Abstract
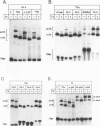
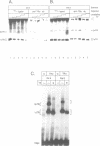
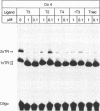
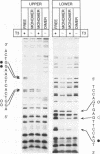
The effects of thyroid hormone agonists on thyroid hormone receptor (TR)/DNA complex formation was investigated to elucidate the mechanism by which TRs transactivate genes in response to ligand. The data, obtained from gel shift experiments, indicate that thyroid hormones alter the conformation of TRs bound to DNA, irrespective of if the element is occupied by monomeric TR, homodimeric TR/TR, or heterodimeric complexes with the retinoid receptors RAR or RXR. Furthermore, triiodo-thyronine (T3) prevents 2 TR molecules from binding to oligonucleotides containing direct repeats or inverted palindromes of the consensus AGGTCA motif, an effect that was not detected with palindromic elements. Heterodimers bound to direct repeats were less affected: RXR/TR were fully and RAR/TR complexes partially resistant to thyroid hormone. The data suggest that a ligand-induced conformational change in TR prevents double TR occupancy of a response element containing 2 direct repeats of the consensus binding motif, possibly by steric hindrance, whereas such an event does not prevent TR/RXR heterodimers from binding to DNA. Finally, our data show that a monomeric, liganded TR bound preferentially to the second half site in a AGGTCActcaAGGTCA element, and therefore indicate that nucleotides adjacent to the consensus half site contribute to binding specificity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois S., Pfahl M., Baulieu E. E. DNA binding properties of glucocorticosteroid receptors bound to the steroid antagonist RU-486. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):751–755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., White R., Hoare S., Sydenham M., Page M., Parker M. G. Inhibition of estrogen receptor-DNA binding by the "pure" antiestrogen ICI 164,384 appears to be mediated by impaired receptor dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6883–6887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D., Sjöberg M., Vennström B. Contrasting developmental and tissue-specific expression of alpha and beta thyroid hormone receptor genes. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1519–1528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden E. Thyroid hormones and the biochemistry of amphibian metamorphosis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1967;23:139–194. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9826-2.50007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Lipkin S. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glineur C., Bailly M., Ghysdael J. The c-erbA alpha-encoded thyroid hormone receptor is phosphorylated in its amino terminal domain by casein kinase II. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1247–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Cato A. C., Henderson D., Ryffel G. U. Two types of antiprogestins identified by their differential action in transcriptionally active extracts from T47D cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1227–1234. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Berrodin T. J., Harding H. P. Differential DNA binding by monomeric, homodimeric, and potentially heteromeric forms of the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5005–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz A., Zenke M., Gehring U., Sap J., Beug H., Vennström B. Characterization of the hormone-binding domain of the chicken c-erbA/thyroid hormone receptor protein. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):155–159. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raaka B. M., Samuels H. H. Regulation of thyroid hormone nuclear receptor levels in GH1 cells by 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine. Use of dense amino acid labeling to determine the influence of hormone on the receptor half-life and the rate of appearance of newly synthesized receptor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6883–6889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E. D., O'Donnell A. L., Koenig R. J. Protein-protein interactions involving erbA superfamily receptors: through the TRAPdoor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;78(1-2):C83–C88. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90175-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., de Magistris L., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. A major thyroid hormone response element in the third intron of the rat growth hormone gene. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):887–896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savouret J. F., Bailly A., Misrahi M., Rauch C., Redeuilh G., Chauchereau A., Milgrom E. Characterization of the hormone responsive element involved in the regulation of the progesterone receptor gene. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1875–1883. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer M., Chalepakis G., Willmann T., Beato M. Binding of hormone accelerates the kinetics of glucocorticoid and progesterone receptor binding to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1123–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanjaard R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. Ligand-binding and heterodimerization activities of a conserved region in the ligand-binding domain of the thyroid hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8587–8591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G., Lange H., Philipson L., van Miltenburg R. T., van der Vliet P. C. High expression of functional adenovirus DNA polymerase and precursor terminal protein using recombinant vaccinia virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2431–2444. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. M., Darling D. S., Carter R. L., Forgione M., Umeda P. K., Chin W. W. Triiodothyronine (T3) decreases binding to DNA by T3-receptor homodimers but not receptor-auxiliary protein heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3565–3568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Magistris L., Stunnenberg H. G. Cis-acting sequences affecting the length of the poly(A) head of vaccinia virus late transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3141–3156. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Ashry D., Oñate S. A., Nordeen S. K., Edwards D. P. Human progesterone receptor complexed with the antagonist RU 486 binds to hormone response elements in a structurally altered form. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1545–1558. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]