Abstract
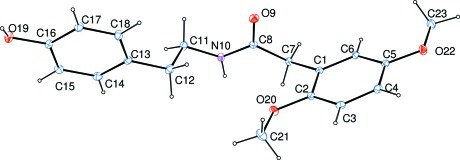
In the title compound, C18H21NO4, the dihedral angles between the acetamide group and the methoxy- and hydroxy-substitured benzene rings are 80.81 (5) and 8.19 (12)°, respectively. The benzene rings are twisted with respect to each other, making a dihedral angle of 72.89 (5)°. In the crystal, N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For general background to tyrosinase, see: Kubo et al. (2000 ▶). For the development of tyrosinase inhibitors, see: Lemic-Stojcevic et al. (1995 ▶); Battaini et al. (2000 ▶); Cabanes et al. (1994 ▶); Thanigaimalai et al. (2010 ▶).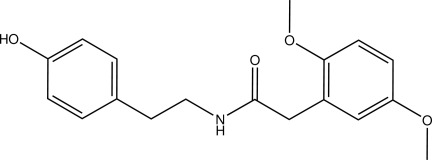
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H21NO4
M r = 315.36
Orthorhombic,
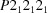
a = 8.1628 (8) Å
b = 12.0701 (11) Å
c = 17.0176 (16) Å
V = 1676.7 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.3 × 0.23 × 0.1 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
8417 measured reflections
3638 independent reflections
2352 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.063
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.088
S = 0.87
3638 reflections
216 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.11 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2002 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008975/tk5063sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008975/tk5063Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008975/tk5063Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N10—H10⋯O19i | 0.88 (2) | 2.16 (2) | 3.023 (2) | 165.4 (19) |
| O19—H19⋯O9ii | 0.87 (3) | 1.76 (3) | 2.6289 (19) | 174 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 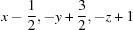 ; (ii)
; (ii) 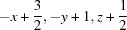 .
.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the DBIO company for partial support of this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Tyrosinase is a copper containing enzyme which acts as a catalyst in two different reactions involving the hydroxylation of monophenols to o-diphenols and the oxidation of the o-diphenols to o-quinones. This class of enzyme is widely distributed in the plant, animal and microorganism kingdoms (Kubo et al., 2000), and its inhibition is one of the major strategies in developing new whitening agents. Over the last few decades, various tyrosinase inhibitors, including azelaic acid (Lemic-Stojcevic et al., 1995), kojic acid (Battaini et al., 2000), arbutin (Cabanes et al., 1994), and N-phenylthiourea (PTU) (Thanigaimalai et al., 2010) have been studied. But some of their individual activities are either not potent enough to be considered of practical use or not compatible with safety regulations for food and cosmetic additives. In our continuing search for tyrosinase inhibitors, we have synthesized the title compound, (I), from the reaction of 2,5-dimethoxyphenyl acetyl chloride and tyramine under ambient conditions. Herein, the crystal structure of (I) is described (Fig. 1).
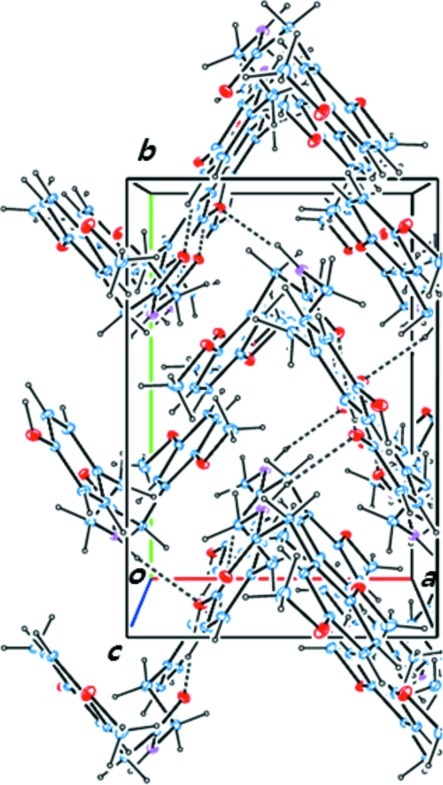
The 2,4-dimethoxyphenyl and 3-hydroxyphenyl moieties are almost planar with r.m.s. deviations of 0.008 and 0.009 Å, respectively, from their corresponding least-squares planes. The dihedral angles between the acetamide group (C7–N10) and the benzene rings (C1–C6 + O20 and O22; and C12–O19) are 80.81 (5) and 8.19 (12)°, respectively. The benzene groups are twisted with respect to each other making a dihedral angle of 72.89 (5)°. The presence of intermolecular N10—H10···O19i and O19—H19···O9ii [symmetry codes: (i) x - 1/2, -y + 3/2, -z + 1, (ii) -x + 3/2, -y + 1, z + 1/2] hydrogen bonds link the molecules into a three-dimensional network (Fig. 2 and Table 1).
Experimental
The starting materials, 2,5-dimethoxyphenyl acetyl chloride and tyramine, were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. Solvents for organic synthesis were redistilled before use. All other chemicals and solvents were of analytical grade and were used without further purification. The title compound was prepared from the reaction of 2,5-dimethoxyphenyl acetyl chloride (0.21 g, 1.0 mmol) and tyramine (0.14 g, 1.0 mmol) by simple substitution in THF (6 ml) triethylamine (0.12 g, 1.2 mmol). The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The mixture was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (2:1 dichloromethane/ethylacetate) to give the title compound. Colourless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of its ethanol solution at room temperature.
Refinement
H atoms of the NH and OH groups were located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely (N—H = 0.88 (2) Å and O—H = 0.87 (3) Å]. Other H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic and methylene, and 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms. In the absence of significant anomalous scattering effects, 1471 Friedel pairs were averaged in the final refinement.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme and 30% probability ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
Part of the packing diagram of the title compound, showing a three-dimensional network of molecules linked by intermolecular N—H···O and O—H···O hydrogen bonds (dashed lines).
Crystal data
| C18H21NO4 | F(000) = 672 |
| Mr = 315.36 | Dx = 1.249 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 2320 reflections |
| a = 8.1628 (8) Å | θ = 2.9–23.6° |
| b = 12.0701 (11) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 17.0176 (16) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 1676.7 (3) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.3 × 0.23 × 0.1 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | Rint = 0.063 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.8° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −4→10 |
| 8417 measured reflections | k = −15→7 |
| 3638 independent reflections | l = −18→21 |
| 2352 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.088 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.87 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0365P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3638 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 216 parameters | Δρmax = 0.11 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.4043 (2) | 0.70567 (12) | 0.09969 (11) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.2961 (2) | 0.62946 (13) | 0.13350 (11) | 0.0488 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.2247 (2) | 0.54873 (14) | 0.08716 (13) | 0.0563 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.153 | 0.4979 | 0.1096 | 0.068* | |
| C4 | 0.2590 (2) | 0.54310 (14) | 0.00842 (12) | 0.0562 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.2107 | 0.4882 | −0.0221 | 0.067* | |
| C5 | 0.3644 (2) | 0.61811 (14) | −0.02606 (12) | 0.0516 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.4357 (2) | 0.69979 (13) | 0.02022 (11) | 0.0472 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.5056 | 0.7513 | −0.0028 | 0.057* | |
| C7 | 0.4814 (2) | 0.79400 (13) | 0.15008 (11) | 0.0475 (5) | |
| H7A | 0.396 | 0.8424 | 0.1699 | 0.057* | |
| H7B | 0.5543 | 0.8383 | 0.1178 | 0.057* | |
| C8 | 0.5769 (2) | 0.74773 (14) | 0.21872 (12) | 0.0496 (5) | |
| O9 | 0.67141 (17) | 0.66858 (11) | 0.21107 (9) | 0.0710 (4) | |
| N10 | 0.5600 (2) | 0.80014 (13) | 0.28703 (10) | 0.0532 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.485 (3) | 0.8525 (17) | 0.2849 (12) | 0.073 (7)* | |
| C11 | 0.6334 (3) | 0.76130 (16) | 0.35966 (12) | 0.0607 (5) | |
| H11A | 0.6477 | 0.8236 | 0.395 | 0.073* | |
| H11B | 0.741 | 0.731 | 0.3484 | 0.073* | |
| C12 | 0.5315 (3) | 0.67421 (17) | 0.39979 (13) | 0.0715 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.421 | 0.7022 | 0.4064 | 0.086* | |
| H12B | 0.5258 | 0.6094 | 0.3662 | 0.086* | |
| C13 | 0.5972 (2) | 0.64031 (15) | 0.47870 (12) | 0.0544 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.5678 (3) | 0.70159 (14) | 0.54505 (13) | 0.0630 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.5077 | 0.7668 | 0.5407 | 0.076* | |
| C15 | 0.6242 (3) | 0.66973 (15) | 0.61796 (13) | 0.0624 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.601 | 0.7126 | 0.662 | 0.075* | |
| C16 | 0.7159 (2) | 0.57352 (14) | 0.62542 (12) | 0.0514 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.7467 (3) | 0.51175 (15) | 0.56022 (12) | 0.0623 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.8067 | 0.4465 | 0.5645 | 0.075* | |
| C18 | 0.6895 (3) | 0.54522 (16) | 0.48775 (13) | 0.0671 (6) | |
| H18 | 0.7137 | 0.5026 | 0.4437 | 0.081* | |
| O19 | 0.7706 (2) | 0.54495 (11) | 0.69866 (9) | 0.0700 (4) | |
| H19 | 0.794 (4) | 0.475 (2) | 0.7052 (16) | 0.139 (12)* | |
| O20 | 0.26868 (18) | 0.64349 (9) | 0.21211 (8) | 0.0633 (4) | |
| C21 | 0.1722 (3) | 0.56269 (18) | 0.25170 (14) | 0.0856 (8) | |
| H21A | 0.162 | 0.5826 | 0.3061 | 0.128* | |
| H21B | 0.2242 | 0.4916 | 0.2475 | 0.128* | |
| H21C | 0.0655 | 0.5594 | 0.2282 | 0.128* | |
| O22 | 0.38811 (19) | 0.60474 (12) | −0.10495 (9) | 0.0749 (5) | |
| C23 | 0.4980 (3) | 0.6780 (2) | −0.14310 (14) | 0.0836 (7) | |
| H23A | 0.5043 | 0.6595 | −0.1979 | 0.125* | |
| H23B | 0.6047 | 0.6714 | −0.1198 | 0.125* | |
| H23C | 0.4595 | 0.7527 | −0.1375 | 0.125* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0431 (10) | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0488 (13) | 0.0005 (8) | −0.0018 (9) | 0.0023 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0517 (11) | 0.0435 (9) | 0.0512 (13) | −0.0025 (8) | 0.0037 (10) | 0.0049 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0487 (11) | 0.0460 (9) | 0.0743 (15) | −0.0108 (9) | 0.0024 (11) | 0.0050 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0532 (12) | 0.0503 (10) | 0.0651 (15) | −0.0140 (10) | −0.0054 (11) | −0.0081 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0463 (10) | 0.0565 (10) | 0.0521 (14) | −0.0034 (9) | −0.0060 (10) | −0.0046 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0465 (9) | 0.0523 (13) | −0.0066 (8) | −0.0032 (9) | 0.0015 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0550 (12) | 0.0409 (8) | 0.0465 (12) | −0.0047 (8) | 0.0034 (9) | 0.0004 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0484 (11) | 0.0423 (8) | 0.0582 (14) | −0.0069 (9) | 0.0022 (10) | −0.0024 (9) |
| O9 | 0.0680 (9) | 0.0593 (8) | 0.0858 (11) | 0.0182 (7) | −0.0068 (8) | −0.0132 (8) |
| N10 | 0.0631 (11) | 0.0482 (8) | 0.0483 (11) | 0.0020 (9) | −0.0041 (9) | 0.0003 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0649 (13) | 0.0622 (11) | 0.0552 (13) | −0.0086 (10) | −0.0084 (11) | 0.0006 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0661 (13) | 0.0735 (13) | 0.0750 (16) | −0.0123 (12) | −0.0153 (12) | 0.0217 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0456 (11) | 0.0557 (10) | 0.0618 (14) | −0.0060 (9) | −0.0070 (10) | 0.0102 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0607 (13) | 0.0487 (10) | 0.0795 (17) | 0.0101 (10) | 0.0030 (12) | 0.0125 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0743 (14) | 0.0474 (10) | 0.0656 (15) | 0.0058 (10) | 0.0069 (12) | −0.0013 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0557 (12) | 0.0453 (9) | 0.0532 (13) | −0.0073 (9) | −0.0089 (10) | 0.0053 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0690 (13) | 0.0551 (10) | 0.0628 (14) | 0.0164 (10) | −0.0085 (13) | −0.0018 (11) |
| C18 | 0.0808 (16) | 0.0606 (11) | 0.0600 (15) | 0.0111 (12) | −0.0088 (12) | −0.0068 (11) |
| O19 | 0.0949 (11) | 0.0539 (8) | 0.0611 (10) | −0.0033 (8) | −0.0192 (9) | 0.0029 (7) |
| O20 | 0.0770 (9) | 0.0559 (7) | 0.0569 (9) | −0.0153 (7) | 0.0127 (8) | 0.0061 (7) |
| C21 | 0.113 (2) | 0.0654 (13) | 0.0782 (17) | −0.0159 (14) | 0.0298 (15) | 0.0162 (12) |
| O22 | 0.0808 (11) | 0.0891 (10) | 0.0548 (10) | −0.0292 (9) | 0.0034 (8) | −0.0165 (8) |
| C23 | 0.0788 (17) | 0.1105 (18) | 0.0614 (16) | −0.0286 (15) | 0.0078 (13) | −0.0088 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.378 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.97 |
| C1—C2 | 1.399 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.97 |
| C1—C7 | 1.506 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.371 (3) |
| C2—O20 | 1.367 (2) | C13—C18 | 1.382 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.382 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.378 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.371 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.93 |
| C3—H3 | 0.93 | C15—C16 | 1.387 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.93 |
| C4—H4 | 0.93 | C16—C17 | 1.360 (3) |
| C5—O22 | 1.366 (2) | C16—O19 | 1.368 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (2) | C17—C18 | 1.379 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.93 | C17—H17 | 0.93 |
| C7—C8 | 1.511 (3) | C18—H18 | 0.93 |
| C7—H7A | 0.97 | O19—H19 | 0.87 (3) |
| C7—H7B | 0.97 | O20—C21 | 1.423 (2) |
| C8—O9 | 1.235 (2) | C21—H21A | 0.96 |
| C8—N10 | 1.331 (2) | C21—H21B | 0.96 |
| N10—C11 | 1.452 (2) | C21—H21C | 0.96 |
| N10—H10 | 0.88 (2) | O22—C23 | 1.417 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.504 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.96 |
| C11—H11A | 0.97 | C23—H23B | 0.96 |
| C11—H11B | 0.97 | C23—H23C | 0.96 |
| C12—C13 | 1.503 (3) | ||
| C6—C1—C2 | 119.14 (16) | C11—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 121.17 (15) | C13—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 119.67 (17) | C11—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| O20—C2—C3 | 125.22 (16) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.7 |
| O20—C2—C1 | 115.11 (15) | C14—C13—C18 | 116.86 (18) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.67 (18) | C14—C13—C12 | 121.78 (18) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.45 (17) | C18—C13—C12 | 121.36 (19) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C13—C14—C15 | 122.16 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C13—C14—H14 | 118.9 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.68 (17) | C15—C14—H14 | 118.9 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C14—C15—C16 | 119.76 (19) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.1 |
| O22—C5—C4 | 115.38 (16) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.1 |
| O22—C5—C6 | 125.57 (17) | C17—C16—O19 | 123.00 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.05 (18) | C17—C16—C15 | 118.94 (18) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.99 (17) | O19—C16—C15 | 118.06 (19) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C16—C17—C18 | 120.41 (18) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C1—C7—C8 | 113.21 (13) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C1—C7—H7A | 108.9 | C17—C18—C13 | 121.8 (2) |
| C8—C7—H7A | 108.9 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.1 |
| C1—C7—H7B | 108.9 | C13—C18—H18 | 119.1 |
| C8—C7—H7B | 108.9 | C16—O19—H19 | 115.6 (19) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 107.7 | C2—O20—C21 | 117.97 (15) |
| O9—C8—N10 | 121.66 (18) | O20—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| O9—C8—C7 | 121.78 (18) | O20—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| N10—C8—C7 | 116.48 (16) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C8—N10—C11 | 123.19 (17) | O20—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C8—N10—H10 | 112.2 (14) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C11—N10—H10 | 123.7 (14) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| N10—C11—C12 | 112.56 (16) | C5—O22—C23 | 117.79 (15) |
| N10—C11—H11A | 109.1 | O22—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 109.1 | O22—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| N10—C11—H11B | 109.1 | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11B | 109.1 | O22—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.8 | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 113.50 (18) | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N10—H10···O19i | 0.88 (2) | 2.16 (2) | 3.023 (2) | 165.4 (19) |
| O19—H19···O9ii | 0.87 (3) | 1.76 (3) | 2.6289 (19) | 174 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (ii) −x+3/2, −y+1, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK5063).
References
- Battaini, G., Monzani, E., Casella, L., Santagostini, L. & Pagliarin, R. (2000). J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 5, 262–268. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2002). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cabanes, J., Chazarra, S. & Garcia-Carmona, F. (1994). J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 46, 982–985. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Kubo, I., Kinst-Hori, I., Chaudhuri, S. K., Kubo, Y., Scanchez, Y. & Ogura, T. (2000). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8, 1749–1755. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lemic-Stojcevic, L., Nias, A. H. & Breathnach, A. S. (1995). Exp. Dermatol. 4, 79–81. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Thanigaimalai, P., Le, H. T. A., Lee, K. C., Bang, S. C., Sharma, V. K., Yun, C. Y., Roh, E., Hwang, B. Y., Kim, Y. S. & Jung, S. H. (2010). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 2991–2993. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008975/tk5063sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008975/tk5063Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812008975/tk5063Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report