Abstract
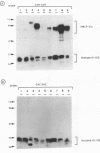
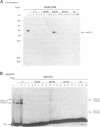
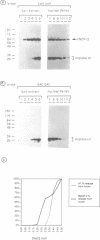
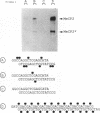
Methylated DNA in vertebrates is associated with transcriptional repression and inactive chromatin. Two activities have been identified, MeCP1 and MeCP2, which bind specifically to DNA containing methyl-CpG pairs. In this report we characterize MeCP2. We show that it is more abundant than MeCP1, is more tightly bound in the nucleus, and is distinguishable chromatographically. The two proteins share widespread expression in somatic mammalian cells, and barely detectable expression in early embryonic cells. DNAs containing thymidine which has a methyl group at position 5 are not ligands for the MeCPs. The possible role of MeCP2 in methylation-associated gene inactivation was tested in in vitro transcription extracts. Purified MeCP2 inhibited transcription from both methylated and nonmethylated DNA templates in vitro, probably due to the presence of nonspecific DNA binding domains within the protein. We hypothesise that MeCP2 normally binds methylated DNA in the context of chromatin, contributing to the long-term repression and nuclease-resistance of methyl-CpGs.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antequera F., Macleod D., Bird A. P. Specific protection of methylated CpGs in mammalian nuclei. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. The essentials of DNA methylation. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90526-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. Repression of genes by DNA methylation depends on CpG density and promoter strength: evidence for involvement of a methyl-CpG binding protein. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):327–333. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Butler M. J., Hyde J. E., Phillips D., Skidmore C. J., Walker I. O. The interaction of core histones with DNA: equilibrium binding studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3643–3663. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation and the regulation of globin gene expression. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. L., Lieber M. R. CpG methylated minichromosomes become inaccessible for V(D)J recombination after undergoing replication. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):315–325. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05054.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantsch M., Hamilton B., Mayr B., Schweizer D. Meiotic chromosome behaviour reflects levels of sequence divergence in Sus scrofa domestica satellite DNA. Chromosoma. 1990 Sep;99(5):330–335. doi: 10.1007/BF01731720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A., Cantoni G. L., Razin A. Inhibition of promoter activity by methylation: possible involvement of protein mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6515–6518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. D., Meehan R. R., Henzel W. J., Maurer-Fogy I., Jeppesen P., Klein F., Bird A. Purification, sequence, and cellular localization of a novel chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90610-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J., Bird A. DNA methylation and chromatin structure. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80795-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Lewis J. D., McKay S., Kleiner E. L., Bird A. P. Identification of a mammalian protein that binds specifically to DNA containing methylated CpGs. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak A., Bryans M., Jost J. P. An avian 40 KDa nucleoprotein binds preferentially to a promoter sequence containing one single pair of methylated CpG. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1029–1034. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Igo-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Nucleotide sequence of a highly repetitive component of rat DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):417–432. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solage A., Cedar H. Organization of 5-methylcytosine in chromosomal DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2934–2938. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. Y., Zhang X. Y., Ehrlich M. A human DNA-binding protein is methylation-specific and sequence-specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1599–1614. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]