Abstract
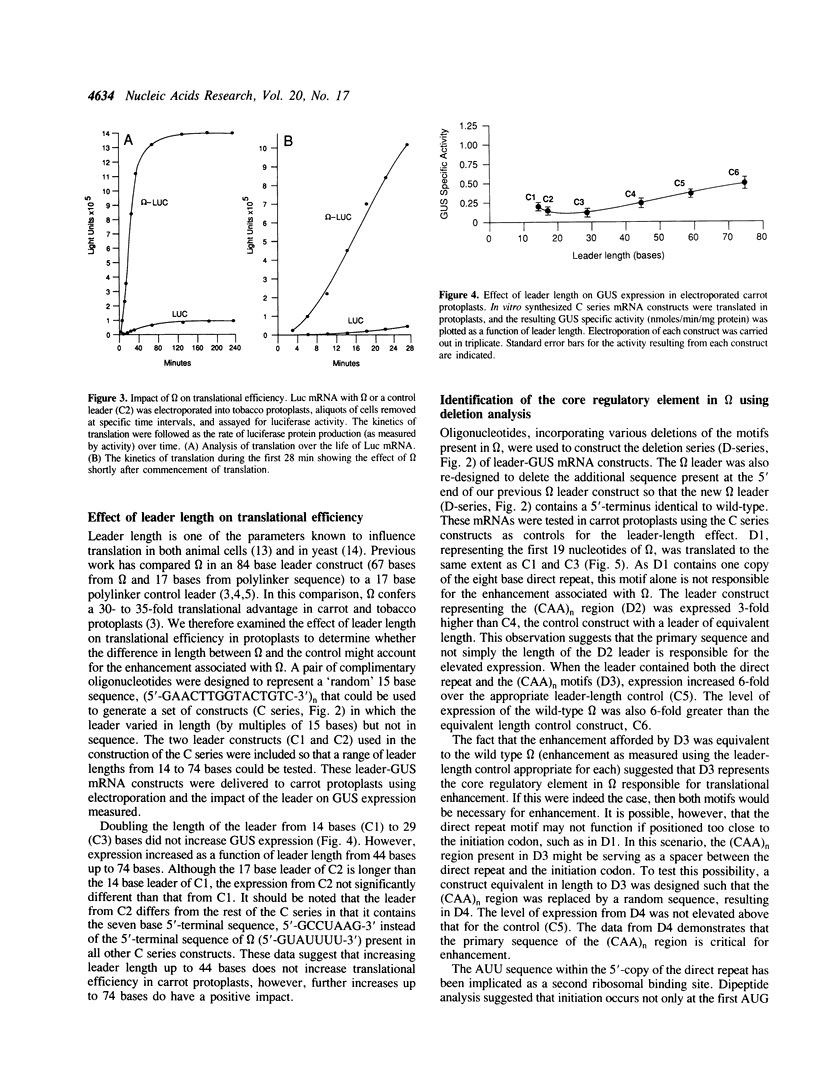
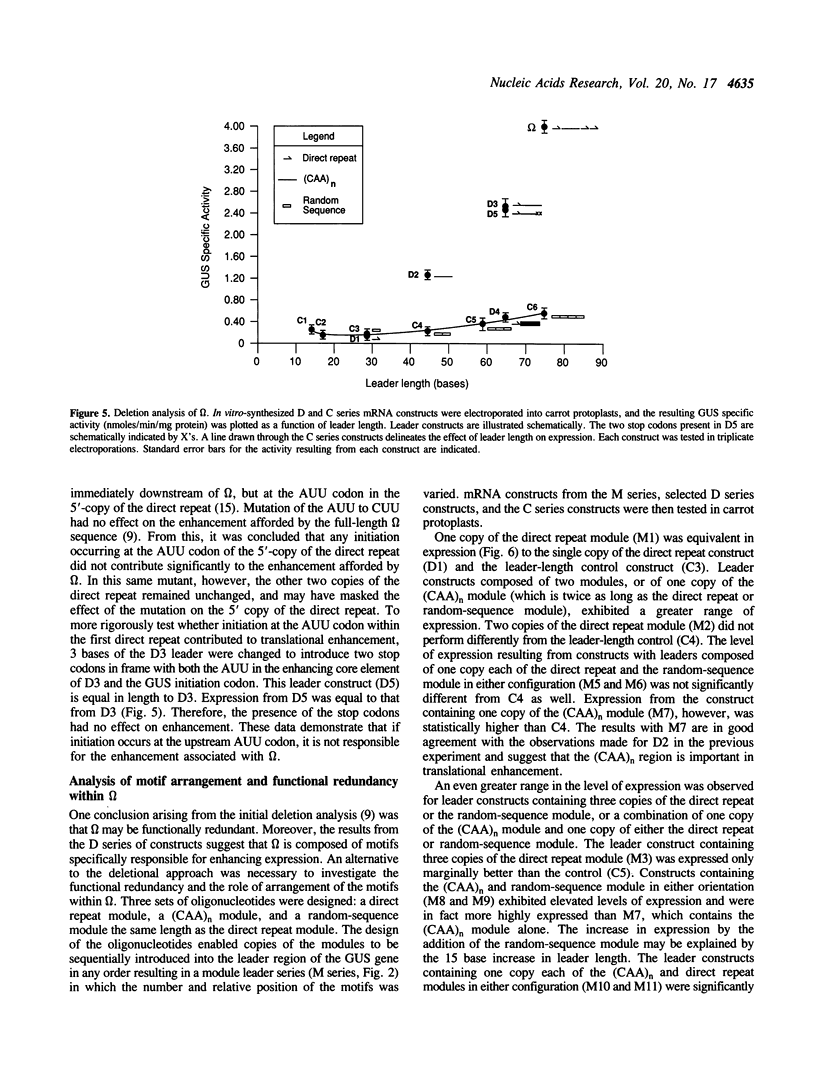
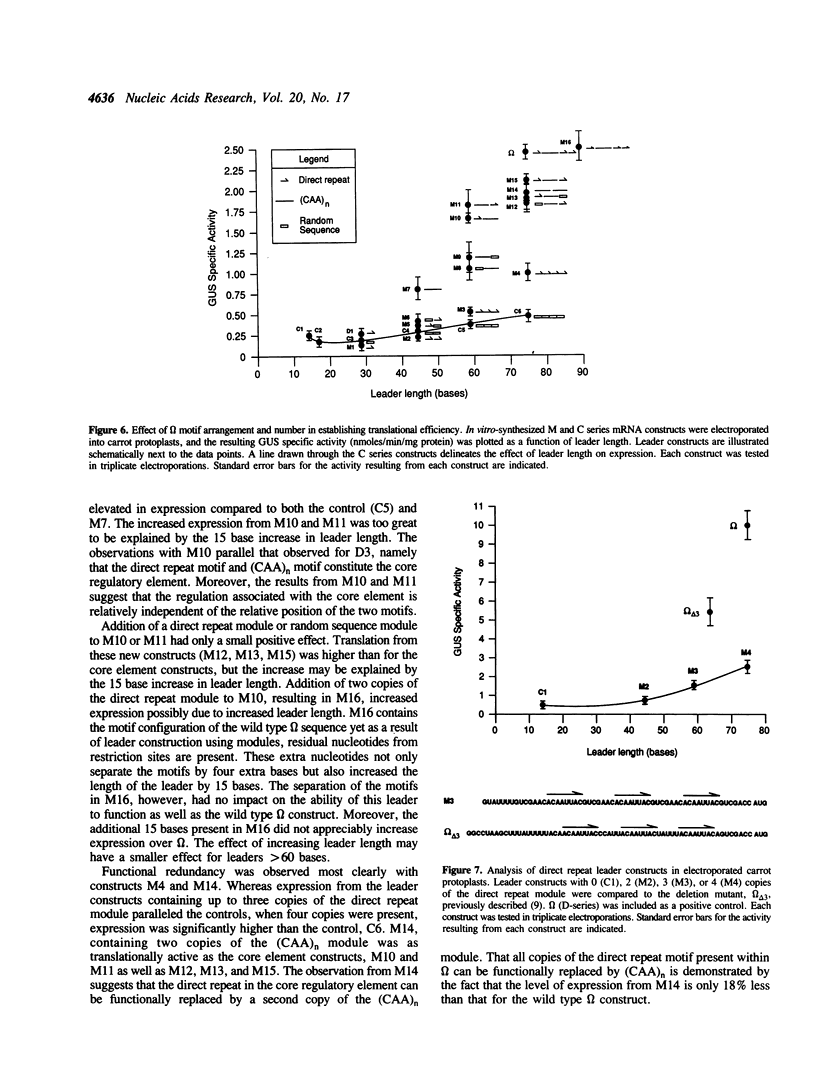
The leader (called omega) of tobacco mosaic virus RNA enhances translation in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Although little secondary structure is predicted to exist within omega, the primary sequence of the 68 base leader is highly organized. Three copies of an eight base direct repeat and a (CAA)n region represent the two motifs found in the leaders of many TMV strains, and together these comprise 72% of omega. In previous deletion studies, no mutants exhibited loss-of-function, suggesting that functional redundancy exists within omega. We report here that a more comprehensive deletion analysis identified the motifs involved in translational enhancement. In a separate approach, oligonucleotides containing the sequence of each motif were used to construct leaders that varied in the number and configuration of the motifs. beta-Glucuronidase mRNA constructs containing these mutant leaders were synthesized in vitro and their translational efficiency measured in vivo following mRNA delivery to carrot protoplasts via electroporation. A combination of one copy of the 8 base direct repeat and a 25 base (CAA)n region was identified as the core regulatory element, although the (CAA)n motif is more critical. Two copies of the (CAA)n region are sufficient to confer a high level of enhancement and a leader composed of multiple copies of the direct repeat is moderately enhancing. Thus, these two motifs are functionally redundant.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila-Rincon M. J., Ferrero M. L., Alonso E., García-Luque I., Díaz-Ruíz J. R. Nucleotide sequences of 5' and 3' non-coding regions of pepper mild mottle virus strain S RNA. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):3025–3031. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-3025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Feder J. N., Schimke R. T., Walbot V. Post-transcriptional regulation in higher eukaryotes: the role of the reporter gene in controlling expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):258–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00282474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Lucas W. J., Walbot V. Visualizing mRNA expression in plant protoplasts: factors influencing efficient mRNA uptake and translation. Plant Cell. 1989 Mar;1(3):301–311. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.3.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Sleat D. E., Watts J. W., Turner P. C., Wilson T. M. A comparison of eukaryotic viral 5'-leader sequences as enhancers of mRNA expression in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8693–8711. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Sleat D. E., Watts J. W., Turner P. C., Wilson T. M. Mutational analysis of the tobacco mosaic virus 5'-leader for altered ability to enhance translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):883–893. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Sleat D. E., Watts J. W., Turner P. C., Wilson T. M. The 5'-leader sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA enhances the expression of foreign gene transcripts in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3257–3273. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Walbot V., Hershey J. W. The ribosomal fraction mediates the translational enhancement associated with the 5'-leader of tobacco mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8675–8694. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Walbot V. RNA pseudoknot domain of tobacco mosaic virus can functionally substitute for a poly(A) tail in plant and animal cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1149–1157. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Akam M. E., Gait M. J., Karn J. Nucleotide sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5818–5822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerineau F., Lucy A., Mullineaux P. Effect of two consensus sequences preceding the translation initiator codon on gene expression in plant protoplasts. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Feb;18(4):815–818. doi: 10.1007/BF00020027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. R., Hunt T., Knowland J., Zimmern D. Messenger RNA for the coat protein of tobacco mosaic virus. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):759–764. doi: 10.1038/260759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R., Anderson W. F., Safer B. The regulation of initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:127–185. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Circumstances and mechanisms of inhibition of translation by secondary structure in eucaryotic mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5134–5142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Leader length and secondary structure modulate mRNA function under conditions of stress. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2737–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukla B. A., Guilley H. A., Jonard G. X., Richards K. E., Mundry K. W. Characterization of long guanosine-free RNA sequences from the Dahlemense and U2 strains of tobacco mosaic virus. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):61–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H. A., Chow K. C., Mickel F. S., Moss K. A., Kern H. F., Scheele G. A. Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandeles S. Location of unique sequences in tobacco mosaic virus ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3671–3674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno T., Aoyagi M., Yamanashi Y., Saito H., Ikawa S., Meshi T., Okada Y. Nucleotide sequence of the tobacco mosaic virus (tomato strain) genome and comparison with the common strain genome. J Biochem. 1984 Dec;96(6):1915–1923. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleat D. E., Gallie D. R., Jefferson R. A., Bevan M. W., Turner P. C., Wilson T. M. Characterisation of the 5'-leader sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA as a general enhancer of translation in vitro. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solis I., Garcia-Arenal F. The complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of the tobamovirus tobacco mild green mosaic virus. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):553–558. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90520-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugaki M., Tomiyama M., Kakutani T., Hidaka S., Kiguchi T., Nagata R., Sato T., Motoyoshi F., Nishiguchi M. The complete nucleotide sequence of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (SH strain) genomic RNA. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1487–1495. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J. K., Melton D. A. Synthesis of long, capped transcripts in vitro by SP6 and T7 RNA polymerases. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:42–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel J. J., Bergkamp R. J., Planta R. J., Raué H. A. Effect of deletions in the 5'-noncoding region on the translational efficiency of phosphoglycerate kinase mRNA in yeast. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



