Abstract
In a chemical screening, we tested the antiangiogenic effects of fumagillin derivatives and identified fumagillin as an inhibitor of definitive hematopoiesis in zebrafish embryos. Fumagillin is known to target methionine aminopeptidase II (MetAP2), an enzyme whose function in hematopoiesis is unknown. We investigated the role of MetAP2 in hematopoiesis by using zebrafish embryo and human umbilical cord blood models. Zebrafish metap2 was expressed ubiquitously during early embryogenesis and later in the somitic region, the caudal hematopoietic tissue, and pronephric duct. metap2 was inhibited by morpholino and fumagillin treatment, resulting in increased mpo expression at 18 hours postfertilization and reduced c-myb expression along the ventral wall of dorsal aorta at 36 hours postfertilization. It also disrupted intersegmental vessels in Tg(fli1:gfp) embryos without affecting development of major axial vasculatures. Inhibition of MetAP2 in CB CD34+ cells by fumagillin had no effect on overall clonogenic activity but significantly reduced their engraftment into immunodeficient nonobese diabetes/severe combined immunodeficiency mice. metap2 knock-down in zebrafish and inhibition by fumagillin in zebrafish and human CB CD34+ cells inhibited Calmodulin Kinase II activity and induced ERK phosphorylation. This study demonstrated a hithertoundescribed role of MetAP2 in definitive hematopoiesis and a possible link to noncanonical Wnt and ERK signaling.
Introduction
In vertebrates, hematopoiesis occurs in successive waves, ie, primitive and definitive, during embryonic development.1 In mammals, primitive hematopoiesis occurs transitorily in the yolk sac and is taken over by definitive hematopoiesis. In zebrafish embryos, primitive hematopoiesis is evident at 10 hours postfertilization (hpf) by the expression of stem cell leukemia (scl), lim-only domain protein 2 (lmo2), and gata2 genes at the posterior lateral plate mesoderm (LPM).2,3 It is mainly erythroid in lineage, as evident by the emergence of gata1 expression first in the LPM at 12 hpf and thereafter in the intermediate cell mass at 18 hpf. Primitive myelopoiesis arises from the anterior LPM, characterized by pu.1 expression at 12 hpf.4,5 The myeloid progenitors then migrate rostrally during 14-16 hpf and then laterally across the yolk sac. Granulocytes and macrophages are characterized by the expression of myeloperoxidase (mpo) and l-plastin.6,7
More recently, a transitory erythromyeloid progenitor has been described in the posterior blood island at 24 hpf.8 Definitive hematopoiesis arises at around 24 hpf from the ventral wall of the dorsal aorta, which is the equivalent of the aorto-gonado-mesonephro in mammals. Thereafter, the definitive HSCs, characterized by the expression of c-myb and runx1, migrate to the caudal hematopoietic tissue (CHT) and subsequently populate the thymus and kidney marrow, where life-long hematopoiesis occurs.9,10 In humans, umbilical cord blood (CB) is a rich source of HSCs during their migration from the fetal liver to BM at the perinatal period. HSCs in CB can be engrafted stably into the irradiated immunodeficient nonobese diabetes/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD/SCID) mouse during xenogeneic transplantation with multilineage differentiations11 and can be enriched by CD34+ selection.12
Methionine aminopeptidases (MetAPs) are cytosolic metalloproteinases that specifically remove the initiator NH2-terminal methionine from newly synthesized peptides.13,14 This step is essential for subsequent cotranslational modifications at the amino terminus, which determine the protein stability, functions, and cellular localization.15,16 In mammals, the family comprises MetAP1 and MetAP2, although the latter has received more attention for its binding to fumagillin and ovalicin, which are antiangiogenic and antineoplastic agents.17–20 In addition to the N-methionine excision, MetAP2 is also known as the eukaryotic initiation factor-2α–associated 67-kDa protein (p67) and can bind to and prevent phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor-2α and ERK1/2 under homeostatic and pathologic stress, thereby fine-tuning the level of cellular protein synthesis and proliferation.21 More recently, MetAP2 also has been shown to be an upstream component in the noncanonical Wnt pathway.22 Although these properties may contribute to the antiangiogenic and antineoplastic activity of fumagillin, it remains unclear whether they may contribute to the physiologic functions of MetAP2, particularly during embryonic development.
In early studies in Caenorhabditis elegans on the basis of siRNA knockdown, investigators demonstrated that metap2 is required for germ-cell proliferation.23 In Drosophila, reduction in metap2 activity resulted in specific eye and wing phenotypes in adults, suggestive of defective Wnt pathways.24 More recently, targeted disruption of metap2 in mice led to an embryonic gastrulation defect.25 However, early embryonic lethality has precluded further mechanistic studies in the embryos, even in the conditional knock-down model in which the mice survived beyond gastrulation. In zebrafish, knockdown of metap2 via the use of morpholino phenocopied the anteroposterior axis tail extension defect in Wnt5 morphants, implicating a link to noncanonical Wnt signaling.22 In a recent chemical screen with the use of zebrafish embryos to examine potential antiangiogenic activities from a panel of fumagillin derivatives, fumagillin was identified as an inhibitor of definitive hematopoiesis. Fumagillin is known to target MetAP2, whose function in hematopoiesis is completely unknown. In this study, we investigated the hematopoietic functions of metap2 during the embryonic development of zebrafish and also in human CB hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC)–enriched CD34+ cells.
Methods
Maintenance of zebrafish and collection of embryos
Zebrafish were maintained at 28°C as described previously.26 Wild-type zebrafish were obtained from local fish farm. Transgenic fish-lines Tg(top:gfp) and Tg (fli1:gfp) were obtained from ZIRC. Embryos were obtained by natural spawning and were maintained in E3 zebrafish water at 28.5°C and staged according to Kimmel et al.27 Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH), morpholino, mRNA microinjection, and real-time quantitative RT-PCR (Q-RT-PCR) for hematopoietic genes have been described previously (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).28,29 The study was approved by the Committee of the Use of Laboratory and Research Animals at the University of Hong Kong.
Amino acid sequence alignment and building of phylogenetic analysis
The amino acid sequences of the MetAPs family in various species were aligned by ClustalW (http://www.genome.jp/tools/clustalw). The sequence alignment demonstrating the evolutionary relationship between each MetAP was illustrated with the use of BioEdit (Version 7.0.5.3). A phylogenetic tree was built with the use of the neighbor-joining method and evaluated with the bootstrapping technique via a sampling of 500 replicates (MEGA 4.0).
Cloning of metap2, metap1, and metap2-like genes for riboprobes
The PCR products used for probe synthesis were amplified with gene-specific primers (supplemental Table 1), subcloned into pGEM-T vector (pGEM-T Vector Systems; Promega), and confirmed by DNA sequencing. The antisense riboprobes were synthesized by T7/SP6 RNA polymerase (Roche Applied Science). The size and integrity of the synthesized riboprobes were confirmed by RNA formaldehyde gel electrophoresis.
Real-time RT-PCR
Total RNA from embryos at different developmental stages was extracted from at least 20 whole embryos by the use of Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen) and reverse-transcribed to first strand cDNA with the use of the Superscript First-strand Synthesis System (Invitrogen). PCR amplified approximately a 100-bp segment from metap1, metap2, and metap2-like (supplemental Table 1), and expression was normalized with respect to β-actin.
Cloning of metap1 and metap2 mRNA for rescue assay
The entire coding sequence of metap1 and metap2 was amplified by PCR from the cDNA of 24 hpf embryos (supplemental Table 1). PCR products were TA-cloned by pGEM-T Vector Systems (Promega). To generate mRNA, metaps clones were linearized by digestion with ApaI and SacII (GE Healthcare) and in vitro transcribed with the mMessage mMachine Kit (Ambion). To increase the stability, mRNA was polyadenylated by the Poly(A) Tailing Kit (Ambion). The size and integrity of the synthesized mRNA were confirmed by RNA formaldehyde gel electrophoresis.
Human umbilical CB studies
Umbilical CB samples were prospectively collected, and mononuclear cells (MNCs) were purified by density gradient centrifugation (Ficoll-Paque Plus; Amersham Biosciences). CD34+ cells were selected by immunomagnetic methods (Miltenyi Biotec) with > 95% purity and cultured in StemSpan H3000 medium supplemented with cytokine mix CC100 (which contains Flt3-ligand, SCF, IL-3, and IL-6; StemCell Technologies) at 0.1-1 × 106 cells/mL for 3 days with fumagillin or the equivalent amount of vehicle as control. Cell numbers were enumerated by trypan blue exclusion and clonogenic activity by CFU in MethoCult GF H4434 (StemCell Technologies). In xenogeneic transplantation, progenies from 0.1-0.2 × 106 CD34+ cells treated for 3 days with fumagillin or vehicle were transplanted intravenously into NOD/SCID mice (γ-irradiated with 250 cGy and primed with anti-CD122 antibody [10 mg/kg] a day before transplantation). Human cells engraftment was determined by the presence of human CD45+/mouse CD45.1− cells in mouse marrow 6 weeks after transplantation. The mouse study was approved by the Committee of the Use of Laboratory and Research Animals in the University of Hong Kong.
GAPDH iso-electric point shifting assay
We dechorionated and lysed 18 hpf embryos in protein lysis buffer. Human CD34+ CB cells were cultured with vehicle or fumagillin for 3 days and lysed. GAPDH 2-dimensional electrophoresis and membrane transfer were performed at the Genome Research Center at the University of Hong Kong. First-dimension isoelectric focusing was performed with the use of 18-cm 6-9 pH linear isoelectric focusing strips, followed by 2-dimensional electrophoresis and membrane transfer. Membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk, followed by overnight incubation at 4°C with rabbit polyclonal anti-GAPDH antibody (1:2000; Abcam plc), and washed and incubated with HRP-linked electrochemiluminescence (ECL) donkey anti–rabbit IgG antibody (1:1000; Amersham Biosciences) at room temperature for 1 hour before detection with SuperSignal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate (Pierce) and Hyperfilm ECL (Amersham Biosciences).
Calmodulin kinase II assay
Protein samples from zebrafish embryos and human CB CD34+ cells were prepared by hypotonic lysis buffer and RIPA buffer in the presence of protease and phosphatase inhibitors cocktail. A protein sample (5 μL), assay dilution buffer I (ADBI, 15 μL, CaM Kinase II Assay Kit; Millipore), CaMKII substrate cocktail (10 μL), PKA/PKC inhibitor cocktail (10 μL), and [γ32P] ATP cocktail (10 μL, NENSure Packaging System; PerkinElmer) were mixed and incubated for 10 minutes at 30°C with constant agitation. An aliquot of the mixture (25 μL) was spotted on the numbered P81 paper (phosphocellulose squares). The assay squares were washed 3 times with phosphoric acid (0.75%), followed by acetone for 5 minutes to eliminate low specific binding and to hasten the drying. The assay squares were transferred to a scintillation vial containing a scintillation cocktail. [γ32P] activity, a surrogate of CamKII activity, was enumerated in counts per minute with a scintillation counter. Negative control for each sample was set up as described previously with 5 μL of ADBI in the reaction mixture being replaced by 5 μL of a soluble CamKII inhibitor (Calmodulin Kinase IINtide, at 1 mg/mL; Calbiochem, EMD Chemicals Inc).
Flow cytometry with Tg (top:gfp) zebrafish line
A transgenic Tg(top:gfp) zebrafish line, in which green fluorescence indicated β-catenin signaling,30 was used to examine the link between metap2 and β-catenin signaling. In each experiment, 20 Tg(top:gfp) embryos at 24 hpf were digested with trypsin/EDTA (0.05%) for 15 minutes at 28.5°C and dissociated to single-cell suspension by repeated pipetting. Trypsin digestion was terminated by 10 μL of CaCl2 (0.1mM). The percentage of gfp+ cells was evaluated by the use of flow cytometry (Cytomics FC 500MPL; Beckman).
Western blotting
Total protein samples were isolated by homogenizing 50 zebrafish embryos at 18 hpf in 50 μL of protein extraction buffer and boiled for 3 minutes. Human CB CD34+ cells cultured with vehicle or fumagillin for 3 days were lysed in RIPA buffer in presence of protease and phosphatase inhibitors cocktail. Protein extracts were fractionated in a 10% (wt/vol) SDS polyacrylamide gel and electro-transferred to nitrocellulose membrane (Protran; PerkinElmer Life Science). The membrane was then blocked, incubated with the primary antibodies (anti–β-actin [1:10 000; Sigma-Aldrich]; anti–β-catenin [1:500], anti-total ERK1/2 and anti-ERK1/2 phospho-T202/Y204 antibodies [1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology]), washed in TBST (TBS + 0.05% [vol/vol] Tween20), and incubated with secondary HRP-linked ECL sheep antimouse IgG antibody (1:1000; Amersham Biosciences). The membrane was washed with TBST and TBS again and detected with SuperSignal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate (Pierce) and Hyperfilm TM ECL (Amersham Biosciences).
Confocal microscopy and imaging
In experiments in which embryos were examined by confocal microscopy, the embryos at 48 hpf were embedded live in 1% low-melting-point agarose (Sigma-Aldrich) and photographed by a Zeiss LSM510 Meta confocal microscope with a 10× objective (Carl Zeiss International) provided by Faculty Imaging Core Facility, LKS Faculty of Medicine, Hong Kong University. Other fluorescent images were taken under Olympus IX70 (Olympus Corporation) and 10×/0.3 NA objective in 3% methylcellulose, with Olympus DP71 (Olympus Corporation) and Olympus DP-BSW basic Software, processed with Adobe Photoshop Version 7.0 (Adobe Systems Inc). Bright-field images were taken under Nikon SMZ800 (Nikon Hong Kong Ltd) and P-Plan 1× objective in 3% methylcellulose with Nikon Digital Sight DS-Fi1 (Nikon Hong Kong Ltd) and processed with Adobe Photoshop Version 7.0.
Statistical analysis
Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Comparisons between numerical data were evaluated by the Student t test. A P value < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
MetAPs were highly conserved
Four metap homologues were identified in zebrafish genome, of which 2 were classified as type II (namely metap2 and metap2-like) and 2 as type I (metap1 and metap1d). Zebrafish metap2 and metap2-like protein share 77% and 78% amino acid sequence identity, respectively, to human MetAP2. The 2 genes also share the residues essential for the interaction with cobalt and fumagillin13,14 as well as a highly conserved region in the catalytic domain unique to the MetAP2 family (supplemental Figure 1). Zebrafish metap2 and metap2-like genes reside in different chromosomes, suggesting that they might arise from the duplication of a genome segment during early teleost development (supplemental Figure 2). Zebrafish metap1 and metap1d protein shared 86% and 65% sequence identity, respectively, with the human orthologs. The 2 zebrafish proteins also shared the putative zinc finger- and cobalt-coordinating residues (supplemental Figure 1).31
Gene expression profiling of metap-2
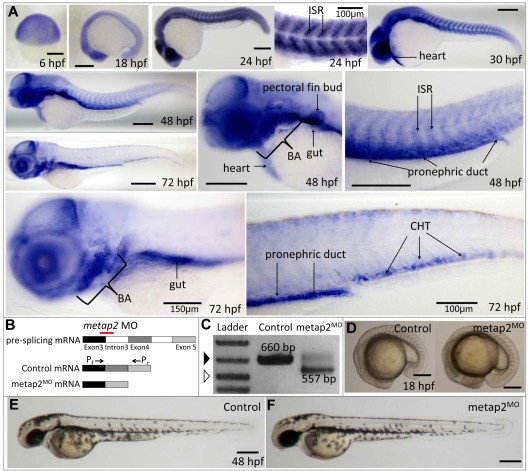
Zebrafish metap2 expression was first detectable at 0 hpf, indicating maternal transcripts (supplemental Figure 3). Thereafter, zygotic gene expression was evident as early as 6 hpf and maintained up to 24 hpf. WISH demonstrated ubiquitous metap2 expression at 6 hpf. At 2 hpf, it was expressed predominantly in eye, brain, and the intersomitic regions and at 30 hpf, it was also expressed in the developing heart. At 48 hpf, metap2 gradually lost its expression in the intersomitic region and became diffusely expressed in the head region, developing heart, pectoral fin bud, brachial arches, gut, and pronephric duct. Later at 72 hpf, its intersomitic and heart expression were almost absent but diffusely expressed in head region and also in the brachial arches, gut, pronephric duct and CHT (Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
Expression of metap2 during embryonic development and metap2 knockdown with morpholino. (A) WISH showing the spatial expression of metap2 at different developmental stages. BA indicates brachial arches; ISR, intersomitic region. (B) Diagram of the action of the metap2 morpholino. Red line represents the binding site of the splice-junction targeted metap2 morpholino, and arrows represent the binding sites of the forward (Pf) and reverse primers (Pr) used for PCR amplification to detect defective splicing of exon4. (C) Defective splicing of metap2 mRNA in metap2MO as shown by the presence of the smaller 557-bp band, which is absent in the control. Open arrowhead, 500-bp DNA ladder; filled arrowhead, 650-bp DNA ladder. (D) General morphology of metap2MO (122 of 131 embryos in 3 separate experiments) compared with the control at 18 hpf (137/145, n = 3). (E-F) General morphology of metap2MO (F; 109/129, n = 3) compared with the control (E; 132/142, n = 3) at 48 hpf. Bars represent 250 μm unless otherwise stated.
Knockdown of metap2 expand primitive myelopoiesis and affect the initiation of definitive HSC
We then examined the role of metap2 in embryonic hematopoiesis. metap2 was knocked down by morpholino targeting at the junction between exon3 and intron3 (Figure 1B). The embryos (referred herewith metap2MO embryos) could tolerate up to 4.5 ng without significant embryonic toxicities, and this dose was injected throughout the study. Molecular targeting was confirmed by RT-PCR at 24 hpf and demonstrated abnormal splicing of exon4, and, hence, a smaller PCR product of 557 bp, instead of 660 bp, in control embryos (Figure 1C). Defective splicing in metap2MO embryos resulted in frame-shift of metap2 protein after amino acid 106 and premature termination after amino acid 154 (supplemental Figure 4A). The effect of morpholino decreased significantly at 96 hpf (supplemental Figure 4B).
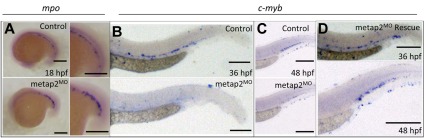
Despite the knockdown of metap2, there was no morphologic abnormality in metap2MO embryos up to 48 hpf (Figure 1E-F). A small portion (< 20%) of metap2MO embryos demonstrated deformity during embryonic development with smaller head, eye, reduced yolk extension, and curved tail (Supplemental Figure 4C) and were excluded from further analysis. We examined the effect of metap2 knockdown on primitive hematopoiesis at 18 hpf, before the onset of circulation. Genes associated with early HSC development (scl), erythropoiesis (gata1, α-eHb1), early myeloid development (pu.1), and macrophages (l-plastin) were not affected (supplemental Figure 5). However, those associated with late myeloid differentiation, myeloperoxidase (mpo), were significantly increased (Figure 2A). These results were confirmed with Q-RT-PCR (Table 1).
Figure 2.
Knockdown of metap2 affected embryonic hematoporesis. (A) WISH comparing expression of mpo at 18 hpf between control and metap2MO (control, 90.6% ± 0.8% with normal mpo expression in total 85 embryos; metap2MO, 72.1% ± 2.6% with increased mpo expression in total 68 embryos; n = 3). (B-C) WISH comparing expression of c-myb between control and metap2MO at 36 hpf (B; control, 93.8% ± 1.3% in total 128 embryos with normal c-myb expression; metap2MO, 82.6% ± 2.7% in total 121 embryos with reduced c-myb expression; n = 5) and 48 hpf (C; control, 89.2% ± 1.0% in total 148 embryos with normal c-myb expression; metap2MO, 78.9% ± 3.0% in total 147 embryos with reduced c-myb expression; n = 5). (D) WISH showing the expression of c-myb at 36 (rescued c-myb expression, 75.3% ± 3.8% in total 72 embryos, n = 3) and 48 hpf (rescued c-myb expression, 77.0% ± 4.0% in total 87 embryos, n = 3) in metap2MO rescued by metap2 mRNA. Bars represent 250 μm.
Table 1.
Fold-change of gene expression associated with primitive hematopoiesis in metap2MO embryos at 18 hpf
| Gene | Control | metap2MO | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| scl | 1.00 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | .17 |
| lmo2 | 1.00 | 0.92 ± 0.08 | .15 |
| gata1 | 1.00 | 1.24 ± 0.07 | .17 |
| ehα1 | 1.00 | 1.14 ± 0.12 | .43 |
| ehβ1 | 1.00 | 1.18 ± 0.08 | .25 |
| pu.1 | 1.00 | 1.24 ± 0.05 | .07 |
| l-plastin | 1.00 | 0.99 ± 0.09 | .25 |
| mpo | 1.00 | 2.06 ± 0.10 | .02 |
Comparison of gene expression between control and the metap2MO embryos in each case was based on ΔCt as described previously. Statistical analysis was evaluated by the Student paired t test. Data as shown represent the average results of 3 experiments.
At 36 hpf, initiation of definitive HSC in the ventral wall of dorsal aorta, as evident by c-myb expression, was reduced in the metap2MO embryos (Figure 2B). The number of c-myb–expressing HSCs remained significantly reduced in metap2MO at 48 hpf when normal HSC migrated to CHT in control embryos (Figure 2C). The results were confirmed by the use of Q-RT-PCR (control, 1.00; metap2MO, 0.32 ± 0.08, P = .01). To examine whether the reduction in HSCs were associated with increased apoptosis, we performed a whole-mount TUNEL assay but found no increase in apoptotic signal along the ventral wall of dorsal aorta at 36 hpf or at CHT at 48 hpf in metap2MO embryos (supplemental Figure 6). To confirm the specificity of metap2 targeting, we coinjected metap2 mRNA up to 25 pg into metap2MO embryos at 1-cell stage and significantly reversed mpo up-regulation at 18 hpf (Table 2) and c-myb down-regulation at 36 and 48 hpf (Table 2, Figure 2D).
Table 2.
Fold-change of mpo (18 hpf) and c-myb (48 hpf) expression in metap2MO coinjected with metap1, metap2 or metap2-like mRNA
| Gene | mpo | P value | c-myb | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 1.00 | N/A | 1.00 | N/A |
| metap2MO | 2.29 ± 0.07 | .04 | 0.28 ± 0.11 | .01 |
| metap1 mRNA | 2.06 ± 0.09 | .04 | 0.38 ± 0.17 | .02 |
| metap2 mRNA | 1.52 ± 0.07 | .05 | 0.75 ± 0.12 | .04 |
| metap2-like mRNA | 2.35 ± 0.12 | .05 | 0.31 ± 0.09 | .02 |
Data as shown represent the average results of 3 experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with the Student paired t test to compare between control and metap2MO coinjected with different metap mRNA.
N/A indicates not available.
Hematopoietic function was specific to metap2 but not other zebrafish metap(s)
Because the expression pattern of other known zebrafish metaps during early embryogenesis were similar to metap2 (supplemental Figure 7A-B), we examined whether there was any functional redundancy between metap2 and other zebrafish metaps, including metap1 and metap2-like. Neither the up-regulation of mpo at 18 hpf nor the down-regulation of c-myb at 36 hpf in metap2MO could be rescued by coinjecting metap1 or metap2-like mRNA as shown by Q-RT-PCR (Table 2). Sharing the highest amino acid sequence similarity with metap2, knockdown of metap2-like by MO (supplemental Figure 8) could not recapitulate the hematopoietic phenotypes observed in metap2MO (supplemental Table 2).
metap2 knockdown perturbed angiogenesis
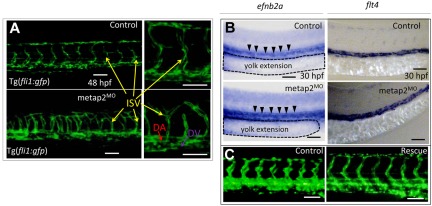
Because inhibition of MetAP2 may inhibit angiogenesis in tumors,16,20,21 we examined the effect of metap2 knockdown on angiogenesis in our zebrafish model. In metap2MO embryos with a Tg(fli1:gfp) transgenic background, vasculogenesis was normal (Figure 3A). Specification of dorsal aorta and dorsal vein at 30 hpf as shown by WISH of arterial (efnb2a; Figure 3B) and venous (flt4) markers (Figure 3B) were unaffected. Axial circulation at 36 hpf was normal in metap2MO embryos (supplemental Videos 1-2). However, angiogenesis as shown by sprouting of intersegmental vessels (ISVs) was significantly perturbed at 48 hpf (Figure 3A) but could be rescued by coinjecting metap2 mRNA (Figure 3C).
Figure 3.
Knockdown of metap2 perturbed angiogenesis but not vasculagenesis. (A) Confocal microscopy of Tg(fil1:gfp) at 48 hpf comparing the development of dorsal aorta (DA), dorsal vein (DV), and intersegmental vessel (ISV) in the trunk region between control and metap2MO. (B) WISH comparing expression of efnb2a (control, 92.4% ± 2.3% with normal efnb2a expression in total 92 embryos; metap2MO, 91.4% ± 2.7% with normal efnb2a expression in total 93 embryos; n = 3) and flt4 (control, 95.5% ± 1.4% with normal flt4 expression in total 88 embryos; metap2MO: 95.3% ± 1.0% with normal flt4 expression in total 86 embryos; n = 3) at 30 hpf between control and metap2MO. Black arrowheads denote efnb2a expression along DA, and the dashed line outlines the extension of the yolk. (C) Fluorescent microscopy of Tg(fil1:gfp) at 48 hpf comparing the development of DA, DV, and ISV in the trunk region between control and metap2MO rescued by metap2 mRNA (control, 96.8% ± 1.4% with normal ISV patterning in total 93 embryos; metap2MO, 80.3% ± 3.4% with perturbed ISV patterning in total 71 embryos; metap2MO rescue, 72.5% ± 4.0% with normal ISV patterning in total 80 embryos; n = 3). Bars represent 50 μm.
metap2 inhibitor recapitulated the phenotypes of metap2MO embryos
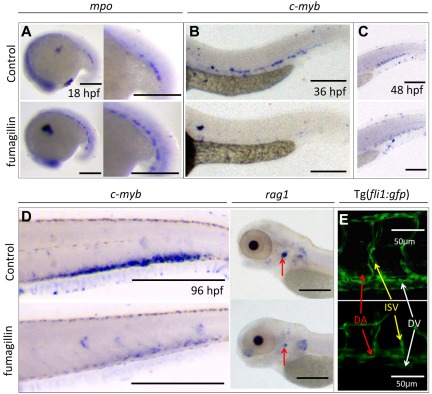
Fumagillin, isolated from a contaminating Aspergillus fumagatus colony in endothelial cell cultures, has been used as a prototypic agent inhibiting MetAP2 activity. We tested whether fumagillin could recapitulate the hematopoietic and antiangiogenic phenotypes of metap2MO embryos. Fumagillin at 10μM was tolerable without significant toxicity. Treatment up to 18 hpf significantly up-regulated mpo expression at 18 hpf (Figure 4A) and reduced c-myb expression at 36 and 48 hpf (Figure 4B-C). At 96 hpf, the expression of c-myb and rag-2 (lymphoid progenitors) remained significantly lower than that of the control (Figure 4D). At 48 hpf, patterning of ISV also was affected in fumagillin-treated embryos (Figure 4E). These changes were reminiscent of the phenotypes of metap2MO embryos.
Figure 4.
Fumagillin treatment recapitulated the effect of metap2 knockdown. (A) WISH comparing expression of mpo between control and fumagillin-treated embryo at 18 hpf (control, 92.8% ± 1.0% with normal mpo expression in total 69 embryos; fumagillin treatment, 69.5% ± 2.5% with increased mpo expression in total 59 embryos; n = 3). (B) WISH comparing expression of c-myb between control and fumagillin-treated embryo at 36 hpf (control, 94.1% ± 1.5% in total 101 embryos with normal c-myb expression; fumagillin treatment, 78.7% ± 3.9% in total 108 embryos with reduced c-myb expression; n = 3). (C) WISH comparing expression of c-myb between control and fumagillin-treated embryo at 48 hpf (control, 94.2% ± 1.5% in total 103 embryos with normal c-myb expression; fumagillin treatment, 75.7% ± 2.4% in total 107 embryos with reduced c-myb expression; n = 3). (D) WISH comparing expression of c-myb (control, 93.1% ± 2.8% in total 102 embryos with normal c-myb expression; fumagillin treatment, 73.0% ± 4.3% in total 89 embryos with reduced c-myb expression; n = 3) and rag1 (red arrow; control, 90.2% ± 1.1% in total 112 embryos with normal rag1 expression; fumagillin treatment, 78.3% ± 2.9% in total 106 embryos with reduced rag1 expression; n = 3) between control and fumagillin-treated embryo at 96 hpf. (E) Confocal microscopy of Tg(fil1:gfp) at 48 hpf comparing the development of dorsal aorta (DA), dorsal vein (DV), and intersegmental vessel (ISV) in the trunk region between control and fumagillin treated embryo (control, 96.6% ± 1.3% in total 116 embryos with normal ISV patterning; fumagillin treatment, 70.3% ± 3.4% in total 118 embryos with perturbed ISV patterning; n = 3). Bars represent 250 μm unless otherwise stated.
metap2 MO and fumagillin modulated N-methionine excision activity of metap2
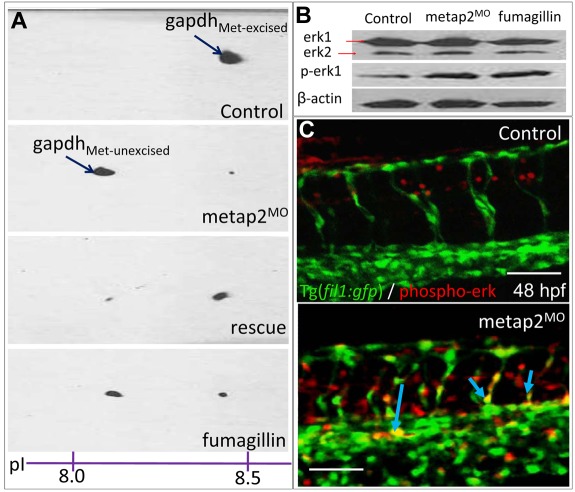
The ubiquitous GAPDH protein undergoes cotranslational modification, including the removal of N-terminal methionine by MetAP2, resulting in a shift in isoelectric point (pI). Therefore, the pI of GAPDH could be used as a surrogate for MetAP2 N-methionine excision activity.20 At both 18 (data not shown) and 36 hpf, 2-dimensional electrophoresis and Western blotting confirmed the pI shifting of GAPDH, hence the abnormal retention of N-terminal methionine in GAPDH and reduced metap2 activity in zebrafish embryos injected with metap2 MO or treated with fumagillin. The activity could be rescued by metap2 mRNA coinjection (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
Inhibition of metap2 in zebrafish embryo affected N-methionine excision and erk phosphorylation. (A) GAPDH pI shifting assay showing Met-excised gapdh protein with a pI of approximately 8.4 and Met-unexcised GAPDH in metap2MO or fumagillin-treated embryos with a lower pI at approximately 8.2. Met-excised gapdh protein with a pI at approximately 8.4 was recovered in metap2MO rescued by metap2 mRNA. (B) Western blot comparing the level of total and phospho-erk1/2 between control, metap2MO, and fumagillin-treated embryos normalized with β-actin. (C) Whole-mount immunostaining of phosphor-erk in Tg(fil1:gfp) at 48 hpf (control, 0 of 99 embryos showed ectopic erk phosphorylation; metap2MO, 71.4% ± 3.2% in total 98 embryos showed ectopic erk phosphorylation; n = 4). Red indicates phospho-erk signal; green, endothelial cell; and yellow, phospho-erk signal colocalized with endothelial cell. Bars represent 50 μm
metap2 MO and fumagillin affected noncanonical Wnt signaling
The authors of in vitro studies have positioned MetAP2 in the noncanonical Wnt pathway upstream of Dishevelled.22 This led us to examine the link between metap2 and noncanonical Wnt signaling, whose roles in embryos hematopoiesis are unknown. Calmodulin kinase II (camkII), which plays an integral part in the noncanonical Wnt pathway, showed a significant reduction in activity (0.69 ± 0.03-fold compared with control embryos, P = .01) at 18 hpf in metap2MO embryos. The response could be ameliorated by metap2 mRNA coinjection (0.82 ± 0.06-fold, P = .04). Similar suppression of camkII activity was observed at 36 hpf (metap2MO: 0.53 ± 0.09-fold, P = .01; Rescue: 0.78 ± 0.05-fold, P = .02). camkII activity was also inhibited, albeit modestly, by fumagillin treatment at both stages (18 hpf: 0.76 ± 0.02-fold, P = .04; 36 hpf: 0.69 ± 0.07-fold, P = .02).
metap2 MO had no effect on the canonical Wnt pathway
We next tested whether metap2 knock-down would also have an effect on canonical Wnt pathway. At 18 hpf, injection of metap2 MO or treating the embryos with fumagillin had no effect on either the level of β-catenin protein by Western blotting (supplemental Figure 9A) or β-catenin signaling as enumerated by the gfp+ population in dissociated Tg(top:gfp) transgenic embryos (supplemental Figure 9B).
metap2 MO and fumagillin induced ectopic erk1 kinase phosphorylation mainly in endothelial cells
Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was known to be modulated by MetAP2.32,33 At 36 hpf, metap2MO or fumagillin-treated zebrafish embryos exhibited a greater erk1 phosphorylation level on Thr202 and Tyr204 (Figure 5B). There was ectopic erk phosphorylation in developing vasculature, as shown by the colocalized phospho-erk and GFP signal in Tg(fli1:gfp) injected with metap2 MO (Figure 5C). Interestingly, a MEK inhibitor at 10μM (U0126; Calbiochem, EMD Chemicals Inc) upstream of ERK1/2 also perturbed angiogenesis (supplemental Figure 10A) but had no effect on HSC initiation on its own and could not rescue the HSC initiation defect in metap2MO (supplemental Figure 10B).
Human MetAP2 was expressed preferentially in a CB CD34+ fraction
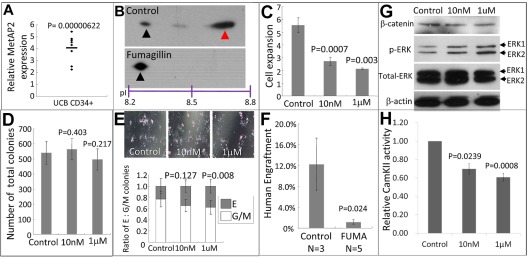
The aforementioned study in “Knockdown of metap2 expand primitive myelopoiesis and affect the initiation of definitive HSC” demonstrated a possible role of metap2 in the initiation of definitive hematopoiesis in zebrafish. However, metap2 expression was rather ubiquitous and not specific to the sites of definitive hematopoiesis. To further delineate the role of MetAP2 in hematopoiesis, we examined MetAP2 expression in human CB CD34+ (HSPC-enriched) and CD34− (HSPC-deprived) cells. MetAP2 expression in CD34+ fraction was significantly greater than that of CD34−, as revealed by Q-RT-PCR (4.06 ± 0.40-fold, P = .00; Figure 6A).
Figure 6.
Inhibition of MetAP2 affected human HSPCs proliferation, differentiation, and engraftment potential. (A) Relative expression of MetAP2 in CB cells revealed by Q-RT-PCR between CD34+ fraction and unfractionated CB MNC (of which ∼ 99% cells are CD34−). MetAP2 expression in unfractionated CB MNC was normalized to 1. N = 8. (B) GAPDH pI shifting assay showing Met-excised GAPDH protein (red arrowhead) with a greater pI and Met-unexcised (black arrowhead) GAPDH in control or fumagillin-treated CB CD34+ cells with a lower pI. (C) Fold change of cell number after 3 days of DMSO (control) or fumagillin treatment (at 10nM or 1μM) of CB CD34+ cells. A total of 0.1-0.25 million cells were treated with vehicle 10nM or fumagillin for 3 days. After treatment, viable cells were enumerated by trypan blue exclusion. N = 5 and the cell numbers at day 0 were normalized to 1. (D) Total number of colonies formed in colony-forming assay between control and fumagillin treated CB CD34+ cells. After 3 days of treatment, 3000 cells (from vehicle) and cell numbers proportional to its expansion (fumagillin-treated) were cultured in methylcellulose medium H4434 without fumagillin for 14 days and total colonies numbers were counted. N = 3. (E) Lineages of colonies in colony-forming assay. Images of colonies acquired 14 days after cells plated (top). Erythroid colonies and granulocyte/macrophage colonies were enumerated and their ratio of were shown (bottom). N = 3. (F) BM engraftment of CB CD34+ cells after vehicle or fumagillin treatment in NOD/SCID mice at 6 weeks after transplantation. Human cells engraftment was determined by human CD45-positive, mouse CD45.1-negative fraction. The comparisons were evaluated by the Student t test. (G) Western blot comparing the level of β-catenin, total and phospho-ERK1/2 between control and fumagillin treated CB CD34+ cells normalized with β-actin. (H) Relative CamKII activity in CD34+ CB cells treated with vehicle, 10nM or 1μM fumagillin for 3 days.
MetAP2 inhibition by fumagillin perturbed human HSPCs proliferation, differentiation, and engraftment potential in NOD/SCID mice
CB CD34+ cells were treated with either vehicle or fumagillin (10nM) for 3 days and N-methionine excision activity was examined by GAPDH pI shifting assay. Similar to the zebrafish model, fumagillin significantly reduced MetAP2 activity (Figure 6B). Furthermore, it significantly reduced expansion of cell numbers in culture (Figure 6C). Cells that were pretreated with fumagillin before being plated for the clonogenic assay did not affect the total number of colonies (Figure 6D), but there was more erythroid relative to myeloid colonies (Figure 6E). If fumagillin was also present in methylcellulose medium, clonogenic activities were inhibited (supplemental Figure 11), suggesting the cell proliferation was affected by treatment with fumagillin. At the HSC level, CD34+ CB cells treated with fumagillin significantly reduced human cell engraftment in NOD/SCID mice (Figure 6F) 6 weeks after transplantation without any significant skewing in lineage differentiation (supplemental Figure 12).
Treatment with fumagillin induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation and reduced CamKII activity in a CB CD34+ fraction
To understand the mechanism of action of fumagillin in CB CD34+ cells, we examined both CamKII activity and ERK1/2 phosphorylation on fumagillin treatment. Similar to the observations in zebrafish embryos, fumagillin induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation on Thr202 and Tyr204 (Figure 6G) and significantly reduced CamKII activity (Figure 6H).
Discussion
In this study, we demonstrated by using morpholino gene knock-down and fumagillin treatment that inhibition of metap2 significantly reduced definitive hematopoiesis and perturbed angiogenesis during zebrafish development as well as HSPC activity in human CB CD34+ cells. The phenotypes in zebrafish embryos were specific to metap2, and knockdown of a closely related metap2-like by MO had no effect on hematopoietic development. Defective initiation of definitive hematopoiesis was also shown by reduced rag1 expression in fumagillin-treated embryos at 96 hpf. The effects of metap2 MO at this development stage were not apparent (A.C.H.N. and A.Y.H.L., unpublished observations, September 2, 2010) because metap2 knockdown was transitory, as shown by RT-PCR at 96 hpf. Because Wnt16 of the noncanonical Wnt pathway might induce notch ligand expression in zebrafish somites to regulate HSC specification without affecting vascular development,34 our observation further supported the notion that metap2 might regulate HSC specification through noncanonical Wnt and Notch pathways in the ventral wall of dorsal aorta in a noncell autonomous fashion. metap2 was robustly expressed in the CHT and pronephric duct at 72 hpf. Therefore, in addition to HSC initiation, metap2 might play a role in HSC maintenance, proliferation, or migration to developing kidney marrow.
To address this issue, we made use of the xenogeneic transplantation model and showed that fumagillin reduced NOD/SCID repopulating activity of CB CD34+ cells. Therefore, at least in humans, MetAP2 may play a cell-autonomous role in maintaining HSPC activity. Continuous treatment of CB CD34+ cells with fumagillin reduced cell expansion in culture. However, a brief treatment for 3 days had no effect on total CFU but significantly reduced the NOD/SCID repopulating cell activity. The latter findings were consistent with the greater MetAP2 expression in purified CD34+ cells (relatively enriched with HSPC) and suggested that HSPC might be more sensitive to MetAP2 inhibition than its progenitors.
In addition to their effects on definitive HSC, both metap2MO and fumagillin-treated embryos demonstrated up-regulation of mpo at 18 hpf. pu.1 expression was not affected, suggesting that metap2 might specifically modulate late myeloid cell differentiation during primitive hematopoiesis. Intriguingly, the treatment of human CB CD34+ cells with fumagillin did not recapitulate the myeloid phenotype of metap2MO or fumagillin-treated zebrafish embryos. Therefore, in contrast to their conserved effects on HSC, MetAP2 could have distinctive effects on myeloid differentiation in zebrafish and human CB. The effects of metap2 knockdown on erythromyeloid progenitor8 at 24 hpf have not been determined.
Furthermore, we demonstrated that metap2 knockdown and fumagillin treatment perturbed angiogenesis in Tg(fli1:gfp) embryos at 48 hpf. Vasculogenesis was intact as shown by the normal specification of dorsal aorta and dorsal vein as well as axial circulation at 36 hpf, when early HSC specification has already occurred. Therefore, the defect in HSC initiation in metap2MO embryos indicated a direct effect on HSC but not the developing vasculature. The ectopic phosphorylation of erk1/2 in the endothelial cells was consistent with our findings in human CB and those of others32,33 that MetAP2 modulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation and provided a possible mechanistic link between metap2, erk1/2 signaling and angiogenesis. Interestingly, inhibiting erk1/2 phosphorylation in zebrafish embryos with a MEK inhibitor also perturbed ISV sprouting.35 Therefore, erk1/2 signaling in zebrafish embryos might be strictly regulated and either stimulation or inhibition could disrupt angiogenesis. Intriguingly, MEK inhibitor had no effects on HSC initiation nor did it rescue the HSC initiation defect in metap2MO embryos.
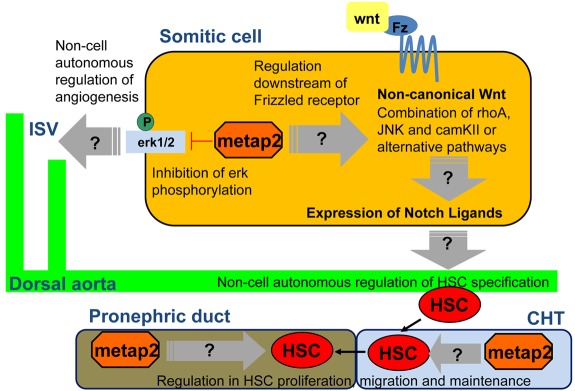
The results have provided us with a tentative model about the regulation of definitive hematopoiesis (Figure 7). During zebrafish embryonic development, metap2 that is expressed in somitic/intersomitic regions may activate the noncanonical Wnt pathway downstream to the frizzled receptor.22 This results in specification of definitive HSC in the ventral wall of dorsal aorta via activation of Notch pathway.34 Later in development, metap2 may play a direct effect on the maintenance and migration of definitive HSC in the CHT and developing kidney marrow. In addition, metap2 modulates erk1/2 phosphorylation, whose level is strictly regulated for angiogenesis.
Figure 7.
The multifunctional model of metap2 in definitive hematopoiesis and angiogenesis during zebrafish embryonic development. Fz indicates frizzled receptor.
This model has generated several hypotheses that can be tested in future studies. For instance, N-methionine excision by metap2 is the first step of protein posttranslational modification, and the gene is expressed ubiquitously during embryonic development. The specific defects in hematopoiesis and HSPC activity on inhibition of metap2 suggested that posttranslational modification of yet-identified target polypeptides may be rate-limiting for definitive HSC initiation and proliferation in both zebrafish and human. The results also corroborated with the recent study that mutation of a similarly ubiquitous gene cpsf1 in zebrafish led to specific defects of HSC.36
The mechanisms of action of metap2 have remained unclear. Although inhibition of metap2 in both zebrafish and human CB significantly reduced CamKII activity, a direct link between CamKII, the noncanonical Wnt pathway, and HSC initiation has yet to be determined. Preliminary studies demonstrated that inhibitors of CamKII, JNK, and RhoA failed to recapitulate the hematopoietic phenotypes of metap2MO embryos (data not shown). Therefore, multiple or alternative signaling pathways downstream to metap2 might be involved in the regulation of definitive hematopoiesis. Both Go proteins and phosphatase PP2A are potential targets of MetAP2,22 and their roles in embryonic hematopoiesis would have to be critically examined. Furthermore, the expression of metap2 in the intersomitic region correlated with those of vascular and endothelial growth factors,37 fibroblast growth factors,38 or stromal cell-derived factor.39 Whether they might mediate the hematopoietic and angiogenic changes in metap2MO embryos would also have to be further evaluated.
Our results were of clinical significance. MetAP2 expression is up-regulated in various human cancers, including mesothelioma,40 B-cell lymphomas,41 colorectal adenocarcinoma,42 neurofibromatosis 1–associated human astrocytic tumor,43 as well as cholangiocarcinoma,44 and modulation of MetAP2 activity could present a target for therapeutic intervention.45–47 The zebrafish model offers a unique opportunity in which the effects of metap2 modulation on hematopoietic and endothelial cells can be simultaneously examined and its high-throughput nature can enable pharmacologic screening for the rapid identification of therapeutic agents.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the General Research Fund (GRF; HKU 771110M) and an Innovative Collaborative Research Program from the LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong.
Footnotes
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: A.C.H.M. and T.K.F. conducted the study and wrote the manuscript; R.L. and M.I.S.C. conducted part of the zebrafish embryo microinjection and WISH experiments; D.Y. initiated the chemical screening of fumagillin; S.C.E. provided suggestions and technical support during the revision of the manuscript; and A.Y.H.L. designed the research, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Dr. Anskar YH Leung, Room K418, K Block, Department of Medicine, Queen Mary Hospital, Pok Fu Lam Road, Hong Kong; e-mail: ayhleung@hku.hk.
References
- 1.Orkin SH, Zon LI. Hematopoiesis: an evolving paradigm for stem cell biology. Cell. 2008;132(4):631–644. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen AT, Zon LI. Zebrafish blood stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(1):35–42. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Davidson AJ, Zon LI. The ‘definitive’ (and ‘primitive’) guide to zebrafish hematopoiesis. Oncogene. 2004;23(43):7233–7246. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Berman JN, Kanki JP, Look AT. Zebrafish as a model for myelopoiesis during embryogenesis. Exp Hematol. 2005;33(9):997–1006. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2005.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Crowhurst MO, Layton JE, Lieschke GJ. Developmental biology of zebrafish myeloid cells. Int J Dev Biol. 2002;46(4):483–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shepard JL, Zon LI. Developmental derivation of embryonic and adult macrophages. Curr Opin Hematol. 2000;7(1):3–8. doi: 10.1097/00062752-200001000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Herbomel P, Thisse B, Thisse C. Ontogeny and behaviour of early macrophages in the zebrafish embryo. Development. 1999;126(17):3735–3745. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.17.3735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bertrand JY, Kim AD, Violette EP, Stachura DL, Cisson JL, Traver D. Definitive hematopoiesis initiates through a committed erythromyeloid progenitor in the zebrafish embryo. Development. 2007;134(23):4147–4156. doi: 10.1242/dev.012385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jin H, Xu J, Wen Z. Migratory path of definitive hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells during zebrafish development. Blood. 2007;109:5208–5214. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-069005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Murayama E, Kissa K, Zapata A, et al. Tracing hematopoietic precursor migration to successive hematopoietic organs during zebrafish development. Immunity. 2006;25:963–975. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cashman J, Bockhold K, Hogge DE, Eaves AC, Eaves CJ. Sustained proliferation, multi-lineage differentiation and maintenance of primitive human haemopoietic cells in NOD/SCID mice transplanted with human cord blood. Br J Haematol. 1997;98(4):1026–1036. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.3233140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Krause DS, Fackler MJ, Civin CI, May WS. CD34: structure, biology and clinical utility. Blood. 1996;87(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wiltschi B, Merkel L, Budisa N. Fine tuning the N-terminal residue excision with methionine analogues. Chembiochem. 2009;10(2):217–220. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lowther WT, Matthews BW. Structure and function of the methionine aminopeptidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1477(1-2):157–167. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(99)00271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hu X, Dang Y, Tenney K, et al. Regulation of c-Src nonreceptor tyrosine kinase activity by bengamide A through inhibition of methionine aminopeptidases. Chem Biol. 2007;14(7):764–774. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.05.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Selvakumar P, Lakshmikuttyamma A, Dimmock JR, Sharma RK. Methionine aminopeptidase 2 and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1765(2):148–154. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2005.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sin N, Meng L, Wang MQ, Wen JJ, Bornmann WG, Crews CM. The anti-angiogenic agent fumagillin covalently binds and inhibits the methionine aminopeptidase, MetAP-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(12):6099–6103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Addlagatta A, Hu X, Liu JO, Matthews BW. Structural basis for the functional differences between type I and type II human methionine aminopeptidases. Biochemistry. 2005;44(45):14741–14749. doi: 10.1021/bi051691k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liu S, Widom J, Kemp CW, Crews CM, Clardy J. Structure of human methionine aminopeptidase-2 complexed with fumagillin. Sciences. 1998;282(5392):1324–1327. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5392.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang J, Tucker LA, Stavropoulos J, et al. Correlation of tumor growth suppression and methionine aminopeptidase-2 activity blockade using and orally active inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad U S A. 2008;105(6):1838–1843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708766105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Datta B. Roles of P67/MetAP2 as a tumor suppressor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1796(2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang Y, Yeh JR, Mara A, et al. A chemical and genetic approach to the mode of action of fumagillin. Chem Biol. 2006;13(9):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.07.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Boxem M, Tsai CW, Zhang Y, Saito RM, Liu JO. The C. elegans methionine aminopeptidase 2 analog map-2 is required for germ cell proliferation. FEBS Lett. 2004;576(1-2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.08.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cutforth Y, Gaul U. A methionine aminopeptidase and putative regulator of translation initiation is required for cell growth and patterning in Drosophila. Mech Dev. 1999;82(1-2):23–28. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(99)00006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yeh JR, Ju R, Brdlik CM, et al. Targeted gene disruption of methionine aminopeptidase 2 results in an embryonic gastrulation defect and endothelial cell growth arrest. Proc Natl Acad U S A. 2006;103(27):10379–10384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511313103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Westerfield M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish. Eugene, Oregon: The University of Oregon Press; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kimmel DB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 1995;203(3):253–310. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002030302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ma AC, Ward AC, Liang R, Leung AY. The role of jak2a in zebrafish hematopoiesis. Blood. 2007;110(6):1824–1830. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-03-078287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ma AC, Chung MI, Liang R, Leung AY. A DEAB-sensitive aldehyde dehydrogenase regulates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells development during primitive hematopoiesis in zebrafish embryos. Leukemia. 2010;24:2090–2099. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Varga M, Maegawa S, Bellipanni G, Weinberg ES. Chordin expression, mediated by Nodal and FGF signaling, is restricted by redundant function of two beta-catenins in the zebrafish embryo. Mech Dev. 2007;124(9-10):775–791. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2007.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li JY, Chen LL, Cui YM, et al. Characterization of full length and truncated type I human methionine aminopeptidases expressed from Escherichia coli. Biocehmistry. 2004;43(24):7892–7898. doi: 10.1021/bi0360859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Datta B, Majumdar A, Datta R, Balusu R. Treatment of cells with the angiogenic inhibitor fumagillin results in increased stability of eukaryotic initiation factor 2-associated glycoprotein, p67, and reduced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2. Biochemistry. 2004;43(46):14821–14831. doi: 10.1021/bi049172p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Datta B, Datta R, Majumdar A, Ghosh A. The stability of eukaryotic initiation factor 2-associated glycoprotein, p67, increases during skeletal muscle differentiation and that inhibits the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2. Exp Cell Res Exp Cell Res. 2005;303(1):174–182. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Clements WK, Kim AD, Ong KG, Moore JC, Lawson ND, Traver D. A somitic Wnt16/Notch pathway specifies haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2011;474(7350):220–224. doi: 10.1038/nature10107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu L, Zhu S, Gong Z, Low BC. K-ras/PI3K-Akt Signaling is essential for zebrafish hematopoiesis and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2008;3(8):e2850. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bolli N, Payne EM, Rhodes J, et al. cpsf1 is required for definitive hematopoietic stem cell survival in zebrafish. Blood. 2011;117(15):3996–4007. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-08-304030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bahary N, Goishi K, Stuckenholz C, et al. Duplicate VegfA genes and orthologues of the KDR receptor tyrosine kinase family mediate vascular development in the zebrafish. Blood. 2007;110(10):3627–3636. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-016378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Songhet P, Adzic D, Reibe S, Rohr KB. fgf1 is required for normal differentiation of erythrocytes in zebrafish primitive hematopoiesis. Dev. Dyn. 2007;236(3):633–643. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chong SW, Nguyet LM, Jiang YJ, Korzh V. The chemokine Sdf-1 and its receptor Cxcr4 are required for formation of muscle in zebrafish. BMC Dev. Biol. 2007;7:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Catalano A, Romano M, Robuffo I, Strizzi L, Procopio A. Methionine aminopeptidase-2 regulates human mesothelioma cell survival: role of Bcl-2 expression and telomerase activity. Am J Pathol. 2001;159(2):721–731. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61743-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kanno T, Endo H, Takeuchi K, Morishita Y, Fukayama M, Mori S. High expression of methionine aminopeptidase type 2 in germinal center B cells and their neoplastic counterparts. Lab Invest. 2002;82(7):893–901. doi: 10.1097/01.lab.0000020419.25365.c4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Selvakumar P, Lakshmikuttyamma A, Kanthan R, Kanthan SC, Dimmock JR, Sharma RK. High expression of methionine aminopeptidase 2 in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(8):2771–2775. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-03-0218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dasgupta B, Yi Y, Hegedus B, Weber JD, Gutmann DH. Cerebrospinal fluid proteomic analysis reveals dysregulation of methionine aminopeptidase-2 expression in human and mouse neurofibromatosis 1-associated glioma. Cancer Res. 2005;65(21):9843–9850. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sawanyawisuth K, Wongkham C, Pairojkul C, et al. Methionine aminopeptidase 2 over-expressed in cholangiocarcinoma: potential for drug target. Acta Oncol. 2007;46(3):378–385. doi: 10.1080/02841860600871061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chun E, Han CK, Yoon JH, Sim TB, Kim YK, Lee KY. Novel inhibitors targeted to methionine aminopeptidase 2 (MetAP2) strongly inhibit the growth of cancers in xenografted nude model. Int J Cancer. 2005;114(1):124–130. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang J, Sheppard GS, Lou P, et al. Tumor suppression by a rationally designed reversible inhibitor of methionine aminopeptidase-2. Cancer Res. 2003;63(22):7861–7869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kim S, LaMontagne K, Sabio M, et al. Depletion of methionine aminopeptidase 2 does not alter cell response to fumagillin or bengamides. Cancer Res. 2004;64(9):2984–2987. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.