Abstract
The piperidine ring of the title compound, C16H15N5, adopts a chair conformation. The pyridine ring is essentially planar, with a maximum deviation of 0.035 (3) Å. The pyrrole and pyridine rings are almost coplanar, forming a dihedral angle of 3.48 (14)°. In the crystal, no classical hydrogen bonds were found. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by aromatic π–π stacking [centroid–centroid separations = 3.4984 (16) and 3.9641 (15) Å between pyrrole and pyridine rings and between pyridine rings, respectively].
Related literature
For the biological activity of cyano-amino pyridines, see: Al-Haiza et al. (2003 ▶); Bhalerao & Krishnaiah (1995 ▶); Doe et al. (1990 ▶); Murata et al. (2003 ▶); Shankaraiah et al. (2010 ▶); Shishoo et al. (1983 ▶); Soliman et al. (2012 ▶); Temple et al. (1992 ▶). For ring conformations, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶).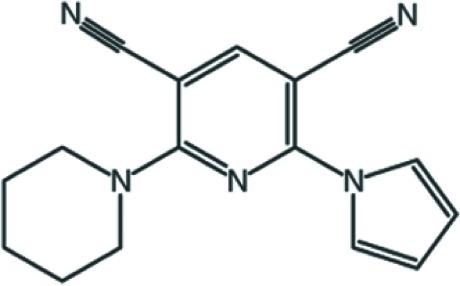
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H15N5
M r = 277.33
Monoclinic,
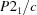
a = 11.9372 (16) Å
b = 6.6919 (8) Å
c = 17.158 (2) Å
β = 92.280 (7)°
V = 1369.5 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.32 × 0.04 × 0.02 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn724+ diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear-SM Expert; Rigaku, 2011 ▶) T min = 0.973, T max = 0.998
7877 measured reflections
3098 independent reflections
1503 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.095
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.073
wR(F 2) = 0.140
S = 0.96
3098 reflections
190 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear-SM Expert (Rigaku, 2011 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear-SM Expert; data reduction: CrystalClear-SM Expert; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2004 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008586/xu5473sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008586/xu5473Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008586/xu5473Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The EPSRC National Crystallography Service is gratefully acknowledged for the X-ray diffraction measurements. The authors are thankful to Manchester Metropolitan University and Sohag University for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Among the wide variety of active heterocycles, cyano-amino pyridines have showed important and useful intermediates in preparing variety of heterocyclic compounds (Shishoo et al., 1983; Doe et al., 1990; Bhalerao & Krishnaiah, 1995; Al-Haiza et al., 2003). In addition to this, many naturally occurring and synthetic compounds containing the pyridine scaffold possess interesting pharmacological properties (Temple et al., 1992). Among them, 2-amino-3-cyanopyridines have been identified as IKK-β inhibitors (Murata et al., 2003) and as antibacterial (Shankaraiah et al., 2010). Therefore, the synthesis of 2-amino-3-cyanopyridine derivatives continues to attract much interest in organic chemistry. In this respect, and also in continuation of our earlier work on synthesis of different heterocyclic system that containing highly biological activity (Soliman et al., 2012), we prompted to prepare the new title compound (I) with potential biological activity.
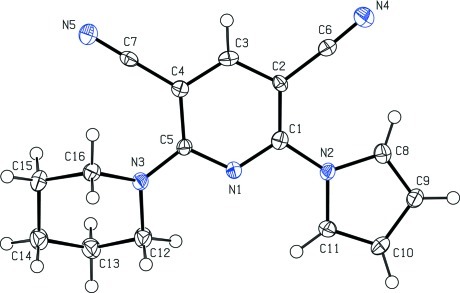
Fig. 1 shows the molecule of (I) which has an open conformation. The N3/C12–C16 piperidine ring adopts a chair conformation [puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975): QT = 0.574 (3) Å, θ = 179.5 (3) ° and φ = 137 (13) °]. The N1/C1–C5 pyridine ring is essentially planar with a maximum deviation of -0.035 (3) Å for C5. The N2/C8–C11 pyrrole and pyridine rings are almost co-planar and they make a dihedral angle of 3.48 (14)° with each other.
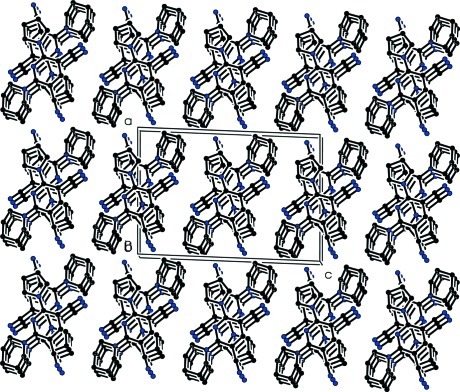
The structure exists no classic hydrogen bonds. The crystal packing exhibits π—π interactions with centroid—centroid distances: Cg1—Cg2i = 3.4984 (16) Å and Cg2—Cg2ii = 3.9641 (15) Å [Fig. 2; Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the N2/C8–C11 pyrrole and N1/C1–C5 pyridine rings, respectively. Symmetry codes: (i) 1 - x, 1 - y, -z and (ii) 1 - x, -y, -z].
Experimental
An equimolar mixture of 2-chloro-6-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl) pyridine-3,5-dicarbonitrile and piperidine in THF/EtOH (1:3) with few drops of TEA was refluxed at 351 K for 2–3 h. The product was obtained on cooling, collected, washed and re-crystallized from ethanol to afford the title compound. 90% yield, m.p. 413 K. Block-like pure crystals of the title compound, suitable for X-ray diffraction, were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution in ethanol for 24 h.
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding on their parent atoms with C—H distances of 0.93 Å and 0.97 Å. Isotropic displacement parameters for these atoms were set to 1.2 (CH, CH2) times Ueq of the parent atom. The (1 3 10) and (-4 6 14) reflections were omitted owing to bad disagreement. The ADDSYM routine in PLATON (Spek, 2009) suggests the space group P21/c which is consistent with the P21/c assignment of our structure.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), showing the atom-numbering scheme and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing of (I) down the b axis. The hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C16H15N5 | F(000) = 584 |
| Mr = 277.33 | Dx = 1.345 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4756 reflections |
| a = 11.9372 (16) Å | θ = 3.3–27.5° |
| b = 6.6919 (8) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 17.158 (2) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 92.280 (7)° | Lath, colourless |
| V = 1369.5 (3) Å3 | 0.32 × 0.04 × 0.02 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn724+ diffractometer | 3098 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating Anode | 1503 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Confocal monochromator | Rint = 0.095 |
| Detector resolution: 28.5714 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.3° |
| profile data from ω–scans | h = −15→15 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear-SM Expert; Rigaku, 2011) | k = −7→8 |
| Tmin = 0.973, Tmax = 0.998 | l = −21→22 |
| 7877 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.073 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.140 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.96 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0431P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3098 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 190 parameters | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. CrystalClear-SM Expert |
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.57393 (18) | 0.2530 (3) | 0.06283 (13) | 0.0173 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.38710 (18) | 0.2792 (3) | 0.03066 (13) | 0.0168 (7) | |
| N3 | 0.75463 (17) | 0.2158 (3) | 0.11176 (13) | 0.0192 (7) | |
| N4 | 0.3876 (2) | 0.2027 (4) | −0.19418 (14) | 0.0312 (9) | |
| N5 | 0.9243 (2) | 0.2228 (3) | −0.06919 (14) | 0.0262 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.4966 (2) | 0.2520 (4) | 0.00532 (16) | 0.0169 (9) | |
| C2 | 0.5227 (2) | 0.2225 (4) | −0.07288 (15) | 0.0150 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.6365 (2) | 0.2034 (4) | −0.08826 (15) | 0.0180 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.7185 (2) | 0.2039 (4) | −0.02904 (15) | 0.0167 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.6829 (2) | 0.2212 (4) | 0.04902 (15) | 0.0153 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.4457 (2) | 0.2118 (4) | −0.13900 (16) | 0.0209 (9) | |
| C7 | 0.8327 (2) | 0.2111 (4) | −0.05098 (15) | 0.0174 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.2865 (2) | 0.2905 (4) | −0.01382 (17) | 0.0207 (9) | |
| C9 | 0.2014 (2) | 0.3079 (4) | 0.03534 (16) | 0.0206 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.2483 (2) | 0.3078 (4) | 0.11287 (16) | 0.0199 (9) | |
| C11 | 0.3609 (2) | 0.2903 (4) | 0.10890 (16) | 0.0191 (9) | |
| C12 | 0.7216 (2) | 0.2875 (4) | 0.18847 (16) | 0.0250 (9) | |
| C13 | 0.8159 (2) | 0.4145 (4) | 0.22429 (17) | 0.0255 (10) | |
| C14 | 0.9264 (2) | 0.3013 (4) | 0.22895 (17) | 0.0263 (10) | |
| C15 | 0.9552 (2) | 0.2224 (4) | 0.14853 (17) | 0.0233 (9) | |
| C16 | 0.8582 (2) | 0.0981 (4) | 0.11522 (16) | 0.0212 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.65750 | 0.19000 | −0.13960 | 0.0220* | |
| H8 | 0.27940 | 0.28670 | −0.06800 | 0.0250* | |
| H9 | 0.12570 | 0.31800 | 0.02100 | 0.0250* | |
| H10 | 0.20860 | 0.31800 | 0.15830 | 0.0240* | |
| H11 | 0.41200 | 0.28630 | 0.15120 | 0.0230* | |
| H12A | 0.70700 | 0.17480 | 0.22220 | 0.0300* | |
| H12B | 0.65350 | 0.36630 | 0.18270 | 0.0300* | |
| H13A | 0.79650 | 0.45540 | 0.27630 | 0.0310* | |
| H13B | 0.82440 | 0.53410 | 0.19310 | 0.0310* | |
| H14A | 0.92100 | 0.19040 | 0.26500 | 0.0320* | |
| H14B | 0.98570 | 0.38940 | 0.24850 | 0.0320* | |
| H15A | 0.96940 | 0.33340 | 0.11390 | 0.0280* | |
| H15B | 1.02240 | 0.14110 | 0.15290 | 0.0280* | |
| H16A | 0.87490 | 0.05300 | 0.06320 | 0.0250* | |
| H16B | 0.84820 | −0.01880 | 0.14760 | 0.0250* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0151 (12) | 0.0199 (13) | 0.0168 (13) | −0.0004 (10) | −0.0007 (10) | 0.0011 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0133 (11) | 0.0187 (12) | 0.0183 (13) | 0.0017 (10) | 0.0011 (9) | −0.0014 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0146 (12) | 0.0250 (13) | 0.0179 (13) | 0.0045 (10) | 0.0004 (10) | −0.0054 (11) |
| N4 | 0.0255 (14) | 0.0450 (17) | 0.0230 (15) | 0.0032 (13) | −0.0010 (12) | −0.0044 (13) |
| N5 | 0.0203 (14) | 0.0315 (15) | 0.0267 (15) | 0.0043 (12) | 0.0014 (11) | −0.0003 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0169 (14) | 0.0124 (15) | 0.0213 (16) | −0.0017 (11) | 0.0012 (12) | 0.0013 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0158 (14) | 0.0143 (15) | 0.0146 (14) | −0.0008 (12) | −0.0030 (11) | 0.0021 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0235 (15) | 0.0159 (15) | 0.0149 (15) | −0.0011 (13) | 0.0049 (12) | −0.0010 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0178 (15) | 0.0158 (15) | 0.0166 (15) | −0.0001 (13) | 0.0006 (12) | 0.0003 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0144 (14) | 0.0155 (15) | 0.0161 (15) | −0.0038 (12) | 0.0009 (11) | −0.0011 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0185 (15) | 0.0262 (16) | 0.0183 (15) | 0.0012 (13) | 0.0038 (13) | 0.0002 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0212 (15) | 0.0182 (15) | 0.0126 (15) | 0.0034 (13) | −0.0012 (12) | 0.0007 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0187 (15) | 0.0206 (16) | 0.0227 (16) | 0.0008 (13) | −0.0016 (12) | 0.0012 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0162 (15) | 0.0227 (16) | 0.0229 (17) | −0.0004 (13) | 0.0025 (12) | −0.0010 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0185 (15) | 0.0186 (16) | 0.0231 (16) | −0.0027 (12) | 0.0065 (12) | 0.0003 (13) |
| C11 | 0.0198 (15) | 0.0214 (15) | 0.0160 (15) | −0.0013 (13) | 0.0003 (12) | −0.0010 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0184 (15) | 0.0321 (17) | 0.0243 (17) | −0.0003 (14) | 0.0000 (12) | −0.0095 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0227 (17) | 0.0302 (18) | 0.0233 (17) | 0.0015 (14) | −0.0017 (13) | −0.0052 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0215 (16) | 0.0304 (18) | 0.0268 (17) | −0.0030 (14) | −0.0022 (13) | −0.0068 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0157 (15) | 0.0266 (17) | 0.0278 (17) | −0.0013 (13) | 0.0019 (12) | −0.0004 (14) |
| C16 | 0.0186 (15) | 0.0251 (16) | 0.0199 (17) | 0.0039 (13) | 0.0016 (13) | −0.0002 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C1 | 1.324 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.521 (4) |
| N1—C5 | 1.348 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.520 (3) |
| N2—C1 | 1.406 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.529 (4) |
| N2—C8 | 1.399 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.519 (4) |
| N2—C11 | 1.392 (4) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C5 | 1.349 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C12 | 1.470 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C16 | 1.465 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N4—C6 | 1.153 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| N5—C7 | 1.152 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.403 (4) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.400 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C6 | 1.433 (4) | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.383 (4) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.426 (4) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C7 | 1.429 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.351 (4) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.423 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C10—C11 | 1.354 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 121.1 (2) | N2—C8—H8 | 126.00 |
| C1—N2—C8 | 128.8 (2) | C9—C8—H8 | 126.00 |
| C1—N2—C11 | 123.5 (2) | C8—C9—H9 | 126.00 |
| C8—N2—C11 | 107.6 (2) | C10—C9—H9 | 126.00 |
| C5—N3—C12 | 121.4 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 126.00 |
| C5—N3—C16 | 123.7 (2) | C11—C10—H10 | 126.00 |
| C12—N3—C16 | 113.3 (2) | N2—C11—H11 | 126.00 |
| N1—C1—N2 | 113.5 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 126.00 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 122.6 (2) | N3—C12—H12A | 110.00 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 124.0 (2) | N3—C12—H12B | 110.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 116.6 (2) | C13—C12—H12A | 110.00 |
| C1—C2—C6 | 127.2 (2) | C13—C12—H12B | 110.00 |
| C3—C2—C6 | 116.3 (2) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.7 (2) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.5 (2) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 117.5 (2) | C14—C13—H13A | 109.00 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 124.6 (2) | C14—C13—H13B | 109.00 |
| N1—C5—N3 | 116.8 (2) | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.00 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 120.2 (2) | C13—C14—H14A | 110.00 |
| N3—C5—C4 | 123.0 (2) | C13—C14—H14B | 110.00 |
| N4—C6—C2 | 177.1 (3) | C15—C14—H14A | 110.00 |
| N5—C7—C4 | 178.0 (3) | C15—C14—H14B | 110.00 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 108.3 (2) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 107.8 (2) | C14—C15—H15A | 110.00 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 107.9 (2) | C14—C15—H15B | 110.00 |
| N2—C11—C10 | 108.3 (2) | C16—C15—H15A | 110.00 |
| N3—C12—C13 | 108.9 (2) | C16—C15—H15B | 110.00 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 111.7 (2) | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.00 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 110.5 (2) | N3—C16—H16A | 110.00 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 109.5 (2) | N3—C16—H16B | 110.00 |
| N3—C16—C15 | 110.5 (2) | C15—C16—H16A | 110.00 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.00 | C15—C16—H16B | 110.00 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.00 | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.00 |
| C5—N1—C1—N2 | 177.4 (2) | N2—C1—C2—C3 | 178.3 (2) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | −1.4 (4) | N2—C1—C2—C6 | −1.0 (4) |
| C1—N1—C5—N3 | −177.0 (2) | N1—C1—C2—C6 | 177.7 (3) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 5.8 (4) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | −3.0 (4) |
| C8—N2—C1—N1 | 178.4 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 3.0 (4) |
| C11—N2—C1—C2 | 174.0 (2) | C6—C2—C3—C4 | −177.6 (3) |
| C1—N2—C8—C9 | 177.1 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C7 | −171.7 (3) |
| C1—N2—C11—C10 | −177.3 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.1 (4) |
| C8—N2—C11—C10 | 0.0 (3) | C3—C4—C5—N1 | −5.5 (4) |
| C8—N2—C1—C2 | −2.8 (4) | C7—C4—C5—N3 | −10.5 (4) |
| C11—N2—C8—C9 | 0.0 (3) | C3—C4—C5—N3 | 177.4 (2) |
| C11—N2—C1—N1 | −4.8 (3) | C7—C4—C5—N1 | 166.6 (2) |
| C5—N3—C16—C15 | 134.0 (2) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | 0.0 (3) |
| C12—N3—C5—N1 | −14.1 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.0 (3) |
| C12—N3—C16—C15 | −60.3 (3) | C9—C10—C11—N2 | 0.0 (3) |
| C16—N3—C5—C4 | −32.4 (4) | N3—C12—C13—C14 | −55.5 (3) |
| C5—N3—C12—C13 | −135.4 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 55.1 (3) |
| C16—N3—C12—C13 | 58.5 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −54.7 (3) |
| C16—N3—C5—N1 | 150.5 (2) | C14—C15—C16—N3 | 56.7 (3) |
| C12—N3—C5—C4 | 163.0 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12B···N1 | 0.97 | 2.36 | 2.740 (3) | 103 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU5473).
References
- Al-Haiza, M. A., Mostafa, M. S. & El-Kady, M. Y. (2003). Molecules, 8, 275–286.
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 115–119.
- Bhalerao, U. T. & Krishnaiah, A. (1995). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 34, 587–590.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Doe, K., Avasthi, K., Pratap, R., Bakuni, D. S. & Joshi, M. N. (1990). Indian J. Chem. Sect B, 29, 459–463.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Murata, T., Shimada, M., Sakakibara, S., Yoshino, T., Kadono, H., Masuda, T., Shimazaki, M., Shintani, T., Fuchikami, K., Sakai, K., Inbe, H., Takeshita, K., Niki, T., Umeda, M., Bacon, K. B., Ziegelbauer, K. B. & Lowinger, T. B. (2003). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13, 913–918. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2011). CrystalClear-SM Expert Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Shankaraiah, G. K., Vishnu, T. K. & Bhaskar, S. D. (2010). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2, 187–191.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shishoo, C. J., Devani, M. B., Bhadti, V. C., Ananthan, S. & Ullas, G. V. (1983). Tetrahedron Lett. 24, 4611–4612.
- Soliman, A. M., Mohamed, S. K., El Remail, M. A. & Abdel Ghany, H. (2012). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 47, 138–142. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Temple, C., Rener, G. A., Raud, W. R. & Noker, P. E. (1992). J. Med. Chem. 35, 3686–3690. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008586/xu5473sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008586/xu5473Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008586/xu5473Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report