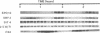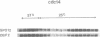Abstract
To help clarify the role of DBF2, a previously described cell cycle protein kinase, high copy number suppressors of the dbf2 mutation were isolated. Three open reading frames (ORF) have been identified. One ORF encodes a protein which has homology to a human small nuclear riboprotein, while the remaining two are genes which have been identified previously, SIT4 and SPO12. SIT4 is known to have a role in the cell cycle but the nature of the interaction between SIT4 and dbf2 is unclear. SPO12 has until now been implicated exclusively in meiosis. However, we show that SPO12 is expressed during vegetative growth, moreover it is expressed under cell cycle control coordinately with DBF2. SPO12 is a nonessential gene, but it becomes essential in a DBF2 delete genetic background. Furthermore, detailed analysis of the cell cycle of SPO12 delete cells revealed a small but significant delay in mitosis. Therefore, SPO12 does have a role during vegetative growth and it probably functions in mitosis in association with DBF2.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. G., Johnston L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cdc9, a structural gene for yeast DNA ligase which complements Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc17. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):315–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra M. F., DeMaggio A. J., Dhillon N. Genetically identified protein kinases in yeast. II: DNA metabolism and meiosis. Trends Genet. 1991 Sep;7(9):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90311-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra M. F., Demaggio A. J., Dhillon N. Genetically identified protein kinases in yeast. I: Transcription, translation, transport and mating. Trends Genet. 1991 Aug;7(8):256–261. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90325-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., Eberly S. L., Chapman J. W., Araki H., Sugino A. The product of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle gene DBF2 has homology with protein kinases and is periodically expressed in the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1358–1366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., Thomas A. P. A further two mutants defective in initiation of the S phase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):445–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00729467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., Thomas A. P. The isolation of new DNA synthesis mutants in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):439–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00729466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., White J. H., Johnson A. L., Lucchini G., Plevani P. The yeast DNA polymerase I transcript is regulated in both the mitotic cell cycle and in meiosis and is also induced after DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5017–5030. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. Isolation of SPO12-1 and SPO13-1 from a natural variant of yeast that undergoes a single meiotic division. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):567–588. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. Recombination and chromosome segregation during the single division meiosis in SPO12-1 and SPO13-1 diploids. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):589–611. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavasic M. J., Elder R. T. Complementary transcripts from two genes necessary for normal meiosis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2809–2819. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. Molecular analysis of a cell lineage. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):670–676. doi: 10.1038/302670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph R. K., Darkin-Rattray S., Schofield P. Growth-related protein kinases. Bioessays. 1990 Mar;12(3):121–124. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick S. G., Nguyen T. M., Ellis J. M., Crowne H., Morris G. E. Rapid mapping by transposon mutagenesis of epitopes on the muscular dystrophy protein, dystrophin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5889–5894. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster E. O., Byers B. Pachytene arrest and other meiotic effects of the start mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 Sep;123(1):29–43. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Immanuel D., Arndt K. T. The SIT4 protein phosphatase functions in late G1 for progression into S phase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2133–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyn J. H., Araki H., Sugino A., Johnston L. H. The cell-cycle-regulated budding yeast gene DBF2, encoding a putative protein kinase, has a homologue that is not under cell-cycle control. Gene. 1991 Jul 31;104(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90465-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H., Barker D. G., Nurse P., Johnston L. H. Periodic transcription as a means of regulating gene expression during the cell cycle: contrasting modes of expression of DNA ligase genes in budding and fission yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1705–1709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]