Abstract
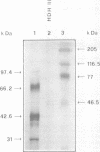
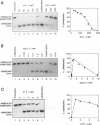
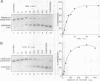
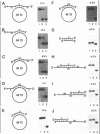
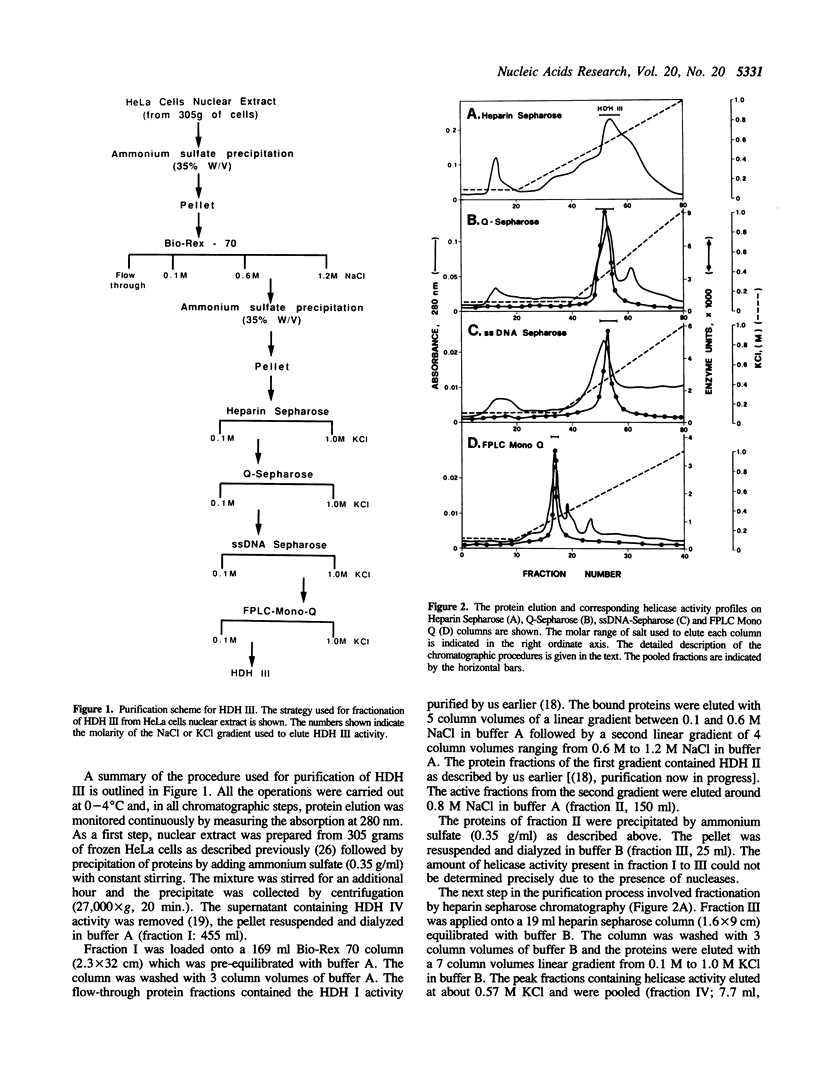
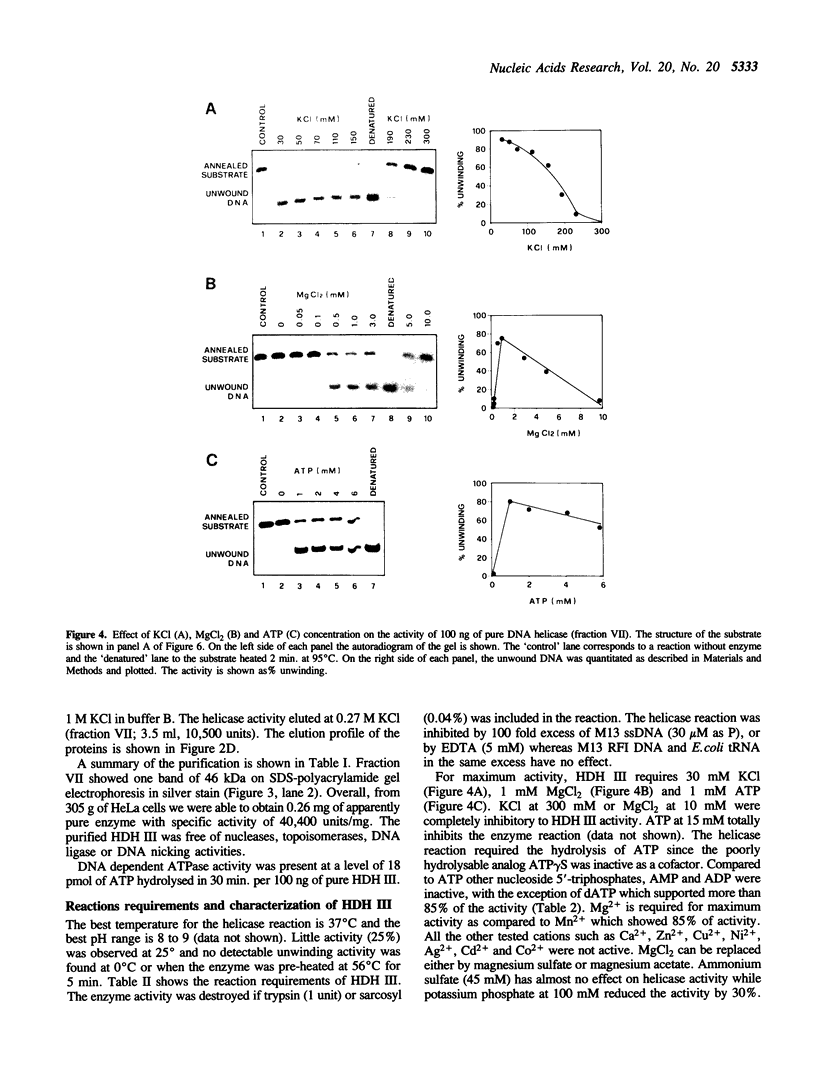
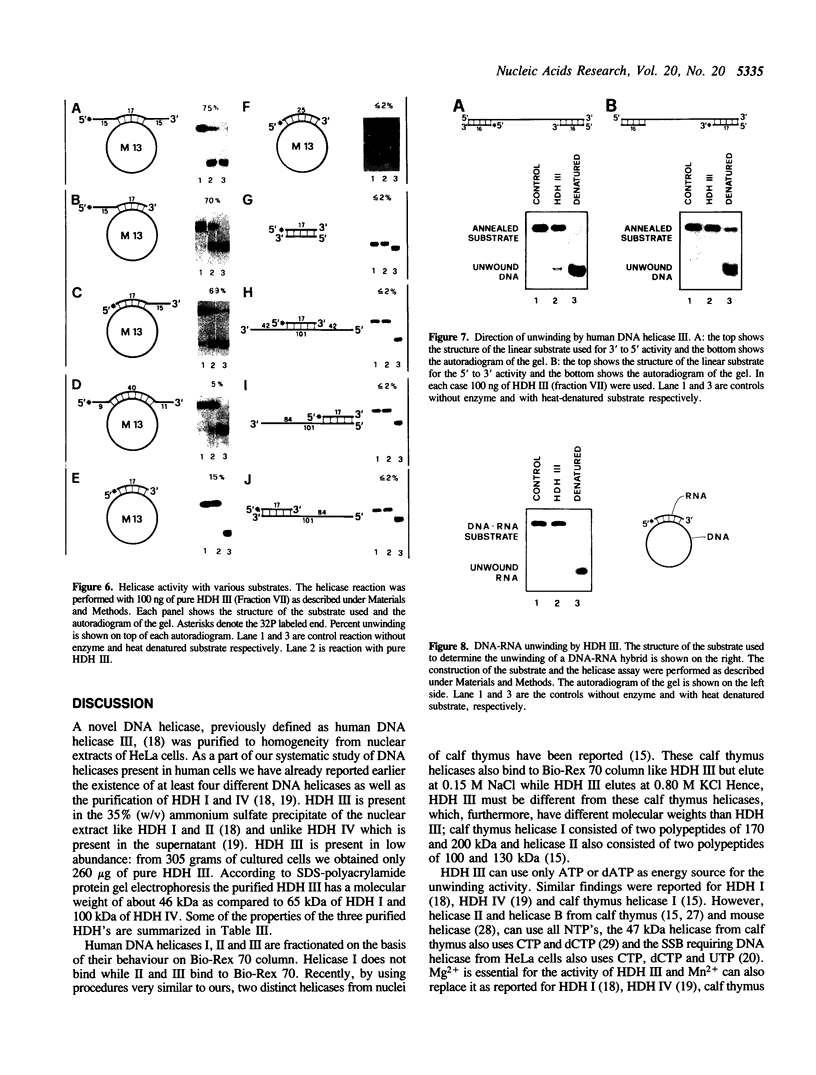
Human DNA helicase III, a novel DNA unwinding enzyme, has been purified to apparent homogeneity from nuclear extracts of HeLa cells and characterized. The activity was measured by using a strand displacement assay with a 32P labeled oligonucleotide annealed to M13 ssDNA. From 305 grams of cultured cells 0.26 mg of pure protein was isolated which was free of DNA topoisomerase, ligase, nicking and nuclease activities. The apparent molecular weight is 46 kDa on SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The enzyme shows also DNA dependent ATPase activity and moves unidirectionally along the bound strand in 3' to 5' direction. It prefers ATP to dATP as a cofactor and requires a divalent cation (Mg2+ > Mn2+). Helicase III cannot unwind either blunt-ended duplex DNA or DNA-RNA hybrids and requires more than 84 bases of ssDNA in order to exert its unwinding activity. This enzyme is unique among human helicases as it requires a fork-like structure on the substrate for maximum activity, contrary to the previously described human DNA helicases I and IV, (Tuteja et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 6785-6792, 1990; Tuteja et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 3613-3618, 1991).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Monem M., Dürwald H., Hoffmann-Berling H. Enzymic unwinding of DNA. 2. Chain separation by an ATP-dependent DNA unwinding enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):441–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Dombroski A. J., Platt T. Transcription termination factor rho is an RNA-DNA helicase. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):945–952. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90703-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Company M., Arenas J., Abelson J. Requirement of the RNA helicase-like protein PRP22 for release of messenger RNA from spliceosomes. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):487–493. doi: 10.1038/349487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K., Hoffmann-Berling H. Proteins controlling the helical structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:233–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. A new superfamily of replicative proteins. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–23. doi: 10.1038/333022b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. J., Liang H. M., Jiricny J., Jost J. P. Purification and characterization of a protein from HeLa cells that binds with high affinity to the estrogen response element, GGTCAGCGTGACC. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9137–9142. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiserman H. B., Ingebritsen T. S., Benbow R. M. Regulation of Xenopus laevis DNA topoisomerase I activity by phosphorylation in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3216–3222. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. Enlarged family of putative helicases. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):478–478. doi: 10.1038/334478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Tan C. K., So A. G., Downey K. M. Purification and characterization of delta helicase from fetal calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3507–3513. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W. Escherichia coli DNA helicase II (uvrD gene product) catalyzes the unwinding of DNA.RNA hybrids in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Kaiser-Rogers K. A. DNA helicases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:289–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Kramer J. C., Cladaras M. H., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. ATP-dependent unwinding of messenger RNA structure by eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7651–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman L. J., Kowalczykowski S. C. Characterization of the helicase activity of the Escherichia coli RecBCD enzyme using a novel helicase assay. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2863–2873. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runyon G. T., Lohman T. M. Escherichia coli helicase II (uvrD) protein can completely unwind fully duplex linear and nicked circular DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17502–17512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Knippers R., Stahl H. RNA unwinding activity of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):955–963. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90334-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki M., Enomoto T., Eki T., Miyajima A., Murakami Y., Hanaoka F., Ui M. DNA helicase and nucleoside-5'-triphosphatase activities of polyoma virus large tumor antigen. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):1003–1009. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki M., Enomoto T., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. DNA-dependent adenosinetriphosphatase B from mouse FM3A cells has DNA helicase activity. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2924–2928. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo Y. S., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Isolation of a DNA helicase from HeLa cells requiring the multisubunit human single-stranded DNA-binding protein for activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13161–13170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Knippers R. The simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 9;910(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz E. J., Brennan C. A., Platt T. A short intervening structure can block rho factor helicase action at a distance. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18408–18413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Ferrari E., Jessberger R., Hübscher U. Four different DNA helicases from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6063–6073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. DNA helicase from calf thymus. Purification to apparent homogeneity and biochemical characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14347–14354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. Eukaryotic DNA helicases. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81279-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Danciger M., Klisak I., Tuteja R., Inana G., Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Farber D. B. Isolation and characterization of cDNA encoding the gamma-subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase in human retina. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90035-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Rahman K., Tuteja R., Falaschi A. DNA helicase IV from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3613–3618. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Tuteja R., Rahman K., Kang L. Y., Falaschi A. A DNA helicase from human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6785–6792. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezu K., Nakayama K., Nakayama H. Escherichia coli RecQ protein is a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5363–5367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. S., Grosse F. Purification and characterization of two DNA helicases from calf thymus nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20483–20490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]