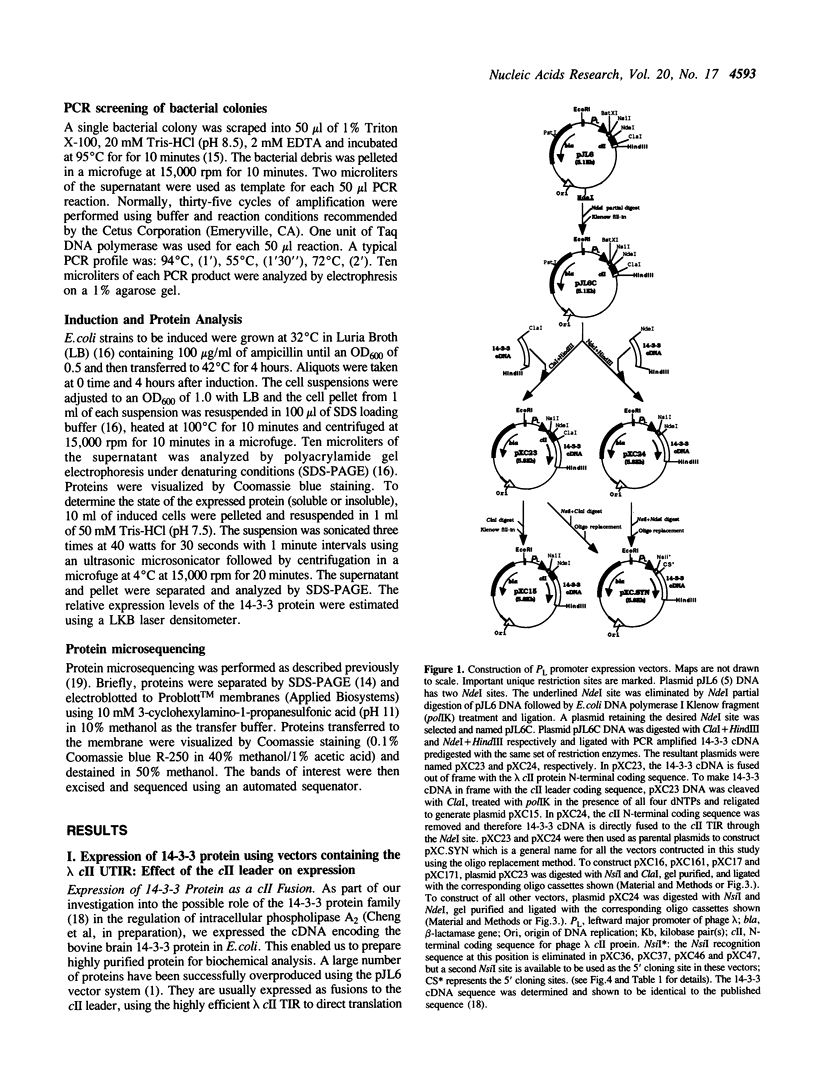
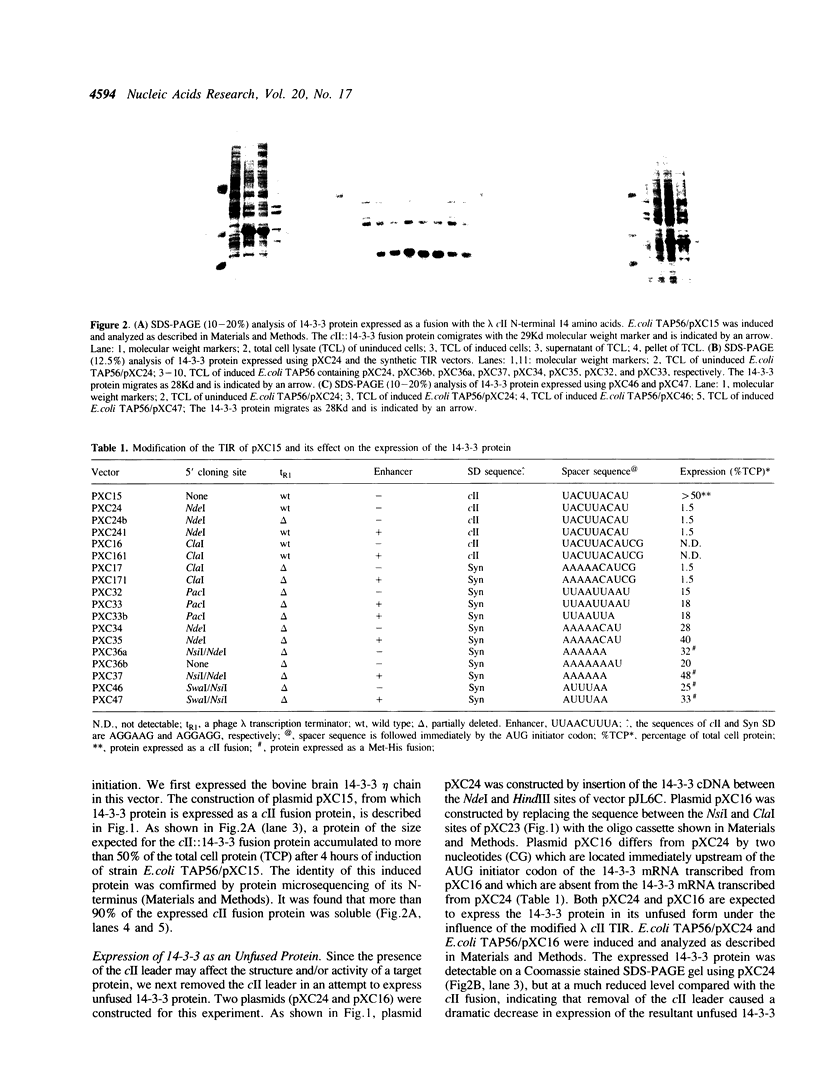
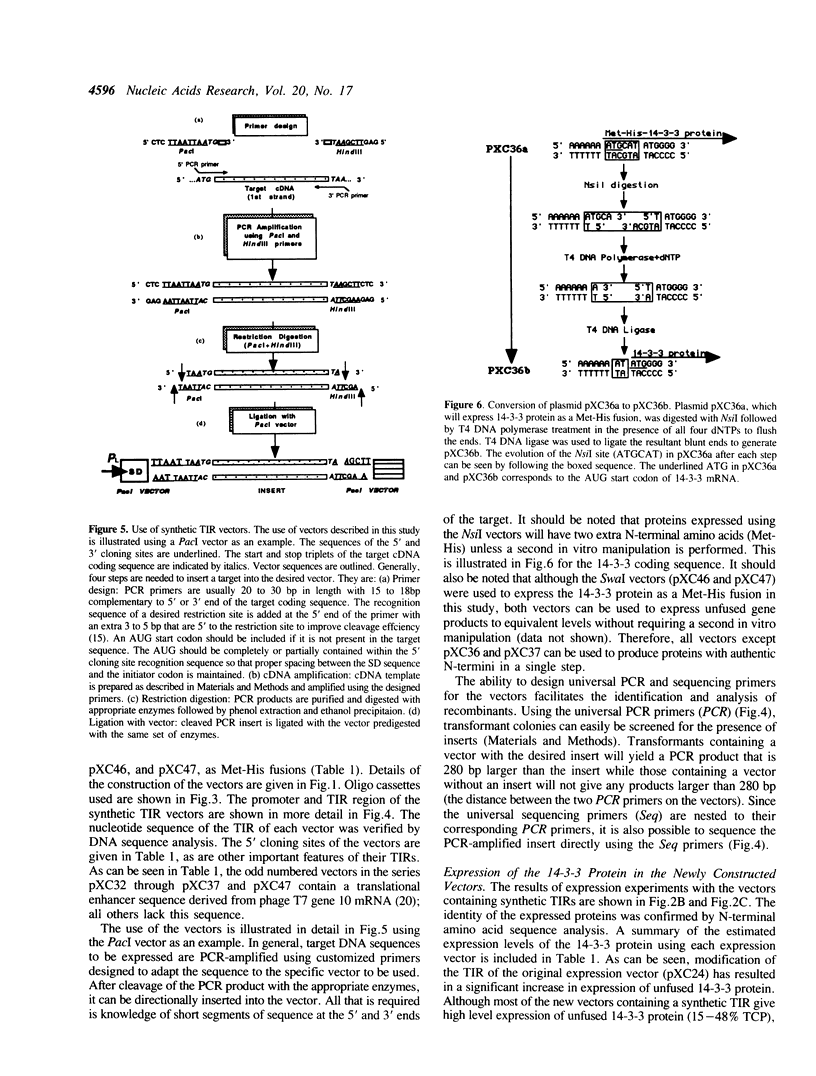
Abstract
A set of plasmid vectors which allow single-step cloning and expression of PCR-amplified DNA coding sequences has been constructed. The vectors contain the phage lambda PL promoter, a synthetic translation initiation region (TIR), and convenient cloning sites. The cloning sites provide all or part of an AUG translation initiation codon and facilitate the precise fusion of target DNA sequences to vector transcriptional and translational signals. The vectors were constructed with synthetic TIRs because there is evidence which suggests that the efficiency of the phage lambda cII gene TIR present in the parental vector depends strongly on information contained within the cII N-terminal coding sequence. Bovine brain 14-3-3 eta chain cDNA was PCR-amplified and used to demonstrate the expression capacity of the newly constructed vectors. A significant increase in expression of 14-3-3 protein was observed when synthetic TIRs were used in the place of the cII TIR. Expression levels vary from 15% to 48% of total cell protein. The effects of a reported translational enhancer from phage T7 on expression of the 14-3-3 protein are also discussed. The vectors should be generally useful for high level heterologous protein expression in Escherichia coli.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bücheler U. S., Werner D., Schirmer R. H. Random silent mutagenesis in the initial triplets of the coding region: a technique for adapting human glutathione reductase-encoding cDNA to expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1990 Dec 15;96(2):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90263-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. M., Takiff H. E., Barber A. M., Dubois G. C., Bardwell J. C., Court D. L. Expression and characterization of RNase III and Era proteins. Products of the rnc operon of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2888–2895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng X. B., Bunville J., Patterson T. A. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for an apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):370–370. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Brady C., Rosenberg M., Wulff D. L., Behr M., Mahoney M., Izumi S. U. Control of transcription termination: a rho-dependent termination site in bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):231–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M. What constitutes the signal for the initiation of protein synthesis on Escherichia coli mRNAs? J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):79–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emory S. A., Belasco J. G. The ompA 5' untranslated RNA segment functions in Escherichia coli as a growth-rate-regulated mRNA stabilizer whose activity is unrelated to translational efficiency. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4472–4481. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4472-4481.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Mielke C., Hollatz I., Blöcker H., Frank R. RNA primary sequence or secondary structure in the translational initiation region controls expression of two variant interferon-beta genes in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17627–17636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillerez J., Gazeau M., Dreyfus M. In the Escherichia coli lacZ gene the spacing between the translating ribosomes is insensitive to the efficiency of translation initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6743–6750. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Gold L. Influence of mRNA determinants on translation initiation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):83–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90875-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichimura T., Isobe T., Okuyama T., Takahashi N., Araki K., Kuwano R., Takahashi Y. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for brain-specific 14-3-3 protein, a protein kinase-dependent activator of tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7084–7088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautenberger J. A., Court D., Papas T. S. High-level expression in Escherichia coli of the carboxy-terminal sequences of the avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29) v-myc protein. Gene. 1983 Jul;23(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. E., Gualerzi C. Translational control of prokaryotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90098-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins P. O., Rangwala S. H. A novel sequence element derived from bacteriophage T7 mRNA acts as an enhancer of translation of the lacZ gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):16973–16976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. The functional stability of the lacZ transcript is sensitive towards sequence alterations immediately downstream of the ribosome binding site. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):179–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00329856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G. B., Stockwell P. A., Hill D. F. Messenger RNA recognition in Escherichia coli: a possible second site of interaction with 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3957–3962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff S. C., Spira A. I., Johnson A. W., Demple B. Yeast structural gene (APN1) for the major apurinic endonuclease: homology to Escherichia coli endonuclease IV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4193–4197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel K. P., Ascione R., Kottaridis S. D., Seth A. K., Lautenberger J. A., Zuber M., Strouboulis J., Papas T. S. Expression of animal and human retroviral gene products in Escherichia coli with the lambda PL promoter pJL6 vector system. Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1990 Nov;7(7):178–208. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(90)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Kumar P., Cobianchi F., Skowronski J., Wilson S. H. Sequence of human DNA polymerase beta mRNA obtained through cDNA cloning. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90916-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatake H., Rosenberg M. Purified lambda regulatory protein cII positively activates promoters for lysogenic development. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):128–132. doi: 10.1038/292128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengart M. L., Fatscher H. P., Fuchs E. The initiation of translation in E. coli: apparent base pairing between the 16srRNA and downstream sequences of the mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1719–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier L. H., Jallat S., Sauvageot M., Crystal R. G., Courtney M. RNA structural elements for expression in Escherichia coli. Alpha 1-antitrypsin synthesis using translation control elements based on the cII ribosome-binding site of phage lambda. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomich C. S., Olson E. R., Olsen M. K., Kaytes P. S., Rockenbach S. K., Hatzenbuhler N. T. Effect of nucleotide sequences directly downstream from the AUG on the expression of bovine somatotropin in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3179–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. Y., McConnell D. J., O'Mahony D. J. An efficient temperature-inducible vector incorporating the T7 gene 10 translation initiation leader region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1070–1070. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smit M. H., van Duin J. Control of prokaryotic translational initiation by mRNA secondary structure. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;38:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60707-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]