Abstract
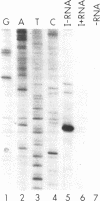
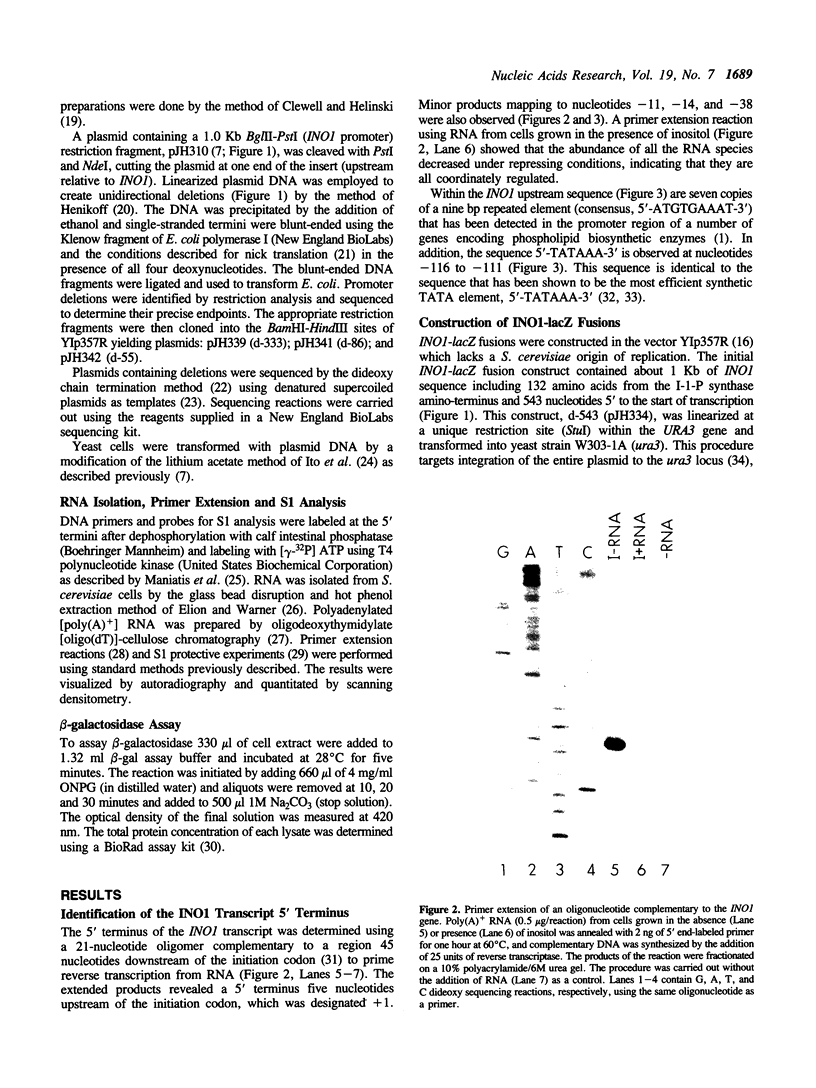
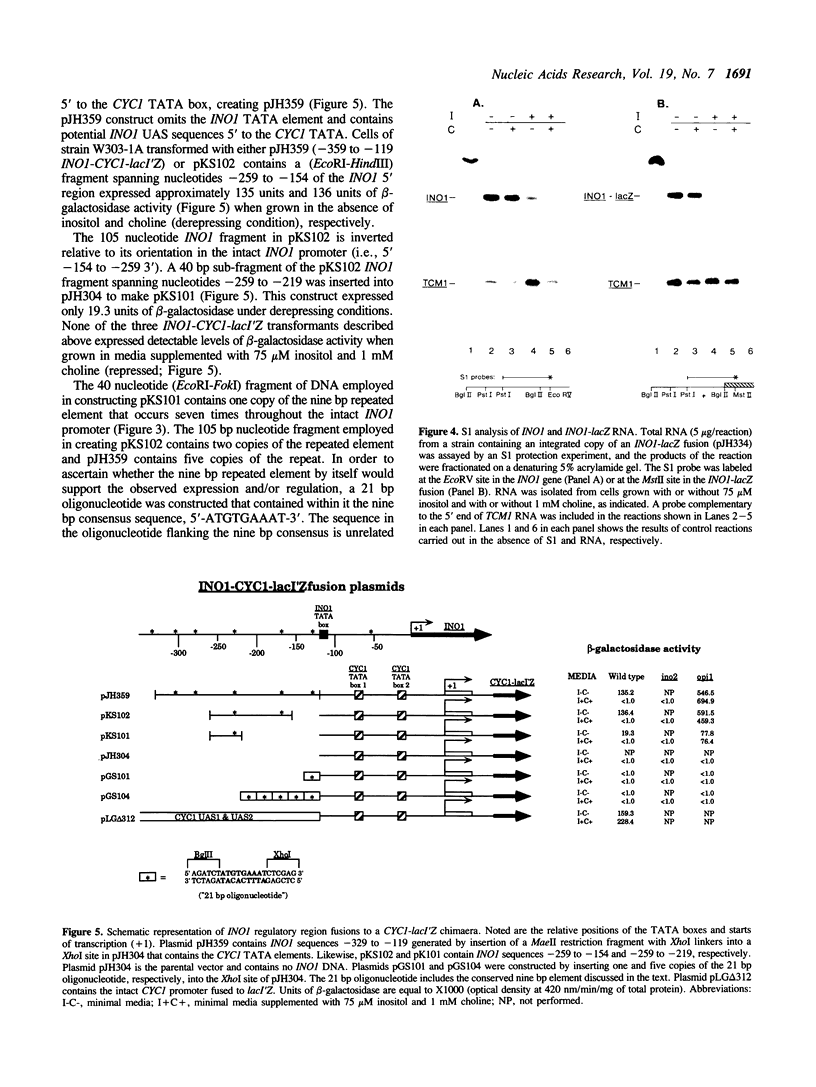
The promoter region of the highly regulated INO1 structural gene of yeast has been investigated. The major transcription initiation start site (+1) was mapped to a position located five nucleotides upstream of the previously identified initiation codon. The INO1 TATA is located at -116 to -111. The INO1 promoter region was used to construct fusions to the Escherichia coli lacZ gene. All INO1 fusion constructs that retained regulation in response to the phospholipid precursors inositol and choline, contained at least one copy of a nine bp repeated element (consensus, 5'-ATGTG-AAAT-3'). The smallest fragment of the INO1 promoter found to activate and regulate transcription of the fusion gene from a heterologous TATA element was 40 nucleotides in length. This fragment contained one copy of the nine bp repeat and spanned the INO1 promoter region from -259 to -219. However, when an oligonucleotide containing the nine bp repeated sequence was inserted 5' to the CYC1 TATA element, it failed to activate transcription.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailis A. M., Poole M. A., Carman G. M., Henry S. A. The membrane-associated enzyme phosphatidylserine synthase is regulated at the level of mRNA abundance. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman G. M., Henry S. A. Phospholipid biosynthesis in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:635–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of a yeast his3 "TATA element": genetic evidence for a specific TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culbertson M. R., Donahue T. F., Henry S. A. Control of inositol biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: properties of a repressible enzyme system in extracts of wild-type (Ino+) cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):232–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.232-242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culbertson M. R., Henry S. A. Inositol-requiring mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1975 May;80(1):23–40. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean-Johnson M., Henry S. A. Biosynthesis of inositol in yeast. Primary structure of myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase (EC 5.5.1.4) and functional analysis of its structural gene, the INO1 locus. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1274–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Henry S. A. myo-Inositol-1-phosphate synthase. Characteristics of the enzyme and identification of its structural gene in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7077–7085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. The major promoter element of rRNA transcription in yeast lies 2 kb upstream. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. L., Goldwasser P., Henry S. A. Characterization of a yeast regulatory mutant constitutive for synthesis of inositol-1-phosphate synthase. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):157–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00331845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. L., Reiner B., Henry S. A. Regulatory mutations of inositol biosynthesis in yeast: isolation of inositol-excreting mutants. Genetics. 1982 Jan;100(1):19–33. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J. P., Henry S. A. Expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae inositol-1-phosphate synthase (INO1) gene is regulated by factors that affect phospholipid synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3320–3328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homann M. J., Henry S. A., Carman G. M. Regulation of CDP-diacylglycerol synthase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1265–1266. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1265-1266.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M. J., Bailis A. M., Henry S. A., Carman G. M. Regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by inositol. Inositol is an inhibitor of phosphatidylserine synthase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18078–18085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewy B. S., Henry S. A. The INO2 and INO4 loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are pleiotropic regulatory genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2479–2485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A., Kinney D. M., Lusty C. J. Yeast shuttle and integrative vectors with multiple cloning sites suitable for construction of lacZ fusions. Gene. 1986;45(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M. L., Young R. A. Intragenic and extragenic suppressors of mutations in the heptapeptide repeat domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):715–724. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Genetic applications of yeast transformation with linear and gapped plasmids. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:228–245. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Piatak M., Weissman S. M. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's. I. Genomic localization of 3' and 5' termini and two major splices in mRNA from transformed and lytically infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):279–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.279-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Szostak J. W., Murray A. W. Cloning regulated yeast genes from a pool of lacZ fusions. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:253–269. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo H. S., Cooper T. G. The DAL7 promoter consists of multiple elements that cooperatively mediate regulation of the gene's expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3231–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]