Abstract
Biliary atresia is a neonatal disorder characterized by aggressive fibroinflammatory obliteration of the biliary tract. Approximately 20 percent of biliary atresia patients demonstrate left-right laterality defects (syndromic biliary atresia). Cilia participate in important physiologic functions in cholangiocytes, and since some ciliopathies have been associated with both laterality defects and hepatic fibrosis, we hypothesized that patients with syndromic biliary atresia exhibit abnormalities of cholangiocyte cilia that disrupt cholangiocyte homeostasis. Nine biliary atresia specimens were studied, including pre-Kasai diagnostic biopsies (n=7) and liver explants (n=2). Five specimens were from patients with laterality defects. These were compared to normal pediatric livers as well as livers affected by primary sclerosing cholangitis, Wilson’s disease, and cardiac cirrhosis. Biopsy sections were stained with antibodies against keratin 19 (a cholangiocyte marker) and acetylated α-tubulin (a cilia marker) and were visualized by confocal microscopy. Computer-assisted relative quantification was used to compare staining of cilia within bile ducts among samples. Surprisingly, cilia in biliary atresia specimens were significantly shorter, abnormal in their orientation, and less abundant compared to normal liver and disease controls regardless of the presence of a laterality defect.
Conclusion
There are significant abnormalities of cholangiocyte cilia in both syndromic and non-syndromic biliary atresia livers compared to normal livers and livers affected by other cholestatic diseases. While this may result from severe cholestasis or inflammation, it may also reflect common mechanistic pathways in different forms of biliary atresia and may have important implications for understanding the progression of the disease.
Keywords: liver fibrosis, ciliopathy, laterality, situs inversus, cholestasis
Introduction
Biliary atresia is a neonatal disease with an incidence of 1 in 8,000–18,000 live births that is characterized by aggressive fibroinflammatory obliteration of the extrahepatic biliary tract.1 The etiology of biliary atresia is unknown but may involve environmental, infectious, and genetic factors. Although most biliary atresia patients undergo a Kasai portoenterostomy at the time of diagnosis to facilitate bile drainage, 70 to 80 percent of patients ultimately require transplant, and the disease is the most common indication for liver transplantation in the pediatric population.1–3
Approximately 20 percent of patients with BA have a variant form called syndromic biliary atresia (also known as embryonic biliary atresia or biliary atresia with splenic malformation syndrome) and demonstrate laterality defects including malrotation, dextrocardia, and polysplenia.4 This suggests that a ciliary defect might be involved in the pathophysiology of biliary atresia, at least in this subset of patients, since abnormal function of primary cilia during embryogenesis has been implicated in the development of laterality defects.1,5 Primary cilia are thin, solitary tubular projections present on the cell membranes of most epithelial and stromal cells. In the liver, cholangiocytes but not hepatocytes possess cilia.6 Cholangiocyte cilia have been well studied and found to have functions including mechanotransduction of luminal flow; detection of biliary nucleotides, bile acids, and luminal tonicity; and interactions with biliary exosomes. 6–11
The classic cholangiocyte ciliopathy is autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, which is associated with congenital hepatic fibrosis. Other ciliopathies associated with liver fibrosis include Meckel syndrome, nephronophthisis, and Joubert syndrome.12–14 The inv mutant mouse, which possesses a defect in inversin (which encodes a ciliary basal body protein that regulates switching between canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways), develops situs inversus and obstructive cholestasis.15–17 Ciliary abnormalities in biliary atresia have not been well studied. There have been only two case reports of patients with immotile cilia syndrome who also developed biliary atresia;18,19 however, a recent study by Hartley et al. found that the primary cilia-associated protein fibrocystin/polyductin is absent in the cholangiocytes of patients with biliary atresia, suggesting that ciliary defects in this disease might be more widespread.20
We hypothesized that patients with syndromic biliary atresia would demonstrate ciliary defects and that this finding might differentiate syndromic from non-syndromic biliary atresia. We therefore undertook to examine cholangiocyte cilia in biopsies from both forms of biliary atresia livers and to compare them to biopsies from patients with normal livers or other forms of cholestatic liver disease.
Materials and Methods
Human tissues
Fixed liver tissue was obtained from the surgical pathology archives at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia with the approval of the Institutional Review Board. Biliary atresia samples were either from diagnostic biopsies or from liver explant tissue. For controls, we examined three histologically normal liver samples from children (two obtained from resected tissue adjacent to hepatoblastoma and one from the explant of a patient with metabolic disease) as well as three cholestatic disease controls (primary sclerosing cholangitis, Wilson’s disease, and cardiac cirrhosis) (Table 1). Tissues were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, dehydrated through serial alcohol washes using an automated processor, and cleared with xylene before embedding with paraffin.
Table 1.
Sources of tissue.
| Control samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen | Pathology | Biopsy Type | Age |
| C1* | Normal tissue adjacent to hepatoblastoma | Resection | NA |
| C2* | Normal tissue adjacent to hepatoblastoma | Resection | 5y |
| C3* | Citrullinemia | Explant | 6m 22d |
| C4 | PSC | Explant | 19y |
| C5 | Cardiac cirrhosis | Explant | 9y |
| C6 | Wilson’s | Explant | 17y |
| BA samples | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen | Pathology | Biopsy Type | Age | Sex | Race | Transplant by 2 yrs |
| B1 | BA | Wedge | 4m 18d | F | Black | No |
| B2 | BA | Needle | 2m 20d | M | Caucasian | No |
| B3 | BA | Wedge | 48d | F | Caucasian | No |
| B4 | BA | Needle | 3m 2d | F | Black | No |
| B5 | BASM | Wedge | 27d | F | Caucasian | No |
| B6 | BASM | Explant | 5m 26d | F | Caucasian | No |
| B7 | BASM | Wedge | 20d | M | Black | No |
| B8a | BASM | Wedge | 33d | M | Hispanic | Yes (see B8b) |
| B8b** | “ | Explant | 6m 5d | “ | “ | “ |
Histologically normal
B8a and B8b were from the same patient, taken at different times.
Abbreviations: NA = not available; PSC = primary sclerosing cholangitis; BA = biliary atresia; BASM = biliary atresia with splenic malformation syndrome (also called syndromic BA)
Immunofluorescence microscopy
Four-micron sections were dewaxed in xylene, rehydrated through serial ethanol washes, and subjected to microwave antigen retrieval in 10 mmol/L citric acid solution (pH 6.0). Sections were blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin in 0.1% Triton X-100/1x PBS and incubated with primary antibodies at 4°C overnight: rabbit anti-cytokeratin 19 (K19; 1:100; Abcam, Cambridge, MA), rabbit anti-Ki67 (1:100; Abcam), and mouse anti-acetylated α-tubulin (1:5000; Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Slides were incubated with the appropriate Cy2- or Cy3- (1:600) secondary antibodies (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA) for 2 hours at room temperature. For conventional immunofluorescence, images were captured using a Nikon E600 microscope (Nikon, Melville, NY) equipped with a QICAM CCD camera (QImaging, Burnaby, BC, Canada) and processed using iVision software (BioVision Technologies, Exton, PA). For confocal imaging, single slice and Z-stack images were captured using a Zeiss LSM-510 Meta confocal microscope (Thornwood, NY).
Cell counting, computer-assisted 3-D reconstructions, and relative quantification of cholangiocyte cilia
Cell counting was performed manually with the assistance of ImageJ software (NIH, Bethesda, MD). 3-D reconstructions of confocal immunofluorescence image Z-stacks were generated using the LSM Image Viewer (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging, Munich, Germany). To compare cholangiocyte cilia, we performed computer-assisted relative quantification by generating the ratio of intraluminal ciliary staining to the number of directly adjacent cholangiocyte nuclei in regions of interest. Only ducts with clear lumens were examined, and 3-D reconstructions were used to generate maximal information about the cilia projecting into a given duct. For any given area that we assessed, two confocal slices separated by at least 1.2 microns were taken from the same Z-stack for evaluation. Quantification of intraluminal biliary cilia staining was performed using iVision software (Biovision Technologies, Exton, PA), and cholangiocyte nuclei were counted manually using ImageJ.
Results
We assessed nine biliary atresia specimens, five from patients with laterality defects (Table 1). Biliary atresia samples were compared to three histologically normal pediatric livers as well as tissue from patients with cirrhosis resulting from other cholestatic liver diseases, including primary sclerosing cholangitis, Wilson’s disease, or cardiac cirrhosis.
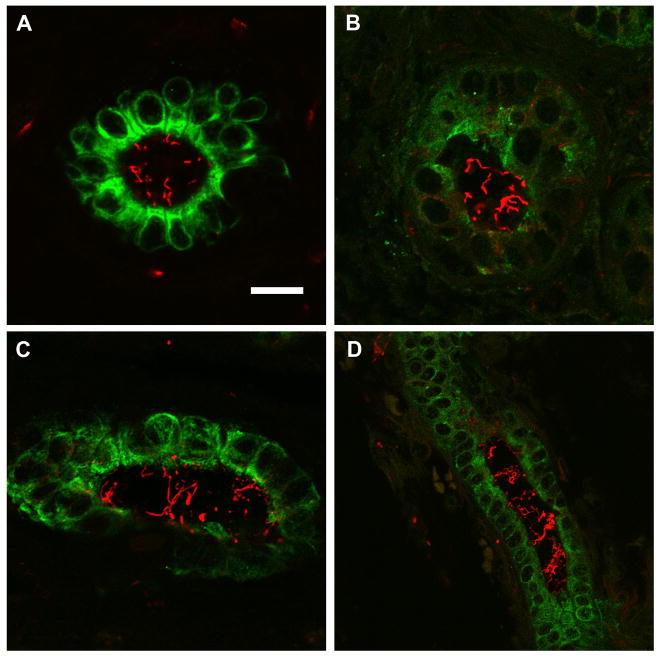
All livers were stained with antibodies against K19, to identify bile ducts, and against acetylated α-tubulin, to identify cilia. Histologically normal control livers demonstrated abundant intraluminal biliary cilia that projected into the lumen (Fig. 1a, Suppl. Fig. 1, Suppl. Movie 1). In the livers of the cholestatic disease controls (Figs. 1b-d, Suppl. Movies 2 and 3), cilia appeared to be relatively preserved when compared to normal tissues, although there was an increased degree of heterogeneity seen in these sections compared to the normal samples.
Figure 1.
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of control livers. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = acetylated α-tubulin (cilia). Note the quantity, length, and orientation of the intraluminal cilia. A) Specimen C1, normal liver adjacent to hepatoblastoma; B) specimen C4, primary sclerosing cholangitis; C) specimen C5, cardiac cirrhosis; D) specimen C6, Wilson’s disease. Scale bar = 20 μm in panels A-C, 10 μm in panel D.
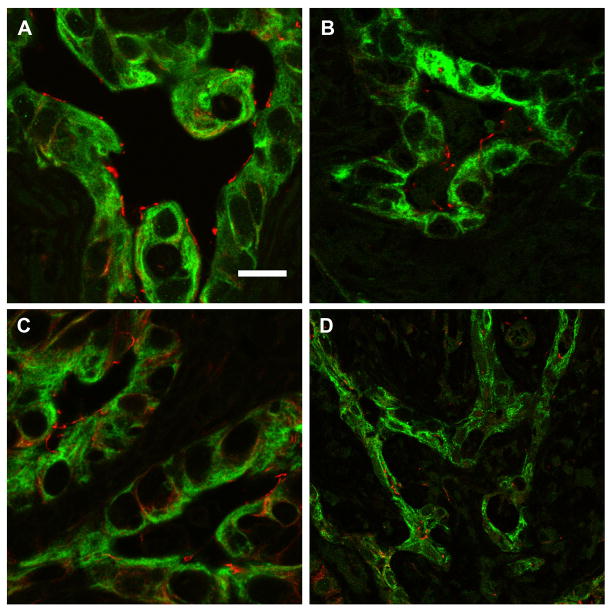
In contrast, the cilia in livers from patients with both the syndromic and non-syndromic forms of biliary atresia showed significant abnormalities when compared to normal and cholestatic disease controls. As demonstrated by single plane images and 3-D z-stack reconstructions (Fig. 2, Suppl. Figs. 2 and 3, Suppl. Movies 4 and 5), cilia in biliary atresia specimens were noticeably shorter, fewer in number, and abnormal in their angulation compared with normal liver and with the alternate disease controls. These differences were seen regardless of the source of the tissue (biopsy vs. explant) or presence of laterality defects. Computer-assisted relative quantification of these samples confirmed a statistically significant reduction in the ratio of cilia to cholangiocyte nuclei in all biliary atresia specimens compared with controls (Fig. 3). We did not detect a difference in this ratio between biliary atresia and syndromic biliary atresia specimens.
Figure 2.
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of biliary atresia livers. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = acetylated α-tubulin (cilia). Note the differences in quantity, length, and orientation of the intraluminal cilia compared to Figure 1. A) Specimen B5, diagnostic wedge biopsy from patient with syndromic biliary atresia; B) specimen B6, explant from patient with syndromic biliary atresia; C) specimen B1, wedge biopsy from patient with biliary atresia; D) specimen B2, diagnostic needle biopsy from patient with biliary atresia. Scale bar = 20 μm in panels A-C, 10 μm in panel D.
Figure 3.
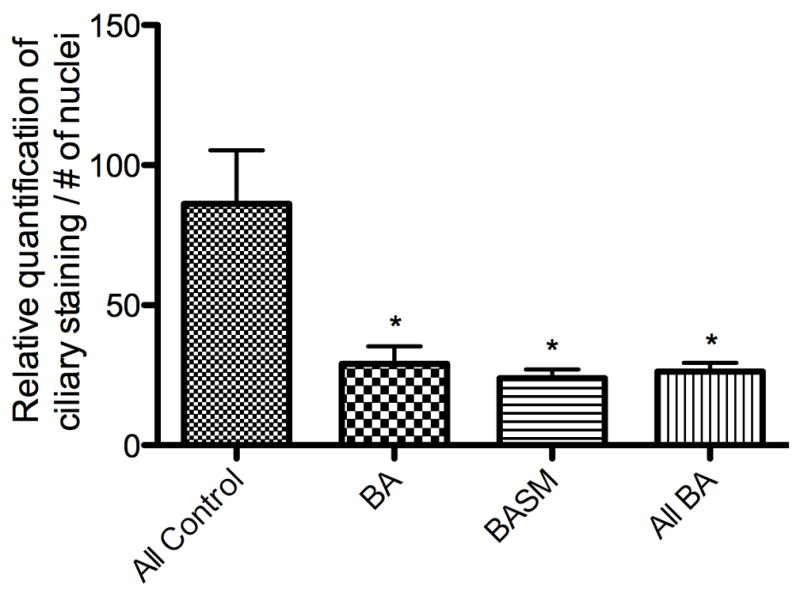
Relative quantification of intraductal cholangiocyte cilia staining. For each sample, intraductal anti-acetylated α-tubulin staining was quantified and divided by the number of associated cholangiocyte nuclei to generate a ratio for comparison among samples. Quantification was performed at two different levels within the Z-stack for each specimen. * = p < 0.05 compared to control.
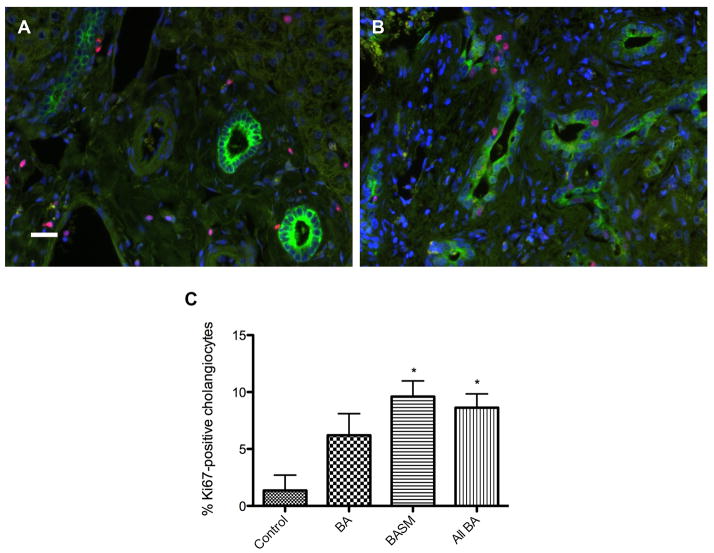
Since one possible explanation for the decreased cilia we observed is resorption in the context of mitosis, we estimated cholangiocyte proliferation using the proliferation marker Ki67 (Fig. 4). As expected, in control livers, biliary Ki67 labeling was low (average of 1.4% of all cholangiocytes; raw count = 3/157; n=2). There was a significant overall increase of biliary Ki67 labeling in biliary atresia (average of 6.2%, p = 0.17 compared with controls; raw count = 63/818; n=2) and BASM (average of 9.6%, p < 0.05 compared with controls; raw count = 71/844; n=5) specimens compared with normal controls.
Figure 4.
Cholangiocyte proliferation by Ki67 immunofluorescence microscopy. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = Ki67 (proliferation marker). A) Specimen C2 (normal); B) specimen B6 (biliary atresia); C) graph comparing average percentages of Ki67-positive cholangiocytes. * = p < 0.05 compared with control. Scale bar = 20 μm.
Discussion
Here we report histologic evidence of abnormalities in cholangiocyte cilia in BA livers compared to normal livers and livers affected by other cholestatic diseases. These changes included reduced numbers, shortened length, and abnormal orientation. Surprisingly, there were no detectable histologic differences in cilia from livers of patients with syndromic compared to non-syndromic BA.
Cilia fall into three broad categories. Motile cilia have a core formed from nine outer pairs of microtubule rods that encircle a single inner pair of microtubules (the “9+2” pattern). Dynein arms on the outer rods act as molecular motors that actively propel cilia in a whip-like manner.21 Case reports linking syndromic biliary atresia to abnormal cilia refer to motile cilia.18,19 Nodal cilia are located on cells of the embryonic node in vertebrates during development. They lack the two inner microtubule rods (“9+0” pattern) but possess rotational movement that is important in establishing morphogen gradients that determine left-right laterality.5 No link, however, between syndromic biliary atresia and defects in nodal cilia has ever been identified. Primary cilia, the cilia found on cholangiocytes, also follow a 9+0 pattern but are not motile. These cilia are abnormal in ciliopathies such as polycystic kidney disease and were found to be abnormal in biliary atresia livers in this study.
There are several potential causes of abnormal cilia in biliary atresia. Biliary atresia is characterized by aggressive portal inflammation, which could inflict ciliary injury. The severe chronic cholestasis seen in biliary atresia is associated with accumulation of cytotoxic hydrophobic bile acids, which damage mitochondria as well as cell membranes, potentially including ciliary membranes.22,23 In addition, the basal bodies that anchor cilia are recycled to form the centrosomes of the spindle apparatus when cells enter the cell cycle.24 Some of the decrease in intraluminal cilia we observed may reflect increased numbers of cholangiocytes undergoing mitosis in biliary atresia livers. Cholangiocyte proliferation is unlikely to fully explain the distortion in ciliary shape and angulation, however, and the relatively modest rise in Ki67 leaves open the possibility that other mechanisms are involved, such as structural damage during the course of inflammation or damage due to the as yet unknown primary insult.
Abnormal cilia may also be relevant to the pathophysiology of biliary atresia. Overgaard et al. showed that in vitro stress-induced deciliation of MDCK II cells causes tight junction remodeling and reduced cell polarity.25 Masyuk et al. demonstrated that chemical deciliation of cholangiocytes results in abnormal ciliary mechanotransduction, with resulting reductions in intracellular calcium, while Gradilone et al. demonstrated increased cholangiocyte proliferation.7,26 Deciliation blunts the chemosensory function of cilia, leading to abnormal interactions with extracellular ADP, increased intracellular cyclic AMP levels, and increased cholangiocyte proliferation.9,27 Normal cilia appear to be important for graded cellular responses to sonic Hedgehog, which cholangiocytes both secrete and respond to during injury and which is pro-fibrogenic.28,29
Our study is limited in that the samples we examined were all from advanced biliary atresia. Although logistically difficult, it would be interesting to examine early biliary atresia livers for similar abnormalities. Additionally, we relied on immunostaining of cilia, which does not detect ultrastructural defects; scanning and transmission electron microscopy of cilia in early biliary atresia samples might clarify the nature of the cilia abnormalities we observed.
This is the first report of pervasive structural abnormalities in cholangiocyte primary cilia in biliary atresia. The lack of distinction between syndromic and non-syndromic biliary atresia was particularly surprising and suggests that there may be common damage pathways in the two forms of the disease. Whether the morphologically abnormal cilia we observe are functionally relevant to the course of the disease has yet to be determined.
Supplementary Material
Supplemental Figure 1: Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of additional control livers. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = acetylated α-tubulin (cilia). A) Specimen C2, normal liver adjacent to hepatoblastoma; B) specimen C3, histologically normal liver from patient with citrullinemia. Scale bar = 10 μm in panel A, 20 μm in panel B.
Supplemental Figure 2: Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of additional BA livers. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = acetylated α-tubulin (cilia). A) Specimen B3; B) specimen B4. Scale bar = 20 μm.
Supplemental Figure 3: Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of additional syndromic biliary atresia livers. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = acetylated α-tubulin (cilia). A) Specimen B7; B) specimen B8a; C) specimen B8b. Scale bar = 20 μm.
Supplemental Movie 1: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of control specimen C1 (normal tissue adjacent to hepatoblastoma).
Supplemental Movie 2: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of cholestatic disease control specimen C4 (primary sclerosing cholangitis).
Supplemental Movie 3: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of cholestatic disease control specimen C6 (Wilson’s disease).
Supplemental Movie 4: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of biliary atresia liver specimen B1 (no laterality defects).
Supplemental Movie 5: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of syndromic biliary atresia liver specimen B5.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jia-Ji Hui, M.D. of the University of Pennsylvania for assistance with image acquisition; Joanne Taylor and the staff of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Histopathology facility for slide preparation; Gary Swain, Ph.D. and the Molecular Pathology and Imaging Core of the UPenn NIDDK Center for Molecular Studies in Digestive and Liver Diseases for assistance with immunofluorescence microscopy; and Xinyu (Jasmine) Zhao and the University of Pennsylvania Cell and Developmental Biology Microscopy Core for technical direction in confocal microscopy.
Footnotes
Supplementary information is available at Modern Pathology’s website.
Disclosure/Conflict of Interest
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health R01 grant DK-058123 (to R.G.W.) and by a grant from the Fred and Suzanne Biesecker Pediatric Liver Center (to R.G.W.). A.C. was supported by a Childhood Liver Disease Research and Education Network training grant and by the American Liver Foundation Alexander M. White, III Postdoctoral Research Fellowship Award.
References
- 1.Mack CL, Sokol RJ. Unraveling the pathogenesis and etiology of biliary atresia. Pediatr Res. 2005;57:87R–94R. doi: 10.1203/01.PDR.0000159569.57354.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schreiber RA, Kleinman RE. Biliary atresia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002;35 (Suppl 1):S11–16. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200207001-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shneider BL, Mazariegos GV. Biliary atresia: a transplant perspective. Liver Transpl. 2007;13:1482–1495. doi: 10.1002/lt.21303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.de Carvalho E, Ivantes CA, Bezerra JA. Extrahepatic biliary atresia: current concepts and future directions. J Pediatr (Rio J) 2007;83:105–120. doi: 10.2223/JPED.1608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fliegauf M, Benzing T, Omran H. When cilia go bad: cilia defects and ciliopathies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:880–893. doi: 10.1038/nrm2278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Michaud EJ, Yoder BK. The primary cilium in cell signaling and cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6463–6467. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Masyuk AI, Masyuk TV, Splinter PL, Huang BQ, Stroope AJ, LaRusso NF. Cholangiocyte cilia detect changes in luminal fluid flow and transmit them into intracellular Ca2+ and cAMP signaling. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:911–920. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gradilone SA, Masyuk AI, Splinter PL, et al. Cholangiocyte cilia express TRPV4 and detect changes in luminal tonicity inducing bicarbonate secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:19138–19143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705964104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Masyuk AI, Gradilone SA, Banales JM, et al. Cholangiocyte primary cilia are chemosensory organelles that detect biliary nucleotides via P2Y12 purinergic receptors. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;295:G725–734. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90265.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Keitel V, Ullmer C, Haussinger D. The membrane-bound bile acid receptor TGR5 (Gpbar-1) is localized in the primary cilium of cholangiocytes. Biol Chem. 2010;391:785–789. doi: 10.1515/BC.2010.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Masyuk AI, Huang BQ, Ward CJ, et al. Biliary exosomes influence cholangiocyte regulatory mechanisms and proliferation through interaction with primary cilia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;299:G990–999. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00093.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hopp K, Heyer CM, Hommerding CJ, et al. B9D1 is revealed as a novel Meckel syndrome (MKS) gene by targeted exon-enriched next-generation sequencing and deletion analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20:2524–2534. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Simms RJ, Hynes AM, Eley L, Sayer JA. Nephronophthisis: A Genetically Diverse Ciliopathy. Int J Nephrol. 2011;2011:527137. doi: 10.4061/2011/527137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Doherty D, Parisi MA, Finn LS, et al. Mutations in 3 genes (MKS3, CC2D2A and RPGRIP1L) cause COACH syndrome (Joubert syndrome with congenital hepatic fibrosis) J Med Genet. 2010;47:8–21. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2009.067249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shimadera S, Iwai N, Deguchi E, Kimura O, Fumino S, Yokoyama T. The inv mouse as an experimental model of biliary atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42:1555–1560. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Simons M, Gloy J, Ganner A, et al. Inversin, the gene product mutated in nephronophthisis type II, functions as a molecular switch between Wnt signaling pathways. Nat Genet. 2005;37:537–543. doi: 10.1038/ng1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mazziotti MV, Willis LK, Heukeroth RO, et al. Anomalous development of the hepatobiliary system in the Inv mouse. Hepatology. 1999;30:372–378. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gershoni-Baruch R, Gottfried E, Pery M, Sahin A, Etzioni A. Immotile cilia syndrome including polysplenia, situs inversus, and extrahepatic biliary atresia. Am J Med Genet. 1989;33:390–393. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Teichberg S, Markowitz J, Silverberg M, et al. Abnormal cilia in a child with the polysplenia syndrome and extrahepatic biliary atresia. J Pediatr. 1982;100:399–401. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hartley JL, O’Callaghan C, Rossetti S, et al. Investigation of primary cilia in the pathogenesis of biliary atresia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;52:485–488. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e318200eb6f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goodenough UW, Heuser JE. Substructure of inner dynein arms, radial spokes, and the central pair/projection complex of cilia and flagella. J Cell Biol. 1985;100:2008–2018. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xia X, Francis H, Glaser S, Alpini G, LeSage G. Bile acid interactions with cholangiocytes. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:3553–3563. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i22.3553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Paumgartner G, Beuers U. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic efficacy of ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8:67–81. vi. doi: 10.1016/S1089-3261(03)00135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Delaval B, Bright A, Lawson ND, Doxsey S. The cilia protein IFT88 is required for spindle orientation in mitosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:461–468. doi: 10.1038/ncb2202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Overgaard CE, Sanzone KM, Spiczka KS, Sheff DR, Sandra A, Yeaman C. Deciliation is associated with dramatic remodeling of epithelial cell junctions and surface domains. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20:102–113. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-07-0741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gradilone SA, Masyuk TV, Huang BQ, et al. Activation of Trpv4 reduces the hyperproliferative phenotype of cystic cholangiocytes from an animal model of ARPKD. Gastroenterology. 2010;39:304–314.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Banales JM, Masyuk TV, Gradilone SA, Masyuk AI, Medina JF, LaRusso NF. The cAMP effectors Epac and protein kinase a (PKA) are involved in the hepatic cystogenesis of an animal model of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) Hepatology. 2009;49:160–174. doi: 10.1002/hep.22636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Caspary T, Larkins CE, Anderson KV. The graded response to Sonic Hedgehog depends on cilia architecture. Dev Cell. 2007;12:767–778. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Omenetti A, Diehl AM. Hedgehog signaling in cholangiocytes. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2011;27:268–275. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e32834550b4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental Figure 1: Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of additional control livers. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = acetylated α-tubulin (cilia). A) Specimen C2, normal liver adjacent to hepatoblastoma; B) specimen C3, histologically normal liver from patient with citrullinemia. Scale bar = 10 μm in panel A, 20 μm in panel B.
Supplemental Figure 2: Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of additional BA livers. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = acetylated α-tubulin (cilia). A) Specimen B3; B) specimen B4. Scale bar = 20 μm.
Supplemental Figure 3: Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of additional syndromic biliary atresia livers. Green (Cy2) = K19 (bile ducts), red (Cy3) = acetylated α-tubulin (cilia). A) Specimen B7; B) specimen B8a; C) specimen B8b. Scale bar = 20 μm.
Supplemental Movie 1: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of control specimen C1 (normal tissue adjacent to hepatoblastoma).
Supplemental Movie 2: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of cholestatic disease control specimen C4 (primary sclerosing cholangitis).
Supplemental Movie 3: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of cholestatic disease control specimen C6 (Wilson’s disease).
Supplemental Movie 4: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of biliary atresia liver specimen B1 (no laterality defects).
Supplemental Movie 5: 3-D reconstruction of confocal images of syndromic biliary atresia liver specimen B5.