Abstract
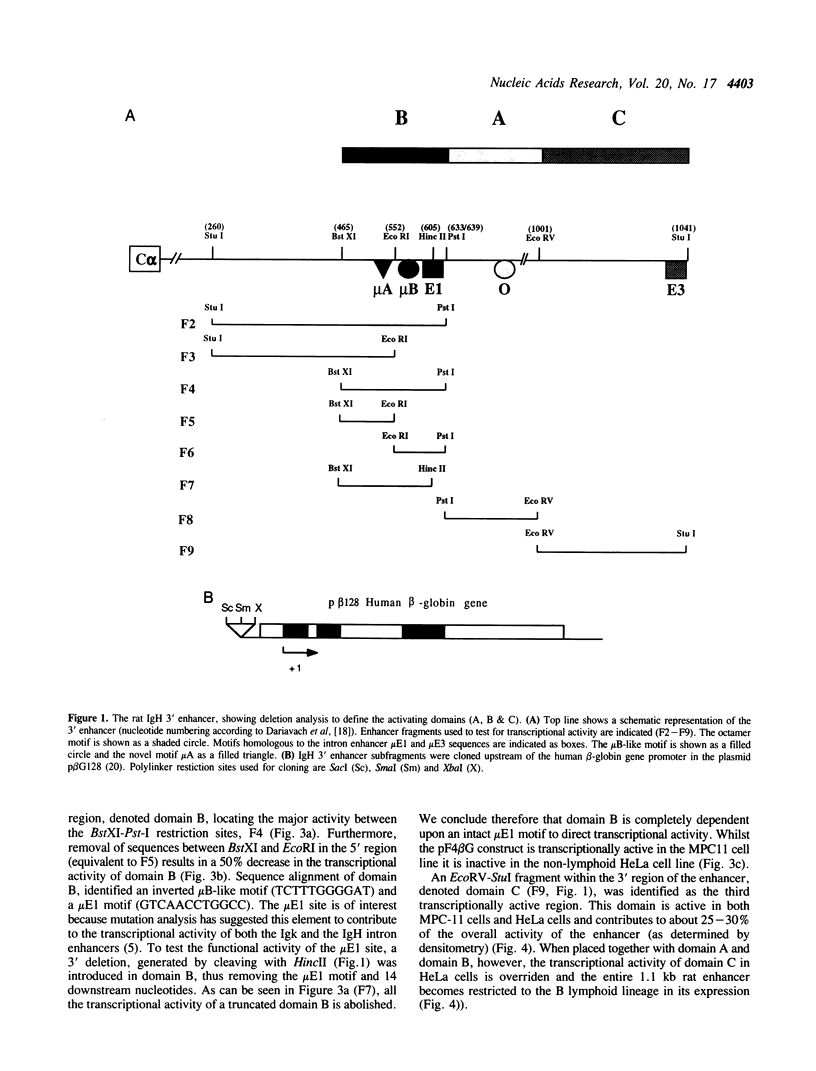
Recently we identified an additional enhancer in the 3' end of the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) locus. To identify individual regulatory elements within the rat IgH 3' enhancer, deletion analysis was performed. Transfection experiments using reporter constructs suggest that the enhancer contains three functionally distinct domains, two of which are lymphoid specific and one domain is active in both lymphoid and in nonlymphoid cells. The three domains together contribute to enhancer function and act synergistically. Further analyses suggest that a putative mu E1 site, octanucleotide motif, mu E3 site, and mu B/Ets-like motif are important for the overall transcriptional activity of the IgH 3' enhancer. Moreover, we provide evidence that an additional Ets-like element, micro A, is involved in the tissue specific regulation of enhancer activity and that binding of a protein to this element correlates with the transcriptional activity of one of the lymphoid restricted domains.
Full text
PDF




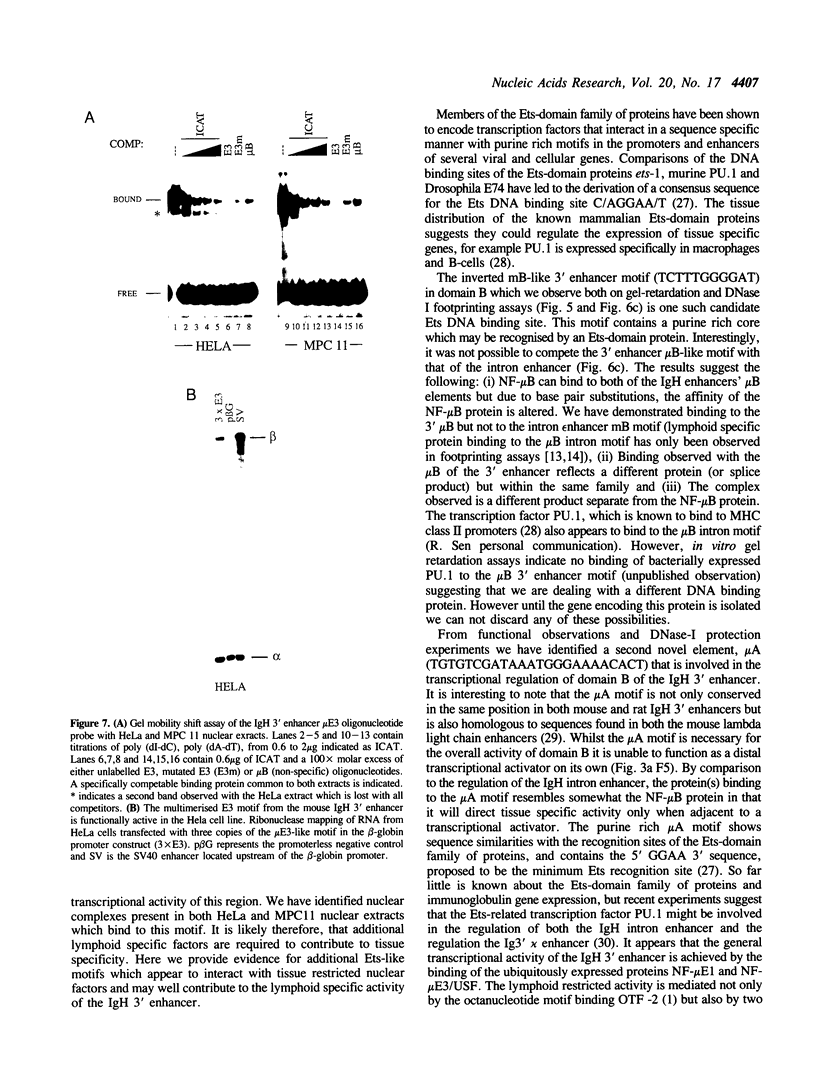

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Sharp P. A. A helix-loop-helix protein related to the immunoglobulin E box-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4384–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. A., Smith T., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G., Murialdo H. Identification of USF as the ubiquitous murine factor that binds to and stimulates transcription from the immunoglobulin lambda 2-chain promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):287–293. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S. Activation of cellular oncogenes in hemopoietic cells by chromosome translocation. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:189–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dariavach P., Williams G. T., Campbell K., Pettersson S., Neuberger M. S. The mouse IgH 3'-enhancer. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1499–1504. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmaleh N., Matthias P., Schaffner W. A factor known to bind to endogenous Ig heavy chain enhancer only in lymphocytes is a ubiquitously active transcription factor. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Feb 14;187(3):507–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagman J., Rudin C. M., Haasch D., Chaplin D., Storb U. A novel enhancer in the immunoglobulin lambda locus is duplicated and functionally independent of NF kappa B. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):978–992. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenuwein T., Grosschedl R. Complex pattern of immunoglobulin mu gene expression in normal and transgenic mice: nonoverlapping regulatory sequences govern distinct tissue specificities. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):932–943. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Su L. K., Kadesch T. Identification and characterization of two functional domains within the murine heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Involvement of a second lymphoid-specific enhancer element in the regulation of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3155–3162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberson R., Giannini S. L., Birshtein B. K., Eckhardt L. A. An enhancer at the 3' end of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):933–937. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen B., Kadesch T., Sen R. Complex regulation of the immunoglobulin mu heavy-chain gene enhancer: microB, a new determinant of enhancer function. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3145–3154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Caskey H. M., Pettersson S., Williams G. T., Surani M. A. Isotype exclusion and transgene down-regulation in immunoglobulin-lambda transgenic mice. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):350–352. doi: 10.1038/338350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Karlsson O., Edlund T. A beta-cell-specific protein binds to the two major regulatory sequences of the insulin gene enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4228–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Mutul J., Macchi M., Wasylyk B. Mutational analysis of the contribution of sequence motifs within the IgH enhancer to tissue specific transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6085–6096. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson S., Cook G. P., Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. A second B cell-specific enhancer 3' of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):165–168. doi: 10.1038/344165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson S., Sharpe M. J., Gilmore D. R., Surani M. A., Neuberger M. S. Cellular selection leads to age-dependent and reversible down-regulation of transgenic immunoglobulin light chain genes. Int Immunol. 1989;1(5):509–516. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Nagulapalli S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Maki R. A., Atchison M. L. PU.1 recruits a second nuclear factor to a site important for immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):368–378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Matera A. G., Cooper C., Artandi S., Blain S., Ward D. C., Calame K. mTFE3, an X-linked transcriptional activator containing basic helix-loop-helix and zipper domains, utilizes the zipper to stabilize both DNA binding and multimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):817–827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Lenardo M. J. Immunoglobulin gene transcription. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:373–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Wang X. F., Peterson C. L., Calame K. In vivo functional analysis of in vitro protein binding sites in the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3239–3253. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K. An enhancer element in the short unique region of human cytomegalovirus regulates the production of a group of abundant immediate early transcripts. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):406–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]