Abstract
In the title compound, C15H12N4OS, the dihedral angle between the nine-membered indolin-2-one ring system and the phenyl ring is 2.72 (7)°. Intramolecular cyclic N—H⋯O and C—H⋯S hydrogen-bonding interactions [graph set S(6)] are present, as are weak N—H⋯N interactions [graph set S(5)]. In the crystal, molecules form centrosymmetric cyclic dimers through pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds [graph set R 2 2(8)] and these are extended by C—H⋯S interactions. The crystal structure also features weak C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For related crystal structures, see: Ali et al. (2012 ▶); Qasem Ali et al. (2011a
▶,b
▶); Ferrari et al. (2002 ▶); Pervez et al. (2010 ▶); Ramzan et al. (2010 ▶). For various biological activities of Schiff bases, see: Bhandari et al. (2008 ▶); Bhardwaj et al. (2010 ▶); Pandeya et al. (1999 ▶); Sridhar et al. (2002 ▶); Suryavanshi & Pai (2006 ▶). For the cytotoxic and anticancer activities of isatin and its derivatives, see: Vine et al. (2009 ▶). For graph-set analysis, see Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).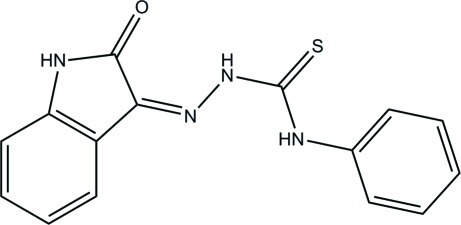
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H12N4OS
M r = 296.35
Monoclinic,

a = 6.3674 (1) Å
b = 15.4594 (3) Å
c = 14.2199 (3) Å
β = 93.383 (1)°
V = 1397.31 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.47 × 0.13 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.897, T max = 0.971
15557 measured reflections
4159 independent reflections
2985 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.040
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.053
wR(F 2) = 0.113
S = 1.02
4159 reflections
202 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.34 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.49 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681200400X/wn2464sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681200400X/wn2464Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681200400X/wn2464Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg2 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring and Cg3 is the centroid of the C10–C15 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N1⋯O1i | 0.88 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.8737 (18) | 173.9 (18) |
| N3—H1N3⋯O1 | 0.87 (2) | 2.07 (2) | 2.7646 (18) | 136 (2) |
| N4—H1N4⋯N2 | 0.88 (2) | 2.05 (2) | 2.5781 (19) | 117.4 (17) |
| C11—H11A⋯S1ii | 0.95 | 2.83 | 3.6017 (19) | 139 |
| C15—H15A⋯S1 | 0.95 | 2.60 | 3.2735 (19) | 128 |
| C2—H2A⋯Cg3iii | 0.95 | 2.80 | 3.510 (2) | 132 |
| C13—H13A⋯Cg2iv | 0.95 | 2.82 | 3.5201 (19) | 131 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Malaysian Government and Universiti Sains Malaysia for a Research University grant (No. 1001/PKIMIA/815067). AQA thanks the Ministry of Higher Education and the University of Sabha (Libya) for a scholarship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Isatin (2,3-dioxindole) is an endogenous compound identified in humans, and its effect has been studied in a variety of systems. The biological properties of isatin and its derivatives include a range of actions in the brain, offer protection against bacterial (Suryavanshi & Pai, 2006) and fungal infections and possess anticonvulsant, anti-HIV (Pandeya et al., 1999), antidepressant and anti-inflammatory activities (Bhandari et al., 2008). Recently, we reported the crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-chloro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-N-phenylhydrazinecarbothioamide (Qasem Ali et al., 2011a). In the present paper we describe the single-crystal X-ray diffraction study of the title compound (Fig. 1).
In the title compound, C15H12N4OS, the dihedral angle between the nine-membered indolin-2-one ring system and the phenyl ring is 2.72 (7)°. These two ring systems are connected by a chain of four atoms N2—N3—C9—N4; this torsion angle is 4.1 (2)°. The torsion angles C7—N2—N3—C9 and C10—N4—C9—N3 are 173.69 (15)° and 174.00 (16)°, respectively. These values are very close to those in a similar structure (Qasem Ali et al., 2011a).
The essentially planar conformation of the molecule is maintained by cyclic intramolecular N3—H1N3···O1 and C15—H15A···S1 hydrogen-bonding interactions [graph set S(6) (Bernstein et al., 1995)] (Table 1), together with a weak S(5) N4—H1N4···N2 interaction.
In the crystal structure, the molecules form centrosymmetric cyclic dimers through intermolecular N1—H1N1···O1 hydrogen bonds [graph set R22(8)] and are extended by C11—H11A···S1 hydrogen bond interactions.
The crystal structure (Fig. 2) is stabilized by weak C—H···π interactions (Table 1) involving the C10–C15 ring (centroid Cg3) and C1–C6 ring (centroid Cg2).
Experimental
The Schiff base has been synthesized by refluxing the reaction mixture of a hot ethanolic solution (30 ml) of 4-phenyl-3-thiosemicarbazide (0.01 mol) and a hot ethanolic solution (30 ml) of isatin (0.01 mol) for 2 h. The precipitate formed during reflux was filtered, washed with cold EtOH and recrystallized from hot EtOH. Yield (m.p.): 90% (510.2–511.6 K). The yellow crystals were grown in acetone–dimethylformamide (3:1) by slow evaporation at room temperature.
Refinement
N-bound H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and were refined freely; N—H = 0.87 (2) Å and 0.88 (2) Å. The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.95 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with 50% probability displacement ellipsoids. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed down the a axis. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bond interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C15H12N4OS | F(000) = 616 |
| Mr = 296.35 | Dx = 1.409 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point = 510.2–511.6 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.3674 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 4743 reflections |
| b = 15.4594 (3) Å | θ = 3.0–30.1° |
| c = 14.2199 (3) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| β = 93.383 (1)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1397.31 (5) Å3 | Needle, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.47 × 0.13 × 0.13 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4159 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2985 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.040 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 30.3°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −9→8 |
| Tmin = 0.897, Tmax = 0.971 | k = −21→18 |
| 15557 measured reflections | l = −17→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.053 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.113 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.038P)2 + 0.7736P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4159 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 202 parameters | Δρmax = 0.34 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.49 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.15701 (8) | 0.72368 (4) | 1.06040 (3) | 0.03145 (15) | |
| O1 | 0.73491 (19) | 0.55698 (8) | 1.00760 (8) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.9075 (2) | 0.50533 (10) | 0.87950 (10) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.4169 (2) | 0.61290 (9) | 0.85318 (10) | 0.0177 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.3689 (2) | 0.63773 (9) | 0.94027 (10) | 0.0191 (3) | |
| N4 | 0.0843 (2) | 0.70518 (9) | 0.87089 (10) | 0.0181 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.8690 (3) | 0.50379 (11) | 0.78102 (12) | 0.0195 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.9950 (3) | 0.47108 (12) | 0.71370 (13) | 0.0241 (4) | |
| H2A | 1.1264 | 0.4445 | 0.7306 | 0.029* | |
| C3 | 0.9210 (3) | 0.47880 (12) | 0.61995 (13) | 0.0253 (4) | |
| H3A | 1.0027 | 0.4560 | 0.5719 | 0.030* | |
| C4 | 0.7296 (3) | 0.51916 (12) | 0.59478 (13) | 0.0231 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.6846 | 0.5243 | 0.5301 | 0.028* | |
| C5 | 0.6042 (3) | 0.55185 (11) | 0.66319 (12) | 0.0206 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.4741 | 0.5794 | 0.6462 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | 0.6740 (3) | 0.54324 (11) | 0.75712 (12) | 0.0184 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.5904 (3) | 0.57114 (11) | 0.84497 (12) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.7491 (3) | 0.54476 (11) | 0.92218 (12) | 0.0188 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.1964 (3) | 0.68962 (11) | 0.95214 (12) | 0.0185 (4) | |
| C10 | −0.1096 (3) | 0.74787 (11) | 0.85012 (12) | 0.0168 (3) | |
| C11 | −0.1753 (3) | 0.74938 (11) | 0.75467 (12) | 0.0190 (4) | |
| H11A | −0.0892 | 0.7245 | 0.7095 | 0.023* | |
| C12 | −0.3656 (3) | 0.78705 (11) | 0.72568 (13) | 0.0237 (4) | |
| H12A | −0.4098 | 0.7878 | 0.6607 | 0.028* | |
| C13 | −0.4917 (3) | 0.82369 (11) | 0.79112 (13) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| H13A | −0.6228 | 0.8492 | 0.7714 | 0.030* | |
| C14 | −0.4248 (3) | 0.82279 (11) | 0.88559 (13) | 0.0229 (4) | |
| H14A | −0.5106 | 0.8486 | 0.9303 | 0.027* | |
| C15 | −0.2349 (3) | 0.78504 (11) | 0.91642 (12) | 0.0196 (4) | |
| H15A | −0.1912 | 0.7846 | 0.9815 | 0.024* | |
| H1N1 | 1.018 (3) | 0.4836 (14) | 0.9106 (15) | 0.037 (6)* | |
| H1N3 | 0.457 (4) | 0.6258 (14) | 0.9879 (16) | 0.039 (6)* | |
| H1N4 | 0.144 (3) | 0.6806 (14) | 0.8234 (15) | 0.029 (6)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0267 (2) | 0.0507 (3) | 0.0168 (2) | 0.0076 (2) | 0.00014 (18) | −0.0045 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0242 (6) | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0189 (6) | 0.0016 (5) | −0.0032 (5) | 0.0026 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0191 (7) | 0.0199 (8) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0043 (6) | −0.0032 (6) | 0.0020 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0153 (7) | 0.0187 (7) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0001 (5) | 0.0008 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0171 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0020 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0193 (8) | 0.0166 (7) | 0.0032 (6) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0000 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0195 (8) | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0254 (9) | 0.0000 (7) | −0.0025 (7) | 0.0014 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0211 (9) | 0.0197 (9) | 0.0315 (10) | 0.0045 (7) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0030 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0265 (9) | 0.0231 (9) | 0.0268 (9) | 0.0049 (8) | 0.0064 (8) | 0.0016 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0248 (9) | 0.0220 (9) | 0.0225 (9) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0018 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0181 (9) | 0.0248 (9) | 0.0010 (7) | −0.0016 (7) | 0.0016 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0190 (8) | 0.0140 (8) | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0005 (7) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0009 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0127 (8) | 0.0213 (8) | −0.0015 (6) | −0.0020 (7) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0254 (9) | −0.0013 (7) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0031 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0186 (8) | 0.0195 (8) | −0.0036 (7) | 0.0016 (6) | 0.0035 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0164 (8) | 0.0136 (8) | 0.0205 (8) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0014 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0198 (8) | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0023 (7) | 0.0013 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0243 (9) | 0.0204 (9) | 0.0257 (9) | −0.0013 (7) | −0.0043 (7) | 0.0044 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0167 (9) | 0.0383 (11) | 0.0006 (7) | −0.0014 (8) | 0.0044 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0339 (10) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0066 (7) | −0.0026 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0214 (8) | 0.0165 (8) | 0.0211 (8) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0024 (7) | −0.0021 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C9 | 1.6600 (18) | C4—C5 | 1.389 (3) |
| O1—C8 | 1.238 (2) | C4—H4A | 0.9500 |
| N1—C8 | 1.352 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.389 (2) |
| N1—C1 | 1.408 (2) | C5—H5A | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1N1 | 0.88 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.452 (2) |
| N2—C7 | 1.291 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.504 (2) |
| N2—N3 | 1.349 (2) | C10—C15 | 1.394 (2) |
| N3—C9 | 1.378 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.397 (2) |
| N3—H1N3 | 0.87 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.385 (2) |
| N4—C9 | 1.343 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9500 |
| N4—C10 | 1.416 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.386 (3) |
| N4—H1N4 | 0.88 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.381 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.385 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.407 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.393 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.390 (2) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9500 | C14—H14A | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.397 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | ||
| C8—N1—C1 | 111.31 (14) | N2—C7—C6 | 125.83 (15) |
| C8—N1—H1N1 | 123.0 (14) | N2—C7—C8 | 127.70 (16) |
| C1—N1—H1N1 | 125.7 (14) | C6—C7—C8 | 106.43 (14) |
| C7—N2—N3 | 117.83 (14) | O1—C8—N1 | 127.51 (15) |
| N2—N3—C9 | 120.23 (14) | O1—C8—C7 | 126.16 (16) |
| N2—N3—H1N3 | 118.7 (15) | N1—C8—C7 | 106.34 (15) |
| C9—N3—H1N3 | 120.6 (15) | N4—C9—N3 | 112.68 (15) |
| C9—N4—C10 | 132.49 (16) | N4—C9—S1 | 129.71 (14) |
| C9—N4—H1N4 | 110.5 (13) | N3—C9—S1 | 117.61 (12) |
| C10—N4—H1N4 | 116.9 (13) | C15—C10—C11 | 119.98 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 122.14 (16) | C15—C10—N4 | 125.29 (15) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 128.43 (15) | C11—C10—N4 | 114.71 (15) |
| C6—C1—N1 | 109.42 (15) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.19 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 117.03 (16) | C12—C11—H11A | 119.9 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 121.5 | C10—C11—H11A | 119.9 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 121.5 | C11—C12—C13 | 120.24 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.63 (18) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.9 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.2 | C13—C12—H12A | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.2 | C14—C13—C12 | 119.32 (16) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.78 (16) | C14—C13—H13A | 120.3 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.6 | C12—C13—H13A | 120.3 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.6 | C13—C14—C15 | 121.48 (17) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.29 (16) | C13—C14—H14A | 119.3 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 120.9 | C15—C14—H14A | 119.3 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 120.9 | C14—C15—C10 | 118.79 (16) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.11 (17) | C14—C15—H15A | 120.6 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 133.33 (16) | C10—C15—H15A | 120.6 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 106.50 (14) | ||
| C7—N2—N3—C9 | 173.69 (15) | C1—N1—C8—O1 | −179.73 (17) |
| C8—N1—C1—C2 | 178.50 (18) | C1—N1—C8—C7 | 0.46 (18) |
| C8—N1—C1—C6 | −0.7 (2) | N2—C7—C8—O1 | 2.3 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (3) | C6—C7—C8—O1 | −179.84 (16) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.09 (17) | N2—C7—C8—N1 | −177.88 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.1 (3) | C6—C7—C8—N1 | −0.03 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.1 (3) | C10—N4—C9—N3 | 174.00 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.1 (3) | C10—N4—C9—S1 | −6.4 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.2 (3) | N2—N3—C9—N4 | 4.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 177.76 (18) | N2—N3—C9—S1 | −175.54 (12) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.3 (3) | C9—N4—C10—C15 | −0.6 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.05 (15) | C9—N4—C10—C11 | −179.21 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −178.61 (16) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | −0.6 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C7 | 0.69 (19) | N4—C10—C11—C12 | 178.11 (15) |
| N3—N2—C7—C6 | −176.52 (15) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.2 (3) |
| N3—N2—C7—C8 | 0.9 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—N2 | 0.6 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.8 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—N2 | 177.50 (16) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | 0.4 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −177.26 (19) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.3 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −0.40 (18) | N4—C10—C15—C14 | −178.24 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring and Cg3 is the centroid of the C10–C15 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N1···O1i | 0.88 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.8737 (18) | 173.9 (18) |
| N3—H1N3···O1 | 0.87 (2) | 2.07 (2) | 2.7646 (18) | 136 (2) |
| N4—H1N4···N2 | 0.88 (2) | 2.05 (2) | 2.5781 (19) | 117.4 (17) |
| C11—H11A···S1ii | 0.95 | 2.83 | 3.6017 (19) | 139 |
| C15—H15A···S1 | 0.95 | 2.60 | 3.2735 (19) | 128 |
| C2—H2A···Cg3iii | 0.95 | 2.80 | 3.510 (2) | 132 |
| C13—H13A···Cg2iv | 0.95 | 2.82 | 3.5201 (19) | 131 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+2; (ii) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (iii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (iv) −x, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WN2464).
References
- Ali, A. Q., Eltayeb, N. E., Teoh, S. G., Salhin, A. & Fun, H.-K. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o285–o286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bhandari, S. V., Bothara, K. G., Raut, M. K., Patil, A. A., Sarkate, A. P. & Mokale, V. J. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 1822–1831. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, S., Kumar, L., Verma, R. & Sing, U. K. (2010). J. Pharm. Res. 3, 2983–2985.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ferrari, M. B., Pelizzi, C., Pelosi, G. & Rodriguez-Argüelles, M. C. (2002). Polyhedron, 21, 2593–2599.
- Pandeya, S. N., Sriram, D., Nath, G. & Clercq, E. De. (1999). Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 61, 358–361.
- Pervez, H., Yaqub, M., Ramzan, M., Tahir, M. N. & Iqbal, M. S. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Qasem Ali, A., Eltayeb, N. E., Teoh, S. G., Salhin, A. & Fun, H.-K. (2011a). Acta Cryst. E67, o3141–o3142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Qasem Ali, A., Eltayeb, N. E., Teoh, S. G., Salhin, A. & Fun, H.-K. (2011b). Acta Cryst. E67, o3476–o3477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ramzan, M., Pervez, H., Yaqub, M. & Tahir, M. N. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S. K., Pandeya, S. N., Stables, J. P. & Ramesh, A. (2002). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 16, 129–132. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Suryavanshi, J. P. & Pai, N. R. (2006). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 45, 1227–1230.
- Vine, K. L., Matesic, L., Locke, J. M., Ranson, M. & Skropeta, D. (2009). Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 9, 397–414. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681200400X/wn2464sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681200400X/wn2464Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681200400X/wn2464Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




