Abstract
AIM
To determine the growth rule and tendency of retinoblastoma (Rb) literature, and to provide the basis for research of diagnosis, treatment and on Rb.
METHODS
Bibliometric analyses were carried out on Rb literatures which contain the descriptors of Rb in their titles or texts from 1929 to 2010 in PubMed database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Pubmed). The biomedical journals referring to Rb by using bibliometric indicators were calculated. The principal bibliometric indicators, i.e., Price's and Bradford's laws to the increase or distribution of scientific literature, the participation index of languages and the journals were applied. By means of manual coding, Rb documents were classified according to documents studied and to statistical analysis.
RESULTS
During 1929-2010, there were 16162 literatures in the PubMed database including the word Rb. According to the literature type, it includes Review (n=2026), Randomized Controlled Trial (n=7), Practice guideline (n=3), meta-analysis (n=4), letter (n=215), editorial (n=98), clinical trial (n=115) and others (n=13694). By the statistical analysis, its equation is near power index (y=3.0477x2.6088, R2=0.9666). From 1929 to 2010, Rb literatures in English were primarily dominant (90.71%) and the amount of the literature in Chinese ranked the fourth (1.37%). By searching PubMed, 1420(8.8%) literatures covered were from 41 of 48 ophthalmological, and 406 (2.5%) literatures from 44 of 86 pediatrics journals that correlated with retinoblastoma (SCI-indexed). The data showed that the literatures of Rb were gradually increasing year by year and were approximate near power index during 1929-2010, and the document publishes published mainly in ophthalmological journals, and in English (90.71%), and showing that the study on Rb is a popular subject in the last half century.
CONCLUSION
The literatures of Rb are gradually increasing, mainly English in ophthalmologic journals.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis, biomedical publications, retinoblastoma, journal, literature
INTRODUCTION
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is the most common eye cancer in children and it can be inherited. The therapeutic goal for Rb is early detection to maximize the visual outcome and the quality of life of the affected child. The study of scientific literature growth law and its application are very important in the area of bibliometrics. Factors affecting literature are complex, and in addition to inherent laws of the subject, and there are disciplinary contexts[1]-[3]. Statistics of Rb literature growth carried out in a specific period and drawing of the correspondent growth curve are of primary importance in evaluating the subject's stage and forecasting its future development[2]-[5].
The Internet has rapidly become a global publishing platform, and journals covering a wide range of subject areas are now available. Information science is no exception, and we now find a significant portion of Rb literature appearing in PubMed since 1929[6]. This article presents some bibliometric data on the currently available journals in this field and the articles appearing in them[7]-[10]. PubMed comprises more than 19 million citations for biomedical articles from MEDLINE and life science journals. Citations may include links to full-text articles from PubMed Central or publisher web sites. PubMed database platform can be used to study Rb related literature for bibliometric analysis, so as to determine the increase regularity of Rb literature and its trend, and to provide the basis for related researches on ophthalmology, pediatrics and oncology.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Database
PubMed database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Pubmed) was used to select literatures that contained the descriptors of Rb in their titles or texts from 1929 to 2010. By bibliometric indicators of Rb, the biomedical journals referring to Rb were calculated. The principal bibliometric indicators, i.e., Price's and Bradford's laws to the increase or distribution of scientific literature, the participation index of languages and the journals were applied. By means of manual coding, documents were classified according to documents studied and to the statistical analysis.
Methods
We logged on the PubMed database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed) and searched literatures including “retinoblastoma” from 1929/01/01 to 2010/12/31, e.g., search (“1” [Publication Date]: “2010/12/31” [Publication Date]) AND (retinoblastoma), language distribution of the literature and amount of the literatures published mainly in periodicals of ophthalmology and pediatrics. Based on this, literatures of the following period, i.e., 1929/01/01-1945/12/31, 1946/01/01-1950/12/31., 2001/01/01-2005/12/31, 2006/01/01-2010/12/31, and literatures published in Chinese were retrieved. Literatures published in 2010 had not been completely covered in PubMed database because of time lag, and thus the amount of retrieved literature might be lower than that of actual one in the time of searching (Dec.31.2010).
RESULTS
Year Distribution of Retinoblastoma Literatures
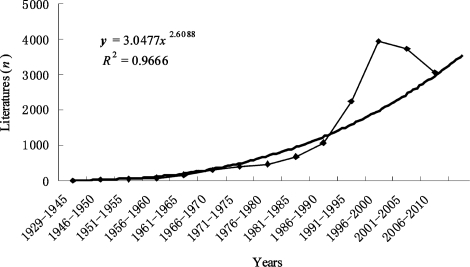
Before 1945, there were 5 Rb doucuments in PubMed database (2 in 1929 and 3 in 1944). From 1945, the Rb literatures increased with the year and by the end of 2010 the literature reached up to 16162, including review (n=2026), randomized controlled trial (n=7), practice guideline (n=3), meta-analysis (n=4), letter (n=215), editorial (n=98), clinical trial (n=115) and others (n=13694). The rise of Rb literatures in every 5 years was shown in Figure 1, i.e., 1929-1945, 5; 1946-1950, 23; 1951-1955, 42; 1956-1960, 64; 1961-1965, 164; 1966-1970, 302; 1971-1975, 403; 1976-1980, 460; 1981-1985, 666; 1986-1990, 1070; 1991-1995, 2232; 1996-2000, 3943; 2001-2005, 3734; 2006-2010, 3106; 1929-2010, 16162. It is revealed that there are three stages of yearly cumulative amount of the literatures. The amount of literatures before 1960 was very low, the literature increased slowly from 1961 to 1985, and rose quickly from 1986 to 2010 (Figure 1). By the statistical analysis, its equation is near power index (y=3.0477x2.6088, R2=0.9666). According to the calculation of equation, it is predicted that there will be 4220 Rb literatures from 2011 to 2015, and 4943 from 2016 to 2020.
Figure 1. Rb literatures in every 5 years from 1929 to 2010.
Language and Distributions
Fifty-seven kinds of languages are listed in the PubMed database. Rb literatures in English were primarily dominant before 2010 (14708/16162, 90.71%), and the amount of the literature in Chinese ranked the fourth place (222/16162, 1.37%). The first 8 languages accounted for 98.41%, while the other forty-nine languages occupied 1.59% (Table 1).
Table 1. Language distribution of Rb literatures in PubMed from 1929 to 2010.
| Languages | Rb | PubMed literatures |
| English | 14708 (90.71) | 16365497 (80.48) |
| French | 339 (2.09) | 651295 (3.20) |
| Japanese | 226 (1.39) | 381577 (1.88) |
| Chinese | 222 (1.37) | 191680 (0.94) |
| German | 214 (1.32) | 782313 (3.85) |
| Russian | 123 (0.76) | 647606 (3.18) |
| Spanish | 87 (0.54) | 271736 (1.34) |
| Italian | 38 (0.23) | 288785 (1.42) |
| Others | 257 (1.59) | 753515(3.70) |
| Total | 16162 (100) | 20334004(100) |
[n (%)]
Journal Distribution
By the end of 2010, more than 5 200 kinds of biomedical journals had been covered in PubMed, which involves 57 languages. Fifty percent of them were from USA and 90% were written in English, and English abstract accounted for 79%. There were 48 kinds of ophthalmological journals and 86 pediatric journals indexed in SCI database (Thomson-Reuters in 2010 for SCI indexed), which was covered by PubMed. By searching PubMed database, the literatures of Rb were found from 1929 to 2010 (Table 2). The results showed that Rb literatures published in ophthalmologic journals (41 of 48 journals included a total of 1420 literatures), and in the pediatric journals (44 of 86 journals included a total of 406 literatures) and the number of documents had no correlation with impact factors (IF) of the journal included in PubMed.
Table 2. Rb literatures published in ophthalmologic and pediatric journals in PubMed (1929-2010).
| ISSN | Ophthalmologic Journals (n=41) | Literatures (n) | Impact Facto r(IF) | ISSN | Pediatrics Journals (n=44) | Literatures (n) | Impact Factor (IF) |
| 0003-9950 | Arch Ophthalmol-Chic | 178 | 3.859 | 0191-3913 | J Pediat Ophth Strab | 106 | 0.627 |
| 0002-9394 | Am J Ophthalmol | 166 | 3.833 | 1545-5009 | Pediatr Blood Cancer | 51 | 2.134 |
| 0146-0404 | Invest Ophth Vis Sci | 147 | 3.431 | 1077-4114 | J Pediat Hematol Onc | 33 | 1.022 |
| 0007-1161 | Br J Ophthalmol | 129 | 2.917 | 1091-8531 | J Aapos | 26 | 1.07 |
| 0161-6420 | Ophthalmology | 108 | 5.491 | 0888-0018 | Pediatr Hemat Oncol | 24 | 0.794 |
| 0191-3913 | J Pediat Ophth Strab | 106 | 0.627 | 0031-4005 | Pediatrics | 13 | 4.687 |
| 0023-2165 | Klin Monatsbl Augenh | 76 | 0.542 | 0003-9888 | Arch Dis Child | 13 | 2.657 |
| 0030-3755 | Ophthalmologica | 63 | 1.028 | 0301-0449 | Pediatr Radiol | 13 | 1.186 |
| 0275-004X | Retina-J Ret Vit Dis | 45 | 2.932 | 0019-6061 | Indian Pediatr | 9 | 0.962 |
| 1381-6810 | Ophthalmic Genet | 43 | 1.406 | 0090-4481 | Pediatr Ann | 9 | 0.368 |
| 0181-5512 | J Fr Ophtalmol | 36 | 0.510 | 0022-3476 | J Pediatr | 8 | 4.092 |
| 0014-4835 | Exp Eye Res | 33 | 2.538 | 0009-9228 | Clin Pediatr | 8 | 0.977 |
| 0021-5155 | Jpn J Ophthalmol | 29 | 1.272 | 0929-693X | Ardn Pediatrie | 8 | 0.406 |
| 0039-6257 | Surv Ophthalmol | 29 | 2.347 | 0031-3955 | Pediatr Clin N Am | 7 | 1.587 |
| 1091-8531 | J Aapos | 26 | 1.070 | 0300-8630 | Klin Padiatr | 6 | 1.862 |
| 0271-3683 | Curr Eye Res | 23 | 1.513 | 0026-9298 | Monatsschr Kinderh | 5 | 0.308 |
| 0008-4182 | Can J Ophthalmol | 19 | 1.443 | 1072-4710 | Arch Pediat Adol Med | 4 | 4.726 |
| 1090-0535 | Mol Vis | 19 | 2.541 | 0041-4301 | Turkish J Pediatr | 4 | 0.333 |
| 0740-9303 | Ophthal Plast Recons | 16 | 0.690 | 0022-3468 | J Pediatr Surg | 4 | 1.43 |
| 0950-222X | Eye | 15 | 1.974 | 0256-7040 | Child Nerv Syst | 4 | 1.214 |
| 0721-832X | Graef Arch Clin Exp | 15 | 2.102 | 0269-5022 | Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol | 4 | 1.797 |
| 1442-6404 | Clin Exp Ophthalmol | 13 | 1.755 | 0305-1862 | Child Care Hlth Dev | 4 | 1.137 |
| 0030-3747 | Ophthal Res | 13 | 1.288 | 0031-3998 | Pediatr Res | 3 | 2.607 |
| 1120-6721 | Eur J Ophthalmol | 11 | 0.887 | 0019-5456 | Indian J Pediatr | 3 | 0.539 |
| 1040-8738 | Curr Opin Ophthalmol | 10 | 2.490 | 1040-8703 | Curr Opin Pediatr | 3 | 2.215 |
| 0012-4486 | Doc Ophthalmol | 9 | 1.837 | 0272-4936 | Ann Trop Paediatr | 3 | 0.895 |
| 0941-293X | Ophthalmologe | 8 | 1.000 | 0012-1622 | Dev Med Child Neurol | 3 | 3.019 |
| 1542-8877 | Ophthal Surg Lasers Imaging | 6 | 0.615 | 0191-9601 | Pediatr Rev | 3 | 0.840 |
| 0042-6989 | Vis Res | 5 | 2.288 | 0165-5876 | Int J Pediatr Otorhi | 3 | 1.148 |
| 0927-3948 | Ocul Immunol Inflamm | 5 | 0.718 | 0179-0358 | Pediatr Surg Int | 3 | 0.945 |
| 0928-6586 | Ophthal Epidemiol | 4 | 1.927 | 1016-2291 | Pediatr Neurosurg | 3 | 0.967 |
| 1080-7683 | J Ocul Pharmacol Ther | 3 | 1.457 | 0803-5253 | Acta Paediatr | 2 | 1.768 |
| 1755-375X | Acta Ophthalmol | 2 | 2.441 | 0340-6199 | Eur J Pediatr | 2 | 1.634 |
| 0886-3350 | J Cataract Refr Surg | 2 | 2.745 | 1328-8067 | Pediatr Int | 2 | 0.707 |
| 0277-3740 | Cornea | 2 | 2.106 | 0891-3668 | Pediatr Infect Dis J | 1 | 2.854 |
| 1040-5488 | Optometry Vis Sci | 1 | 1.530 | 0931-041X | Pediatr Nephrol | 1 | 2.425 |
| 0275-5408 | Ophthal Physl Opt | 1 | 1.148 | 0334-018X | J Pediatr Endocr Met | 1 | 0.738 |
| 0816-4622 | Clin Exp Optom | 1 | 1.236 | 1034-4810 | J Paediatr Child Health | 1 | 1.138 |
| 0952-5238 | Vis Neurosci | 1 | 1.273 | 0142-6338 | J Trop Pediatrics | 1 | 1.224 |
| 1530-4086 | Ann Ophthalmol (Skokie) | 1 | 0.157 | 0378-3782 | Early Hum Dev | 1 | 2.122 |
| 1350-9462 | Prog Retin Eye Res | 1 | 7.755 | 1359-2998 | Arch Dis Child-Fetal | 1 | 2.493 |
| 1155-5645 | Pediatr Anesth | 1 | 2.149 | ||||
| 1093-5266 | Pediatr Devel Pathol | 1 | 1.163 | ||||
| 0164-1263 | Pediatr Dent | 1 | - |
DISCUSSION
From the above research, it is clear that the amount of Rb documents presents the tendency of slow increasing and reaches its highest from 1986 to 2005, revealing that Rb researches have been in popular stage over the last half century. No large fluctuation appeared in the amount. During 2006-2010, the PubMed literature database was incomplete for including the literatures, so there are a relatively small number of Rb documents. Simultaneously, the amounts of retinoblastoma literatures are consistent with Rb progress and development in the world. Rb documents in English hold a leading part (90.71%) by the end of 2010 and the following is in French, Japanese, Chinese, German, Russian, Spanish etc. The documents in Chinese only accounted for 1.37%, which resulted from fewer Chinese journals covered by PubMed (by the end of 2010). Among the 111 Chinese journals, 93 were edited and published by China Continent, 13 by Taiwan province, 4 by Hong Kong and 1 by Macao Special Administrative Region. Research indicated that the Rb research was still a hotspot in the international society. Rb document was covered by PubMed from 1929, rising obviously after 1986, but its equation is near power index(y=3.0477x2.6088, R2=0.9666).The research literatures on Rb were mainly published in ophthalmological and related pediatric periodicals. Rb is the most common eye cancer in children and it can be inherited. Despite being the most common eye cancer in children, Rb is quite rare and occurs in approximately 0.5 in every 100 000 births. Fortunately, the survival rate for affected children is 96%[3]-[5],[11],[12].
Bibliometrics adopts the quantitative approach to study all kinds of documents and mathematic laws in their exchange in order to forecast the discipline development and ascertain its developing trend. Quantitative analysis can be used to aim at the study of discipline developing trend, document quantitative change law, and scientific management of information. It is important to analyze and forecast various characteristics of discipline documents and their change law based on the statistics, which is closely related to the research subject. Discipline documents increase drastically during some period and are relatively stable in some other period[11]-[13]. Some scientific literatures increase in exponent, some in logistic curves, some in linearity and some in other patterns. Carrying out quantitative analysis on the countries and languages that the documents originate from may reveal the status and change tendencies of the subject research between countries. Since the exponential and logic growth laws of scientific literatures were put forward, many experts and scholars have carried out the research and exploration on them widely and thoroughly. Some approaches in defining the parameters have been improved, exponential curve and the logistic curve have been modified by the use of adding parameters or new means, and new mathematic model in describing the document growth law has been suggested. Great achievements have been made. Conducting the analysis on information and contents of Rb document can give guidance to the research and deepen our professional knowledge. Quantitative analysis can also be carried out from the aspect of document content or its field to understand its research hotspots and progress[2],[14]. Research on the laws of growth, ageing and scattering of the published papers has been regarded as one of the important bases of scientific and technological progress, which are the basic laws of document development[8]-[10],[13]-[15]. In the field of biomedicine, Rb bibliometric study can be conducted from quantitative aspect. Through statistic analysis on yearly Rb documents, their growing regularity can be found, and the past and current situation of studies can be explored, and its developing trend can be forecasted. Document increase is a complicated process. Our studies show that scientific literatures increase with time, but they increase in different speed and degrees. Negative grow indicates that this subject research is given less importance to in the social progress. Scientific literature increases not only according to the development law of itself, but it is restrained by various social conditions. In addition, the scientific literature increase is also influenced by media technology, publishing technology, electronic computer, modern information technology and the network development, etc, and therefore it presents a random process and makes the document increase in various patterns[16]-[18].
The amount of scientific literature has a tendency of increase in pace with scientific knowledge, and their growth laws also share some similarities to a large degree. Changes of scientific literature increase can reflect technology development of some subject. The entire process and trend in the production and development of some scientific branch or technology may be of great help in selecting research project and determining technological development or technology introduction scheme. Study of scientific literature growth law is an information research conducted by scientific and informational staff, which aims at mastering developing trend of science and technology and giving theory guidance and reliable means to scientific forecast. The scientific literature growth law and scientific knowledge increase law are usually interrelated and mutually promoted. Findings of scientific literature increase law can provide a basis for the research on increase law of scientific knowledge amount. The increase law of scientific knowledge amount will in turn help deepen the cognition of document increase law. Therefore document increase law plays an important role in knowledge amount and administration and has wide application prospect[14]-[17]. It is the same in the study of Rb document. The document rise of Rb year by year indicates that the researchers give much importance to the subject, which is closely correlated with human beings.
Major factors affecting the increase of Rb documents are inherent developing law of the discipline. Until 1945 there are only 5 Rb documents. The Rb literatures reach 129 documents in a total of 5 years (1956-1960). During 1961-1985, the literatures increase only a few hundred articles every five years. From 1986, the amount of Rb documents reached over a thousand every 5 years, which is closely related with the development of medical science and technology. Rb documents in Chinese are relatively few mainly because PubMed indexed few Chinese journals. The growth law of scientific literature quantity is determined by objective process of science, including environment and inherent development law of science. Science inherent development law has its own characteristics. Every discipline grows through the different stages of birth, development, maturity, etc. If the total amount of newly increased Rb document every year is a fixed value, it shows that there is no big breakthrough in the discipline theory and that personnels and material resources in the field needed by the society are constant. Therefore the subject is in a relatively stable environment[12]-[15],[18]-[20].
All these results are determined by Rb inherent development law of its document. Inherent law and social environment are two completely different factors affecting the Rb document increase law. It is difficult for us to effectively and correctly differentiate them even if the bibliometric index is used. Environmental factors are very complicated and whether they affect the development speed of scientific field, national politics, economy, culture and education or not is of great importance to the document increase in all subjects. It can also influence some special fields, for example, society moral concept, the transformation of biomedical pattern to bio-psychological and social medical science pattern[21]-[23]. All these affect Rb document increases, e.g., the establishment and implementation of human gene project will produce far-reaching effects on the amounts of science document. The establishment and alteration of country's policy may influence different fields of science. A lot of researches on discipline increase law demonstrate that the increasing trend of document parallels to the national policy. Since the reform and opening up proceeds in China, every field develops in high speed, and medical science is no exception. The investment in scientific research, the number of scientific and technological staff and periodicals increased rapidly. Accordingly, science and technology papers increase quickly. It gathers the theories of preclinical medicine, clinical medicine as well as other subjects and is established based on the achievements of science and technology used in the clinical practice. At present it has already become one of the important parts in clinical medicine[24]-[26].
Stable demand for Rb researchers and investment of staff and material resources may reflect the sustained stable developing trend in the future[3],[16]-[18]. According to the increase law theory of the document and our comprehensive statistical results, international Rb document presents a linear increase, and Rb document amount in the next few years can be estimated by use of straight line equation. The amount of newly increased document every year is relatively fixed, and is in the third stage of the subject development. Bibliometrics is widely used in all kinds of fields both at home and abroad at present, such as, measurement of core journals, research of readers, research of scientific law, analysis of talented persons, document law analysis, information retrieving system, document query optimization, and estimation and forecast of scientific trend in every field, etc. Bibliometrics application in medical science field increases with the time going. Especially from the trans-century, the document amount in this field has a trend of increasing significantly, but bibliometrics on literatures related to medical science accounts for a lower percentage of medical papers[1]-[3],[6],[27]-[29].
There are many artificial factors that affect the document flow and it is true of Rb. At present it is still difficult to quantify documentation research. Based on several statistical laws of experience, bibliometrics is widely used. Microcosmic application of bibliometrics can favor us to determine the core document, evaluate publications and examine the utilization ratio of document, and thus it realizes scientific management of library and information[30]-[32]. Macroscopic application of bibliometrics has the advantages of designing information system and network economically, improving information handling efficiency, finding malpractice and defects in document service, forecasting the trend of publications, developing and perfecting the basic theories of information, etc. Because of the complexity and unstability of document system, to get sufficient and effective information to uncover the macroscopic law of document is difficult. Development of bibliometrics depends on the support of mathematic implements and statistical technology. Transplanting or making use of effective mathematic instruments and statistical method is an important development direction of bibliometrics[33],[34].
Footnotes
Foundation item: National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 39580683)
REFERENCES
- 1.Lohmann D. Retinoblastoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;685:220–227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6448-9_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chintagumpala M, Chevez-Barrios P, Paysse EA, Plon SE, Hurwitz R. Retinoblastoma: review of current management. Oncologist. 2007;12(10):1237–1246. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-10-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cozza R, De Ioris MA, Ilari I, Devito R, Fidani P, De Sio L, Demelas F, Romanzo A, Donfrancesco A. Metastatic retinoblastoma: single institution experience over two decades. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93(9):1163–1166. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2008.148932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yang IH, Kuo HK, Chen YJ, Lee JJ, Lin SA. Review of 20 years' clinical experience with retinoblastomas in southern Taiwan. Changgung Med J. 2008;31(5):484–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Saket RR, Mafee MF. Anterior-segment retinoblastoma mimicking pseudoinflammatory angle-closure glaucoma: review of the literature and the important role of imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(8):1607–1609. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Benedict WL. Homologous retinoblastoma in identical twins. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1929;27:173–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chow DS, Itagaki MW. Interventional oncology research in the United States: slowing growth, limited focus, and a low level of funding. Radiology. 2010;257(2):410–417. doi: 10.1148/radiol.10100070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.de Oliveira GF, Luchesi LB. The discourse on alcohol in the Brazilian Journal of Nursing: 1932-2007. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2010;18:626–633. doi: 10.1590/s0104-11692010000700020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Michàn L, Llorente-Bousquets J. Bibliometry of biological systematics in Latin America during the twentieth century in three global databases. Rev Biol Trop. 2010;58(2):531–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nykiforuk CI, Osler GE, Viehbeck S. The evolution of smoke-free spaces policy literature: a bibliometric analysis. Health Policy. 2010;97(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mazboudi M, Ben Abdelaziz A. Medical research productivity of Lebanon: a bibliometric study of papers indexed in Medline, 1985-2004. Tunis Med. 2010;88(8):579–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.MacCarthy A, Bayne AM, Draper GJ, Eatock EM, Kroll ME, Stiller CA, Vincent TJ, Hawkins MM, Jenkinson HC, Kingston JE, Neale R, Murphy MF. Non-ocular tumours following retinoblastoma in Great Britain 1951 to 2004. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93(9):1159–1162. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2008.146035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Krishna SM, Yu GP, Finger PT. The effect of race on the incidence of retinoblastoma. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2009;46(5):288–293. doi: 10.3928/01913913-20090903-06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Robert C, Wilson CS, Donnadieu S, Gaudy JF, Arreto CD. Evolution of the scientific literature on pain from 1976 to 2007. Pain Med. 2010;11(5):670–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2010.00816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Scotch M, Duggal M, Brandt C, Lin Z, Shiffman R. Use of statistical analysis in the biomedical informatics literature. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010;17(1):3–5. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vioque J, Ramos JM, Navarrete-Muñoz EM, García-de-la-Hera M. A bibliometric study of scientific literature on obesity research in PubMed (1988-2007) Obes Rev. 2010;11(8):603–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Carbonell X, Guardiola E, Beranuy M, Bellés A. A bibliometric analysis of the scientific literature on internet, video games, and cell phone addiction. J Med Libr Assoc. 2009;97(2):102–107. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.97.2.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Canturk S, Qaddoumi I, Khetan V, Ma Z, Furmanchuk A, Antoneli CB, Sultan I, Kebudi R, Sharma T, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Abramson DH, Chantada GL. Survival of retinoblastoma in less-developed countries impact of socioeconomic and health-related indicators. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010;94(11):1432–1436. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2009.168062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Woo KI, Harbour JW. Review of 676 second primary tumors in patients with retinoblastoma: association between age at onset and tumor type. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128(7):865–870. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Holdt M, Jurklies C, Schueler A, Otterbach F, Bornfeld N. Intraocular medulloepithelioma-series of 10 cases and review of the literature. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2009;226(12):1017–1022. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Arora RS, Eden TO, Kapoor G. Epidemiology of childhood cancer in India. Indian J Cancer. 2009;46(4):264–273. doi: 10.4103/0019-509X.55546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim SM, Myoung H, Choung PH, Kim MJ, Lee SK, Lee JH. Metastatic leiomyosarcoma in the oral cavity: case report with protein expression profiles. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2009;37(8):454–460. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2009.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jurkiewicz E, PakuIa-Kosciesza I, Rutynowska O, Nowak K. Trilateral retinoblastoma: an institutional experience and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst. 2010;26(1):129–132. doi: 10.1007/s00381-009-0958-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lin P, O'Brien JM. Frontiers in the management of retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009;148(2):192–198. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2009.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Broaddus E, Topham A, Singh AD. Incidence of retinoblastoma in the USA:1975-2004. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93(1):21–23. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2008.138750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Canty CA. Retinoblastoma: an overview for advanced practice nurses. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2009;21(3):149–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7599.2008.00378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Manipalviratn S, DeCherney A, Segars J. Imprinting disorders and assisted reproductive technology. Fertil Steril. 2009;91(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mastrangelo D, De Francesco S, Di Leonardo A, Lentini L, Hadjistilianou T. The retinoblastoma paradigm revisited. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14(12):231–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Neelanjana M, Sabaratnam A. Malignant conditions in children born after assisted reproductive technology. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2008;63(10):669–676. doi: 10.1097/OGX.0b013e318181a9f0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Maire G, Brown CW, Bayani J, Pereira C, Gravel DH, Bell JC, Zielenska M, Squire JA. Complex rearrangement of chromosomes 19, 21, and 22 in Ewing sarcoma involving a novel reciprocal inversion-insertion mechanism of EWS-ERG fusion gene formation: a case analysis and literature review. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2008;181(2):81–92. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2007.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Martin NE, Kim JW, Abramson DH. Fibrin sealant for retinoblastoma: where are we? J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2008;24(5):433–438. doi: 10.1089/jop.2007.0110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mueller CM, Caporaso N, Greene MH. Familial and genetic risk of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary tract. Urol Oncol. 2008;26(5):451–464. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.02.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.MacCarthy A, Bunch KJ, Fear NT, King JC, Vincent TJ, Murphy MF. Paternal occupation and retinoblastoma: a case-control study based on data for Great Britain 1962-1999. Occup Environ Med. 2009;66(10):644–649. doi: 10.1136/oem.2007.037218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kissin I. The development of new analgesics over the past 50 years: a lack of real breakthrough drugs. Anesth Analg. 2010;110(3):780–789. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181cde882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]