Abstract
Despite the impressive progress over the past decade, in the field of tumor immunology, such as the identification of tumor antigens and antigenic peptides, there are still many obstacles in eliciting an effective immune response to eradicate cancer. It has become increasingly clear that tumor microenvironment plays a crucial role in the control of immune protection. Tumors have evolved to utilize hypoxic stress to their own advantage by activating key biochemical and cellular pathways that are important in progression, survival, and metastasis. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) play a determinant role in promoting tumor cell growth and survival. Hypoxia contributes to immune suppression by activating HIF-1 and VEGF pathways. Accumulating evidence suggests a link between hypoxia and tumor tolerance to immune surveillance through the recruitment of regulatory cells (regulatory T cells and myeloid derived suppressor cells). In this regard, hypoxia (HIF-1α and VEGF) is emerging as an attractive target for cancer therapy. How the microenvironmental hypoxia poses both obstacles and opportunities for new therapeutic immune interventions will be discussed.
Keywords: hypoxia, HIFα, angiogenesis, immune tolerance, tumor progression
Introduction
Cancer vaccines are expected to augment already established anti-tumor immune responses and to induce de novo immunity or reverse tolerance. Major advances have led to several immunization strategies to boost immune responses against some tumor-associated antigens. In this regard, strategies involving various forms of peptides either alone or in combination with different cytokines, adjuvant, or dendritic cells have been used to enhance specific immune responses. Despite the enthusiasm for current vaccination approaches, it should be noted that tumor rejection in patients does not always follow successful induction of tumor-specific immune responses by cancer vaccines. Even, if a strong and sustained cytotoxic response is induced, complex issues remain such as tumor evasion, tolerance and selection of tumor resistant variants (Rosenberg et al., 1998, 2004; Hamai et al., 2010). Nevertheless, systemic administration of monoclonal antibodies targeting immune modulatory receptors: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4; Eggermont et al., 2010) and Programmed Death 1 (PD1) on T reg and effector cells have been recently reported to increase anti-tumor immunity both experimentally and clinically (Alexandrescu et al., 2010; Callahan et al., 2010; Eggermont and Robert, 2011; Mansh, 2011; Mellman et al., 2011; Pandolfi et al., 2011). In early phase I trials, PD1 have shown good activity in a variety of cancer types and have a toxicity profile that seems safer than ipilimumab (Brahmer et al., 2010). A recent clinical trial with the longest follow-up of melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab has shown that ipilimumab can induce durable, potentially curative tumor regression in a small percentage of patients with metastatic melanoma (Prieto et al., 2012).
It has become increasingly clear that tumor microenvironment plays a crucial role in the control of immune protection and contains many overlapping mechanisms to evade antigenic specific immunotherapy (Zou, 2005; Nagaraj and Gabrilovich, 2007; Marigo et al., 2008). Several reports underscore the contribution of the microenvironment to tumor development and it is well admitted that tumors are not merely masses of neoplastic cells, but instead, are complex tissues composed of both non-cellular (matrix proteins) and cellular components, in addition to the ever-evolving neoplastic cells. Tumor microenvironment is a complex and highly dynamic environment, providing very important clues to tumor development and progression (Petrulio et al., 2006). In the context of microenvironment complexity and plasticity, tumor cells orchestrate the modification of the microenvironment by attracting or activating many non-tumoral cells, including fibroblasts, blood and lymphatic endothelial cells, bone marrow-derived cells, immune and inflammatory cells. Moreover, it is now acknowledged that tumor cells and their stroma co-evolve during tumorigenesis and tumor progression (Hiscox et al., 2011). Therefore, tumor growth and spread depend as much on the host response as on the biologic characteristics of the tumor itself and on the influence of the tumor microenvironment (Petrulio et al., 2006).
The hypoxia’s critical role in radio-resistance, chemoresistance, tumor stemness, and its significance as an adverse prognosis factor have been well established and at present hypoxia-induced angiogenesis has become an attractive target for cancer therapy (Semenza, 2010). Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) overexpression and its association with poor treatment response and outcome has been demonstrated in an extensive range of human tumors (Semenza, 2010; Wilson and Hay, 2011). In addition, a direct link between tumor hypoxia and tolerance through the recruitment of regulatory cells has been established (Facciabene et al., 2011). Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) produced by most tumors plays an important role in tumor angiogenesis (Takenaga, 2011). It also plays a key role in immune escape by licensing invasion, metastasis, impacting therapeutic response and favoring immune escape mechanisms.
Hypoxia is therefore attracting a particular attention in the field of tumor immune biology since hypoxic stress impact angiogenesis, tumor progression and immune tolerance. Modulating the stromal hypoxia may constitute in fact a very potent strategy for targeted therapeutic approaches. How peripheral immune tolerance and angiogenesis programs are closely connected and cooperate under hypoxic conditions to sustain tumor growth will be discussed in this article.
Hypoxia-Induced Angiogenesis and Resistance to Cytotoxic Treatments
Hypoxia-inducible factors: determinant factors in tumor cell adaptation to hypoxic stress
Tumor cells adapt to hypoxic microenvironment by the regulation of HIFs family of transcription factors. This family is composed of three members namely HIF-1, HIF-2, and HIF-3. HIFs are a heterodimeric proteins composed of a constitutively expressed HIF-β subunit and an O2-regulated HIF-α subunit (Wang et al., 1995). Both HIF-1α and HIF-2α have common target genes as well as their respective target genes (Lau et al., 2007). The genes induced by hypoxia-dependent HIF-1α and HIF-2α play important roles in regulating different aspects of tumor biology especially angiogenesis, cell survival, chemo- and radio-resistance, proliferation, invasion and metastasis, pH regulation and metabolism, resistance to immune system, and maintenance of cancer stem cells (Keith and Simon, 2007; Lukashev et al., 2007; Keith et al., 2011).
In the presence of O2, HIF-1α is hydroxylated on proline residue 402 and/or 564 by prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 (PHD2), resulting in its interaction with the von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) protein, which recruits an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that eventually catalyzes polyubiquitination of HIF-1α thereby targeting it for proteasomal degradation (Salceda and Caro, 1997). Under hypoxic conditions, hydroxylation is inhibited and HIF-1α rapidly accumulates, translocates to the nucleus, dimerizes with HIF-1β and activates transcription. Similar to HIF-1α, HIF-2α is also regulated by oxygen-dependent hydroxylation (Patel and Simon, 2008). HIF-1α and HIF-2α differ in their transactivation domains but are structurally similar in DNA binding and dimerization domains. HIF-3α lacks the transactivation domain and may function as an inhibitor of HIF-1α and HIF-2α and its expression is transcriptionally regulated by HIF-1 (Makino et al., 2007). HIF-1α and HIF-2α are also regulated by several oxygen-independent mechanisms involving mutation of VHL, PTEN, BRAF, SDH, FH, and MITF (Semenza, 2010; Noman et al., 2011c).
Hypoxia-induced VEGF as a key event in promoting angiogenesis
Growing tumor mass requires neo-vascularization to provide rapidly proliferating tumor cells with an adequate supply of oxygen and metabolites. Diffusion distances from the existing vasculature increases as tumor expands resulting in local hypoxia (Harris, 2002; Brahimi-Horn et al., 2007; Dewhirst et al., 2008). Increasing evidence shows that the hypoxic stress plays a key role in the regulation of angiogenesis that is required for invasive tumor growth and metastasis (Semenza, 2010). HIF-1α stabilization and nuclear accumulation results in the subsequent activation of a wide range of target genes belonging to angiogenesis and promoting endothelial cell proliferation, migration, permeability, and survival (Wang et al., 1995). HIF-2 is also able to promote tumor angiogenesis through mobilization of circulating progenitor endothelial cells (Kim et al., 2009) and through VEGF induction (Raval et al., 2005; Li et al., 2009). HIF-1α and HIF-2α can also be regulated by oxygen-independent mechanisms leading to increased HIF transcriptional program under normal level of O2 and promoting tumor growth and angiogenesis (Semenza, 2010). In this regard, the double allele loss of function (deletion, mutation, CpG island hypermethylation) VHL−/− gives rise to increased constitutive level of HIF-1α and/or HIF-2α (Baldewijns et al., 2010). VHL can also directly regulate the stability of certain mRNAs such as that of VEGF (Datta et al., 2005) and mRNAs related to growth factor signaling, suggesting that mRNA changes observed after VHL loss are not solely due to the subsequent HIF accumulation (Kaelin, 2008).
Although vessel growth and maturation are complex and highly coordinated processes requiring the sequential activation of a multitude of factors, there is a consensus that VEGF signaling represents a crucial step in tumor angiogenesis (Liao and Johnson, 2007). It should also be noted that antiangiogenic drugs and vascular destructive agents may in turn promote tumor cell invasion and metastasis in association with drug-induced tumor hypoxia.
Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis leads to increased resistance to cytotoxic treatments
Tumor hypoxia-induced abnormal neo-angiogenesis leads to increased resistance to cytotoxic treatments. Indeed, tumor vessels are labyrinthine and branched in an irregular and chaotic manner with uneven diameters due to the compression of their walls by tumor or stromal cells (Jain, 1988, 2005; Nagy et al., 2010). These abnormalities in hypoxia-induced tumor vessels have been found in a wide range of tumor types, in mice both in transplantable tumors and in spontaneous tumors arising from exposure to carcinogens or expression of oncogenes (Baluk et al., 2005; Hamzah et al., 2008; Van de Veire et al., 2010) and in tumors from patients (Willett et al., 2004; Batchelor et al., 2007). Tumor vessel blood flow is compromised and stagnant due to increased vascular resistance and improper vasoregulation (Jain, 2005; Fukumura et al., 2010). Similarly hypoxia-induced tumor endothelial cells are abnormal. Normal vessels are lined with a monolayer of interconnected endothelial cells, whereas tumor endothelial cells are often leaky, with wide open junctions and many fenestrations resulting in limited tissue perfusion (Jain, 1988). These abnormal neo-vessels with leaky walls facilitate the escape of tumor cells (Jain, 2005). All these abnormalities lead to a decrease in uniform and efficient delivery of nutrients and drugs (Jain, 2005; Jain and Stylianopoulos, 2010) as well as influx of immune cells (Hamzah et al., 2008). As irradiation and certain chemotherapeutics rely on the formation of reactive oxidative species to kill cancer cells, tumor hypoxia also reduces the efficacy of conventional anticancer treatments (Moeller et al., 2007). Thus, it is clear that hypoxia-induced angiogenesis is responsible for an abnormal tumor vasculature (Carmeliet and Jain, 2011), which can influence tumor response to anticancer treatments as well as tumor infiltration by immunocompetent cells.
Role of hypoxia-induced VEGF in modulating tumor response to cytotoxic T-lymphocytes
We have shown that hypoxic exposure of tumor cells inhibits autologous cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL)-mediated lysis (Noman et al., 2009, 2011b). We provided evidence indicating that HIF-1α induction and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) activation are associated with hypoxia-induced lysis inhibition. This suggests a new role for hypoxia-dependent induction of HIF-1α and activation of STAT3 in tumor resistance to the immune system.
Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 activation within tumor microenvironment is known to be associated with cytokine-induced proliferation, anti-apoptosis, and transformation. Moreover, STAT3 modulates the cross-talk between tumor and immune cells (Wang et al., 2004; Yu et al., 2007). More interestingly, we have shown that VEGF neutralization resulted in the attenuation of hypoxic tumor target resistance to CTL-mediated killing (Noman et al., 2009). We have also demonstrated that STAT3 phosphorylation can be stimulated by autocrine signaling through VEGF, suggesting that tumor microenvironment through hypoxia-induced VEGF may play a key role in the induction of active form of STAT3. In this regard, it is very likely that STAT3 activation is associated with the regulation of gene expression potentially involved in the alteration of hypoxic tumor target-specific killing. Therefore, understanding how VEGF and other soluble factors lead to STAT3 activation via the tumor microenvironment may provide a more effective cancer treatment strategy for hypoxic tumors with elevated P-STAT3 levels. This also suggests that reduction of VEGF release in tumor microenvironment may favor induction of a stronger anti-tumor CTL response against tumors expressing VEGF receptor (VEGFR). In this regard, inhibition of VEGF may be a valuable adjuvant in the immunotherapy of cancer (Gabrilovich et al., 1996) pointing to the existence of a synergy between tumor immunotherapy and antiangiogenic therapy (Nair et al., 2003).
Hypoxia induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a complex molecular process during which epithelial cells lose their apico-basal polarity and acquire a mesenchymal and motile phenotype. The hallmarks of EMT are the down regulation of epithelial markers (E-cadherin) and the up regulation of mesenchymal markers (Vimentin, Fibronectin, the transcriptional factors Snail, Slug, Twist, and Zeb1/2) leading to an organized disassembly of epithelial cell-to-cell contacts enabling motility and invasiveness (Thiery, 2002). EMT has therefore become a prominent program involved in carcinogenesis, metastasis, tumor recurrence and resistance to apoptosis and to chemotherapy (Barrallo-Gimeno and Nieto, 2005, p. 172; Thiery and Sleeman, 2006, p. 173). The activation of EMT in tumor cells has been reported to be associated with interactions of tumor cells with tumor-associated stromal cells, implicating neoplastic microenvironmental stimuli in EMT induction. In this regard, tumor hypoxia through HIF-1α has recently been proposed to be an important trigger and modulator of EMT (Lundgren et al., 2009; Sleeman and Thiery, 2011).
During hypoxic stress, different signaling pathways seem to be involved in triggering EMT (Jiang et al., 2011). In this regard, the existence of cooperation between hypoxia and TGFβ signaling resulting in EMT activation has been reported (Schaffer et al., 2003; Nishi et al., 2004). Recent findings also demonstrate that, in breast cancer cells, the Notch pathway plays a role in hypoxia-activated EMT since its inhibition abrogates hypoxia-mediated increase in Slug and Snail expression, and decreases cell migration and invasion (Chen et al., 2010). Lysyl oxidase (LOX) and the related LOX-like 2 (LOXL2) have recently been reported to be direct transcriptional targets of HIF-1α that are sufficient to repress E-cadherin and induce EMT under hypoxia (Schietke et al., 2010). Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), another direct transcriptional target of HIF-1α (Buchler et al., 2009), is described to be involved in E-cadherin repression and EMT activation during hypoxic stress in medulloblastoma cells (Gupta et al., 2011). Interestingly, Luo et al. (2011) have recently identified a hypoxia-response element in close proximity with the minimal promoter of human and mouse Snail, which binds both HIF-1 and HIF-2 proteins and which activates snail transcription. This provides new evidence of the direct involvement of HIFs in Snail activation and EMT-regulation.
It should be noted that EMT contributes to malignancy not only by enhancing motility, invasiveness, resistance to apoptosis and drugs, but also by inducing immune escape. In fact, Kudo-Saito et al. report that Snail expression in melanoma cells resulted in the impairment of dendritic cell maturation, expansion of T regulatory cells, and resistance to CTL-mediated lysis. Moreover, intratumoral targeting of Snail in melanoma significantly inhibited tumor growth and metastasis in correlation with an increase of tumor-specific tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and of systemic immune responses (Kudo-Saito et al., 2009). It seems that EMT program in tumors is able to redirect the immune system toward immune tolerance. Since hypoxia has been also reported to mediate immune tolerance, the role of EMT factors in this process remains to be investigated.
Tumor Hypoxia Promotes Angiogenesis and Immune Tolerance
It is well known that immune system can effectively inhibit tumor growth (Zhang et al., 2003; Koebel et al., 2007; Fridman et al., 2011). However, tumors are known to establish diverse potent mechanisms, which help them to escape the immune system (Zou, 2005; Nagaraj and Gabrilovich, 2007; Marigo et al., 2008; Hamai et al., 2010). Emerging evidence indicates a link between hypoxia-induced angiogenesis and tolerance to immune system (Manning et al., 2007; Buckanovich et al., 2008; Tartour et al., 2011). Tumor hypoxia drives angiogenesis by inducing synthesis of VEGF and other pro-angiogenic factors in tumor cells via HIFs and promotes immunosuppression (Noman et al., 2009, 2011a). The association between angiogenesis and immunosuppression comes from the immunosuppressive activities of angiogenic factors such as VEGF, a cytokine secreted by most tumors (Toi et al., 1996a,b), making it a critical actor in tumor angiogenesis and immune tolerance (Motz and Coukos, 2011). Hypoxic zones in tumors attract a variety of immune cells in which HIF stabilization is associated with the acquisition of both pro-angiogenic and immunosuppressive phenotype (Noman et al., 2011c).
Myeloid cells
Myeloid cells are perhaps the best-studied cell types in terms of their ability to promote immunosuppression and angiogenesis in tumors (Gabrilovich and Nagaraj, 2009; Motz and Coukos, 2011).
Tumor-associated macrophages
Macrophages constitute a major component of the immune infiltrate seen in tumors (Bingle et al., 2002). In the tumor microenvironment, they differentiate into tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) with expression of TAM markers such as CD206 (Mantovani et al., 2002). High TAM numbers in tumors in majority of cases are correlated with reduced survival (Bingle et al., 2002). Exposure of TAM to tumor-derived cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-10 is able to convert them into polarized type II or M2 macrophages with immune-suppressive activities and pro-angiogenic effects, resulting in tumor progression (Mantovani et al., 2002). TAM are found to be preferentially located in tumor hypoxic areas, where they accumulate HIF-1 and HIF-2 and up regulate VEGF and other pro-angiogenic factors (Lewis et al., 2000). The relative contribution of HIF-1 and HIF-2 in the regulation of gene expression in TAM is not yet completely elucidated. In human macrophages, HIF-2 has been reported to be a crucial inducer of pro-angiogenic molecules (White et al., 2004). In another study, Werno et al. (2010) proposes that HIF-1 is indispensable for angiogenic-promoting properties of TAM, at least in murine macrophages. Besides this angiogenesis promoting activity, HIF-1α was also reported to be crucial for macrophage-mediated inhibition of T cells in hypoxic conditions (Doedens et al., 2010). In hypoxic areas of tumors, TAM also up-regulate the expression of MMP-7 protein in hypoxic areas of tumors (Burke et al., 2003). MMP-7 is known to cleave the Fas ligand from neighboring cells, making tumor cells less responsive to lysis by NK and T cells (Fingleton et al., 2001). MMP-7 is also known to stimulate endothelial cell proliferation and migration, which can support tumor angiogenesis (Nishizuka et al., 2001).
Myeloid derived suppressor cells
Myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) have also been demonstrated to directly promote angiogenesis (Yang et al., 2004) and immune tolerance (Gabrilovich and Nagaraj, 2009). In tumor bearing hosts, tumor-derived factors such as VEGF, GM-CSF, prostaglandins also restrain DC maturation and promote the accumulation of MDSCs in tumoral tissues and secondary lymphoid organs (Gabrilovich, 2004). In these sites, MDSCs induce T cell anergy, restrain the effector phase of the CD8+ T cell, and can promote antigen-specific T reg proliferation (Gabrilovich, 2004; Serafini et al., 2008). Moreover, HIF-1α has been directly shown to regulate the function and differentiation of MDSC within the hypoxic tumor microenvironment (Corzo et al., 2010). A cross-talk between MDSC and macrophages has been reported, proposing that MDSC down-regulate IL-12 production by macrophages and increase their own production of IL-10 in response to signals from macrophages. This interaction between MDSC and macrophages polarizes classically activated (M1) macrophages toward a type 2 and immunosuppressive phenotype and accentuates the M2 phenotype of M2 macrophages, which is likely to establish an environment that skew CD4+ and CD8+ T cell immunity toward a tumor-promoting type 2 response (Trinchieri, 2003). As a result, MDSC directly and through their cross-talk with macrophages, suppress both adaptive and innate anti-tumor immunity, which facilitate tumor growth. MDSC also have pro-angiogenic activities that can mediate tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment (Shojaei et al., 2007).
Dendritic cells
The dendritic cell subset is also diverted by VEGF from its highly specialized antigen-presenting and T cell activating functions. Indeed, production of VEGF by human tumors inhibits the functional maturation of dendritic cells and thereby promotes immune escape of tumor cells (Gabrilovich et al., 1996). Recombinant VEGF administered to tumor-free mice resulted in repressed dendritic cell development associated with accumulation of Gr-1+ immature myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) that inhibit T cell functions (Gabrilovich et al., 1998), illustrating the proper immune-suppressive functions of VEGF. Tumor-associated myeloid dendritic cells, in response to tumor-derived VEGF, increase the expression of PDL-1 which is a negative regulator of T cell function (Curiel et al., 2003). Moreover, anti-VEGF therapy was associated with a decrease in immature myeloid and dendritic cells in patients (Osada et al., 2008).
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes play a crucial role in immunosuppression and tolerance (Fridman et al., 2011). In an ovarian cancer model, very recently, it has been shown that hypoxia promotes the recruitment of the immunosuppressive CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ T regulatory cells (T reg) through the induction of CCL28 expression by hypoxic tumor cells. T reg in turn secrete VEGF, contributing to the VEGF pool in the tumor microenvironment and to immune tolerance (Facciabene et al., 2011). Moreover, CD4-deficient mice have an impaired angiogenesis response to hypoxia during ischemia (Stabile et al., 2003). Moreover VEGF targeting reduces intratumoral T regulatory cells and increases the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy in B16 melanoma and the CT26 colon carcinoma models (Li et al., 2006). In addition, an inverse correlation between angiogenesis and tumor-infiltrating T cells has already been reported (Zhang et al., 2003; Buckanovich et al., 2007, 2008; Kandalaft et al., 2009). Other lymphocyte cells (including regulatory B cells, NK cells, and NKT cells) with immunosuppressive functions have been reported to produce VEGFA (Motz and Coukos, 2011). However, the precise role of these cells in tumor angiogenesis remains largely unknown. Therefore, the exact contribution of these lymphocytes in mediating VEGF-induced immune suppression requires further investigation.
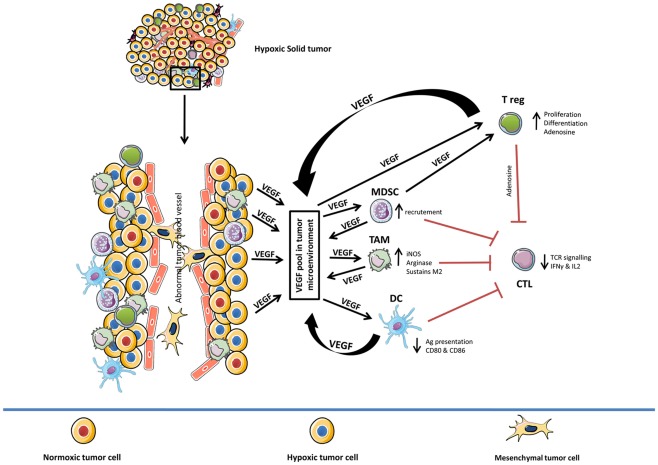
Different facets of VEGF-induced immunosuppression in diverse cell types in hypoxic tumor microenvironment is summarized in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Role of hypoxia-induced VEGF in mediating immune tolerance. Diverse effects of hypoxia-induced VEGF on different components of the immune system (TAM, MDSC, DC, CTL, and T reg). In general, hypoxia-induced VEGF pool in tumor microenvironment (VEGF secreted by hypoxic tumor cells, TAM, MDSC, DC, and T reg) amplifies the activity of TAM, MDSC, and T reg while suppressing the function of CTL and delaying the maturation of DC cells. TAM, tumor-associated macrophages; MDSC, myeloid derived suppressor cells; DC, dendritic cells; CTL, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte; T reg, T regulatory cells.
Hypoxia, pro-inflammatory mediators, and immune suppression
Hypoxia induces both angiogenesis and immunosuppression also by upregulating COX-2 in tumor cells (Greenhough et al., 2009). COX-2 is an inflammatory enzyme converting arachidonic acid into prostaglandin PGE2 which has angiogenic properties by promoting VEGF expression (Jain et al., 2008) and immunosuppressive functions by causing, in cooperation with hypoxia-induced increased extra-cellular adenosine, cAMP accumulation in effector T cells resulting in the suppression of their anti-tumor functions (Whiteside et al., 2011). PGE2 can also inhibit tumor immunity by inhibiting dendritic cell maturation, their expression of co-stimulatory molecules, and their production of IL-12. In addition, PGE2 enhances the suppressive activity of T reg and is involved in the conversion of CD4+ CD25− into T reg. Finally, PGE2 can stimulate the immunosuppressive functions of MDSC by binding the EP-4 receptor (Rodriguez et al., 2005; Sinha et al., 2007; Serafini, 2010).
Thus hypoxia connects peripheral immune tolerance and angiogenic programs to sustain tumor growth. The counter-activation of tolerance mechanisms at the site of tumor hypoxia is therefore a crucial condition for maintaining the immunological escape of tumors.
Therapeutic Interventions Targeting Angiogenesis
Hypoxia-induced VEGF produced by most tumors plays an important role in tumor angiogenesis (Takenaga, 2011). Recognition of the VEGF pathway as a key regulator of angiogenesis has led to the development of several VEGF-targeted molecules (Porta et al., 2011). These molecules include neutralizing antibodies to VEGF (Escudier et al., 2008) or VEGFRs, mTOR kinase inhibitors (Azim et al., 2010), and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs; Porta et al., 2011) with selectivity for VEGFRs. The pioneers in the field of angiogenesis inhibitors are bevacizumab (an anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to the VEGF ligand and neutralizes its activity; Ferrara et al., 2004) and two multi-targeted kinase inhibitors (sorafenib and sunitinib; non-specific small molecules that inhibit multiple kinase receptors; Zhong and Bowen, 2011). Indirectly, the macrocyclic lactones temsirolimus and everolimus, inhibit also VEGF (Azim et al., 2010). These molecules inhibit the mTOR complex formation targeting mTORC1 that inhibits HIF-1α expression and consequently inhibits HIF-1α dependent VEGF transcription decreasing angiogenesis (Azim et al., 2010). These angiogenesis inhibitors have proven their therapeutic efficacy in several mouse models of cancer and in a large number of human cancers (Porta et al., 2011). However, clinical benefits are often followed by a restoration of tumor growth and progression (Burger et al., 2011; Perren et al., 2011). The Bevacizumab-chemotherapy combination seems to be successful in second-line settings in the treatment of patients with advanced colorectal cancer, compared to the disappointing efficacy of combining bevacizumab with chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of the patients (Jenab-Wolcott and Giantonio, 2010). Several intrinsic and adaptive mechanisms were shown to be involved in resistance to angiogenic therapy (Bergers and Hanahan, 2008).
Antiangiogenic therapy can lead to hypoxia as a compensatory mechanism (Casanovas et al., 2005; Bergers and Hanahan, 2008). It is now clear that hypoxia-induced by angiogenesis inhibitors might further elevate VEGF and other pro-angiogenic factors expression in tumors (Shaked et al., 2005; Mancuso et al., 2006). Sathornsumetee et al. (2008) have shown that hypoxic profiles can predict survival in malignant astrocytoma patients treated with bevacizumab. Another mechanism underlying resistance to anti-VEGF therapy involves infiltration of various pro-angiogenic bone marrow-derived cells, in part through increases in HIF-1α and its downstream effectors such as VEGF (Ceradini et al., 2004; Shaked et al., 2006). In a metastatic colorectal cancer model, bevacizumab therapy improved the impairment of lymphocyte subsets, especially for T cells. These effects correlated with more favorable clinical outcome (Manzoni et al., 2011). Interestingly, anti-VEGF agents can have contradictory effects on immune system (Seliger et al., 2010). Sorafenib appears to impair, while sunitinib stimulates terminal DC maturation (Hipp et al., 2008). Sunitinib induces Th-1 immune response (IFN-γ expression) while reducing T reg in renal cell carcinoma patients (Finke et al., 2008). Sunitinib, but not Sorafenib has been shown to inhibit MDSC immune-suppressive activity and reduces MDSC and T reg circulating numbers (Ko et al., 2009). Another study has shown that sunitinib administration in mouse renal cell carcinoma tumor bearing mice led to the inhibition of Stat3 in tumor-associated myeloid cells, including dendritic cells and MDSCs, which was accompanied by a reduction of tumor T reg (Xin et al., 2009). Du et al. (2008) have shown that impairment of VEGF signaling leads to an adaptive pro-invasive tumor phenotype.
A better understanding of the complex interaction between cancer cells, immune system and anti-VEGF agents is therefore needed for improving and sustaining the benefits of antiangiogenic therapy.
Conclusion
Advances in immunology and molecular biology have shown that cancers are potentially immunogenic and that host immune responses influence survival (Galon et al., 2006). However, immune surveillance and activation is frequently ineffective in preventing and/or controlling tumor growth. In fact, an active and bi-directional molecular cross-talk between tumor microenvironment and host cells has profound implications for immunological recognition and progression of tumor cells (Petrulio et al., 2006; Lorusso and Ruegg, 2008). The cross-talk between tumor cells and stromal cells within the tumor microenvironment mediates tumor initiation, progression, and response to anticancer therapy. In this regard, microenvironmental components including hypoxia appear to regulate gene expression in tumor cells thereby directing the tumor toward aggressiveness, angiogenesis, and metastasis. It is well documented that inflammation is an important part of hypoxic tumor microenvironment (Eltzschig and Carmeliet, 2011). Increasing evidence suggest the existence of a link between hypoxic stress and several inflammatory molecules (PEG2, COX-2, chemokines, and cytokines) responsible for tumor initiation and progression. These pro-inflammatory mediators not only support tumor survival and expansion but also the function of several immune cells notably dendritic and effector cells (Chow et al., 2011). Therefore, a well-integrated understanding of this intricate microenvironment may offer new opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Recent insights into cellular and molecular cross-talk suggest a model in which hypoxia, HIF, VEGF, and several other HIF target genes participate in the coordinated collaboration between tumor, endothelial, inflammatory/hematopoietic, and circulating endothelial precursor cells to enhance and promote tumor vascularization. Given its central role in tumor progression and resistance to therapy, tumor hypoxia might well be considered as one potential target that has yet to be exploited in oncology. Its targeting may be therefore an innovative approach to design new approaches in cancer therapy. Recently, a growing number of drugs that inhibit HIF-1 have been identified and validated as anticancer agents (Semenza, 2010; Wilson and Hay, 2011). It is also becoming evident that characterizing the tumor microenvironment can provide important prognostic and predictive information about tumors, independently of the tumor cell phenotype. Whether the inhibition of hypoxic signaling pathways in different compartments of the solid tumor microenvironment will open new therapeutic opportunities in cancer immunotherapy has to be established.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
A part of the work reviewed in this article was supported by the ARC/INCA, Ligue de Recherche contre le Cancer, ARC, ANR, and Cancéropôle Ile-de-France.
References
- Alexandrescu D. T., Ichim T. E., Riordan N. H., Marincola F. M., Di Nardo A., Kabigting F. D., Dasanu C. A. (2010). Immunotherapy for melanoma: current status and perspectives. J. Immunother. 33, 570–590 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181e032e8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azim H., Azim H. A., Jr., Escudier B. (2010). Targeting mTOR in cancer: renal cell is just a beginning. Target. Oncol. 5, 269–280 10.1007/s11523-010-0141-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldewijns M. M., Van Vlodrop I. J., Vermeulen P. B., Soetekouw P. M., Van Engeland M., De Bruine A. P. (2010). VHL and HIF signalling in renal cell carcinogenesis. J. Pathol. 221, 125–138 10.1002/path.2689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baluk P., Hashizume H., Mcdonald D. M. (2005). Cellular abnormalities of blood vessels as targets in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 15, 102–111 10.1016/j.gde.2004.12.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrallo-Gimeno A., Nieto M. A. (2005). The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in development and cancer. Development 132, 3151–3161 10.1242/dev.01907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor T. T., Sorensen A. G., Di Tomaso E., Zhang W. T., Duda D. G., Cohen K. S., Kozak K. R., Cahill D. P., Chen P. J., Zhu M., Ancukiewicz M., Mrugala M. M., Plotkin S., Drappatz J., Louis D. N., Ivy P., Scadden D. T., Benner T., Loeffler J. S., Wen P. Y., Jain R. K. (2007). AZD2171, a pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, normalizes tumor vasculature and alleviates edema in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Cell 11, 83–95 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.11.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergers G., Hanahan D. (2008). Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 592–603 10.1038/nrc2442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingle L., Brown N. J., Lewis C. E. (2002). The role of tumour-associated macrophages in tumour progression: implications for new anticancer therapies. J. Pathol. 196, 254–265 10.1002/path.1027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahimi-Horn M. C., Chiche J., Pouyssegur J. (2007). Hypoxia and cancer. J. Mol. Med. 85, 1301–1307 10.1007/s00109-007-0281-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahmer J. R., Drake C. G., Wollner I., Powderly J. D., Picus J., Sharfman W. H., Stankevich E., Pons A., Salay T. M., Mcmiller T. L., Gilson M. M., Wang C., Selby M., Taube J. M., Anders R., Chen L., Korman A. J., Pardoll D. M., Lowy I., Topalian S. L. (2010). Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J. Clin. Oncol. 28, 3167–3175 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.7609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchler P., Reber H. A., Tomlinson J. S., Hankinson O., Kallifatidis G., Friess H., Herr I., Hines O. J. (2009). Transcriptional regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is crucial for invasion of pancreatic and liver cancer. Neoplasia 11, 196–206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckanovich R. J., Facciabene A., Kim S., Benencia F., Sasaroli D., Balint K., Katsaros D., O’Brien-Jenkins A., Gimotty P. A., Coukos G. (2008). Endothelin B receptor mediates the endothelial barrier to T cell homing to tumors and disables immune therapy. Nat. Med. 14, 28–36 10.1038/nm1699 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckanovich R. J., Sasaroli D., O’Brien-Jenkins A., Botbyl J., Hammond R., Katsaros D., Sandaltzopoulos R., Liotta L. A., Gimotty P. A., Coukos G. (2007). Tumor vascular proteins as biomarkers in ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 25, 852–861 10.1200/JCO.2006.08.8583 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. A., Brady M. F., Bookman M. A., Fleming G. F., Monk B. J., Huang H., Mannel R. S., Homesley H. D., Fowler J., Greer B. E., Boente M., Birrer M. J., Liang S. X. (2011). Incorporation of bevacizumab in the primary treatment of ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 2473–2483 10.1056/NEJMoa1104390 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Giannoudis A., Corke K. P., Gill D., Wells M., Ziegler-Heitbrock L., Lewis C. E. (2003). Hypoxia-induced gene expression in human macrophages: implications for ischemic tissues and hypoxia-regulated gene therapy. Am. J. Pathol. 163, 1233–1243 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63483-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan M. K., Wolchok J. D., Allison J. P. (2010). Anti-CTLA-4 antibody therapy: immune monitoring during clinical development of a novel immunotherapy. Semin. Oncol. 37, 473–484 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2010.09.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet P., Jain R. K. (2011). Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 10, 417–427 10.1038/nrd3455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanovas O., Hicklin D. J., Bergers G., Hanahan D. (2005). Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell 8, 299–309 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.09.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceradini D. J., Kulkarni A. R., Callaghan M. J., Tepper O. M., Bastidas N., Kleinman M. E., Capla J. M., Galiano R. D., Levine J. P., Gurtner G. C. (2004). Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat. Med. 10, 858–864 10.1038/nm1075 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Imanaka N., Chen J., Griffin J. D. (2010). Hypoxia potentiates notch signaling in breast cancer leading to decreased E-cadherin expression and increased cell migration and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 102, 351–360 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M. T., Moller A., Smyth M. J. (2011). Inflammation and immune surveillance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.12.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corzo C. A., Condamine T., Lu L., Cotter M. J., Youn J. I., Cheng P., Cho H. I., Celis E., Quiceno D. G., Padhya T., Mccaffrey T. V., Mccaffrey J. C., Gabrilovich D. I. (2010). HIF-1alpha regulates function and differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. J. Exp. Med. 207, 2439–2453 10.1084/jem.20100587 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel T. J., Wei S., Dong H., Alvarez X., Cheng P., Mottram P., Krzysiek R., Knutson K. L., Daniel B., Zimmermann M. C., David O., Burow M., Gordon A., Dhurandhar N., Myers L., Berggren R., Hemminki A., Alvarez R. D., Emilie D., Curiel D. T., Chen L., Zou W. (2003). Blockade of B7-H1 improves myeloid dendritic cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Nat. Med. 9, 562–567 10.1038/nm863 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta K., Mondal S., Sinha S., Li J., Wang E., Knebelmann B., Karumanchi S. A., Mukhopadhyay D. (2005). Role of elongin-binding domain of von Hippel Lindau gene product on HuR-mediated VPF/VEGF mRNA stability in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 24, 7850–7858 10.1038/sj.onc.1208912 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhirst M. W., Cao Y., Moeller B. (2008). Cycling hypoxia and free radicals regulate angiogenesis and radiotherapy response. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 425–437 10.1038/nrc2397 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doedens A. L., Stockmann C., Rubinstein M. P., Liao D., Zhang N., Denardo D. G., Coussens L. M., Karin M., Goldrath A. W., Johnson R. S. (2010). Macrophage expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha suppresses T-cell function and promotes tumor progression. Cancer Res. 70, 7465–7475 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du R., Lu K. V., Petritsch C., Liu P., Ganss R., Passegue E., Song H., Vandenberg S., Johnson R. S., Werb Z., Bergers G. (2008). HIF1alpha induces the recruitment of bone marrow-derived vascular modulatory cells to regulate tumor angiogenesis and invasion. Cancer Cell 13, 206–220 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.01.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggermont A. M., Robert C. (2011). New drugs in melanoma: it’s a whole new world. Eur. J. Cancer 47, 2150–2157 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggermont A. M., Testori A., Maio M., Robert C. (2010). Anti-CTLA-4 antibody adjuvant therapy in melanoma. Semin. Oncol. 37, 455–459 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2010.09.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltzschig H. K., Carmeliet P. (2011). Hypoxia and inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 364, 656–665 10.1056/NEJMra0910283 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escudier B., Cosaert J., Pisa P. (2008). Bevacizumab: direct anti-VEGF therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 8, 1545–1557 10.1586/14737140.8.10.1545 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facciabene A., Peng X., Hagemann I. S., Balint K., Barchetti A., Wang L. P., Gimotty P. A., Gilks C. B., Lal P., Zhang L., Coukos G. (2011). Tumour hypoxia promotes tolerance and angiogenesis via CCL28 and T(reg) cells. Nature 475, 226–230 10.1038/nature10169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Hillan K. J., Gerber H. P., Novotny W. (2004). Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 391–400 10.1038/nrd1381 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingleton B., Vargo-Gogola T., Crawford H. C., Matrisian L. M. (2001). Matrilysin [MMP-7] expression selects for cells with reduced sensitivity to apoptosis. Neoplasia 3, 459–468 10.1038/sj.neo.7900190 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke J. H., Rini B., Ireland J., Rayman P., Richmond A., Golshayan A., Wood L., Elson P., Garcia J., Dreicer R., Bukowski R. (2008). Sunitinib reverses type-1 immune suppression and decreases T-regulatory cells in renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 6674–6682 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman W. H., Galon J., Pages F., Tartour E., Sautes-Fridman C., Kroemer G. (2011). Prognostic and predictive impact of intra- and peritumoral immune infiltrates. Cancer Res. 71, 5601–5605 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumura D., Duda D. G., Munn L. L., Jain R. K. (2010). Tumor microvasculature and microenvironment: novel insights through intravital imaging in pre-clinical models. Microcirculation 17, 206–225 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2010.00029.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrilovich D. (2004). Mechanisms and functional significance of tumour-induced dendritic-cell defects. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 941–952 10.1038/nri1498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrilovich D., Ishida T., Oyama T., Ran S., Kravtsov V., Nadaf S., Carbone D. P. (1998). Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits the development of dendritic cells and dramatically affects the differentiation of multiple hematopoietic lineages in vivo. Blood 92, 4150–4166 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrilovich D. I., Chen H. L., Girgis K. R., Cunningham H. T., Meny G. M., Nadaf S., Kavanaugh D., Carbone D. P. (1996). Production of vascular endothelial growth factor by human tumors inhibits the functional maturation of dendritic cells. Nat. Med. 2, 1096–1103 10.1038/nm1096-1096 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrilovich D. I., Nagaraj S. (2009). Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 162–174 10.1038/nri2506 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galon J., Costes A., Sanchez-Cabo F., Kirilovsky A., Mlecnik B., Lagorce-Pages C., Tosolini M., Camus M., Berger A., Wind P., Zinzindohoue F., Bruneval P., Cugnenc P. H., Trajanoski Z., Fridman W. H., Pages F. (2006). Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science 313, 1960–1964 10.1126/science.1129139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhough A., Smartt H. J., Moore A. E., Roberts H. R., Williams A. C., Paraskeva C., Kaidi A. (2009). The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis 30, 377–386 10.1093/carcin/bgp014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R., Chetty C., Bhoopathi P., Lakka S., Mohanam S., Rao J. S., Dinh D. E. (2011). Downregulation of uPA/uPAR inhibits intermittent hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in DAOY and D283 medulloblastoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 38, 733–744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamai A., Benlalam H., Meslin F., Hasmim M., Carre T., Akalay I., Janji B., Berchem G., Noman M. Z., Chouaib S. (2010). Immune surveillance of human cancer: if the cytotoxic T-lymphocytes play the music, does the tumoral system call the tune? Tissue Antigens 75, 1–8 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2009.01401.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamzah J., Jugold M., Kiessling F., Rigby P., Manzur M., Marti H. H., Rabie T., Kaden S., Grone H. J., Hammerling G. J., Arnold B., Ganss R. (2008). Vascular normalization in Rgs5-deficient tumours promotes immune destruction. Nature 453, 410–414 10.1038/nature06868 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L. (2002). Hypoxia – a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 38–47 10.1038/nrc704 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipp M. M., Hilf N., Walter S., Werth D., Brauer K. M., Radsak M. P., Weinschenk T., Singh-Jasuja H., Brossart P. (2008). Sorafenib, but not sunitinib, affects function of dendritic cells and induction of primary immune responses. Blood 111, 5610–5620 10.1182/blood-2007-02-075945 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscox S., Barrett-Lee P., Nicholson R. I. (2011). Therapeutic targeting of tumor-stroma interactions. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 15, 609–621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain N. K., Ishikawa T. O., Spigelman I., Herschman H. R. (2008). COX-2 expression and function in the hyperalgesic response to paw inflammation in mice. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 79, 183–190 10.1016/j.plefa.2008.08.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. K. (1988). Determinants of tumor blood flow: a review. Cancer Res. 48, 2641–2658 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. K. (2005). Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307, 58–62 10.1126/science.1104819 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. K., Stylianopoulos T. (2010). Delivering nanomedicine to solid tumors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 7, 653–664 10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenab-Wolcott J., Giantonio B. J. (2010). Antiangiogenic therapy in colorectal cancer: where are we 5 years later? Clin. Colorectal Cancer 9(Suppl. 1), S7–S15 10.3816/CCC.2010.s.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Tang Y. L., Liang X. H. (2011). EMT: a new vision of hypoxia promoting cancer progression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 11, 714–723 10.4161/cbt.11.8.15274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr. (2008). The von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor protein: O2 sensing and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 865–873 10.1038/nrc2502 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandalaft L. E., Facciabene A., Buckanovich R. J., Coukos G. (2009). Endothelin B receptor, a new target in cancer immune therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 4521–4528 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0543 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith B., Johnson R. S., Simon M. C. (2011). HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 9–22 10.1038/nrn2949 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith B., Simon M. C. (2007). Hypoxia-inducible factors, stem cells, and cancer. Cell 129, 465–472 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. Y., Perera S., Zhou B., Carretero J., Yeh J. J., Heathcote S. A., Jackson A. L., Nikolinakos P., Ospina B., Naumov G., Brandstetter K. A., Weigman V. J., Zaghlul S., Hayes D. N., Padera R. F., Heymach J. V., Kung A. L., Sharpless N. E., Kaelin W. G., Jr., Wong K. K. (2009). HIF2alpha cooperates with RAS to promote lung tumorigenesis in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 119, 2160–2170 10.1172/JCI38443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko J. S., Zea A. H., Rini B. I., Ireland J. L., Elson P., Cohen P., Golshayan A., Rayman P. A., Wood L., Garcia J., Dreicer R., Bukowski R., Finke J. H. (2009). Sunitinib mediates reversal of myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation in renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 2148–2157 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koebel C. M., Vermi W., Swann J. B., Zerafa N., Rodig S. J., Old L. J., Smyth M. J., Schreiber R. D. (2007). Adaptive immunity maintains occult cancer in an equilibrium state. Nature 450, 903–907 10.1038/nature06309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo-Saito C., Shirako H., Takeuchi T., Kawakami Y. (2009). Cancer metastasis is accelerated through immunosuppression during snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer Cell 15, 195–206 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau K. W., Tian Y. M., Raval R. R., Ratcliffe P. J., Pugh C. W. (2007). Target gene selectivity of hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha in renal cancer cells is conveyed by post-DNA-binding mechanisms. Br. J. Cancer 96, 1284–1292 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603774 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. S., Landers R. J., Underwood J. C., Harris A. L., Lewis C. E. (2000). Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor by macrophages is up-regulated in poorly vascularized areas of breast carcinomas. J. Pathol. 192, 150–158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B., Lalani A. S., Harding T. C., Luan B., Koprivnikar K., Huan Tu G., Prell R., Vanroey M. J., Simmons A. D., Jooss K. (2006). Vascular endothelial growth factor blockade reduces intratumoral regulatory T cells and enhances the efficacy of a GM-CSF-secreting cancer immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 6808–6816 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1558 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z., Bao S., Wu Q., Wang H., Eyler C., Sathornsumetee S., Shi Q., Cao Y., Lathia J., Mclendon R. E., Hjelmeland A. B., Rich J. N. (2009). Hypoxia-inducible factors regulate tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells. Cancer Cell 15, 501–513 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao D., Johnson R. S. (2007). Hypoxia: a key regulator of angiogenesis in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26, 281–290 10.1007/s10555-007-9066-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorusso G., Ruegg C. (2008). The tumor microenvironment and its contribution to tumor evolution toward metastasis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 130, 1091–1103 10.1007/s00418-008-0530-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukashev D., Ohta A., Sitkovsky M. (2007). Hypoxia-dependent anti-inflammatory pathways in protection of cancerous tissues. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26, 273–279 10.1007/s10555-007-9054-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Nordenskjold B., Landberg G. (2009). Hypoxia, snail and incomplete epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 101, 1769–1781 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo D., Wang J., Li J., Post M. (2011). Mouse snail is a target gene for HIF. Mol. Cancer Res. 9, 234–245 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino Y., Uenishi R., Okamoto K., Isoe T., Hosono O., Tanaka H., Kanopka A., Poellinger L., Haneda M., Morimoto C. (2007). Transcriptional up-regulation of inhibitory PAS domain protein gene expression by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1): a negative feedback regulatory circuit in HIF-1-mediated signaling in hypoxic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 14073–14082 10.1074/jbc.M700732200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso M. R., Davis R., Norberg S. M., O’Brien S., Sennino B., Nakahara T., Yao V. J., Inai T., Brooks P., Freimark B., Shalinsky D. R., Hu-Lowe D. D., Mcdonald D. M. (2006). Rapid vascular regrowth in tumors after reversal of VEGF inhibition. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 2610–2621 10.1172/JCI24612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning E. A., Ullman J. G., Leatherman J. M., Asquith J. M., Hansen T. R., Armstrong T. D., Hicklin D. J., Jaffee E. M., Emens L. A. (2007). A vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor enhances antitumor immunity through an immune-based mechanism. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 3951–3959 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0374 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansh M. (2011). Ipilimumab and cancer immunotherapy: a new hope for advanced stage melanoma. Yale J. Biol. Med. 84, 381–389 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani A., Sozzani S., Locati M., Allavena P., Sica A. (2002). Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 23, 549–555 10.1016/S1471-4906(02)02302-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni M., Rovati B., Ronzoni M., Loupakis F., Mariucci S., Ricci V., Gattoni E., Salvatore L., Tinelli C., Villa E., Danova M. (2011). Immunological effects of bevacizumab-based treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncology 79, 187–196 10.1159/000320609 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marigo I., Dolcetti L., Serafini P., Zanovello P., Bronte V. (2008). Tumor-induced tolerance and immune suppression by myeloid derived suppressor cells. Immunol. Rev. 222, 162–179 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00602.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Coukos G., Dranoff G. (2011). Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature 480, 480–489 10.1038/nature10673 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeller B. J., Richardson R. A., Dewhirst M. W. (2007). Hypoxia and radiotherapy: opportunities for improved outcomes in cancer treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26, 241–248 10.1007/s10555-007-9056-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motz G. T., Coukos G. (2011). The parallel lives of angiogenesis and immunosuppression: cancer and other tales. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 702–711 10.1038/nri3064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraj S., Gabrilovich D. I. (2007). Myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 601, 213–223 10.1007/978-0-387-72005-0_22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J. A., Chang S. H., Shih S. C., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. (2010). Heterogeneity of the tumor vasculature. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 36, 321–331 10.1055/s-0030-1253454 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair S., Boczkowski D., Moeller B., Dewhirst M., Vieweg J., Gilboa E. (2003). Synergy between tumor immunotherapy and antiangiogenic therapy. Blood 102, 964–971 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3738 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi H., Nakada T., Hokamura M., Osakabe Y., Itokazu O., Huang L. E., Isaka K. (2004). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 transactivates transforming growth factor-beta3 in trophoblast. Endocrinology 145, 4113–4118 10.1210/en.2003-1639 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka I., Ichikawa Y., Ishikawa T., Kamiyama M., Hasegawa S., Momiyama N., Miyazaki K., Shimada H. (2001). Matrilysin stimulates DNA synthesis of cultured vascular endothelial cells and induces angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Lett. 173, 175–182 10.1016/S0304-3835(01)00634-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noman M. Z., Benlalam H., Hasmim M., Chouaib S. (2011a). Cytotoxic T cells – stroma interactions. Bull. Cancer 98, E19–E24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noman M. Z., Janji B., Kaminska B., Van Moer K., Pierson S., Przanowski P., Buart S., Berchem G., Romero P., Mami-Chouaib F., Chouaib S. (2011b). Blocking hypoxia-induced autophagy in tumors restores cytotoxic T-cell activity and promotes regression. Cancer Res. 71, 5976–5986 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noman M. Z., Messai Y., Carre T., Akalay I., Meron M., Janji B., Hasmim M., Chouaib S. (2011c). Microenvironmental hypoxia orchestrating the cell stroma cross talk, tumor progression and antitumor response. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 31, 357–377 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noman M. Z., Buart S., Van Pelt J., Richon C., Hasmim M., Leleu N., Suchorska W. M., Jalil A., Lecluse Y., El Hage F., Giuliani M., Pichon C., Azzarone B., Mazure N., Romero P., Mami-Chouaib F., Chouaib S. (2009). The cooperative induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and STAT3 during hypoxia induced an impairment of tumor susceptibility to CTL-mediated cell lysis. J. Immunol. 182, 3510–3521 10.4049/jimmunol.0800854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osada T., Chong G., Tansik R., Hong T., Spector N., Kumar R., Hurwitz H. I., Dev I., Nixon A. B., Lyerly H. K., Clay T., Morse M. A. (2008). The effect of anti-VEGF therapy on immature myeloid cell and dendritic cells in cancer patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 57, 1115–1124 10.1007/s00262-007-0441-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi F., Cianci R., Pagliari D., Casciano F., Bagala C., Astone A., Landolfi R., Barone C. (2011). The immune response to tumors as a tool toward immunotherapy. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 894704. 10.1155/2011/894704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. A., Simon M. C. (2008). Biology of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha in development and disease. Cell Death Differ. 15, 628–634 10.1038/cdd.2008.17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perren T. J., Swart A. M., Pfisterer J., Ledermann J. A., Pujade-Lauraine E., Kristensen G., Carey M. S., Beale P., Cervantes A., Kurzeder C., Du Bois A., Sehouli J., Kimmig R., Stahle A., Collinson F., Essapen S., Gourley C., Lortholary A., Selle F., Mirza M. R., Leminen A., Plante M., Stark D., Qian W., Parmar M. K., Oza A. M. (2011). A phase 3 trial of bevacizumab in ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 2484–2496 10.1056/NEJMoa1103799 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrulio C. A., Kim-Schulze S., Kaufman H. L. (2006). The tumour microenvironment and implications for cancer immunotherapy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 6, 671–684 10.1517/14712598.6.7.671 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porta C., Szczylik C., Escudier B. (2011). Combination or sequencing strategies to improve the outcome of metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients: a critical review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2011.06.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto P. A., Yang J. C., Sherry R. M., Hughes M. S., Kammula U. S., White D. E., Levy C. L., Rosenberg S. A., Phan G. Q. (2012). CTLA-4 blockade with ipilimumab: long-term follow-up of 177 patients with metastatic melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raval R. R., Lau K. W., Tran M. G., Sowter H. M., Mandriota S. J., Li J. L., Pugh C. W., Maxwell P. H., Harris A. L., Ratcliffe P. J. (2005). Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 5675–5686 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5675-5686.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez P. C., Hernandez C. P., Quiceno D., Dubinett S. M., Zabaleta J., Ochoa J. B., Gilbert J., Ochoa A. C. (2005). Arginase I in myeloid suppressor cells is induced by COX-2 in lung carcinoma. J. Exp. Med. 202, 931–939 10.1084/jem.20050715 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Yang J. C., Restifo N. P. (2004). Cancer immunotherapy: moving beyond current vaccines. Nat. Med. 10, 909–915 10.1038/nm1100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Yang J. C., Schwartzentruber D. J., Hwu P., Marincola F. M., Topalian S. L., Restifo N. P., Dudley M. E., Schwarz S. L., Spiess P. J., Wunderlich J. R., Parkhurst M. R., Kawakami Y., Seipp C. A., Einhorn J. H., White D. E. (1998). Immunologic and therapeutic evaluation of a synthetic peptide vaccine for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. Nat. Med. 4, 321–327 10.1038/nm0398-321 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salceda S., Caro J. (1997). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 22642–22647 10.1074/jbc.272.36.22642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathornsumetee S., Cao Y., Marcello J. E., Herndon J. E., II, Mclendon R. E., Desjardins A., Friedman H. S., Dewhirst M. W., Vredenburgh J. J., Rich J. N. (2008). Tumor angiogenic and hypoxic profiles predict radiographic response and survival in malignant astrocytoma patients treated with bevacizumab and irinotecan. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 271–278 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.3652 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer L., Scheid A., Spielmann P., Breymann C., Zimmermann R., Meuli M., Gassmann M., Marti H. H., Wenger R. H. (2003). Oxygen-regulated expression of TGF-beta 3, a growth factor involved in trophoblast differentiation. Placenta 24, 941–950 10.1016/S0143-4004(03)00166-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schietke R., Warnecke C., Wacker I., Schodel J., Mole D. R., Campean V., Amann K., Goppelt-Struebe M., Behrens J., Eckardt K. U., Wiesener M. S. (2010). The lysyl oxidases LOX and LOXL2 are necessary and sufficient to repress E-cadherin in hypoxia: insights into cellular transformation processes mediated by HIF-1. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 6658–6669 10.1074/jbc.M109.042424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seliger B., Massa C., Rini B., Ko J., Finke J. (2010). Antitumour and immune-adjuvant activities of protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Trends. Mol. Med. 16, 184–192 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.02.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. L. (2010). Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene 29, 625–634 10.1038/onc.2009.441 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini P. (2010). Editorial: PGE2-producing MDSC: a role in tumor progression? J. Leukoc. Biol. 88, 827–829 10.1189/jlb.0510303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini P., Mgebroff S., Noonan K., Borrello I. (2008). Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote cross-tolerance in B-cell lymphoma by expanding regulatory T cells. Cancer Res. 68, 5439–5449 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6621 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaked Y., Bertolini F., Man S., Rogers M. S., Cervi D., Foutz T., Rawn K., Voskas D., Dumont D. J., Ben-David Y., Lawler J., Henkin J., Huber J., Hicklin D. J., D’Amato R. J., Kerbel R. S. (2005). Genetic heterogeneity of the vasculogenic phenotype parallels angiogenesis; Implications for cellular surrogate marker analysis of antiangiogenesis. Cancer Cell 7, 101–111 10.1016/S1535-6108(04)00369-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaked Y., Ciarrocchi A., Franco M., Lee C. R., Man S., Cheung A. M., Hicklin D. J., Chaplin D., Foster F. S., Benezra R., Kerbel R. S. (2006). Therapy-induced acute recruitment of circulating endothelial progenitor cells to tumors. Science 313, 1785–1787 10.1126/science.1127592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shojaei F., Wu X., Malik A. K., Zhong C., Baldwin M. E., Schanz S., Fuh G., Gerber H. P., Ferrara N. (2007). Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 911–920 10.1038/nbt1323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha P., Clements V. K., Fulton A. M., Ostrand-Rosenberg S. (2007). Prostaglandin E2 promotes tumor progression by inducing myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res. 67, 4507–4513 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleeman J. P., Thiery J. P. (2011). SnapShot: the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell 145, e161. 10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabile E., Burnett M. S., Watkins C., Kinnaird T., Bachis A., La Sala A., Miller J. M., Shou M., Epstein S. E., Fuchs S. (2003). Impaired arteriogenic response to acute hindlimb ischemia in CD4-knockout mice. Circulation 108, 205–210 10.1161/01.CIR.0000079225.50817.71 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenaga K. (2011). Angiogenic signaling aberrantly induced by tumor hypoxia. Front. Biosci. 16, 31–48 10.2741/3674 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartour E., Pere H., Maillere B., Terme M., Merillon N., Taieb J., Sandoval F., Quintin-Colonna F., Lacerda K., Karadimou A., Badoual C., Tedgui A., Fridman W. H., Oudard S. (2011). Angiogenesis and immunity: a bidirectional link potentially relevant for the monitoring of antiangiogenic therapy and the development of novel therapeutic combination with immunotherapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 30, 83–95 10.1007/s10555-011-9281-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P. (2002). Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 442–454 10.1038/nrc822 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Sleeman J. P. (2006). Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 131–142 10.1038/nrm1835 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toi M., Kondo S., Suzuki H., Yamamoto Y., Inada K., Imazawa T., Taniguchi T., Tominaga T. (1996a). Quantitative analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor in primary breast cancer. Cancer 77, 1101–1106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toi M., Taniguchi T., Yamamoto Y., Kurisaki T., Suzuki H., Tominaga T. (1996b). Clinical significance of the determination of angiogenic factors. Eur. J. Cancer 32A, 2513–2519 10.1016/S0959-8049(96)00397-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. (2003). Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 133–146 10.1038/nri1001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Veire S., Stalmans I., Heindryckx F., Oura H., Tijeras-Raballand A., Schmidt T., Loges S., Albrecht I., Jonckx B., Vinckier S., Van Steenkiste C., Tugues S., Rolny C., De Mol M., Dettori D., Hainaud P., Coenegrachts L., Contreres J. O., Van Bergen T., Cuervo H., Xiao W. H., Le Henaff C., Buysschaert I., Kharabi Masouleh B., Geerts A., Schomber T., Bonnin P., Lambert V., Haustraete J., Zacchigna S., Rakic J. M., Jimenez W., Noel A., Giacca M., Colle I., Foidart J. M., Tobelem G., Morales-Ruiz M., Vilar J., Maxwell P., Vinores S. A., Carmeliet G., Dewerchin M., Claesson-Welsh L., Dupuy E., Van Vlierberghe H., Christofori G., Mazzone M., Detmar M., Collen D., Carmeliet P. (2010). Further pharmacological and genetic evidence for the efficacy of PlGF inhibition in cancer and eye disease. Cell 141, 178–190 10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Jiang B. H., Rue E. A., Semenza G. L. (1995). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 5510–5514 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3933 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Niu G., Kortylewski M., Burdelya L., Shain K., Zhang S., Bhattacharya R., Gabrilovich D., Heller R., Coppola D., Dalton W., Jove R., Pardoll D., Yu H. (2004). Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat. Med. 10, 48–54 10.1038/nm1140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werno C., Menrad H., Weigert A., Dehne N., Goerdt S., Schledzewski K., Kzhyshkowska J., Brune B. (2010). Knockout of HIF-1alpha in tumor-associated macrophages enhances M2 polarization and attenuates their pro-angiogenic responses. Carcinogenesis 31, 1863–1872 10.1093/carcin/bgq088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R., Harris R. A., Lee S. R., Craigon M. H., Binley K., Price T., Beard G. L., Mundy C. R., Naylor S. (2004). Genetic amplification of the transcriptional response to hypoxia as a novel means of identifying regulators of angiogenesis. Genomics 83, 1–8 10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00215-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside T. L., Mandapathil M., Schuler P. (2011). The role of the adenosinergic pathway in immunosuppression mediated by human regulatory T cells (Treg). Curr. Med. Chem. 18, 5217–5223 10.2174/092986711798184334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett C. G., Boucher Y., Di Tomaso E., Duda D. G., Munn L. L., Tong R. T., Chung D. C., Sahani D. V., Kalva S. P., Kozin S. V., Mino M., Cohen K. S., Scadden D. T., Hartford A. C., Fischman A. J., Clark J. W., Ryan D. P., Zhu A. X., Blaszkowsky L. S., Chen H. X., Shellito P. C., Lauwers G. Y., Jain R. K. (2004). Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat. Med. 10, 145–147 10.1038/nm0604-649c [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Hay M. P. (2011). Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 11, 393–410 10.1038/nrc3064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin H., Zhang C., Herrmann A., Du Y., Figlin R., Yu H. (2009). Sunitinib inhibition of Stat3 induces renal cell carcinoma tumor cell apoptosis and reduces immunosuppressive cells. Cancer Res. 69, 2506–2513 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Debusk L. M., Fukuda K., Fingleton B., Green-Jarvis B., Shyr Y., Matrisian L. M., Carbone D. P., Lin P. C. (2004). Expansion of myeloid immune suppressor Gr+CD11b+ cells in tumor-bearing host directly promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 6, 409–421 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.08.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Kortylewski M., Pardoll D. (2007). Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 41–51 10.1038/nri1995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Conejo-Garcia J. R., Katsaros D., Gimotty P. A., Massobrio M., Regnani G., Makrigiannakis A., Gray H., Schlienger K., Liebman M. N., Rubin S. C., Coukos G. (2003). Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 203–213 10.1056/NEJMoa020177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong H., Bowen J. P. (2011). Recent advances in small molecule inhibitors of VEGFR and EGFR signaling pathways. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 11, 1571–1590 10.2174/156802611795860924 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou W. (2005). Immunosuppressive networks in the tumour environment and their therapeutic relevance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 263–274 10.1038/nrc1586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]