Abstract
The activity of the adenovirus major late promoter is substantially increased as the infection proceeds from the early to late phase. To gain insight into the regulation of this promoter, we analyzed protein-DNA interactions by in vivo DMS and DNasel footprinting during the course of adenovirus infection. Little or no protein interaction at promoter sequences was detected early (5 hr) after infection but strong interactions at the major late transcription factor (MLTF/USF) binding site and at the TATA box were evident late (12 hr) after infection. Comparison of in vivo and in vitro footprints revealed that the in vivo interaction late after infection results from binding of the cellular transcription factor MLTF/USF. Nuclear extracts prepared from uninfected cells as well as cells harvested at 5 and 12 hr after infection contained similar levels of MLTF/USF footprint activity, therefore the lack of a detectable interaction early after infection is not due to reduced levels of the factor early in the viral growth cycle. Viral DNA replication was required for MLTF/USF binding at the major late promoter. These results indicate that DNA replication participates in the regulation of adenovirus late gene expression by facilitating the binding of a transcription factor to the major late promoter.
Full text
PDF

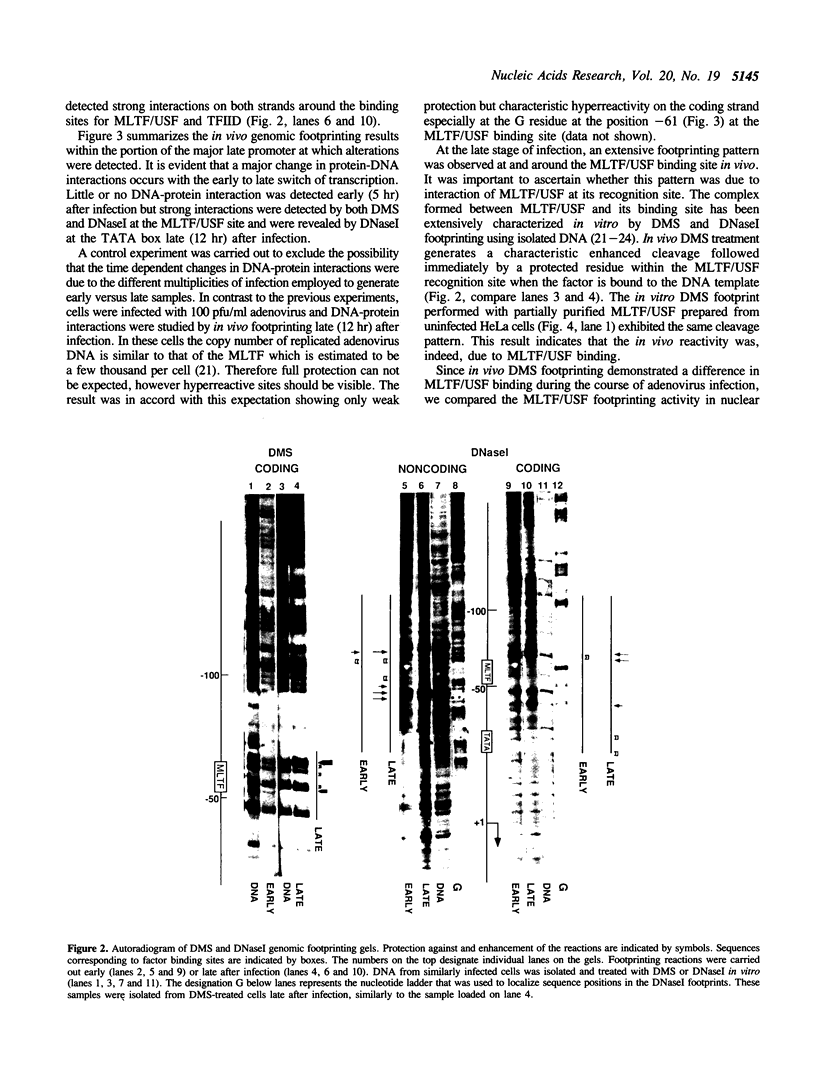



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht G., Devaux B., Kedinger C. Genomic footprinting detects factors bound to major late and IVa2 promoters in adenovirus-infected HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1534–1539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. The major late transcription factor binds to and activates the mouse metallothionein I promoter. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):973–980. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee P. K., Vayda M. E., Flint S. J. Adenoviral protein VII packages intracellular viral DNA throughout the early phase of infection. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1633–1644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Morgan J. G., Crabtree G. R., Sharp P. A. The adenovirus major late transcription factor activates the rat gamma-fibrinogen promoter. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):684–688. doi: 10.1126/science.3672119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M. D., Weissmann C. Modular structure of the beta-globin and the TK promoters. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2453–2459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Déry C. V., Toth M., Brown M., Horvath J., Allaire S., Weber J. M. The structure of adenovirus chromatin in infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2671–2684. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Selection and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of type 5 adenovirus. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):328–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.328-339.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enver T., Brewer A. C., Patient R. K. Role for DNA replication in beta-globin gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. M. Temporal order of replication of Xenopus laevis 5S ribosomal RNA genes in somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2924–2928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A., Holmquist G. P., Gray M. C., Caston L. A., Nag A. Replication timing of genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):686–692. doi: 10.1126/science.6719109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinta D. R., Korn L. J. Differential order of replication of Xenopus laevis 5S RNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2536–2542. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Engel D. A., Shenk T. An adenovirus early region 4 gene product is required for induction of the infection-specific form of cellular E2F activity. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1062–1074. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt M. M., Bowman T. L., Marzluff W. F. A common transcriptional activator is located in the coding region of two replication-dependent mouse histone genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2929–2936. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Durr P., Mondésert G., Kédinger C. Replication-dependent activation of the adenovirus major late promoter is mediated by the increased binding of a transcription factor to sequences in the first intron. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5124–5132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5124-5132.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck J. G., Baldick C. J., Jr, Moss B. Role of DNA replication in vaccinia virus gene expression: a naked template is required for transcription of three late trans-activator genes. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90190-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Shenk T. In vivo identification of sequence elements required for normal function of the adenovirus major late transcriptional control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6327–6335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Grodzicker T., Tjian R. Downstream sequences affect transcription initiation from the adenovirus major late promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2684–2694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Roizman B. Activation of herpes simplex virus 1 gamma 2 genes by viral DNA replication. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):593–598. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Specific interaction between a transcription factor and the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondésert G., Kédinger C. Cooperation between upstream and downstream elements of the adenovirus major late promoter for maximal late phase-specific transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3221–3228. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Mathews M. B. DNA replication and the early to late transition in adenovirus infection. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth M., Müller U., Doerfler W. Establishment of de novo DNA methylation patterns. Transcription factor binding and deoxycytidine methylation at CpG and non-CpG sequences in an integrated adenovirus promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):673–683. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90285-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winnacker E. L. Adenovirus DNA: structure and function of a novel replicon. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):761–773. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G., Kingston R. E. An upstream transcription factor, USF (MLTF), facilitates the formation of preinitiation complexes during in vitro chromatin assembly. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1299–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]