Abstract
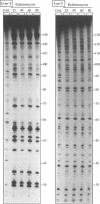
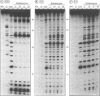
The 2-amino group of guanine is believed to be a critical determinant of potential DNA binding sites for echinomycin and related quinoxaline antibiotics. In order to probe its importance directly we have studied the interaction between echinomycin and DNA species in which guanine N(2) is deleted by virtue of substitution of inosine for guanosine residues. The polymerase chain reaction was used to prepare inosine-substituted DNA. Binding of echinomycin, assessed by DNAse I footprinting, was practically abolished by incorporation of inosine into one or both strands of DNA. We conclude that both the purines in the preferred CpG binding site need to bear a 2-amino group to interact with echinomycin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfredson T. V., Maki A. H. Phosphorescence and optically detected magnetic resonance studies of echinomycin-DNA complexes. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 25;29(38):9052–9064. doi: 10.1021/bi00490a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfredson T. V., Maki A. H., Waring M. J. Optically detected triplet-state magnetic resonance studies of the DNA complexes of the bisquinoline analogue of echinomycin. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9665–9675. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Reich E., Ward D. C., Goldberg I. H. The interaction of actinomycin with DNA: requirement for the 2-amino group of purines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1036–1042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Marks J. N., Waterloh K. Echinomycin binding to alternating AT. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6725–6730. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. The use of micrococcal nuclease as a probe for drug-binding sites on DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 14;909(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. L., Patel D. J. Antitumour drug-DNA interactions: NMR studies of echinomycin and chromomycin complexes. Q Rev Biophys. 1989 May;22(2):93–138. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. L., Patel D. J. NMR studies of echinomycin bisintercalation complexes with d(A1-C2-G3-T4) and d(T1-C2-G3-A4) duplexes in aqueous solution: sequence-dependent formation of Hoogsteen A1.T4 and Watson--Crick T1.A4 base pairs flanking the bisintercalation site. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1744–1751. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauvreau D., Waring M. J. Directed biosynthesis of novel derivatives of echinomycin by Streptomyces echinatus. I. Effect of exogenous analogues of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid on the fermentation. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Apr;30(4):439–450. doi: 10.1139/m84-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. E., Feigon J. The DNA sequence at echinomycin binding sites determines the structural changes induced by drug binding: NMR studies of echinomycin binding to [d(ACGTACGT)]2 and [d(TCGATCGA)]2. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2483–2494. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodisman J., Dabrowiak J. C. Structural changes and enhancements in DNase I footprinting experiments. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 4;31(4):1058–1064. doi: 10.1021/bi00119a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen C., Nielsen P. E. Photofootprinting of drug-binding sites on DNA using diazo- and azido-9-aminoacridine derivatives. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 15;182(2):437–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. B., Holistein U., Allen F. S. Site specificity of binding of antitumor antibiotics to DNA. Biopolymers. 1987 Jan;26(1):121–135. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Sequence-specific binding of echinomycin to DNA: evidence for conformational changes affecting flanking sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4865–4879. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean M. J., Seela F., Waring M. J. Echinomycin-induced hypersensitivity to osmium tetroxide of DNA fragments incapable of forming Hoogsteen base pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9687–9691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean M. J., Waring M. J. Chemical probes reveal no evidence of Hoogsteen base pairing in complexes formed between echinomycin and DNA in solution. J Mol Recognit. 1988 Jun;1(3):138–151. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., White R. J., Dean D., Crothers D. M. Monte-Carlo simulation of multisite echinomycin-DNA interactions detected by in vitro transcription analysis. Biochemistry. 1990 May 22;29(20):4812–4819. doi: 10.1021/bi00472a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfuss R., Goodisman J., Dabrowiak J. C. Quantitative footprinting analysis. Binding to a single site. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 23;29(3):777–781. doi: 10.1021/bi00455a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ughetto G., Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A. A comparison of the structure of echinomycin and triostin A complexed to a DNA fragment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2305–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. M., Dervan P. B. Echinomycin binding sites on DNA. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1122–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.6089341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin L. P. Polyfunctional DNA intercalating agents. Med Res Rev. 1986 Jul-Sep;6(3):275–340. doi: 10.1002/med.2610060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin S. P., Waring M. J. The binding of echinomycin to deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):721–740. doi: 10.1042/bj1570721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Ughetto G., Quigley G. J., Rich A. Interactions of quinoxaline antibiotic and DNA: the molecular structure of a triostin A-d(GCGTACGC) complex. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Dec;4(3):319–342. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10506353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. DNA modification and cancer. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:159–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J., Wakelin L. P. Echinomycin: a bifunctional intercalating antibiotic. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):653–657. doi: 10.1038/252653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterloh K., Fox K. R. Interaction of echinomycin with An.Tn. and (AT)n regions flanking its CG binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6719–6724. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver J., Tomasz M. Reactivity of mitomycin C with synthetic polyribonucleotides containing guanine or guanine analogs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 31;697(2):252–254. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90084-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]