Abstract
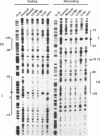
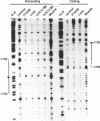
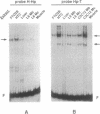
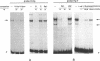
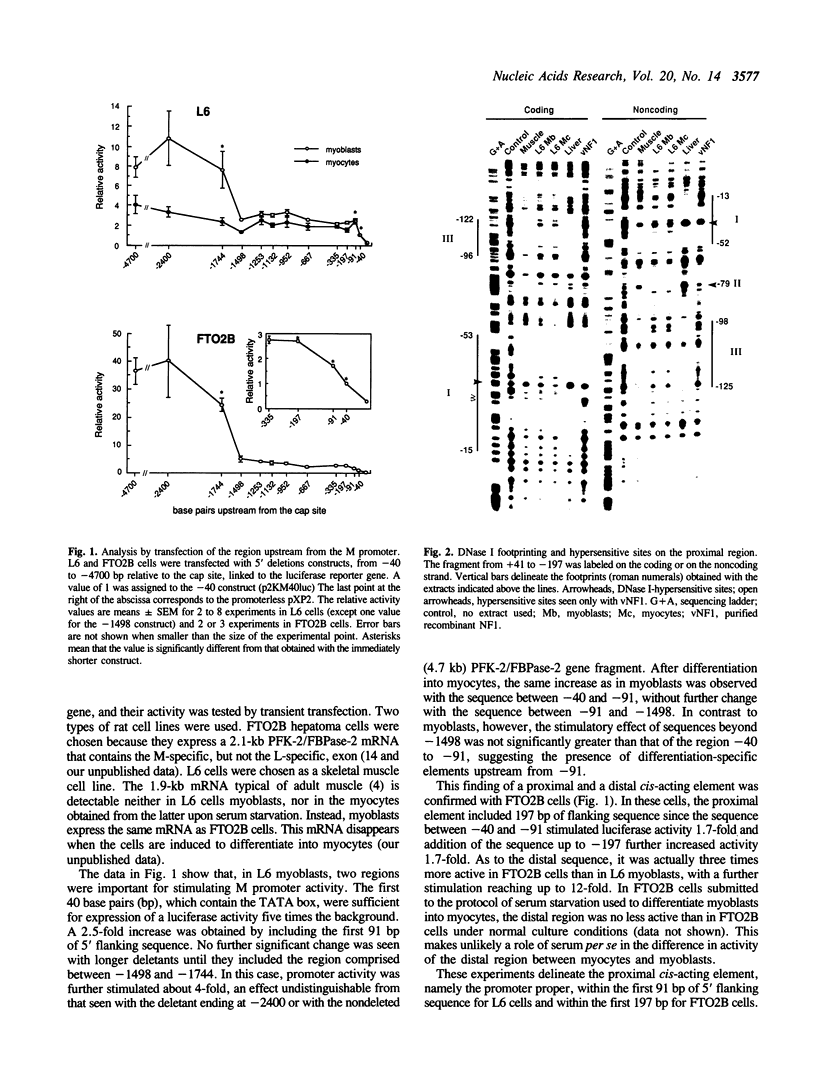
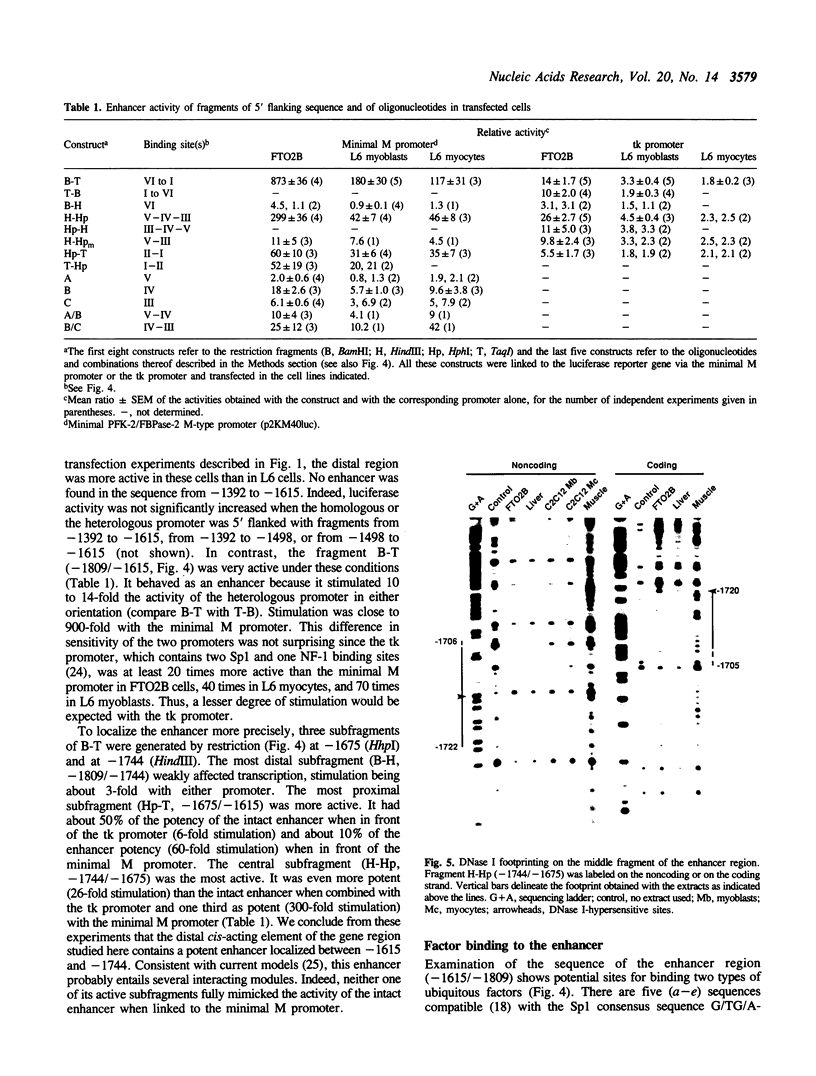
The muscle-type isozyme of rat 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase is encoded by a mRNA transcribed from the M promoter of a 55-kb gene, which also produces the liver-type isozyme from an alternative promoter. By transient transfection and in vitro protein-DNA binding assays we have delineated, within 4.7 kb of 5' flanking sequence, the M promoter proper and an enhancer located between -1615 and -1809. This enhancer stimulated up to 12-fold the activity of the promoter in the context of an intact 5' flanking sequence and close to 900-fold the activity of the minimal (+41 to -40) M promoter cloned directly downstream from it. A functional dissection of the enhancer by site-directed mutagenesis and use of oligonucleotides suggested that its activity involves the cooperative effect of six binding sites for trans-acting factors clustered within 150 bp. These sites contain either an EF-1A/E4TF1 motif (also known to bind the ets oncogene product) or a Sp1 motif, or both. The activity of the enhancer could be demonstrated in L6 myoblasts and myocytes and in FTO2B hepatoma cells. When left within the intact 5' flanking sequence, however, enhancer activity was inhibited upon differentiation of myoblasts into myocytes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosca L., Mojena M., Ghysdael J., Rousseau G. G., Hue L. Expression of the v-src or v-fps oncogene increases fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in chick-embryo fibroblasts. Novel mechanism for the stimulation of glycolysis by retroviruses. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):595–599. doi: 10.1042/bj2360595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosca L., Rousseau G. G., Hue L. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and insulin increase the concentration of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and stimulate glycolysis in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6440–6444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent G. A., Moore D. D., Larsen P. R. Thyroid hormone regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:17–35. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder J. T., Hearing P. Nuclear factor EF-1A binds to the adenovirus E1A core enhancer element and to other transcriptional control regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5143–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes M. E., Espinet C., Lange A. J., Pilkis S. J., Hod Y. Hormonal control of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase gene expression in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1557–1563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepin K. M., Darville M. I., Hue L., Rousseau G. G. Characterization of distinct mRNAs coding for putative isozymes of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;183(2):433–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby S. D., Puetz J. J., Simburger K. S., Fahrner T. J., Milbrandt J. The early response gene NGFI-C encodes a zinc finger transcriptional activator and is a member of the GCGGGGGCG (GSG) element-binding protein family. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3835–3841. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darville M. I., Crepin K. M., Hue L., Rousseau G. G. 5' flanking sequence and structure of a gene encoding rat 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6543–6547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., DiRenzo J., Kurokawa R., Han Z. H. Regulation of gene expression by retinoic acid receptors. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;10(9):623–638. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounari F., De Francesco R., Schmitt J., van der Vliet P., Cortese R., Stunnenberg H. Amino-terminal domain of NF1 binds to DNA as a dimer and activates adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):559–566. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. Nuclear targets for transcription regulation by oncogenes. Trends Genet. 1991 Feb;7(2):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90231-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Rider M. H. Role of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the control of glycolysis in mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2450313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaigre F. P., Durviaux S. M., Rousseau G. G. Identification of regulatory sequences and protein-binding sites in the liver-type promoter of a gene encoding 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1099–1106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A. Glucokinase gene structure. Functional implications of molecular genetic studies. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):523–527. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paonessa G., Gounari F., Frank R., Cortese R. Purification of a NF1-like DNA-binding protein from rat liver and cloning of the corresponding cDNA. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3115–3123. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Klarsfeld A., Changeux J. P. Interaction of nuclear factors with the upstream region of the alpha-subunit gene of chicken muscle acetylcholine receptor: variations with muscle differentiation and denervation. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):687–694. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Annarella M. B. Developmental expression of Sp1 in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2189–2199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal R., Berk A. J. Promoter activity and distance constraints of one versus two Sp1 binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20406–20411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Jackson S., Tjian R., Echols H. DNA looping between sites for transcriptional activation: self-association of DNA-bound Sp1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):820–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. R., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. A MyoD1-independent muscle-specific enhancer controls the expression of the beta-myosin heavy chain gene in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22678–22688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorn J. T., Todd A. V., Warrilow D., Watt F., Molloy P. L., Iland H. J. Characterization of the human N-ras promoter region. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1843–1850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremp G. L., Boquet D., Ripoche M. A., Cognet M., Lone Y. C., Jami J., Kahn A., Daegelen D. Expression of the rat L-type pyruvate kinase gene from its dual erythroid- and liver-specific promoter in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19904–19910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuil D., Clergue N., Montarras D., Pinset C., Kahn A., Phan-Dinh-Tuy F. CC Ar GG boxes, cis-acting elements with a dual specificity. Muscle-specific transcriptional activation and serum responsiveness. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):677–686. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80255-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Imai T., Sharp P. A., Handa H. Identification of two transcription factors that bind to specific elements in the promoter of the adenovirus early-region 4. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1290–1300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Wada T., Handa H. Transcription factor E4TF1 contains two subunits with different functions. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):841–847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Paulsen R. E., Padgett K. A., Milbrandt J. Participation of non-zinc finger residues in DNA binding by two nuclear orphan receptors. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):107–110. doi: 10.1126/science.1314418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahradka P., Larson D. E., Sells B. H. RNA polymerase II-directed gene transcription by rat skeletal muscle nuclear extracts. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Nov;185(1):8–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]