.7, CH | 6.89, d (8.3) | C-10,11,16 | 120.6, CH | 6.70, d (8.3) | C-11,16,19 |
| 19 | 129.7, qC | 124.0, qC | ||||
| 20 | 61.8, qC | 58.7, qC | ||||
| 21 | 58.2, CH | 5.55, s | C-6,19,20,22,23,52 | 59.7, CH | 5.25, s | C-6,19,20,22,23,51,52 |
| 22 | 64.6, qC | 64.8, qC | ||||
| 23 | 167.1, qC | 166.2, qC | ||||
| 25-NH | 7.44, s | C-4,6,21,26 | 7.78, s | C-22 | ||
| 26 | 174.2, qC | 173.7, qC | ||||
| 27 | 17.0, CH3 | 1.68, s | C-7,8,28 | 18.2, CH3 | 1.60, s | C-6,7,8,28 |
| 28 | 26.6, CH3 | 1.83, s | C-6,7,8,27 | 27.5, CH3 | 1.76, s | C-6,7,8,27 |
| 29 | 27.4, CH3 | 1.15, s | C-13,14,30 | 27.6, CH3 | 1.26, s | C-13,14,30 |
| 30 | 27.4, CH3 | 1.28, s | C-13,14,29 | 28.9, CH3 | 1.47, s | C-13,14,29 |
| 31a | 44.6, CH2 | 3.62, m | C-31,32,34 | 45.0, CH2 | 3.73, m | |
| 31b | 3.47, m | |||||
| 32 | 25.0, CH2 | 2.11, m | C-31,33,34 | 28.7, CH2 | 2.12, m | C-34,56 |
| 2.20, m | C-56 | |||||
| 33a | 29.9, CH2 | 1.99, m | C-32,33,34,56 | 29.5, CH2 | 2.09, m | C-34,35,56 |
| 33b | 2.94, m | 2.95, m | C-34,56 | |||
| 34 | 68.8, qC | 68.5, qC | ||||
| 35a | 30.9, CH2 | 2.02, m | C-36,37,52,56 | 31.7, CH2 | 1.99 | C-34 |
| 35b | 2.42, dd (10.5, 12.5) | 2.44, dd (9.8, 12.8 | ||||
| 36 | 46.9, CH | 3.08, dd (6.7, 10.3) | C-35,37,52,53,57,58 | 51.2, CH | 3.12, dd (8.5, 17.5) | C-35,37,52.53 |
| 37 | 34.2, qC | 37.0, qC | ||||
| 38 | 141.4, qC | 146.8, qC | ||||
| 39 | 7.58, s | C-38,40,49,50 | ||||
| 40 | 132.7, qC | 139.1, qC | ||||
| 41 | 104.6, qC | 112.6, qC | ||||
| 42 | 117.0, CH | 6.40, d (9.8) | C-41,44,46 | 116.9, CH | 7.48, d (10.3) | C-44,46 |
| 43 | 129.7, CH | 5.58, d (9.8) | C-41,44 | 131.4, CH | 5.61, d (10.3) | C-41,44 |
| 44 | 75.6, qC | 76.3, qC | ||||
| 46 | 148.8, qC | 154.9, qC | ||||
| 47 | 111.0, CH | 6.64, d (8.3) | C-41,46,48 | 118.4, CH | 6.78, d (8.3) | C-41,46,49 |
| 48 | 120.1, CH | 7.14, d (8.8) | C-40,46,49,50 | 122.8, CH | 7.06, d (8.3) | C-40,46,50 |
| 49 | 120.4, qC | 124.0, qC | ||||
| 50 | 103.5, qC | 76.9, qC | ||||
| 51 | 43.4, CH | 5.14, s | C-,8,10,19,20,36,50,52,53 | 52.2, CH | 4.46, s | C-20,36,53,8,49,50,52 |
| 52 | 70.4, qC | 71.1, qC | ||||
| 53 | 168.8, qC | 169.5, qC | ||||
| 56 | 174.3, qC | 174.0, qC | ||||
| 57 | 22.4, CH3 | 1.02, s | C-36,37,38,58 | 27.4, CH3 | 1.22, s | C-36,37,38,58 |
| 58 | 27.5, CH3 | 1.26, s | C-36, 37,38,57 | 26.4, CH3 | 1.74, s | C-36,37,38,57 |
| 59 | 27.4, CH3 | 1.37, s | C-43,44,60 | 19.5, CH3 | 1.25, s | C-43,44,60 |
| 60 | 27.4, CH3 | 1.39, s | C-43,44,59 | 28.8, CH3 | 1.47, s | C-43,44,59 |
| 62-OH | 6.46, s | C-49,50,51 | ||||
: δC was assigned based on 1H→13C HSQC and HMBC NMR data
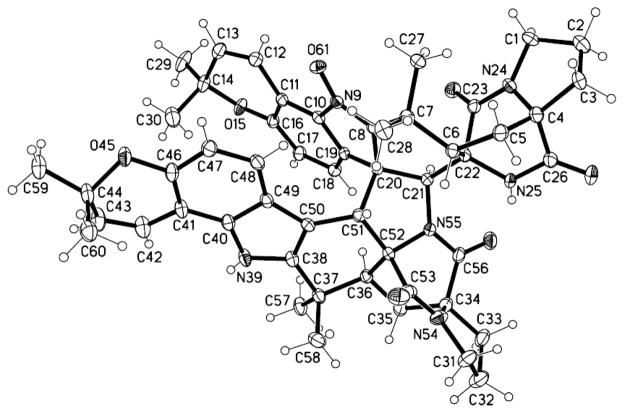
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction was used to confirm the proposed structure of 1. A concentrated solution of 1 in MeOH (held at 4 °C for ~2 weeks) provided colorless prism-shaped crystals suitable for analysis. The X-ray diffraction data for 1 showed that the new metabolite was an asymmetric pseudo-dimer similar to 17 (Figure 1). In agreement with our NMR-based structure proposal, the N-39 N-hydroxylamine in 17 was replaced by an amine in 1. The absolute configuration of 1 was determined by refinement of the Flack parameter27 as 4S,6S,20S,21S,22R,34S,36S,51R,52R. In contrast to 17, which has been reported to degrade in several organic solvents,19, 26, 28 compound 1 was very stable for days in MeOH and varying H2O-MeOH mixtures, CHCl3, CH2Cl2, and EtOAc. Moreover, 1 was readily observed by LC-MS in crude organic extracts prepared from the Hawaiian Aspergillus sp. isolate (Supporting Information, Figure S1), which suggested that this compound may not be an artifact of the isolation process as had been proposed for 17.26
Figure 1.
ORTEP structure generated from the X-ray diffraction data for a single crystal of 1 that was obtained from MeOH.
The HRESIMS of the second new metabolite, waikialoid B (14), provided a m/z that corresponded to a molecular formula of C52H54N6O9, which represented 29 degrees of unsaturation. Examination of the 1H NMR data (Table 1) established that 14 was structurally related to 1. In contrast to the seven oxygen atoms in 1, compound 14 possessed nine oxygens. Several of the carbon resonances in proximity to N-39 were shifted downfield (Table 1), which indicated where one of the new oxygen atoms was likely bonded. Based on the 1H-13C HSQC and 1H-13C HMBC data (Table 1), we rationalized that the N-39 amine in 1 was converted to a nitrone. The downfield shift of C-50 in 14 (δC 76.9) could be explained if this carbon was attached to a hydroxyl oxygen; the location of the hydroxyl group was confirmed based on 2–3JH-C couplings observed from OH-62 to C-49, C-50, and C-51 (Table 1).
No suitable crystals of 14 could be generated for single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. However, comparisons of the 1H-1H NOESY data for 1 and 1H-1H ROESY data for 14 (Supporting Information, Figures S8 and S16, respectively) revealed strong similarities between the two compounds suggesting a shared relative configuration for both metabolites (4S*,6S*,20S*,21S*,22R*,34S*,36S*,51R*,52R*). One exception was the set of ROESY correlations arising from the additional OH-62 hydroxyl group in 14. Analysis of the ROE crosspeaks from OH-62 to H-27, H-51, and H-57 enabled us to propose an R* configuration for C-50. In light of the likely shared biogenic origins for 1 and 14, as well as the decidedly similar Cotton effects observed in their respective UV–CD spectra (Δε values for 1 were +29.2 at 231 nm, −82.7 at 254 nm, and −14.4 at 311 nm compared to +16.3 at 226 nm, −18.2 at 243 nm, −8.7 at 320 nm for 14; Supporting Information Figure S10 and S18, respectively), we propose that the absolute configuration of metabolite 14 is 4S,6S,20S,21S,22R,34S,36S,50R,51R,52R.
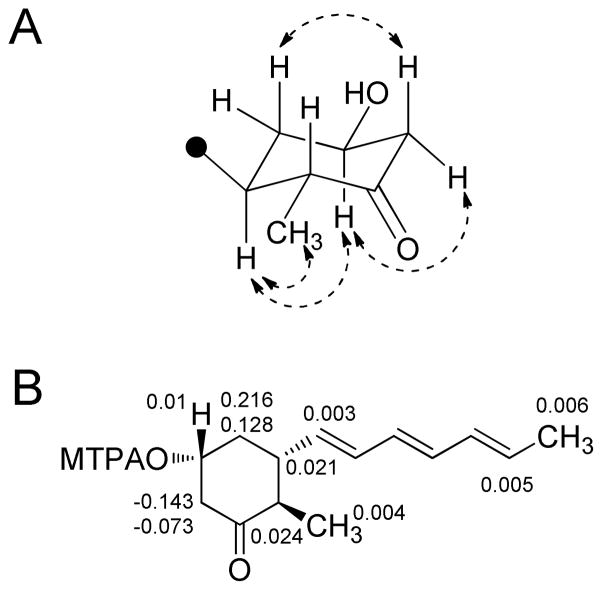
Waikialides A (15) and B (16) were purified from liquid-state cultures of the Hawaiian Aspergillus sp. isolate. The molecular formula of compound 15 was determined to be C14H20O2 by HRESIMS indicating five degrees of unsaturation. Analysis of the 13C NMR spectrum (Table 2) provided evidence for six olefinic carbons at δC 130.5, 133.2, 133.6, 131.7, 133.0, 136.4. A combination of 1H-1H COSY, 1H-13C HSQC, and 1H-13C HMBC (Table 2) supported a partial structure for 15 in which the six olefinic carbons formed a conjugated polyene tail (C-2 though C-7) that terminated with an allylic methyl group (C-1). In view of the constraints imposed by the proposed molecular formula, chemical shifts of the unassigned proton and carbon resonances, as well as the presence of a single downfield carbonyl (δC 211.7), we determined that the remaining degree of unsaturation could be accounted for by a monocyle. Constructing this portion of 15 was largely achieved based on the first-order (2–3JH-H) splitting patterns in the 1H NMR spectrum, as well as 13C NMR shift data (Table 2). With three of the remaining hydrogen atoms accounted for by a methyl doublet (δH 0.93, J = 6.7 Hz, H-14), and one hydrogen not accounted for in the 1H NMR data due to deuterium exchange with CD3OD, a tri-substituted cyclohexanone seemed to be the only feasible substructure for the remaining portion of 15. The 1H-13C HMBC data enabled us to construct a hydroxymethylcyclohexanone that was substituted at C-8 by the aforementioned polyene tail. Vicinal 3JH-H couplings and 1H-1H NOESY data (Figure 2A) were instrumental in proposing the 8S*,10R*,13R* relative configuration for 15. A crystal of 15 was obtained upon slow evaporation from MeOH, which served to corroborate the proposed planar structure and relative configuration of 15 (Supporting Information, Figure S27).
Table 2.
1H (400 MHz), 13C (100 MHz), and 1H-13C HMBC NMR data for 15 and 16 (CD3OD)
| waikialide A (15) | waikialide B (16) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| position | δC, type | δH, mult. (J in Hz) | HMBC(H→C) | δC, type | δH, mult. (J in Hz) | HMBC(H→C) |
| 1 | 18.5, CH3 | 1.78, d (6.8) | C-2,3 | 18.6, CH3 | 1.77, d (6.7) | C-2,3 |
| 2 | 130.5, CH | 5.73, qd (14.3, 6.8) | C-1,3 | 129.8, CH | 5.66, m | C-3,1 |
| 3 | 133.2, CH | 6.13, m | 131.8, CH | 6.06, m | ||
| 4 | 133.6, CH | 6.13, m | 131.8, CH | 6.06, m | ||
| 5 | 131.7, CH | 6.13, m | 132.6, CH | 6.06, m | ||
| 6 | 133.0, CH | 6.13, m | 133.3, CH | 6.06, m | ||
| 7 | 136.4, CH | 5.55, dd (13.7, 9.0) | C-5,6 | 138.8, CH | 5.46, dd (13.7, 9.0) | C-6,8 |
| 8 | 46.0, CH | 1.95, dddd (9.0, 11.3, 13.0, 3.8)a | C-6,7,13,9,14 | 42.2, CH | 2.11, m | C-6,7 |
| 9a | 42.9, CH2 | 1.67, ddd (11.3, 11.3, 11.6)a | C-7,8,10,11,13 | 43.4, CH2 | 1.16, ddd (11.6, 10.0, 11.6) a | C-7,8,10 |
| 9b | 2.08, ddddd (11.3, 3.8, 3.9, 2.2,2.2)a | C-11 | 1.88, dddd (12.1, 2.0, 3.5, 4.0) a | C-8,10 | ||
| 10 | 69.7, CH | 3.78, dddd (11.6, 3.9, 4.2, 11.4)a | C-8,9 | 66.3, CH | 3.95, m | C-9 |
| 11a | 52.0, CH2 | 2.45, ddd (11.2, 11.4, 2.5)a | C-10,9,12 | 43.5, CH2 | 1.39, ddd (12.0, 11.7, 2.7)a | C-10,12 |
| 11b | 2.65, ddd (11.2, 4.8, 2.5)a | C-9,10,12,13 | 2.16, m | C-9,10 | ||
| 12 | 211.7, qC | 72.8, CH | 3.90, m | C-10,14 | ||
| 13 | 49.5, CH | 2.25, dq (13.0, 6.5) | C-7,8,12,14 | 41.8, CH | 1.28, m | C-14 |
| 14 | 12.6, CH3 | 0.93, d (6.7) | C-8,12,13 | 16.8, CH3 | 0.91, d (7.0) | C-12,13 |
: J assignments were confirmed by modeling using ACD predictor software.
Figure 2.
A) 1H-1H NOESY correlations (dashed double-headed arrows) used to corroborate the relative configuration of the cyclohexanone substructure in metabolite 15. B) Calculated δH(S) − δ H(R) = ΔδSR values for the Mosher ester derivatives 15a and 15b.
The absolute configuration of 15 was assessed by the octant rule29 and Mosher ester method.30 The UV–CD spectrum of 15 exhibited a strong negative Cotton effect at 290 nm due to the n → π* transition of the cyclohexanone carbonyl. By examining which octants the majority of the 8S,10R,13R and 8R,10S,13S enantiomers occupied (the ‘negative’ rear upper-left octant and ‘positive’ rear upper-right octant, respectively), we determined that the observed negative Cotton effect (Supporting Information, Figure S28) could only be obtained with the 8S,10R,13R enantiomer. This conclusion was substantiated by results from the Mosher ester experiment in which analysis of the C-10 MTPA ester derivatives 15a and 15b supported a 10R configuration (Figure 2B).
Waikialide B (16) possessed a molecular formula of C14H22O2 as determined by HRESIMS. The loss of one degree of unsaturation in 16 compared to 15 was readily explained upon examination of the 13C NMR data, which revealed that the carbonyl was absent; while a new carbon resonance at δC 72.8 supported the presence of a hydroxyl group at the C-10 position. 1H-1H COSY, 1H-13C HSQC, and 1H-13C HMBC correlation data indicated that the remaining portion of 16 was the same as 15. Likewise, 1H-1H NOESY data demonstrated that the relative 8S*,10R*,13R* configuration of these stereogenic centers was the same as 15. With these asymmetric carbon atoms accounted for, a prominent NOE enhancement from H-12 (δH 3.90) to H-9b (δH 1.88) became instrumental in securing a 12R* configuration for C-12. In light of the presumed similar biosynthetic origins for metabolites 15 and 16, we propose that the absolute configuration of 16 is 8S,10R,12R,13R. It is of interest to note that the waikialides bear considerable resemblance to the diastereomeric natural product 2,3-didehydropalitantin, which was reported from a fungal epiphyte (Paraphaeosphaeria sp.).31
Assessment of the C. albicans Biofilm Inhibition by Purified Metabolites
Purified compounds were tested for their abilities to inhibit both cell viability and biofilm formation of C. albicans. None of the 15 metabolites from the Hawaiian Aspergillus sp. isolate inhibited C. albicans cell viability at concentrations up to 200 μM. In contrast, compound 1 demonstrated dose-dependent activity in the biofilm inhibition assay with an IC50 value of 1.4 ± 0.2 μM (Table 3). This is in sharp contrast to the meager activity afforded by the widely investigated positive control farnesol,32 which did not impede cell survival, but had an IC50 value of 128.6 ± 2.6 μM for biofilm inhibition. Compound 15 also afforded modest inhibition of biofilm formation with an IC50 value of 32.4 ± 2.0 μM. Three additional metabolites, 7, 14, and 6, were also detected that weakly inhibited C. albicans biofilm formation with IC50 values of 43.3 ± 3.5, 46.3 ± 1.6, and 55.2 ± 2.4 μM, respectively (Table 3).
Table 3.
Inhibition of C. albicans biofilm formation and cell growth
| Compound | IC50a of biofilm inhibition (μM) | MICb of growth inhibition (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | >200 |
| 2 | 108.6 ± 3.7 | >200 |
| 3 | 93.5 ± 3.6 | >200 |
| 5 | 97.3 ± 5.5 | >200 |
| 6 | 55.2 ± 2.4 | >200 |
| 7 | 43.3 ± 3.5 | >200 |
| 14 | 46.3 ± 1.6 | >200 |
| 15 | 32.4 ± 2.0 | >200 |
| 16 | 97.0 ± 2.1 | >200 |
| farnesol | 128.6 ± 2.6 | >200 |
IC50 expressed as the concentration of compound corresponding to a 50% reduction of C. albicans biofilm formation
MIC values were defined as the lowest concentration causing ≥80% reduction in the metabolic activity of C. albicans as determined by conversion of XTT to its colored product
The effects of metabolites 1 and 15 on C. albicans hyphae formation were evaluated by phase contrast microscopy. Hyphae formation is an important step in C. albicans virulence that marks the transition from initial surface colonization to invasive growth into the underlying matrix.33–35 Both metabolites 1 and 15 inhibited C. albicans hyphae formation in a dose dependent manner (Figure 3 and Supporting Information, Figure S41). Whereas vehicle-treated C. albicans cells were observed to form germ tubes at 2.5 h, hyphae at 6 h, and mature biofilms at 24 h post inoculation, cells treated with 1 or 15 did not form germ tubes or hyphae by 6 h and exhibited severely truncated hyphae at 24 h (Supporting Information, Figure S41).
Figure 3.
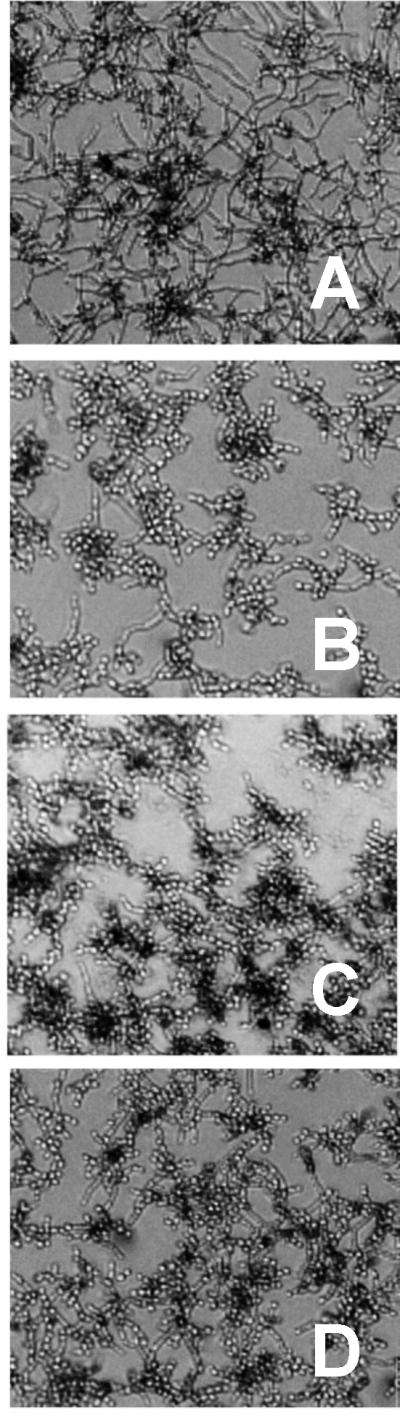
Testing the impact of purified secondary metabolites on C. albicans DAY185 hyphae formation. Freshly inoculated cells were treated with A) vehicle only (DMSO), B) farnesol (50 μM), C) waikialoid A (1) (50 μM), D) waikialide A (15) (50 μM), and incubated for 6 h prior to visualization by phase contrast microscopy (magnification ×200). Note the significant network of hyphal growth in the vehicle control, which is significantly reduced or absent from nearly all cells in the treatment groups. The effects of addition doses of these compounds are shown in the Supporting Information, Figure S41.
Compound 1 was further evaluated in a time-of-addition study to determine when during the process of biofilm formation the inhibitory effects of the new metabolite were being manifested. The effectiveness of 1 at inhibiting C. albicans biofilm formation showed a strong dependence on the time of drug addition (Figure 4). Whereas early time points displayed a small, but steady loss in the effectiveness of 1 at blocking biofilm generation, the later time points (6 and 8 h) exhibited marked drops in the ability of 1 to suppress biofilm formation. Taken together, these data suggest that 1 is likely not effective at inhibiting or disrupting preformed biofilms, but instead exerts its activity against C. ablicans during the early stages of surface colonization involving cell adherence, hyphal development, and/or biofilm assembly.
Figure 4.
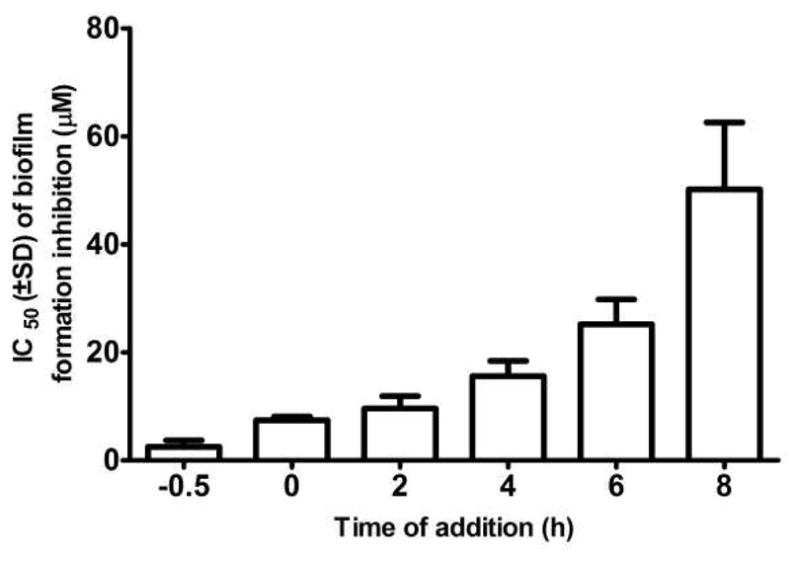
Time-of-addition study of compound 1. The compound was added to each well (doses ranging from 100 μM to 0.2 μM) at designated time points immediately before (−0.5 h) or after (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h) inoculation of C. albicans DAY185 into microplates. Following 48 h of incubation, the wells were washed twice with PBS and the extent of biofilm formation determined by XTT assay. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) value for biofilm inhibition was calculated using GraphPad Prism software. The experiment was replicated three times with each treatment tested in triplicate during each trial. The effects of single doses of compound 1 at these time points are shown in the Supporting Information, Figures S42 and S43. The difference in the relative potency of 1 at the −0.5 and 0 h addition time points is due to the delay in solubilization of 1 in aqueous medium at room temperature (25 °C).
Although the inability of 1 to disrupt established biofilms may limit the potential in vivo applications of this metabolite, it is notable that 1 was not toxic to mammalian cells (MIA PACA-2 cell line) at concentrations up to 200 μM (this was rather unexpected since some stephacidins/notoamides are potent human cell toxins; we did observe that 7 and 14 were toxic to MIAPACA-2 cells with IC50 values of 11.3 and 8.2 μM, respectively). In light of these results, 1 may have value for exploring in animal model systems since many questions remain concerning the predicted in vivo therapeutic utility of inhibitors that selectively and non-lethally block biofilm formation and hyphae development. Several studies have convincingly demonstrated that both biofilm formation and hyphal morphogenesis are important factors intimately associated with drug resistance36–38 and virulence,34, 39, 40 respectively, in C. albicans. Therefore, both drug resistance traits and virulence factors have been proposed as novel high-value targets for suppressing microbial infections.40–42 Compounds inhibiting these features are thought to evade the rapid evolution of resistance, since unlike fungicidal antibiotics, they do not pose a lethal, selective threat to microorganisms.40 Therefore, compound 1 and other secondary metabolites emerging from our C. albicans biofilm inhibition screening program hold considerable promise for designing bioactive lead molecules that may function as adjunctive agents in concert with antibiotics.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
General Experimental Procedures
Melting points were obtained on a Mel-Temp capillary melting point apparatus. Optical rotation measurements were determined on a Rudolph Research Autopol III automatic polarimeter. UV data were obtained on Hewlett Packard 8452A diode array spectrometer. UV–CD spectra were measured on an AVIV circular dichroism spectrometer model 202-01. IR spectra were measured on A2 Technology Nano FTIR and Bruker Vector 22 FTIR spectrometers. NMR data were obtained on Varian VNMR spectrometers (400 and 500 MHz for 1H, 100 and 125 MHz for 13C) with broad band and triple resonance probes at 20 ± 0.5 °C. Electrospray-ionization mass spectrometry data were collected on an Agilent 6538 high-mass-resolution QTOF mass spectrometer. LC-ESIMS data were obtained using a Thermo-Finnigan Surveyor LC system and Finnigan LCQ Deca mass analyzer. Crude extracts were separated on a Biotage Isolera chromatography system. The HPLC system utilized SCL-10A VP pumps and system controller with a Gemini 5 μm C18 column (110 Å, 250 × 21.2 mm, flow rates of 1 to 10 mL/min). X-ray diffraction data for compound 1 were collected on a Bruker APEX II CCD system equipped with a Cu ImuS micro-focus source with Quazar MX optics (λ = 1.54178 Å). X-ray data for compound 15 were collected using a diffractometer with a Bruker APEX CCD area detector and graphite-monochromated Mo K radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å). All solvents were of ACS grade or better.
Organism Collection, Identification, and Culture Methods
An ~1 g portion of a sandy-loam soil sample collected 50 m inland from Waikiki Beach (Honolulu, Hawaii) in July, 2010 was placed in sterile H2O (10 mL) and diluted 10- and 100-fold. Aliquots (300 μL) of the soil suspensions were spread over the surfaces of 10 cm diameter Petri plates containing Czapek agar with chloramphenicol (100 mg/L). Plates were maintained at 25 °C while exposed to light cycles consisting of 16 h light/8 h dark for four weeks. Colonies were selected from the plates and transferred to fresh Petri plates containing Czapek agar with chloramphenicol (100 mg/L). This process was repeated for each isolate until pure fungal cultures (judged by fungi that presented patterns of color, growth rate, and morphology that were uniform across an entire colony) were established. Pure isolates were transferred to new Petri plates containing Czapek agar (without chloramphenicol) and after 2–3 weeks of incubation at 25 °C, pieces of the agar with mycelia (~0.5 cm2) were cut and placed in cryogenic storage tubes with sterile glycerol-H2O (15:85). The tubes were then stored at −80 °C until the fungus was needed for scale-up studies. The fungus investigated in this study was identified as an Aspergillus sp. based on sequence analysis of its large-ribosomal-subunit ITS1 region of the rDNA gene. The sequence of the isolate (GenBank accession JQ693975; Supporting Information, Table S3) was compared by BLAST analysis to sequences publicly available through the NCBI database.
For the static preparative-scale culture, fungal mycelia and spores were inoculated into 50 mL potato-dextrose media and grown for one week at 25 °C on an orbital shaker (125 rpm). The cellular material was placed in a sterile Falcon tube and mixed by vortexing for several minutes to create a uniform fungal cell/spore suspension. For the static cultures, aliquots (500 μL) of the fungal suspension were used to inoculate 110 Erlenmeyer flasks (1 L) containing autoclaved medium (0.1 g rice, 0.1 g oatmeal, 0.1 g cornmeal, 0.32 g nutrient broth, ~0.5 g vermiculite, and 50 mL of deionized H2O; with or without the epigenetic modifier suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid). Culture vessels were maintained on the bench-top at 25 °C for 21 days. For the liquid-state preparative fermentation cultures, aliquots (500 mL) of the fungal suspension were used to inoculate 12 L portions of sterilized potato-dextrose broth in a 20 L fermentor maintained under constant aeration with ~20 L/min of filtered air with stirring at 200 rpm (Nalgene culture vessel with BioTech mixer). The culture was fermented at 25 °C for 14 days.
Preparative-Scale Cultures, Extraction, and Compound Purification
The scale-up static cultures were extracted overnight with ethyl acetate and the organic layer was removed under vacuum. The resulting organic extract was separated over silica gel on the Isolera MPLC system (mobile phase 1:1 hexane-CH2Cl2 to 100% CH2Cl2 over 8 min, held at 100% CH2Cl2 for 8 min, 100% CH2Cl2 to 1:5 MeOH-CH2Cl2 over 20 min, and 1:5 MeOH-CH2Cl2 to 100% MeOH in 8 min), which yielded four fractions containing compounds for purification. Fraction Fr2 (500 mg, eluted with ~20% CH2Cl2 in MeOH) was subjected to preparative HPLC (mobile phase 40% to 100% MeOH in H2O). This yielded sub-fractions Fr11-14 (~80% MeOH), which were subjected to semi-preparative HPLC to obtain 1 (4 mg), 2 (1 mg), 3 (1.8 mg), 4 (20 mg), 5 (1 mg), 6 (1 mg), 7 (1 mg), 10 (2 mg), 11 (0.3 mg), 12 (13 mg), 13 (2.2 mg), and 14 (1 mg).
The scale-up liquid-state cultures were extracted 3× with ethyl acetate (1:1, vol:vol). The organic layers were retained and the solvent removed under vacuum. The organic extract was separated over silica gel on an Isolera MPLC system (mobile phase 1:1 hexane-CH2Cl2 to 100% CH2Cl2 over 8 min, held at 100% CH2Cl2 for 8 min, 100% CH2Cl2 to 1:5 MeOH-CH2Cl2 over 20 min, and 1:5 MeOH-CH2Cl2 to 100% MeOH in 8 min). The ~15% CH2Cl2 in MeOH fraction (660 mg) was subjected to further silica gel MPLC chromotography with 100% CH2Cl2 to 1:1 MeOH-CH2Cl2. The sub-fraction eluting with ~12% MeOH (320 mg) was subjected to prep-HPLC (mobile phase 30% to 100% MeOH in water) to provide compounds 8 (10 mg), 9 (12 mg), 15 (9.5 mg) and 16 (61.8 mg).
Waikialoid A (1)
clear prism-shaped crystals (MeOH); mp: 174–176 °C, [α]21D −12.0 (c 0. 15, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 206 (4.99), 264 (4.75), 302 (4.39) nm; CD (MeOH; Δε) 231(+29.2), 254 (−82.7), 311 (−14.4); IR νmax 1680, 2980, 3120, 3320, 3490 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 875.4119 [M + H]+ (calcd for C52H55N6O7, 875.4132).
Waikialoid B (14)
yellow, amorphous solid; [α]21D 28.5 (c 0.035, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 206 (4.74), 264 (4.29) nm; CD (MeOH; Δε) 226 (+16.3), 243 (−18.2), 320 (−8.7); IR νmax 1590, 2920, 2980, 3390 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 905.3827 [M − H]− (calcd for C52H53N6O9, 905.3874).
Waikialide A (15)
white, crystalline solid; mp: 115–117 °C, [α]21D 11.4 (c 0.035, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 202 (4.38), 266 (4.81) nm; CD (MeOH; Δε) 266 (10.9), 293(−9.9); IR νmax 1690, 2910, 2920, 2950, 2980, 3000, 3430 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 243.1378 (calcd for C14H20O2Na, 243.1361).
Waikialide B (16)
white, amorphous solid; [α]21D 97.1 (c 0.175, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 202 (4.43), 268 (3.93) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 2910, 3400 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 221.1543 [M − H]− (calcd for C14H21O2, 221.1542).
Preparation of Mosher Ester Derivatives 15a and 15b
Compound 15 was transferred into two NMR tubes (0.25 mg each, 0.0011 mmol) and dried under vacuum. The samples in each tube were treated with dry pyridine (0.4 mL each) and 0.5μL (0.00267 mmol) of (S)-(+)-R-methoxy-R-(trifluoromethyl)-phenylacetyl chloride (MTPA chloride) or (R)-(−)-R-methoxy-R-(trifluoromethyl) phenylacetyl chloride reagent. The mixture was reacted at room temperature for 4 h and its completion was confirmed by 1H-NMR. This provided the two derivatives 15a and 15b. 1H-NMR spectra of both derivatives were collected in pyridine-d5, along with 1H-1H COSY data, which were used to assign the proton resonances.
S-MPTA ester of derivative of 15 (15a)
1H NMR (500 MHz, pyridine-d5) δH 6.12–6.36 (4H, m, H-3, H-4, H-5, H-6), 5.74 (1H, dd, J = 7.1, 14.4 Hz, H-2), 5.44–5.57 (2H, m, H-3, H-10), 3.11 (1H, d, J = 10.8 Hz, H-11), 2.79 (1H, t, J = 12.2 Hz, H-11), 2.20–2.34 (2H, m, H-8, H-13), 2.06–2.16 (1H, m, H-9),1.76–1.87 (1H, m, H-9), 1.69 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz, H-1), 1.06 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz, H-14).
R-MPTA ester of derivative of 15 (15b)
1H NMR (500 MHz, pyridine-d5) δH 6.13–6.39 (4H, m, H-3, H-4, H-5, H-6), 5.69–5.80 (1H, m, H-2), 5.45–5.59 (2H, m, H-3, H-10), 3.04 (1H, ddd, J = 2.0, 5.1, 13.0 Hz, H-11), 2.65 (1H, t, J = 12.0 Hz, H-11), 2.32 (1H, dt, J = 5.1, 12.2 Hz, H-9), 2.25 (1H, dt, J = 6.4, 12.1 Hz, H-13), 2.13 (1H, tdd, J = 2.9, 8.7, 11.8 Hz, H-8), 1.86–1.96 (1H, m, H-9), 1.69 (3H, dd, J = 1.2, 6.6 Hz, H-1), 1.07 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz, H-14).
X-ray Crystal Structure Analysis
X-ray diffraction data of 1 were collected on a Bruker APEX II CCD system equipped with a Cu ImuS micro-focus source with Quazar MX optics. A total of 67703 data were measured in the range 3.54 < θ < 67.16° using ϕ and ω oscillation frames. The data were merged to form a set of 7859 independent data with R(int) = 0.0272 and a coverage of 97.6 %. A total of 635 parameters were refined against 21 restraints and 7859 data to give wR(F2) = 0.0845 and S = 1.005 for weights of w = 1/[σ2 (F2) + (0.0530 P)2 + 0.9000 P], where P = [F02 + 2Fc2]/3. The final R(F) was 0.0316 for the 7855 observed, [F > 4σ(F)], data. The calculated minimum and maximum transmission coefficients (based on crystal size) are 0.6520 and 0.8418. The structure was solved by direct methods and refined by full-matrix least-squares methods on F2. The goodness-of-fit was 1.005. The largest shift/s.u. was 0.033 in the final refinement cycle. The final difference map had maxima and minima of 0.343 and −0.281 e/Å3. On the basis of the final model, the calculated density was 1.309 g/cm3 and F(000), 984 e-. The X-ray crystallographic data for 1 has been deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center under accession number CCDC864505. This data can be accessed free of charge at http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/.
X-ray diffraction data of 15 were collected on a Bruker APEX CCD area detector and graphite-monochromated Mo K radiation (= 0.71073 Å). A total of 4,287 data were measured in the range 2.36 < θ < 22.99° using ϕ and ω oscillation frames, the data were corrected for absorption by semi-epirical methods giving minimum and maximum transmission factors of 0.9613 and 0.9970. The data were merged to form a set of 1000 independent data with R(int) = 0.1127 and a coverage of 99.8%. The structure was solved by direct methods and refined by full-matrix least-squares methods on F2. Hydrogen atom positions were initially determined by geometry and refined by a riding model. Non-hydrogen atoms were refined with anisotropic displacement parameters. A total of 150 parameters were refined against one space group restraint and 1,000 data to give wR(F2)=0.1720 and S=1.051 for weights of w=1/[σ2(F2)+(0.0880P)2+0.4400P], where P=[F02+2FC2]/3. The final R(F) was 0.0710 for the 730 observed, [F>4σ(F)], data. The largest shift/s.u. was 0.000 in the final refinement cycle. The final difference map had maxima and minima of 0.227 and −0.257 e/Å3, respectively. The X-ray crystallographic data for 15 has been deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center under accession number CCDC864506. This data can be accessed free of charge at http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/.
Assay for Growth Inhibition and Biofilm Formation
The effects of compounds on the growth of C. albicans DAY185 were tested using the method described in the NCCLS 2002 CLSI M27-A2 guidelines.43 The biofilm assay was performed as described 44 with the following modifications. C. albicans DAY185 was cultured in BHI medium (brain heart infusion, Becton Dickinson and Company) at 37 °C overnight. The cells were pelleted by centrifugation, washed with sterile PBS (phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.4, EMD Chemicals, Inc.), and resuspended in RPMI 1640 medium (Sigma Chemical Corporation) buffered to pH 7.0 with MOPS (0.165 M, Sigma). Test compounds were prepared in DMSO at stock concentrations of 20 mM before being serially diluted in RPMI 1640 plus MOPS medium for testing. Farnesol was used as a positive control for assessing biofilm inhibition.45 Aliquots of yeast suspension (100 μL containing 2.5×103 cells/mL) were added to the medium containing the diluted compounds or DMSO (1% by vol.) before being transferred to 96-well microplates (Costar 3370, Corning, Inc.). After 48 h of incubation at 37 °C, the viability of the yeast were measured using the XTT assay.46 In brief, yeast cells were treated with 0.1 mg/mL XTT at 37 °C for 1 h. The absorbance was taken at 490 nm using a microplate reader (Infinite M200, Tecan Group Ltd.). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for growth was defined as the lowest antifungal concentrations that caused ≥80% reduction in the metabolic activity.
For measuring biofilm formation, the medium was aspirated and the wells were washed twice with sterile PBS to remove non-adherent cells. Fresh medium (100 μL RPMI 1640 plus MOPS) was then added back to each well. The formation of biofilms was measured using the XTT assay.46 All experiments were performed in triplicate on three separate occasions. The 50% inhibitory concentration value (IC50) for biofilm inhibition was calculated using GraphPad Prism software.
Hyphae Formation Assay
C. albicans DAY185 was grown in BHI medium at 37 °C overnight. The cells were pelleted, washed, and suspended in sterile PBS (pH 7.4, EMD). Cells were seeded in 96-well plates at 1×106 cells/well and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. Wells were washed twice with sterile PBS to remove non-adherent cells. RPMI 1640 containing 2% glucose and compounds (1, 15, or farnesol – positive control45) in DMSO (1% by vol.) was added to each well and the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Hyphae formation was monitored with a phase contrast microscope at 2.5, 6 and 24 h.44
Biofilm Time of Addition Assay
Using the techniques described above for the biofilm formation inhibition assay, compound 1 (from 100 μM to 0.2 μM) was added at −0.5, 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h after seeding C. albicans DAY185 cells in a 96-well microplate. At 48 h after inoculation, the wells were washed twice with PBS and the amount of biofilm formation in each well was determined by XTT assay.47 The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) value for biofilm inhibition was calculated using GraphPad Prism software. All experiments were performed in triplicate on three separate occasions.
Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
The mammalian cell cytotoxicity screening assay was performed by adding 104 MIA PaCa-2 cells per well of a 96-well plate and allowing the cells to attach overnight at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with a 5% CO2 atmosphere. The next day, test compounds in DMSO were added to the wells (final DMSO concentration 1% by vol.) and incubated for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the National Institutes of Health (1RO1GM092219 and 1RO1AI085161) for financial support. The X-ray diffractometer was purchased through a grant from the NSF (CHE-0130835). We gratefully acknowledge the help of C. Campana for collection the X-ray diffraction data for 1. We also thank C. A. Kumamoto (Tufts University, USA) and A. Mitchell (Carnegie Mellon University, USA) for the supplying the C. albicans DAY185 strain.
Footnotes
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
NMR (1H and 13C NMR, HSQC, HMBC, COSY, ROESY and NOESY) data for compounds 1, 14, 15, and 16. CD spectra for compounds 1, 14, and 15. Structures of all secondary metabolites isolated from the Hawaiian Aspergillus sp. isolate, associated schemes, tables, and additional bioassay data. This information is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.Williams RB, Henrikson JC, Hoover AR, Lee AE, Cichewicz RH. Org Biomol Chem. 2008;6:1895–1897. doi: 10.1039/b804701d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Janso JE, Carter GT. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76(13):4377–4386. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02959-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lass-Flörl C. Mycoses. 2009;52:197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2009.01691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ruan SY, Hsueh PR. J Formos Med Assoc. 2009;108:443–451. doi: 10.1016/S0929-6646(09)60091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Playford EG, Nimmo GR, Tilse M, Sorrell TC. J Hosp Infect. 2010;76:46–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2010.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Falagas ME, Roussos N, Vardakas KZ. Int J Infec Dis. 2010;14:954–966. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2010.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:133–163. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00029-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Julia LD. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:30–36. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(02)00002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Harriott MM, Lilly EA, Rodriguez TE, Fidel PL, Noverr MC. Microbiology. 2010;156:3635–3644. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.039354-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dongari-Bagtzoglou A, Kashleva H, Dwivedi P, Diaz P, Vasilakos J. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e7967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Harriott MM, Noverr MC. Trends Microbiol. 2011;19:557–563. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2011.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.LaFleur MD, Qi Q, Lewis K. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:39–44. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00860-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.LaFleur MD, Kumamoto CA, Lewis K. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:3839–3846. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00684-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cichewicz RH. Nat Prod Rep. 2010;27:11–22. doi: 10.1039/b920860g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kato H, Yoshida T, Tokue T, Nojiri Y, Hirota H, Ohta T, Williams RM, Tsukamoto S. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46:2254–2256. doi: 10.1002/anie.200604381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Whyte AC, Gloer JB, Wicklow DT, Dowd PF. J Nat Prod. 1996;59:1093–1095. doi: 10.1021/np960607m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tsukamoto S, Kato H, Samizo M, Nojiri Y, Onuki H, Hirota H, Ohta T. J Nat Prod. 2008;71:2064–2067. doi: 10.1021/np800471y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tsukamoto S, Umaoka H, Yoshikawa K, Ikeda T, Hirota H. J Nat Prod. 2010;73:1438–1440. doi: 10.1021/np1002498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Qian-Cutrone J, Huang S, Shu YZ, Vyas D, Fairchild C, Menendez A, Krampitz K, Dalterio R, Klohr SE, Gao Q. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:14556–14557. doi: 10.1021/ja028538n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sugie Y, Hirai H, Inagaki T, Ishiguro M, Kim YJ, Kojima Y, Sakakibara T, Sakemi S, Sugiura A, Suzuki Y, Brennan L, Duignan J, Huang LH, Sutcliffe J, Kojima N. J Antibiot. 2001;54:911–916. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.54.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rahbaek L, Breinholt J, Frisvad JC, Christophersen C. J Org Chem. 1999;64:1689–1692. doi: 10.1021/jo981536u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rahbaek L, Breinholt J, Circumdatins DEF. J Nat Prod. 1999;62:904–905. doi: 10.1021/np980495u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Furtado NAJC, Pupo MT, Carvalho I, Campo VL, Duarte MCT, Bastos JK. J Braz Chem Soc. 2005;16:1448–1453. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li HJ, Cai YT, Chen YY, Lam CK, Lan WJ. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2010;26:415–419. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dunn G, Newbold GT, Spring FS. J Chem Soc. 1949:2586–2587. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Herzon SB, Myers AG. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:5342–5344. doi: 10.1021/ja0510616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Flack H. Acta Crystallogr A. 1983;39:876–881. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wulff JE, Herzon SB, Siegrist R, Myers AG. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:4898–4899. doi: 10.1021/ja0690971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Murphy WS. J Chem Edu. 1975;52:774. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hoye TR, Jeffrey CS, Shao F. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:2451–2458. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lee HB, Oh H. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2006;27:779–782. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ramage G, Saville SP, Wickes BL, López-Ribot JL. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002;68:5459–5463. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.11.5459-5463.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kumamoto CA, Vinces MD. Cell Microbiol. 2005;7:1546–1554. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brand A. Int J Microbiol. 2012;2012:517529. doi: 10.1155/2012/517529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sudbery PE. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9:737–748. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Finkel JS, Mitchell AP. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9:109–118. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Uppuluri P, Srinivasan A, Ramasubramanian A, Lopez-Ribot JL. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:3591–3593. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01701-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Al-Fattani MA, Douglas LJ. J Med Microbiol. 2006;55:999–1008. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46569-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pukkila-Worley R, Peleg AY, Tampakakis E, Mylonakis E. Eukaryot Cell. 2009;8:1750–1758. doi: 10.1128/EC.00163-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shareck J, Belhumeur P. Eukaryot Cell. 2011;10:1004–1012. doi: 10.1128/EC.05030-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gauwerky K, Borelli C, Korting HC. Drug Discov Today. 2009;14:214–222. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2008.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Alksne LE, Projan SJ. Curr Opin in Biotechnol. 2000;11:625–636. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(00)00155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts - Approved Standard (CLSI document M27-A3) 3. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chandra J, Mukherjee PK, Ghannoum MA. Nat Protoc. 2008;3:1909–1924. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Deveau A, Hogan DA. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;692:219–233. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-971-0_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nett JE, Cain MT, Crawford K, Andes DR. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:1426–1433. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02273-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhang Y, Cai C, Yang Y, Weng L, Wang L. J Med Microbiol. 2011;60:1643–1650. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.029058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.