Abstract
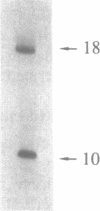
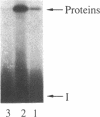
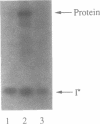
A modified oligodeoxyribonucleotide duplex containing an unnatural internucleotide trisubstituted 3' to 5' pyrophosphate bond in one strand [5'(oligo1)3'-P(OCH3)P-5'(oligo2) 3'] reacts with nucleophiles in aqueous media by acting as a phosphorylating affinity reagent. When interacted with a protein, a portion of the oligonucleotide [--P-5'(oligo2)3'] becomes attached to an amino acid nucleophilic group through a phosphate of the O-methyl-modified pyrophosphate linkage. We demonstrate the affinity labeling of nucleophilic groups at the active sites of the EcoRI and RsrI restriction and modification enzymes with an oligodeoxyribonucleotide duplex containing a modified scissile bond in the EcoRI recognition site. With the EcoRI and RsrI endonucleases in molar excess approximately 1% of the oligonucleotide becomes attached to the protein, and with the companion methyltransferases the yield approaches 40% for the EcoRI enzyme and 30% for the RsrI methyltransferase. Crosslinking proceeds only upon formation of a sequence-specific enzyme-DNA complex, and generates a covalent bond between the 3'-phosphate of the modified pyrophosphate in the substrate and a nucleophilic group at the active site of the enzyme. The reaction results in the elimination of an oligodeoxyribonucleotide remnant that contains the 3'-O-methylphosphate [5'(oligo1)3'-P(OCH3)] derived from the modified phosphate of the pyrophosphate linkage. Hydrolysis properties of the covalent protein-DNA adducts indicate that phosphoamide (P-N) bonds are formed with the EcoRI endonuclease and methyltransferase.
Full text
PDF


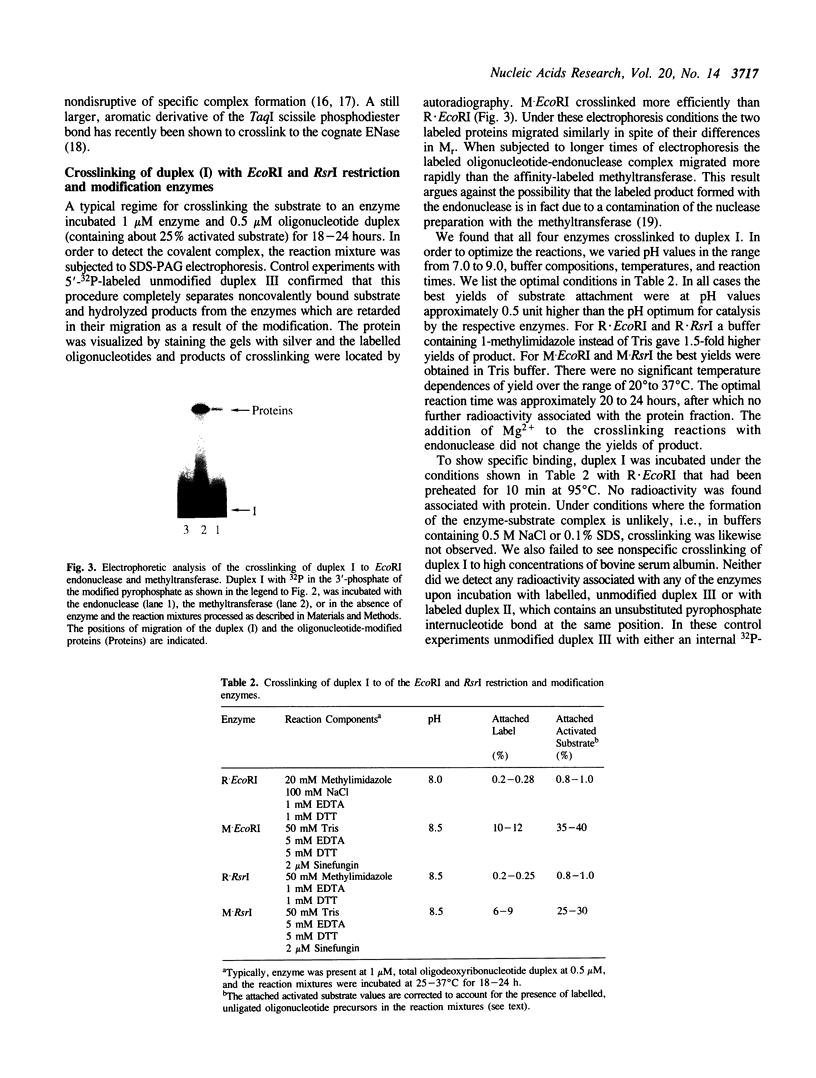
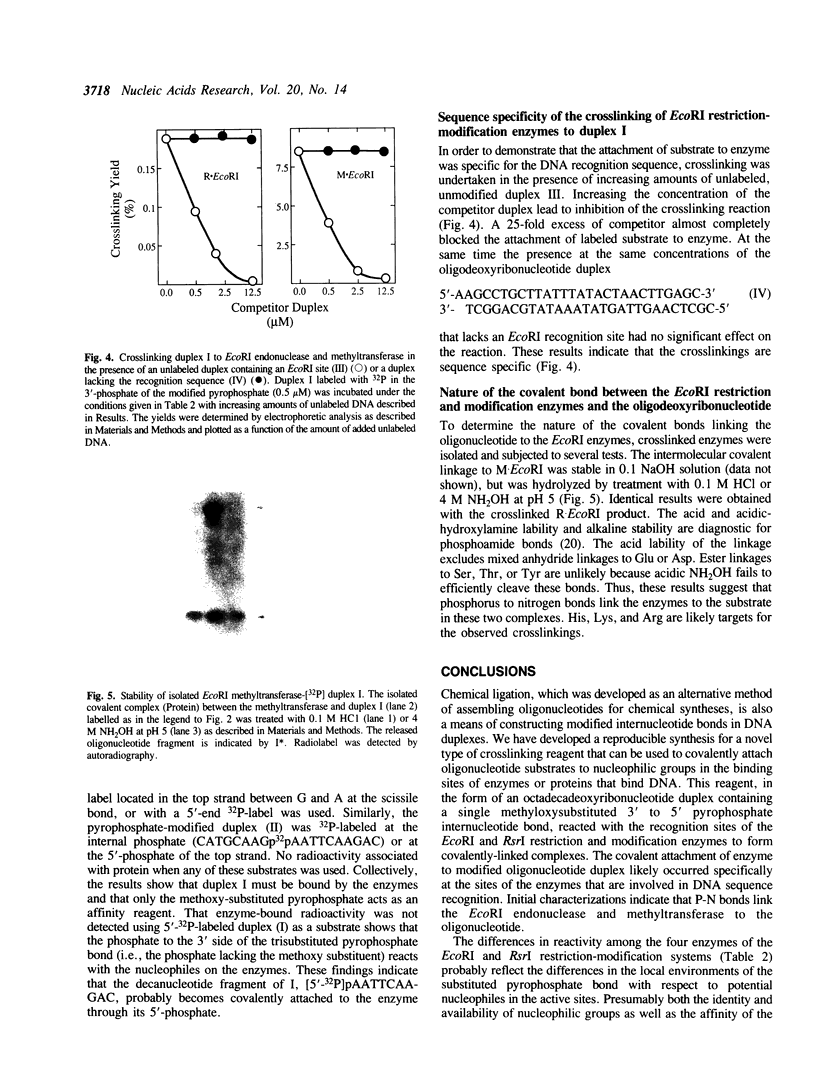

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken C. R., McLaughlin L. W., Gumport R. I. The highly homologous isoschizomers RsrI endonuclease and EcoRI endonuclease do not recognize their target sequence identically. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19070–19078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiken C., Gumport R. I. Restriction endonuclease RsrI from Rhodobacter sphaeroides, an isoschizomer of EcoRI: purification and properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):7901–7916. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.7901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Van Cleve M. D., Gumport R. I. The effects of base analogue substitutions on the cleavage by the EcoRI restriction endonuclease of octadeoxyribonucleotides containing modified EcoRI recognition sequences. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7270–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. C., Kim R., King K., Kim S. H., Modrich P. Isolation of gram quantities of EcoRI restriction and modification enzymes from an overproducing strain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11571–11575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay E., Bambara R., Padmanabhan R., Wu R. DNA sequence analysis: a general, simple and rapid method for sequencing large oligodeoxyribonucleotide fragments by mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):331–353. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaszubska W., Aiken C., O'Connor C. D., Gumport R. I. Purification, cloning and sequence analysis of RsrI DNA methyltransferase: lack of homology between two enzymes, RsrI and EcoRI, that methylate the same nucleotide in identical recognition sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10403–10425. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova S. A., Ivanovskaia M. G., Shabarova Z. A. Khimicheskie reaktsii v dvuspiral'nykh nukleinovykh kislotakh. IX. Napravlennoe vvedenie zameshchennykh pirofosfatnykh sviazei v strukturu DNK. Bioorg Khim. 1990 Feb;16(2):219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesser D. R., Kurpiewski M. R., Jen-Jacobson L. The energetic basis of specificity in the Eco RI endonuclease--DNA interaction. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):776–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2237428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikiforov T. T., Connolly B. A. Oligodeoxynucleotides containing 4-thiothymidine and 6-thiodeoxyguanosine as affinity labels for the Eco RV restriction endonuclease and modification methylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1209–1214. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purmal' A. A., Drutsa V. L., Shabarova Z. A. Novyi tip modifikatsii DNK. Napravlennoe vvedenie 3'-5'-pirofosfatnykh mezhnukleotidnykh sviazei. Bioorg Khim. 1984 Mar;10(3):394–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabarova Z. A., Dolinnaya N. G., Drutsa V. L., Melnikova N. P., Purmal A. A. DNA-like duplexes with repetitions. III. Efficient template-guided chemical polymerization of d(TGGCCAAGCTp). Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5747–5761. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabarova Z. A. Synthetic nucleotide-peptides. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1970;10:145–182. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60564-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfes H., Fliess A., Winkler F., Pingoud A. Cross-linking of bromodeoxyuridine-substituted oligonucleotides to the EcoRI and EcoRV restriction endonucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]