Abstract
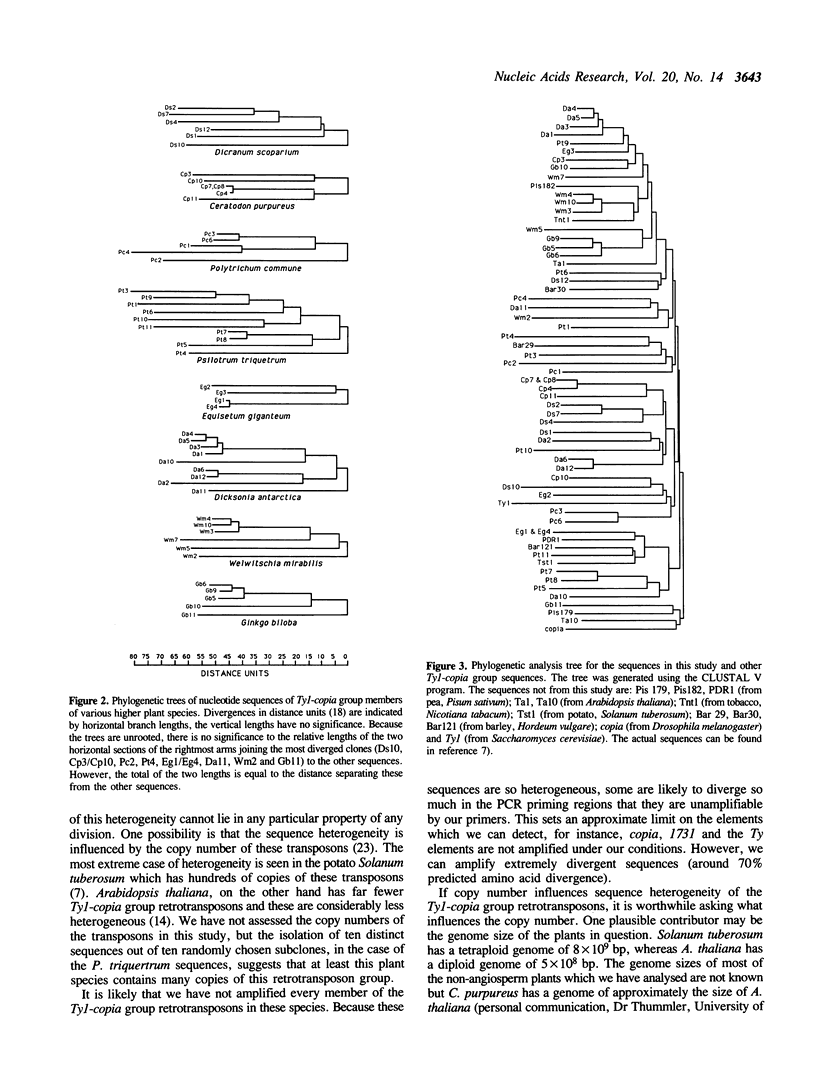
We have used the polymerase chain reaction to isolate fragments of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons from a wide variety of members of the higher plant kingdom. 56 out of 57 species tested generate an amplified fragment of the size expected for reverse transcriptase fragments of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons. Sequence analysis of subclones shows that the PCR fragments display varying degrees of sequence heterogeneity. Sequence heterogeneity therefore seems a general property of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons of higher plants, in contrast to the limited diversity seen in retrotransposons of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Drosophila melanogaster. Phylogenetic analysis of all these sequences shows, with some significant exceptions, that the degree of sequence divergence in the retrotransposon populations between any pair of species is proportional to the evolutionary distance between those species. This implies that sequence divergence during vertical transmission of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons within plant lineages has been a major factor in the evolution of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in higher plants. Additionally, we suggest that horizontal transmission of this transposon group between different species has also played a role in this process.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charlesworth B. Genetic divergence between transposable elements. Genet Res. 1986 Oct;48(2):111–118. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300024836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F. Nearest neighbor procedure for relating progressively aligned amino acid sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:659–669. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Shiba T., Kanaya S., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. The nucleotide sequences of copia and copia-related RNA in Drosophila virus-like particles. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):773–776. doi: 10.1038/315773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive alignment and phylogenetic tree construction of protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:375–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Levis R., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. The 5' termini of RNAs encoded by the transposable element copia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6279–6291. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Smith D. B. A Ty1-copia group retrotransposon sequence in a vertebrate. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):322–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00587596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Smith D. B., Kumar A. Extreme heterogeneity of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in plants. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jan;231(2):233–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00279796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gojobori T., Moriyama E. N., Kimura M. Molecular clock of viral evolution, and the neutral theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10015–10018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandbastien M. A. Retroelements in higher plants. Trends Genet. 1992 Mar;8(3):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90198-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandbastien M. A., Spielmann A., Caboche M. Tnt1, a mobile retroviral-like transposable element of tobacco isolated by plant cell genetics. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):376–380. doi: 10.1038/337376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Voytas D. F., Cummings M. P., Ausubel F. M. A superfamily of Arabidopsis thaliana retrotransposons. Genetics. 1991 Apr;127(4):801–809. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saghai-Maroof M. A., Soliman K. M., Jorgensen R. A., Allard R. W. Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):8014–8018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.8014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki S., Ishimaru S., Inouye S., Saigo K. Identification of genes for reverse transcriptase-like enzymes in two Drosophila retrotransposons, 412 and gypsy; a rapid detection method of reverse transcriptase genes using YXDD box probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3017–3030. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



