Abstract
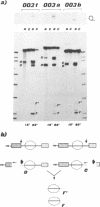
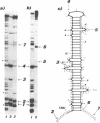
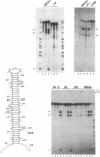
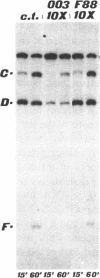
Sequences corresponding to the third intron of the X.laevis L1 ribosomal protein gene were isolated from the second copy of the X.laevis gene and from the single copy of X.tropicalis. Sequence comparison revealed that the three introns share an unusual sequence conservation which spans a region of 110 nucleotides. In addition, they have the same suboptimal 5' splice sites. The three introns show similar features upon oocyte microinjection: they have very low splicing efficiency and undergo the same site specific cleavages which lead to the accumulation of truncated molecules. Computer analysis and RNAse digestions have allowed to assign to the conserved region a specific secondary structure. Mutational analysis has shown that this structure is important for conferring the cleavage phenotype to these three introns. Competition experiments show that the cleavage phenotype can be prevented by coinjection of excess amounts of homologous sequences.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Luo Z. X., Amaldi F. Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes: isolation of recombinant cDNA clones and study of the genomic organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1069–1086. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Fragapane P., Annesi F., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F., Beccari E. Expression of two Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes in injected frog oocytes. A specific splicing block interferes with the L1 RNA maturation. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):987–1005. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffarelli E., Fragapane P., Bozzoni I. Inefficient in vitro splicing of the regulatory intron of the L1 ribosomal protein gene of X.laevis depends on suboptimal splice site sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):680–687. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90536-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffarelli E., Fragapane P., Gehring C., Bozzoni I. The accumulation of mature RNA for the Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein L1 is controlled at the level of splicing and turnover of the precursor RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3493–3498. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Post-Beittenmiller M. A., Warner J. R. Autogenous regulation of splicing of the transcript of a yeast ribosomal protein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5854–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fragapane P., Caffarelli E., Lener M., Prislei S., Santoro B., Bozzoni I. Identification of the sequences responsible for the splicing phenotype of the regulatory intron of the L1 ribosomal protein gene of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1117–1125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B. Ras C-terminal processing enzymes--new drug targets? Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90352-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M., LeGrange J., Austin B. Dependence of DNA helix flexibility on base composition. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):752–754. doi: 10.1038/304752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. Control of retroviral RNA splicing through maintenance of suboptimal processing signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):696–704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreni F., Ruberti I., Bozzoni I., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F. Nucleotide sequence of the L1 ribosomal protein gene of Xenopus laevis: remarkable sequence homology among introns. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3483–3488. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagoshi R. N., Baker B. S. Regulation of sex-specific RNA splicing at the Drosophila doublesex gene: cis-acting mutations in exon sequences alter sex-specific RNA splicing patterns. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):89–97. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. The regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA is dependent on the relative efficiencies of mu s poly(A) site usage and the c mu 4-to-M1 splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):726–738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Bozzoni I., Cardinali B. Expression of the gene for ribosomal protein L1 in Xenopus embryos: alteration of gene dosage by microinjection. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):23–31. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti I., Fragapane P., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E., Amaldi F., Bozzoni I. Characterization of histone genes isolated from Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis genomic libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7543–7559. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlrab F., McLean M. J., Wells R. D. The segment inversion site of herpes simplex virus type 1 adopts a novel DNA structure. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6407–6416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]