Abstract
In the title compound, C17H12ClNO2, the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 42.9 (1)°. There are no sgnificant intermolecular interactions.
Related literature
For background to the synthetic procedure, see: Bakthadoss & Murugan (2010 ▶). For related structures, see: Manikandan et al. (2012 ▶); Prasanna et al. (2011 ▶). 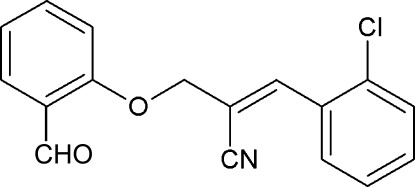
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H12ClNO2
M r = 297.73
Triclinic,
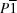
a = 7.5022 (4) Å
b = 7.8301 (4) Å
c = 13.2379 (8) Å
α = 75.470 (3)°
β = 84.696 (2)°
γ = 70.935 (2)°
V = 711.43 (7) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.27 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.24 × 0.21 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.937, T max = 0.960
14438 measured reflections
3433 independent reflections
2685 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.114
S = 1.04
3433 reflections
190 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2 and SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT and XPREP (Bruker, 2004 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008410/bt5830sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008410/bt5830Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008410/bt5830Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Babu Vargheese, SAIF, IIT, Madras, India, for his help with the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound is a stereodefined trisubstituted olefin, synthesized from the corresponding bromoderivative of Baylis–Hillman adduct with salicylaldehyde via simple SN2 reaction in good yields. This o-salicyladehyde derivative is an important precursor for many heterocyclic frameworks (Bakthadoss & Murugan, 2010).
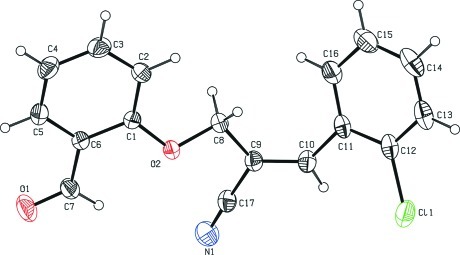
The title compound comprises a benzaldehyde moiety connected to a chlorophenyl ring through a chain formed by a methoxy methyl and a propenenitrile group. The X-ray analysis confirms the molecular structure and atom connectivity as illustrated in Fig. 1.
The dihedral angle between the two aromatic rings is 42.9 (1)°. The propenenitrile (N1/C17/C8–C11) plane forms dihedral angles of 12.4 (1)° and 36.0 (1)°, respectively, with the formyl phenyl and chloro phenyl rings. The Cl1 atom deviates from the plane of attached ring by 0.019 (1) Å. The bond length C9—C17 [1.443 (2) Å] is significantly shorter than the expected value for a C—C single bond because of conjugation effects (Prasanna et al., 2011). The carbonitrile side chain (C9—C17—N1) is almost linear, with the angle around the central C atom being 178.1 (2)°. The geometric parameters of the title molecule agree well with those reported for similar structures (Manikandan et al., 2012; Prasanna et al., 2011).
Experimental
A solution of salicylaldehyde (1.0 mmol, 0.122 g) and potassium carbonate (1.5 mmol, 0.207 g) in acetonitrile solvent was stirred for 15 min at room temperature. To this solution, (E)-2-(bromomethyl)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)prop-2-enenitrile (1.2 mmol, 0.308 g) was added drop wise till the addition is complete. After the completion of the reaction, as indicated by TLC, acetonitrile was evaporated. EtOAc (15 ml) and water (15 ml) were added to the crude mass. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Removal of solvent led to a crude product, which was purified through a pad of silica gel (100–200 mesh) using ethyl acetate and hexanes (1:9) as solvents. The pure title compound was obtained as a colorless solid (0.270 g, 90% yield). Recrystallization was carried out using ethyl acetate as solvent.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically, with C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å and constrained to ride on their parent atom, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound showing displacement ellipsoids at the 30% probability level. H atoms are presented as a small spheres of arbitrary radii.
Crystal data
| C17H12ClNO2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 297.73 | F(000) = 308 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.390 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.5022 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 3463 reflections |
| b = 7.8301 (4) Å | θ = 2.8–28.1° |
| c = 13.2379 (8) Å | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| α = 75.470 (3)° | T = 293 K |
| β = 84.696 (2)° | Block, colourless |
| γ = 70.935 (2)° | 0.24 × 0.21 × 0.15 mm |
| V = 711.43 (7) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3433 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2685 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.029 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.1°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω scans | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | k = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.937, Tmax = 0.960 | l = −17→17 |
| 14438 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.114 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.053P)2 + 0.159P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3433 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 190 parameters | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.31341 (8) | 0.23140 (7) | 0.01456 (3) | 0.07011 (17) | |
| N1 | 0.1141 (2) | −0.1357 (2) | 0.40658 (12) | 0.0660 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.3876 (2) | −0.21291 (18) | 0.75288 (10) | 0.0765 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.28615 (15) | 0.15782 (13) | 0.48411 (7) | 0.0436 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.32059 (19) | 0.22280 (18) | 0.56458 (10) | 0.0364 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.3173 (2) | 0.4030 (2) | 0.55536 (12) | 0.0471 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.2830 | 0.4913 | 0.4928 | 0.057* | |
| C3 | 0.3655 (3) | 0.4509 (2) | 0.64002 (14) | 0.0562 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.3639 | 0.5724 | 0.6336 | 0.067* | |
| C4 | 0.4160 (3) | 0.3238 (2) | 0.73390 (13) | 0.0559 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.4513 | 0.3578 | 0.7896 | 0.067* | |
| C5 | 0.4132 (2) | 0.1464 (2) | 0.74357 (11) | 0.0474 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.4442 | 0.0603 | 0.8071 | 0.057* | |
| C6 | 0.36463 (19) | 0.09286 (18) | 0.66019 (10) | 0.0377 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.3555 (2) | −0.0949 (2) | 0.67304 (12) | 0.0479 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.3225 | −0.1251 | 0.6153 | 0.057* | |
| C8 | 0.1837 (2) | 0.2928 (2) | 0.39872 (11) | 0.0428 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.2576 | 0.3715 | 0.3627 | 0.051* | |
| H8B | 0.0670 | 0.3705 | 0.4233 | 0.051* | |
| C9 | 0.1425 (2) | 0.1907 (2) | 0.32654 (11) | 0.0407 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.1257 (2) | 0.2525 (2) | 0.22304 (11) | 0.0453 (3) | |
| H10 | 0.0988 | 0.1754 | 0.1876 | 0.054* | |
| C11 | 0.1448 (2) | 0.4273 (2) | 0.15926 (11) | 0.0450 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.2291 (2) | 0.4332 (2) | 0.05996 (12) | 0.0505 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.2510 (3) | 0.5949 (3) | −0.00219 (14) | 0.0639 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.3080 | 0.5953 | −0.0676 | 0.077* | |
| C14 | 0.1887 (3) | 0.7543 (3) | 0.03273 (17) | 0.0725 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.2040 | 0.8635 | −0.0090 | 0.087* | |
| C15 | 0.1029 (3) | 0.7550 (3) | 0.12961 (16) | 0.0693 (5) | |
| H15 | 0.0605 | 0.8643 | 0.1528 | 0.083* | |
| C16 | 0.0804 (3) | 0.5936 (2) | 0.19183 (13) | 0.0562 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.0212 | 0.5955 | 0.2566 | 0.067* | |
| C17 | 0.1252 (2) | 0.0091 (2) | 0.37263 (11) | 0.0463 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0911 (4) | 0.0811 (3) | 0.0395 (2) | −0.0294 (3) | 0.0038 (2) | −0.0151 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0812 (11) | 0.0554 (9) | 0.0620 (9) | −0.0321 (8) | 0.0090 (8) | −0.0041 (7) |
| O1 | 0.1249 (12) | 0.0518 (7) | 0.0519 (7) | −0.0394 (8) | −0.0187 (7) | 0.0113 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0599 (6) | 0.0349 (5) | 0.0322 (5) | −0.0102 (4) | −0.0091 (4) | −0.0044 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0398 (7) | 0.0358 (7) | 0.0329 (6) | −0.0113 (5) | 0.0013 (5) | −0.0083 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0612 (9) | 0.0358 (7) | 0.0424 (8) | −0.0170 (7) | 0.0022 (7) | −0.0043 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0757 (11) | 0.0435 (8) | 0.0598 (10) | −0.0286 (8) | 0.0056 (8) | −0.0197 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0689 (11) | 0.0625 (10) | 0.0472 (9) | −0.0272 (8) | 0.0005 (7) | −0.0242 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0562 (9) | 0.0514 (9) | 0.0344 (7) | −0.0170 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | −0.0089 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0424 (7) | 0.0352 (7) | 0.0341 (7) | −0.0121 (6) | 0.0002 (5) | −0.0062 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0610 (9) | 0.0390 (8) | 0.0421 (8) | −0.0176 (7) | −0.0056 (7) | −0.0025 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0504 (8) | 0.0388 (7) | 0.0339 (7) | −0.0099 (6) | −0.0036 (6) | −0.0037 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0417 (7) | 0.0429 (7) | 0.0354 (7) | −0.0138 (6) | 0.0005 (5) | −0.0050 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0520 (8) | 0.0507 (8) | 0.0358 (7) | −0.0215 (7) | −0.0031 (6) | −0.0069 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0469 (8) | 0.0512 (9) | 0.0339 (7) | −0.0172 (7) | −0.0113 (6) | 0.0017 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0520 (9) | 0.0601 (10) | 0.0358 (7) | −0.0200 (7) | −0.0105 (6) | 0.0020 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0614 (10) | 0.0752 (13) | 0.0447 (9) | −0.0263 (9) | −0.0070 (8) | 0.0132 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0733 (13) | 0.0589 (12) | 0.0736 (13) | −0.0287 (10) | −0.0198 (10) | 0.0222 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0788 (13) | 0.0479 (10) | 0.0730 (13) | −0.0153 (9) | −0.0219 (10) | 0.0017 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0621 (10) | 0.0509 (9) | 0.0478 (9) | −0.0124 (8) | −0.0107 (7) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0510 (8) | 0.0507 (9) | 0.0366 (7) | −0.0191 (7) | 0.0028 (6) | −0.0062 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C12 | 1.7353 (18) | C8—C9 | 1.499 (2) |
| N1—C17 | 1.137 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| O1—C7 | 1.2004 (18) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| O2—C1 | 1.3672 (16) | C9—C10 | 1.3367 (19) |
| O2—C8 | 1.4199 (16) | C9—C17 | 1.443 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.378 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.460 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.3992 (18) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.379 (2) | C11—C16 | 1.395 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.402 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.378 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.376 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.364 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.369 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.381 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.377 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.460 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C1—O2—C8 | 116.56 (10) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.5 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 123.98 (12) | C10—C9—C17 | 117.74 (14) |
| O2—C1—C6 | 115.96 (11) | C10—C9—C8 | 125.17 (13) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.05 (13) | C17—C9—C8 | 117.06 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.14 (14) | C9—C10—C11 | 127.43 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C9—C10—H10 | 116.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C11—C10—H10 | 116.3 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.89 (14) | C16—C11—C12 | 117.11 (14) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.1 | C16—C11—C10 | 122.99 (14) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.1 | C12—C11—C10 | 119.90 (14) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.66 (15) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.65 (17) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.7 | C13—C12—Cl1 | 118.70 (14) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.7 | C11—C12—Cl1 | 119.63 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.20 (14) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.65 (18) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.2 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.2 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.97 (13) | C13—C14—C15 | 120.53 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.44 (13) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.58 (12) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 124.58 (15) | C16—C15—C14 | 120.0 (2) |
| O1—C7—H7 | 117.7 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 117.7 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| O2—C8—C9 | 107.51 (11) | C15—C16—C11 | 121.09 (18) |
| O2—C8—H8A | 110.2 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 110.2 | C11—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| O2—C8—H8B | 110.2 | N1—C17—C9 | 178.10 (17) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 110.2 | ||
| C8—O2—C1—C2 | −21.16 (19) | C17—C9—C10—C11 | −177.54 (15) |
| C8—O2—C1—C6 | 160.05 (12) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.5 (3) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | −176.06 (14) | C9—C10—C11—C16 | −37.5 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 2.7 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 143.27 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (3) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 1.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.7 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −179.48 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.4 (3) | C16—C11—C12—Cl1 | 179.72 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.9 (2) | C10—C11—C12—Cl1 | −1.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −177.70 (15) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.4 (3) |
| O2—C1—C6—C5 | 175.89 (12) | Cl1—C12—C13—C14 | −178.89 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −2.9 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.3 (3) |
| O2—C1—C6—C7 | −5.54 (19) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 175.62 (13) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.7 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | 0.0 (3) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −1.4 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | −178.53 (16) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 179.34 (15) |
| C1—O2—C8—C9 | −173.38 (11) | C10—C9—C17—N1 | 36 (6) |
| O2—C8—C9—C10 | −149.36 (14) | C8—C9—C17—N1 | −142 (6) |
| O2—C8—C9—C17 | 28.70 (17) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5830).
References
- Bakthadoss, M. & Murugan, G. (2010). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 5825–5830.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and XPREP Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, U. S. A.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Manikandan, N., Murugavel, S., Kannan, D. & Bakthadoss, M. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, C. M. S., Sethusankar, K., Rajesh, R. & Raghunathan, R. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008410/bt5830sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008410/bt5830Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008410/bt5830Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report