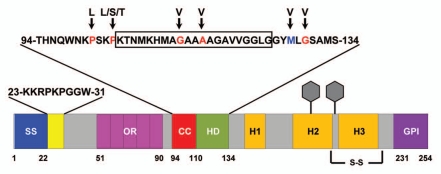
Figure 2.
Schematic of murine PrP showing domain structure and mutations. ER signal sequence (SS, blue, aa 1–22); polybasic domain (yellow, aa 23–31); octapeptide repeats (OR, magenta, aa 51–90); charge cluster (CC, red, aa 94–110); hydrophobic domain (HD, green, aa 111–134); GPI signal sequence (GPI, purple, 231–254). Three α helices (H1, H2 and H3), two N-linked oligosaccharides (hexagons), and one disulfide bond (S-S) are present in the C-terminal half of PrP. The sequences for amino acids 23–31 and 94–134 are shown above the schematic. The boxed residues (105–125) indicate those deleted in ΔCR PrP. Residues mutated in familial prion diseases are indicated in red, and a nonpathogenic polymorphism in blue, with arrows pointing to the substituted amino acid.