Abstract
In the title compound, C13H12BrN3O4, the dihedral angle between the benzene and imidazole rings is 30.6 (2)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked into chains parallel to [001] by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The crystal packing is further consolidated by π–π interactions [centroid–centroid distance = 3.482 (2) Å].
Related literature
For background information and the crystal structure of the 4-flouro analogue of the title compound, see: Yousuf et al. (2012 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H12BrN3O4
M r = 354.17
Monoclinic,

a = 14.554 (4) Å
b = 8.836 (2) Å
c = 11.563 (3) Å
β = 105.427 (6)°
V = 1433.3 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.89 mm−1
T = 273 K
0.33 × 0.20 × 0.19 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.449, T max = 0.610
8200 measured reflections
2601 independent reflections
1959 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.114
S = 1.04
2601 reflections
191 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.68 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.51 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, PARST (Nardelli, 1995 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812012688/pv2520sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812012688/pv2520Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812012688/pv2520Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—H8A⋯O4i | 0.97 | 2.51 | 3.183 (4) | 127 |
Symmetry code: (i) 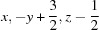 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound is an ester derivative of a broad spectrum antibiotic, metronidazole, commonly known as flagyl. In continuation of our research (Yousuf et al., 2012) we have now synthesized the title compound to evaluate its antiglycation potential. In this article, we report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
The title compound (Fig. 1) is structurally similar to its 4-flouro analogue (Yousuf et al., 2012). The mean planes of the benzene (C1–C6) and imidazole (C10—C12/N1—N2) rings are inclined at 30.6 (2)° with respect to each other. In the crystal structure, the molecules are linked to form chains via C8—H8A···O4 intermolecular interactions along the c-axis (Fig. 2 and Tab. 1). The Crystal packing is further strengthened by a significant π–π interaction between centroids of imidazole rings lying about inversion centers (Cg···Cg distance = 3.482 (2) Å).
Experimental
The synthesis of the title compounds was acheived by reacting metronidazole (171 mg, 1.0 mmole) with 2-bromobenzoic acid (1.2 equiv.) in the presence of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (245 mg, 1.2 mmole) and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (0.35 mmole) in dichloromethane (10 ml) at room temperature for 40–45 h. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. The reaction was quenched with 20 ml HCl (0.5 M) and then basified with sat. NaHCO3. It was extracted with dichloromethane and evaporated in vaccuo to obtain a crude product. The crude product was purified by using silica gel chromatography (EtOAc: hexane, 3.0: 7.0 to 7.0: 3.0) which afforded the title compound in 85% yield. Recrystallization by the slow evaporation of a dichloromethane solution of the title compound afforded pure crystals found suitable for single-crystal X-ray diffraction studies. All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
Refinement
H atoms on methyl, methylene and methine were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.96, 0.97 and 0.93 Å respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with Uiso(H)= 1.2Ueq(CH and CH2) and 1.5Ueq(CH3). A rotating group model was applied to the methyl groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. H atoms are presented as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
A view of the C—-H···O hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) in the crystal structure of the title compound. H atoms non-participating in hydrogen- bonding were omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C13H12BrN3O4 | F(000) = 712 |
| Mr = 354.17 | Dx = 1.641 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2494 reflections |
| a = 14.554 (4) Å | θ = 2.7–24.1° |
| b = 8.836 (2) Å | µ = 2.89 mm−1 |
| c = 11.563 (3) Å | T = 273 K |
| β = 105.427 (6)° | Block, colorles |
| V = 1433.3 (7) Å3 | 0.33 × 0.20 × 0.19 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2601 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1959 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.024 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000) | h = −17→17 |
| Tmin = 0.449, Tmax = 0.610 | k = −10→10 |
| 8200 measured reflections | l = −14→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.114 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0598P)2 + 0.7664P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2601 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 191 parameters | Δρmax = 0.68 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.51 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.39287 (3) | 0.03857 (5) | 0.11564 (3) | 0.0748 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.3629 (3) | 0.3331 (3) | 0.2376 (3) | 0.1003 (11) | |
| O2 | 0.25716 (17) | 0.3109 (3) | 0.3428 (2) | 0.0606 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.1411 (3) | 0.7613 (3) | 0.4002 (3) | 0.0981 (10) | |
| O4 | 0.1559 (3) | 0.8059 (3) | 0.5864 (3) | 0.1087 (11) | |
| N1 | 0.11680 (18) | 0.4509 (3) | 0.4402 (2) | 0.0471 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.1099 (2) | 0.3517 (4) | 0.6143 (3) | 0.0667 (8) | |
| N3 | 0.1438 (2) | 0.7198 (4) | 0.5010 (3) | 0.0696 (9) | |
| C1 | 0.3499 (3) | 0.0609 (4) | 0.4570 (3) | 0.0623 (9) | |
| H1A | 0.3271 | 0.1295 | 0.5038 | 0.075* | |
| C2 | 0.3779 (3) | −0.0807 (5) | 0.5015 (4) | 0.0747 (11) | |
| H2B | 0.3749 | −0.1072 | 0.5783 | 0.090* | |
| C3 | 0.4103 (3) | −0.1832 (5) | 0.4319 (4) | 0.0778 (12) | |
| H3A | 0.4292 | −0.2792 | 0.4620 | 0.093* | |
| C4 | 0.4151 (3) | −0.1450 (4) | 0.3185 (4) | 0.0664 (10) | |
| H4A | 0.4367 | −0.2151 | 0.2717 | 0.080* | |
| C5 | 0.3879 (2) | −0.0030 (4) | 0.2746 (3) | 0.0498 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.3552 (2) | 0.1034 (4) | 0.3431 (3) | 0.0475 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.3277 (3) | 0.2592 (4) | 0.3011 (3) | 0.0541 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.2178 (3) | 0.4561 (4) | 0.2996 (3) | 0.0618 (9) | |
| H8A | 0.2169 | 0.4689 | 0.2160 | 0.074* | |
| H8B | 0.2556 | 0.5368 | 0.3459 | 0.074* | |
| C9 | 0.1188 (3) | 0.4590 (4) | 0.3138 (3) | 0.0575 (9) | |
| H9A | 0.0875 | 0.5514 | 0.2785 | 0.069* | |
| H9B | 0.0832 | 0.3743 | 0.2704 | 0.069* | |
| C10 | 0.1311 (2) | 0.5647 (3) | 0.5247 (3) | 0.0511 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.1268 (3) | 0.5010 (4) | 0.6297 (3) | 0.0631 (9) | |
| H11A | 0.1343 | 0.5528 | 0.7016 | 0.076* | |
| C12 | 0.1047 (2) | 0.3241 (4) | 0.4998 (3) | 0.0555 (8) | |
| C13 | 0.0869 (3) | 0.1719 (4) | 0.4440 (4) | 0.0826 (12) | |
| H13A | 0.0630 | 0.1058 | 0.4952 | 0.124* | |
| H13B | 0.1453 | 0.1316 | 0.4332 | 0.124* | |
| H13C | 0.0408 | 0.1798 | 0.3675 | 0.124* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.1056 (4) | 0.0702 (3) | 0.0535 (3) | 0.0046 (2) | 0.0298 (2) | −0.00709 (18) |
| O1 | 0.134 (3) | 0.0601 (16) | 0.141 (3) | 0.0125 (17) | 0.096 (2) | 0.0205 (18) |
| O2 | 0.0806 (16) | 0.0593 (14) | 0.0483 (13) | 0.0208 (12) | 0.0282 (12) | 0.0138 (11) |
| O3 | 0.158 (3) | 0.0530 (16) | 0.095 (2) | −0.0046 (18) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0083 (15) |
| O4 | 0.169 (3) | 0.0605 (17) | 0.108 (3) | −0.011 (2) | 0.056 (2) | −0.0356 (18) |
| N1 | 0.0498 (14) | 0.0417 (14) | 0.0480 (15) | 0.0060 (11) | 0.0097 (12) | −0.0016 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0730 (19) | 0.068 (2) | 0.0620 (19) | 0.0077 (16) | 0.0231 (16) | 0.0130 (16) |
| N3 | 0.083 (2) | 0.0497 (17) | 0.081 (2) | 0.0018 (15) | 0.0311 (19) | −0.0153 (17) |
| C1 | 0.067 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0040 (18) | 0.0192 (17) | 0.0049 (17) |
| C2 | 0.075 (3) | 0.088 (3) | 0.064 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.029 (2) |
| C3 | 0.074 (3) | 0.063 (2) | 0.097 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.025 (2) | 0.028 (2) |
| C4 | 0.069 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.079 (3) | 0.0061 (18) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0020 (19) |
| C5 | 0.0503 (18) | 0.0488 (17) | 0.0488 (19) | −0.0028 (14) | 0.0106 (15) | −0.0015 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0488 (17) | 0.0480 (16) | 0.0456 (17) | −0.0023 (14) | 0.0123 (14) | −0.0019 (14) |
| C7 | 0.070 (2) | 0.0479 (17) | 0.0491 (19) | −0.0027 (16) | 0.0235 (17) | −0.0046 (15) |
| C8 | 0.088 (3) | 0.054 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.0189 (18) | 0.0245 (19) | 0.0130 (16) |
| C9 | 0.074 (2) | 0.0487 (19) | 0.0434 (19) | 0.0132 (17) | 0.0044 (17) | 0.0003 (15) |
| C10 | 0.0562 (19) | 0.0445 (17) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0075 (14) | 0.0159 (16) | −0.0058 (14) |
| C11 | 0.071 (2) | 0.068 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0093 (18) | 0.0186 (18) | −0.0037 (17) |
| C12 | 0.0513 (19) | 0.0473 (18) | 0.066 (2) | 0.0026 (15) | 0.0128 (16) | 0.0060 (17) |
| C13 | 0.095 (3) | 0.050 (2) | 0.102 (3) | −0.011 (2) | 0.024 (3) | −0.002 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C5 | 1.895 (3) | C3—C4 | 1.374 (5) |
| O1—C7 | 1.195 (4) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C7 | 1.326 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.372 (5) |
| O2—C8 | 1.439 (4) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| O3—N3 | 1.213 (4) | C5—C6 | 1.393 (4) |
| O4—N3 | 1.221 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.479 (5) |
| N1—C12 | 1.351 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.494 (5) |
| N1—C10 | 1.379 (4) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C9 | 1.472 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| N2—C12 | 1.328 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| N2—C11 | 1.345 (5) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| N3—C10 | 1.420 (5) | C10—C11 | 1.355 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.372 (5) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.391 (5) | C12—C13 | 1.485 (5) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.376 (6) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9300 | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C7—O2—C8 | 117.1 (3) | O2—C7—C6 | 111.7 (3) |
| C12—N1—C10 | 105.0 (3) | O2—C8—C9 | 106.5 (3) |
| C12—N1—C9 | 125.9 (3) | O2—C8—H8A | 110.4 |
| C10—N1—C9 | 129.0 (3) | C9—C8—H8A | 110.4 |
| C12—N2—C11 | 105.8 (3) | O2—C8—H8B | 110.4 |
| O3—N3—O4 | 123.4 (4) | C9—C8—H8B | 110.4 |
| O3—N3—C10 | 120.3 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.6 |
| O4—N3—C10 | 116.3 (4) | N1—C9—C8 | 112.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.0 (3) | N1—C9—H9A | 109.1 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 119.5 | C8—C9—H9A | 109.1 |
| C6—C1—H1A | 119.5 | N1—C9—H9B | 109.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.6 (4) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.1 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 120.2 | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.8 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 120.2 | C11—C10—N1 | 107.4 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.6 (4) | C11—C10—N3 | 127.8 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.7 | N1—C10—N3 | 124.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.7 | N2—C11—C10 | 109.8 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.6 (4) | N2—C11—H11A | 125.1 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.2 | C10—C11—H11A | 125.1 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.2 | N2—C12—N1 | 112.1 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.0 (3) | N2—C12—C13 | 123.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—Br1 | 117.1 (3) | N1—C12—C13 | 124.1 (3) |
| C6—C5—Br1 | 121.9 (2) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.0 (3) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 118.9 (3) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 123.0 (3) | C12—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—O2 | 122.4 (3) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 125.9 (3) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.9 (6) | C10—N1—C9—C8 | 80.5 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.1 (6) | O2—C8—C9—N1 | 64.2 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.5 (6) | C12—N1—C10—C11 | −0.1 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.2 (5) | C9—N1—C10—C11 | −177.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—Br1 | −178.1 (3) | C12—N1—C10—N3 | −177.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.2 (5) | C9—N1—C10—N3 | 5.3 (5) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −177.7 (3) | O3—N3—C10—C11 | −176.0 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.6 (5) | O4—N3—C10—C11 | 3.1 (6) |
| Br1—C5—C6—C1 | 177.1 (3) | O3—N3—C10—N1 | 1.1 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 178.2 (3) | O4—N3—C10—N1 | −179.8 (3) |
| Br1—C5—C6—C7 | −4.0 (5) | C12—N2—C11—C10 | 0.5 (4) |
| C8—O2—C7—O1 | 5.6 (5) | N1—C10—C11—N2 | −0.2 (4) |
| C8—O2—C7—C6 | −174.4 (3) | N3—C10—C11—N2 | 177.3 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | 145.8 (4) | C11—N2—C12—N1 | −0.6 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | −33.1 (6) | C11—N2—C12—C13 | 179.9 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—O2 | −34.2 (4) | C10—N1—C12—N2 | 0.5 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—O2 | 147.0 (3) | C9—N1—C12—N2 | 177.6 (3) |
| C7—O2—C8—C9 | 156.0 (3) | C10—N1—C12—C13 | 179.9 (3) |
| C12—N1—C9—C8 | −95.9 (4) | C9—N1—C12—C13 | −3.0 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8A···O4i | 0.97 | 2.51 | 3.183 (4) | 127 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2520).
References
- Bruker (2000). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, S., Zeb, A. & Basha, F. Z. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812012688/pv2520sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812012688/pv2520Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812012688/pv2520Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




