Abstract
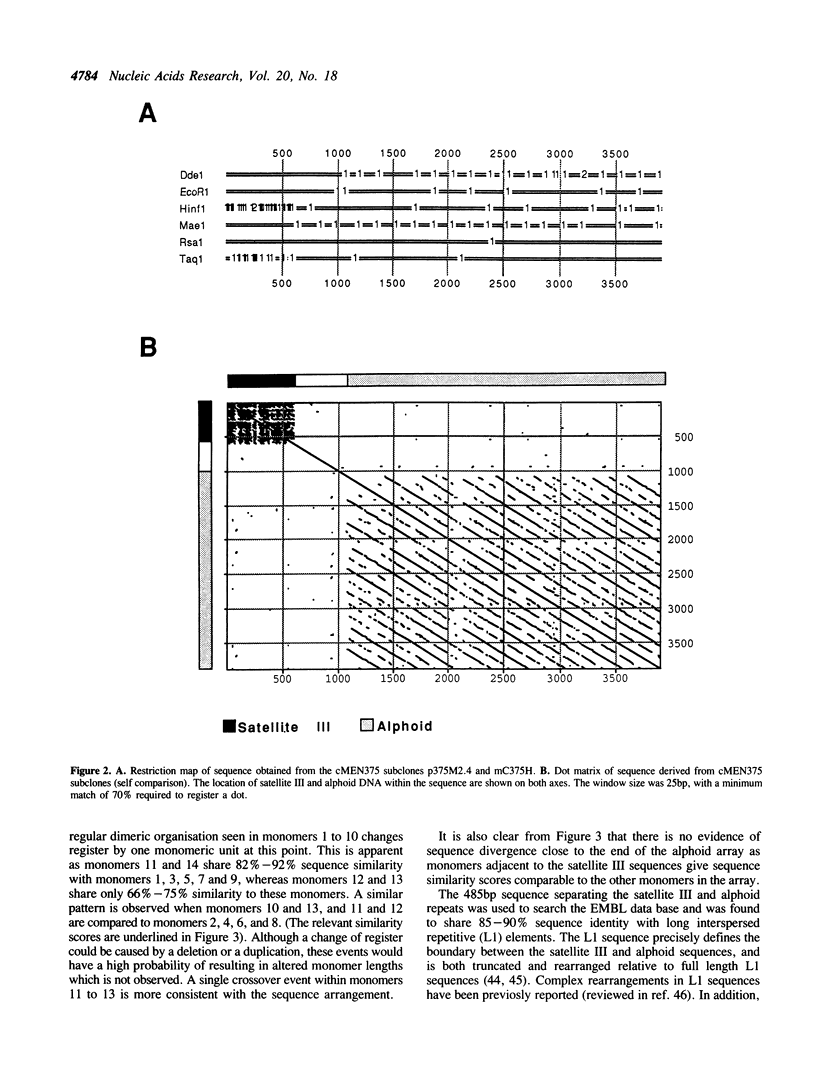
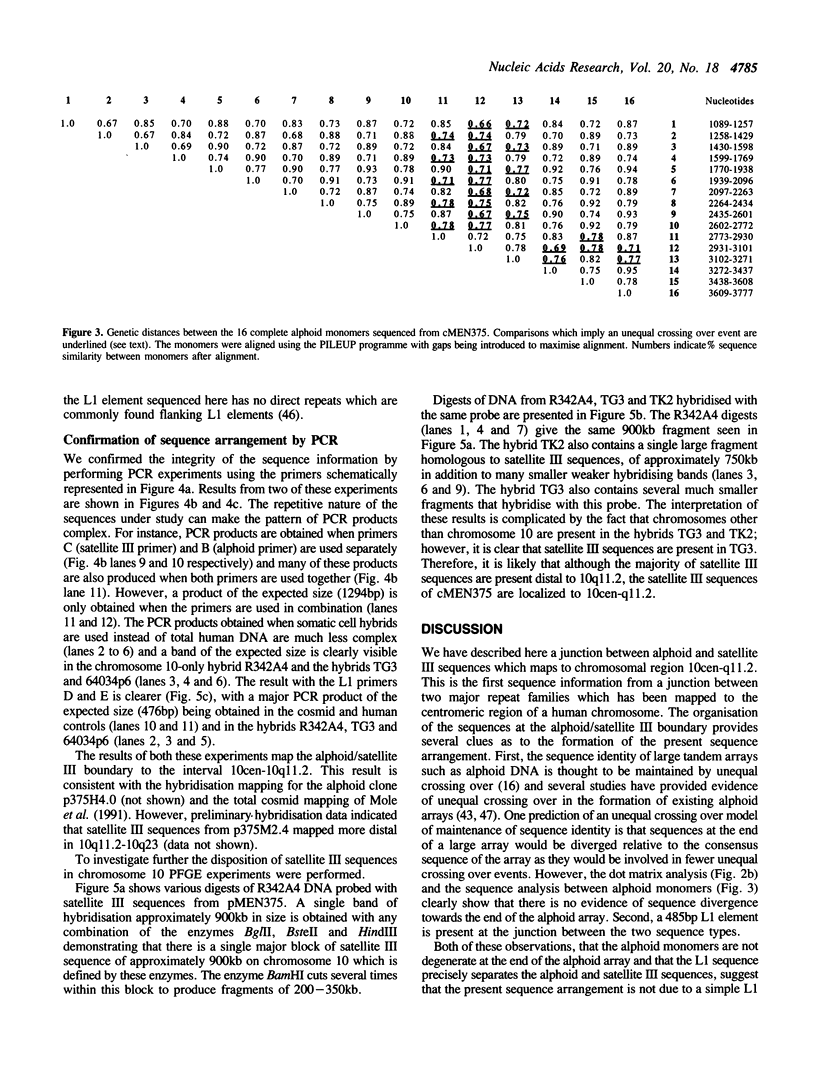
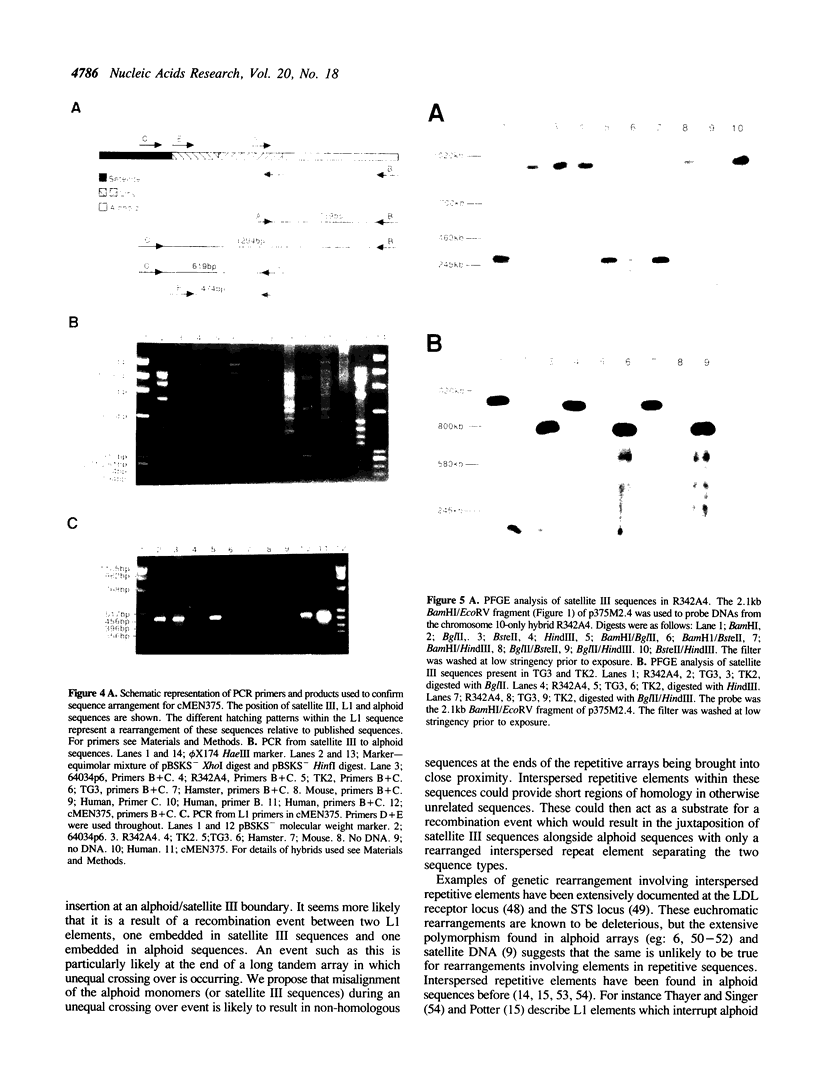
Alphoid and satellite III sequences are arranged as large tandem arrays in the centromeric regions of human chromosomes. Several recent studies using in situ hybridisation to investigate the relative positions of these sequences have shown that they occupy adjacent but non-overlapping domains in metaphase chromosomes. We have analysed the DNA sequence at the junction between alphoid and satellite III sequences in a cosmid previously mapped to chromosome 10. The alphoid sequence consists of tandemly arranged dimers which are distinct from the known chromosome 10-specific alphoid family. Polymerase chain reaction experiments confirm the integrity of the sequence data. These results, together with pulsed field gel electrophoresis data place the boundary between alphoid and satellite III sequences in the mapping interval 10 centromere-10q11.2. The sequence data shows that these repetitive sequences are separated by a partial L1 interspersed repeat sequence less than 500bp in length. The arrangement of the junction suggests that a recombination event has brought these sequences into close proximity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agresti A., Meneveri R., Siccardi A. G., Marozzi A., Corneo G., Gaudi S., Ginelli E. Linkage in human heterochromatin between highly divergent Sau3A repeats and a new family of repeated DNA sequences (HaeIII family). J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):625–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov I. A., Mitkevich S. P., Yurov Y. B. The phylogeny of human chromosome specific alpha satellites. Chromosoma. 1988;96(6):443–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00303039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini A., Smith D. I., Rocchi M., Miller O. J., Miller D. A. A human alphoid DNA clone from the EcoRI dimeric family: genomic and internal organization and chromosomal assignment. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):822–828. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. F., Harberd N. P., Jarvis M. G., Flavell R. B. Structure and evolution of the intergenic region in a ribosomal DNA repeat unit of wheat. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90434-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp R. S., Mitchell A. R., Buckland R. A., Bostock C. J. Specific arrangements of human satellite III DNA sequences in human chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1979 Feb 21;71(2):153–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00292820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Earle E., McQuillan C. A homologous subfamily of satellite III DNA on human chromosomes 14 and 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5641–5648. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Earle E., Vissel B., Filby R. G. Identification of two distinct subfamilies of alpha satellite DNA that are highly specific for human chromosome 15. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Earle E., Vissel B., Kalitsis P. A chromosome 14-specific human satellite III DNA subfamily that shows variable presence on different chromosomes 14. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):706–716. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Vissel B., Earle E. Evolution of alpha-satellite DNA on human acrocentric chromosomes. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):332–344. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Vissel B., Nagy A., Earle E., Kalitsis P. A survey of the genomic distribution of alpha satellite DNA on all the human chromosomes, and derivation of a new consensus sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1179–1182. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Hindley J. Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3177–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Kievits T., Waye J. S., Pearson P. L., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA: isolation and mapping of a polymorphic alphoid repeat from human chromosome 10. Genomics. 1988 Jul;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. H., Kao F. T., Jones C., White R. T., Benson B. J., Mason R. J. The coding sequence for the 32,000-dalton pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A is located on chromosome 10 and identifies two separate restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jun;40(6):503–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Mitchell A. R., Buckland R. A., Clayton R. P., Evans H. J. The location of four human satellite DNAs on human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Apr;92(1):148–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90648-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig G. M., England S. B., Bedford H. M., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA from the centromere of human chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):862–872. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. Members of the KpnI family of long interspersed repeated sequences join and interrupt alpha-satellite in the monkey genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):321–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Willard H. F. Organization, polymorphism, and molecular cytogenetics of chromosome-specific alpha-satellite DNA from the centromere of chromosome 2. Genomics. 1992 May;13(1):122–128. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90211-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. J., Wang H. S., Shtromas I., Haliotis T., Roder J. C., Holden J. J., White B. N. Organization of a repetitive human 1.8 kb KpnI sequence localized in the heterochromatin of chromosome 15. Chromosoma. 1985;93(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01259449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. The LDL receptor locus in familial hypercholesterolemia: mutational analysis of a membrane protein. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:133–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft R., Tardiff J., Krauter K. S., Leinwand L. A. Using mini-prep plasmid DNA for sequencing double stranded templates with Sequenase. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):544-6, 549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman M. I., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Kpn I family of long interspersed repeated DNA sequences in primates: polymorphism of family members and evidence for transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looijenga L. H., Oosterhuis J. W., Smit V. T., Wessels J. W., Mollevanger P., Devilee P. Alpha satellite DNAs on chromosomes 10 and 12 are both members of the dimeric suprachromosomal subfamily, but display little identity at the nucleotide sequence level. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90027-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew C. G., Wakeling W., Jones E., Easton D., Fisher R., Strong C., Smith B., Chin K., Little P., Nakamura Y. Regional localization of polymorphic markers on chromosome 10 by physical and genetic mapping. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 May;54(Pt 2):121–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen M. D., Hunter B., Phillips R. L., Rubenstein I. The structure of the maize ribosomal DNA spacer region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4953–4968. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneveri R., Agresti A., Della Valle G., Talarico D., Siccardi A. G., Ginelli E. Identification of a human clustered G + C-rich DNA family of repeats (Sau3A family). J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzdorf R., Göttert E., Blin N. A novel centromeric repetitive DNA from human chromosome 22. Chromosoma. 1988;97(2):154–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00327372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. R., Gosden J. R., Miller D. A. A cloned sequence, p82H, of the alphoid repeated DNA family found at the centromeres of all human chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1985;92(5):369–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00327469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A., Jeppesen P., Hanratty D., Gosden J. The organisation of repetitive DNA sequences on human chromosomes with respect to the kinetochore analysed using a combination of oligonucleotide primers and CREST anticentromere serum. Chromosoma. 1992 Mar;101(5-6):333–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00346012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. Rearranged sequences of a human Kpn I element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi M., Archidiacono N., Ward D. C., Baldini A. A human chromosome 9-specific alphoid DNA repeat spatially resolvable from satellite 3 DNA by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):517–523. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90419-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. Unit-length line-1 transcripts in human teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1385–1397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Interruption of an alpha-satellite array by a short member of the KpnI family of interspersed, highly repeated monkey DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):967–973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokino T., Takiguchi S., Tanigami A., Bragg T., Jones C., Nakamura Y. Thirty-one new RFLP systems detected by twenty-four DNA markers on human chromosome 10. Genomics. 1992 Feb;12(2):401–402. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90391-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B. J., van den Engh G., Christensen M., Massa H. F., Gray J. W., Van Dilla M. Characterization of somatic cell hybrids by bivariate flow karyotyping and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1991 Mar;17(2):117–136. doi: 10.1007/BF01232970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler-Smith C. Structure of repeated sequences in the centromeric region of the human Y chromosome. Development. 1987;101 (Suppl):93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., England S. B., Willard H. F. Genomic organization of alpha satellite DNA on human chromosome 7: evidence for two distinct alphoid domains on a single chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):349–356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Chromosome specificity of satellite DNAs: short- and long-range organization of a diverged dimeric subset of human alpha satellite from chromosome 3. Chromosoma. 1989 May;97(6):475–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00295032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Molecular analysis of a deletion polymorphism in alpha satellite of human chromosome 17: evidence for homologous unequal crossing-over and subsequent fixation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6915–6927. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Structure, organization, and sequence of alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 17: evidence for evolution by unequal crossing-over and an ancestral pentamer repeat shared with the human X chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3156–3165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wevrick R., Willard H. F. Physical map of the centromeric region of human chromosome 7: relationship between two distinct alpha satellite arrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2295–2301. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Z., Wilson V., Jeffreys A. J., Thein S. L. Cloning a selected fragment from a human DNA 'fingerprint': isolation of an extremely polymorphic minisatellite. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4605–4616. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Kidd K. K. Extensive sequence polymorphisms associated with chromosome 10 alpha satellite DNA and its close linkage to markers from the pericentromeric region. Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;84(3):279–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00200575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Li X. M., Tsai S. P., Johnson C., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. Frequent deletions of the human X chromosome distal short arm result from recombination between low copy repetitive elements. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90472-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Hu G. Y., Deisseroth A. Improvement of PCR sequencing by formamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6649–6649. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]