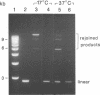
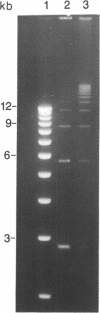
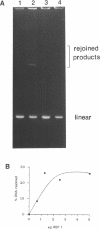
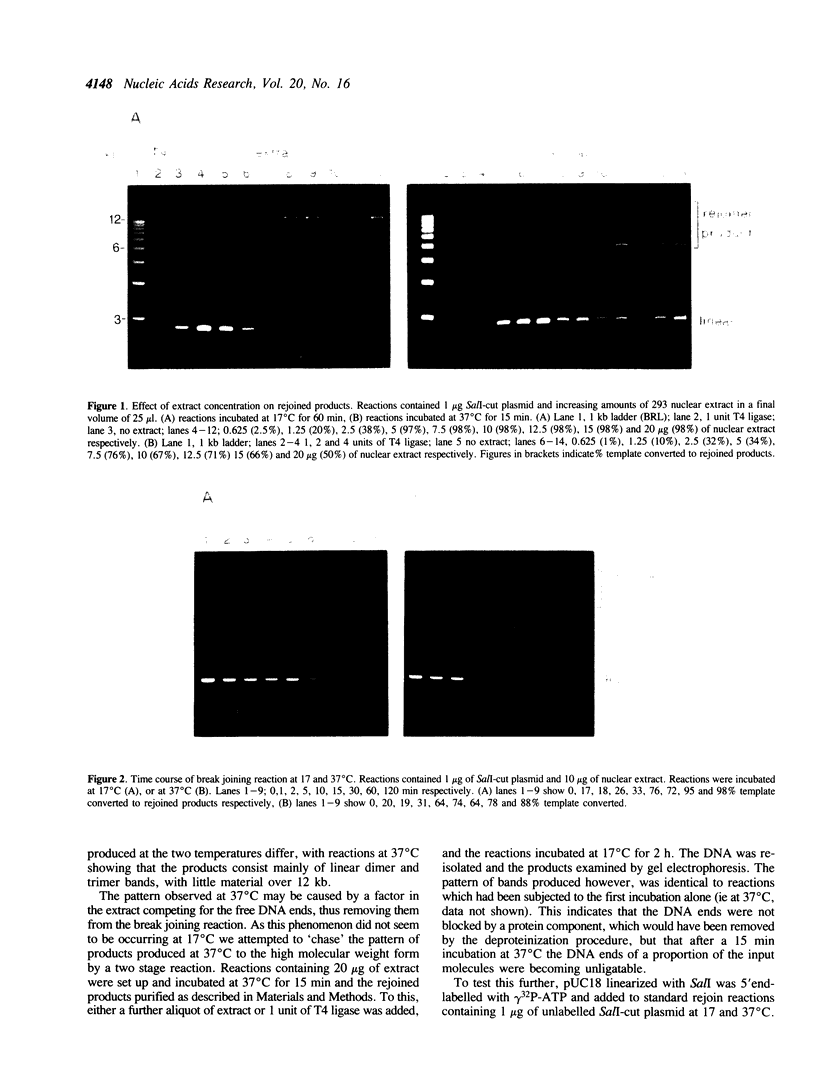
Abstract
We describe a rapid and efficient in vitro system for the rejoining of double stranded breaks in DNA based on extracts of human 293 cells. Using this system as an assay, we have separated the nuclear extract into several components involved in break rejoining. The unfractionated system can convert approx. 100% of the input DNA, linearized with a restriction enzyme, to high molecular weight material at low temperature (17 degrees C), and at the physiological temperature of 37 degrees C we have shown that competing activities in the extract can also act on the DNA template. We present the fractionation of the extract and the partial purification of a novel factor which will stimulate a crude rejoin activity and in addition increases the activity of purified DNA ligase I. We have also partially purified the break joining activity and show that the chromatographic properties do not directly correspond with the three DNA ligases previously described, indicating that the activity observed may not be due to a single enzyme species. By studying the rejoining of double stranded DNA breaks as a biochemical process, we have demonstrated that the efficient joining of such breaks requires factors in addition to DNA ligases.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan J. Y., Thompson L. H., Becker F. F. DNA-ligase activities appear normal in the CHO mutant EM9. Mutat Res. 1984 May-Jun;131(5-6):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman M. P., Stillman B. Cellular factors required for multiple stages of SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1211–1218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman M., Prelich G., Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Identification of cellular components required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 20;951(2-3):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Zinder N. D., Model P. Repair of the Escherichia coli chromosome after in vivo scission by the EcoRI endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2281–2285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne K., Ljungquist S. Expression of a DNA-ligase-stimulatory factor in Bloom's syndrome cell line GM1492. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jun 15;174(3):465–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Barnes D. E. Mammalian DNA ligases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:251–281. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez B. S., Corteggiani E., Bertrand-Mercat P., Coppey J. Directional recombination is initiated at a double strand break in human nuclear extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):501–506. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North P., Ganesh A., Thacker J. The rejoining of double-strand breaks in DNA by human cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6205–6210. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali Noy G. C., Spadari S., Ciarrocchi G., Pedrini A. M., Falaschi A. Two forms of the DNA ligase of human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):343–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. Joining of nonhomologous DNA double strand breaks in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):907–924. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Stillman B. Coordinated leading and lagging strand synthesis during SV40 DNA replication in vitro requires PCNA. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargentini N. J., Smith K. C. Quantitation of the involvement of the recA, recB, recC, recF, recJ, recN, lexA, radA, radB, uvrD, and umuC genes in the repair of X-ray-induced DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli. Radiat Res. 1986 Jul;107(1):58–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Ciarrocchi G., Falaschi A. Purification and properties of a polynucleotide ligase from human cell cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 13;22(1):75–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamato T. D., Hu J. Normal DNA ligase activity in a gamma-ray-sensitive Chinese hamster mutant. Mutat Res. 1987 Jan;183(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Gluzman Y. Replication and supercoiling of simian virus 40 DNA in cell extracts from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2051–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thode S., Schäfer A., Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. A novel pathway of DNA end-to-end joining. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90340-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Lasko D. D., Daly G., Lindahl T. Mammalian DNA ligases. Catalytic domain and size of DNA ligase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12611–12617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Roberts E., Daly G., Totty N. F., Lindahl T. Three distinct DNA ligases in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21728–21735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. F. DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: identities, mechanisms of formation, and reparability. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:95–125. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60611-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Coverley D. DNA excision repair in mammalian cell extracts. Bioessays. 1991 Sep;13(9):447–453. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]