Abstract
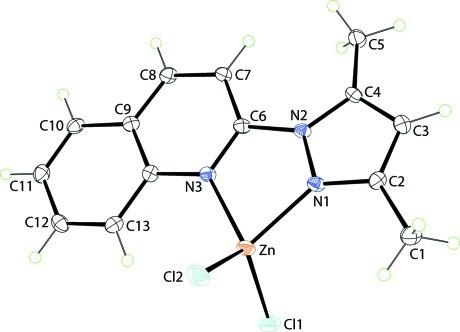
The ZnII atom in the title compound, [ZnCl2(C14H13N3)], is coordinated by a Cl2N2 donor set defined by quinoline and pyrazole N atoms of the chelating ligand and two Cl atoms. Distortions from the ideal tetrahedral geometry relate to the restricted bite angle of the chelating ligand [N—Zn—N = 78.54 (12)°]. In the crystal, molecules are connected into a three-dimensional structure by C—H⋯Cl interactions, involving both Cl atoms, and π–π interactions that occur between the pyrazole ring and each of the pyridine and benzene rings of the quinoline residue [intercentroid distances = 3.655 (2) and 3.676 (2) Å].
Related literature
For background to luminescent coordination complexes, see: Bai et al. (2012 ▶); Chou et al., (2011 ▶); Hu et al. (2011 ▶); Wang (2001 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Savel’eva et al. (2009 ▶); Scott et al. (1952 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[ZnCl2(C14H13N3)]
M r = 359.54
Monoclinic,
a = 14.3353 (10) Å
b = 8.7683 (5) Å
c = 11.9839 (8) Å
β = 102.181 (7)°
V = 1472.42 (17) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.02 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.25 × 0.20 × 0.02 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas detector
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.597, T max = 1.000
6070 measured reflections
3370 independent reflections
2438 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.050
wR(F 2) = 0.124
S = 1.02
3370 reflections
183 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 1.04 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.66 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014390/hg5206sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014390/hg5206Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Zn—N1 | 2.021 (3) |
| Zn—N3 | 2.072 (3) |
| Zn—Cl1 | 2.2099 (11) |
| Zn—Cl2 | 2.2076 (11) |
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1A⋯Cl1i | 0.98 | 2.81 | 3.680 (4) | 148 |
| C12—H12A⋯Cl2ii | 0.95 | 2.82 | 3.579 (4) | 138 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 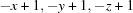 ; (ii)
; (ii) 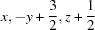 .
.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge funding from the Brunei Research Council, and thank the Ministry of Higher Education (Malaysia) for funding structural studies through the High-Impact Research scheme (UM.C/HIR/MOHE/SC/3).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Luminescent coordination complexes are used as emitting materials in light-emitting devices (Chou et al., 2011) and it is known that many ZnII nitrogen donor complexes are brightly luminescent in the blue region of the spectrum (Wang, 2001). The title compound (I) was prepared as part of our on-going quest for luminescent organometallic and coordination complexes with improved quantum efficiencies and colour purity (Bai et al., 2012; Hu et al., 2011;).
The ZnII atom in (I), Fig. 1, is chelated by quinolinyl- and pyrazolyl-N atoms and two chloride atoms, Table 1. The resulting Cl2N2 donor set defines a tetrahedron with a significant distortion apparent owing to the restricted bite angle of the chelating ligand, i.e. N1—Zn—N3 78.54 (12)°; the remaining angles lie in the range 111.52 (9)°, for N1—Zn—Cl1, to 115.73 (9)°, for N1—Zn—Cl2. The five-membered chelate ring is essentially planar with a r.m.s. deviation = 0.035 Å with maximum deviations of 0.034 (3) and -0.029 (3) Å for the N2 and N1 atoms, respectively. A small twist is apparent in the bidentate ligand with the dihedral angle between the quinolinyl and pyrazolyl rings being 6.84 (17)°. The overall coordination geometry found for (I) matches that seen in the species carrying an additional methyl group in the 4-position of the quinolinyl residue (Savel'eva et al., 2009).
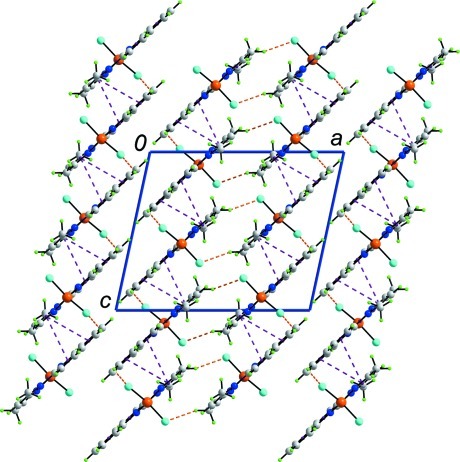
In the crystal packing, Fig. 2, molecules are connected into a three-dimensional architecture by C—H···Cl interactions, Table 1, involving both chloride atoms, and π—π interactions between the pyrazoyl ring and each of the pyridyl and benzene rings of the quinolinyl residue [inter-centroid distances = 3.655 (2) and 3.676 (2) Å, respectively; angles of inclination = 3.2 (2) and 3.5 (2)°, respectively; for symmetry operation: x, 1/2 - y, -1/2 + z].
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by modification of literature procedures (Savel'eva et al., 2009; Scott et al. 1952). 3,5-Dimethyl-1-(2'-quinolyl)pyrazole (0.080 g) in a mixture of EtOH (4 ml) and CH2Cl2 (2 ml) was added to a solution of ZnCl2 (0.061 g) in EtOH (8 ml). A white precipitate formed and was collected by filtration after 1 h, washed with EtOH and air-dried. The crude product was recrystallized from its CH2Cl2/hexane solution. Yield 0.054 g (42%). M. pt: 607–608 K. IR ν/cm-1: 1619, 1596, 1579, 1559, 1511, 1479, 1439, 1386, 1380, 1346, 1319, 1142, 1090, 994, 983, 825, 783, 760.
Refinement
Carbon-bound H-atoms were placed in calculated positions [C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å, Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C)] and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation. The maximum and minimum residual electron density peaks of 1.04 and 0.66 e Å-3, respectively, were located 1.00 Å and 0.95 Å from the Zn atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atom-labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of the unit-cell contents of (I) in projection down the b axis. The C—H···Cl and π—π interactions are shown as orange and purple dashed lines, respectively.
Crystal data
| [ZnCl2(C14H13N3)] | F(000) = 728 |
| Mr = 359.54 | Dx = 1.622 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1666 reflections |
| a = 14.3353 (10) Å | θ = 2.5–27.5° |
| b = 8.7683 (5) Å | µ = 2.02 mm−1 |
| c = 11.9839 (8) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 102.181 (7)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 1472.42 (17) Å3 | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.02 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas detector | 3370 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Mo) X-ray Source | 2438 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.047 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4041 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 2.7° |
| ω scan | h = −17→18 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010) | k = −11→8 |
| Tmin = 0.597, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −9→15 |
| 6070 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.124 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0519P)2 + 0.2907P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3370 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 183 parameters | Δρmax = 1.04 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.66 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Zn | 0.26453 (3) | 0.53715 (5) | 0.58123 (4) | 0.02140 (16) | |
| Cl1 | 0.37804 (7) | 0.65835 (11) | 0.70222 (9) | 0.0296 (3) | |
| Cl2 | 0.14937 (7) | 0.67975 (11) | 0.48204 (9) | 0.0300 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.3193 (2) | 0.3781 (3) | 0.4912 (3) | 0.0185 (7) | |
| N3 | 0.2198 (2) | 0.3372 (3) | 0.6458 (3) | 0.0179 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.4079 (3) | 0.5145 (4) | 0.3689 (4) | 0.0255 (9) | |
| H1A | 0.4758 | 0.5071 | 0.3671 | 0.038* | |
| H1B | 0.3979 | 0.6015 | 0.4163 | 0.038* | |
| H1C | 0.3706 | 0.5289 | 0.2911 | 0.038* | |
| C2 | 0.3767 (3) | 0.3710 (4) | 0.4180 (3) | 0.0194 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.4000 (3) | 0.2193 (4) | 0.4009 (3) | 0.0200 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.4400 | 0.1841 | 0.3524 | 0.024* | |
| C4 | 0.3546 (2) | 0.1306 (4) | 0.4674 (3) | 0.0186 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.3603 (3) | −0.0381 (4) | 0.4822 (4) | 0.0249 (9) | |
| H5A | 0.3798 | −0.0626 | 0.5636 | 0.037* | |
| H5B | 0.4073 | −0.0793 | 0.4415 | 0.037* | |
| H5C | 0.2977 | −0.0833 | 0.4513 | 0.037* | |
| C6 | 0.2458 (2) | 0.2097 (4) | 0.6031 (3) | 0.0174 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.2184 (3) | 0.0628 (4) | 0.6327 (3) | 0.0189 (8) | |
| H7A | 0.2373 | −0.0265 | 0.5984 | 0.023* | |
| C8 | 0.1632 (3) | 0.0549 (4) | 0.7129 (3) | 0.0207 (8) | |
| H8A | 0.1442 | −0.0421 | 0.7358 | 0.025* | |
| C9 | 0.1340 (2) | 0.1877 (4) | 0.7623 (3) | 0.0186 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.0765 (2) | 0.1852 (4) | 0.8457 (3) | 0.0216 (8) | |
| H10A | 0.0563 | 0.0905 | 0.8710 | 0.026* | |
| C11 | 0.0505 (3) | 0.3181 (5) | 0.8891 (3) | 0.0243 (9) | |
| H11A | 0.0119 | 0.3161 | 0.9446 | 0.029* | |
| C12 | 0.0805 (3) | 0.4586 (4) | 0.8521 (3) | 0.0229 (9) | |
| H12A | 0.0617 | 0.5506 | 0.8830 | 0.027* | |
| C13 | 0.1360 (3) | 0.4656 (4) | 0.7729 (3) | 0.0222 (8) | |
| H13A | 0.1565 | 0.5614 | 0.7499 | 0.027* | |
| C14 | 0.1628 (2) | 0.3301 (4) | 0.7257 (3) | 0.0187 (8) | |
| N2 | 0.3048 (2) | 0.2299 (3) | 0.5218 (3) | 0.0173 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Zn | 0.0306 (3) | 0.0144 (2) | 0.0210 (3) | −0.00055 (19) | 0.00946 (19) | 0.00027 (19) |
| Cl1 | 0.0423 (6) | 0.0242 (5) | 0.0237 (6) | −0.0104 (4) | 0.0104 (4) | −0.0047 (4) |
| Cl2 | 0.0364 (6) | 0.0193 (5) | 0.0355 (6) | 0.0071 (4) | 0.0102 (5) | 0.0038 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0250 (16) | 0.0152 (16) | 0.0151 (16) | −0.0005 (13) | 0.0042 (13) | −0.0004 (13) |
| N3 | 0.0248 (16) | 0.0180 (16) | 0.0116 (16) | −0.0026 (13) | 0.0054 (13) | −0.0017 (13) |
| C1 | 0.031 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.021 (2) | −0.0040 (18) | 0.0050 (17) | 0.0009 (17) |
| C2 | 0.0212 (18) | 0.023 (2) | 0.0139 (19) | −0.0034 (16) | 0.0029 (15) | 0.0013 (16) |
| C3 | 0.0205 (18) | 0.024 (2) | 0.0145 (19) | 0.0024 (16) | 0.0024 (14) | 0.0005 (16) |
| C4 | 0.0213 (18) | 0.0184 (19) | 0.0154 (19) | 0.0020 (16) | 0.0025 (15) | −0.0039 (16) |
| C5 | 0.033 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0027 (17) | 0.0137 (18) | 0.0029 (17) |
| C6 | 0.0211 (19) | 0.0185 (19) | 0.0113 (19) | −0.0014 (16) | 0.0004 (14) | −0.0012 (15) |
| C7 | 0.0243 (19) | 0.0157 (18) | 0.0168 (19) | −0.0003 (16) | 0.0047 (15) | −0.0017 (15) |
| C8 | 0.027 (2) | 0.0168 (19) | 0.019 (2) | −0.0016 (16) | 0.0064 (16) | 0.0047 (16) |
| C9 | 0.0199 (18) | 0.0198 (19) | 0.0149 (19) | −0.0009 (16) | 0.0011 (14) | 0.0004 (16) |
| C10 | 0.024 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.0061 (16) | 0.0044 (16) | 0.0004 (17) |
| C11 | 0.024 (2) | 0.033 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.0044 (18) | 0.0078 (16) | −0.0030 (18) |
| C12 | 0.0244 (19) | 0.025 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.0049 (17) | 0.0024 (16) | −0.0033 (17) |
| C13 | 0.0230 (19) | 0.023 (2) | 0.020 (2) | −0.0048 (17) | 0.0036 (16) | 0.0005 (17) |
| C14 | 0.0191 (18) | 0.0210 (19) | 0.0153 (19) | 0.0005 (16) | 0.0020 (15) | 0.0021 (16) |
| N2 | 0.0230 (16) | 0.0139 (15) | 0.0152 (16) | −0.0003 (13) | 0.0039 (13) | 0.0007 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Zn—N1 | 2.021 (3) | C5—H5B | 0.9800 |
| Zn—N3 | 2.072 (3) | C5—H5C | 0.9800 |
| Zn—Cl1 | 2.2099 (11) | C6—C7 | 1.414 (5) |
| Zn—Cl2 | 2.2076 (11) | C6—N2 | 1.429 (5) |
| N1—C2 | 1.325 (5) | C7—C8 | 1.370 (5) |
| N1—N2 | 1.378 (4) | C7—H7A | 0.9500 |
| N3—C6 | 1.316 (5) | C8—C9 | 1.409 (5) |
| N3—C14 | 1.385 (5) | C8—H8A | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.497 (5) | C9—C14 | 1.414 (5) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9800 | C9—C10 | 1.423 (5) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9800 | C10—C11 | 1.361 (5) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9800 | C10—H10A | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.397 (5) | C11—C12 | 1.407 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.373 (5) | C11—H11A | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C12—C13 | 1.362 (5) |
| C4—N2 | 1.375 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.490 (5) | C13—C14 | 1.403 (5) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | C13—H13A | 0.9500 |
| N1—Zn—N3 | 78.54 (12) | H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| N1—Zn—Cl2 | 115.73 (9) | N3—C6—C7 | 124.0 (3) |
| N3—Zn—Cl2 | 115.15 (9) | N3—C6—N2 | 114.6 (3) |
| N1—Zn—Cl1 | 111.52 (9) | C7—C6—N2 | 121.3 (3) |
| N3—Zn—Cl1 | 113.89 (9) | C8—C7—C6 | 117.0 (3) |
| Cl2—Zn—Cl1 | 116.38 (4) | C8—C7—H7A | 121.5 |
| C2—N1—N2 | 106.4 (3) | C6—C7—H7A | 121.5 |
| C2—N1—Zn | 138.7 (3) | C7—C8—C9 | 121.3 (3) |
| N2—N1—Zn | 114.3 (2) | C7—C8—H8A | 119.3 |
| C6—N3—C14 | 119.2 (3) | C9—C8—H8A | 119.3 |
| C6—N3—Zn | 116.0 (2) | C8—C9—C14 | 117.9 (3) |
| C14—N3—Zn | 124.8 (2) | C8—C9—C10 | 123.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C14—C9—C10 | 118.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C11—C10—C9 | 120.1 (4) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C11—C10—H10A | 119.9 |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C9—C10—H10A | 119.9 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C10—C11—C12 | 120.2 (4) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C10—C11—H11A | 119.9 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 110.0 (3) | C12—C11—H11A | 119.9 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 120.0 (3) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.4 (4) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 129.9 (3) | C13—C12—H12A | 119.3 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 107.3 (3) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.3 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 126.3 | C12—C13—C14 | 119.5 (4) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.3 | C12—C13—H13A | 120.3 |
| C3—C4—N2 | 105.9 (3) | C14—C13—H13A | 120.3 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 127.7 (3) | N3—C14—C13 | 119.5 (3) |
| N2—C4—C5 | 126.4 (3) | N3—C14—C9 | 120.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C13—C14—C9 | 120.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C4—N2—N1 | 110.4 (3) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C4—N2—C6 | 133.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5C | 109.5 | N1—N2—C6 | 116.3 (3) |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 | ||
| N3—Zn—N1—C2 | −172.9 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.8 (4) |
| Cl2—Zn—N1—C2 | 74.6 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −179.6 (3) |
| Cl1—Zn—N1—C2 | −61.5 (4) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | −0.2 (5) |
| N3—Zn—N1—N2 | −3.5 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.2 (5) |
| Cl2—Zn—N1—N2 | −116.1 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.2 (6) |
| Cl1—Zn—N1—N2 | 107.8 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.0 (6) |
| N1—Zn—N3—C6 | 0.5 (2) | C6—N3—C14—C13 | 179.0 (3) |
| Cl2—Zn—N3—C6 | 113.7 (2) | Zn—N3—C14—C13 | −3.6 (5) |
| Cl1—Zn—N3—C6 | −108.2 (2) | C6—N3—C14—C9 | 0.9 (5) |
| N1—Zn—N3—C14 | −177.0 (3) | Zn—N3—C14—C9 | 178.3 (2) |
| Cl2—Zn—N3—C14 | −63.8 (3) | C12—C13—C14—N3 | −179.5 (3) |
| Cl1—Zn—N3—C14 | 74.3 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −1.5 (5) |
| N2—N1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (4) | C8—C9—C14—N3 | −1.5 (5) |
| Zn—N1—C2—C3 | 169.6 (3) | C10—C9—C14—N3 | 179.1 (3) |
| N2—N1—C2—C1 | −179.2 (3) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | −179.6 (3) |
| Zn—N1—C2—C1 | −9.3 (6) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 1.1 (5) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (4) | C3—C4—N2—N1 | −0.6 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.7 (4) | C5—C4—N2—N1 | 177.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | 0.5 (4) | C3—C4—N2—C6 | −178.4 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −177.3 (4) | C5—C4—N2—C6 | −0.6 (6) |
| C14—N3—C6—C7 | 0.7 (5) | C2—N1—N2—C4 | 0.5 (4) |
| Zn—N3—C6—C7 | −176.9 (3) | Zn—N1—N2—C4 | −172.2 (2) |
| C14—N3—C6—N2 | −179.8 (3) | C2—N1—N2—C6 | 178.7 (3) |
| Zn—N3—C6—N2 | 2.6 (4) | Zn—N1—N2—C6 | 6.0 (4) |
| N3—C6—C7—C8 | −1.7 (5) | N3—C6—N2—C4 | 172.0 (3) |
| N2—C6—C7—C8 | 178.9 (3) | C7—C6—N2—C4 | −8.5 (6) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 1.0 (6) | N3—C6—N2—N1 | −5.7 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—C14 | 0.5 (5) | C7—C6—N2—N1 | 173.8 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1A···Cl1i | 0.98 | 2.81 | 3.680 (4) | 148 |
| C12—H12A···Cl2ii | 0.95 | 2.82 | 3.579 (4) | 138 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG5206).
References
- Agilent (2010). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Bai, S.-Q., Young, A. M., Hu, J. J., Young, D. J., Zhang, X., Zong, Y., Xu, J., Zuo, J.-L. & Hor, T. S. A. (2012). CrystEngComm, 14, 961–971.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Chou, P.-T., Chi, Y., Chung, M.-W. & Lin, C.-C. (2011). Coord. Chem. Rev 255, 2653–2665.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Hu, J. J., Bai, S. Q., Yeh, H. H., Young, D. J., Chi, Y. & Hor, T. S. A. (2011). Dalton Trans. 40, 4402–4406. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Savel’eva, Z. A., Popov, S. A., Klevtsova, R. F., Glinskaya, L. A., Uskov, E. M., Tkachev, A. V. & Larionov, S. V. (2009). Russ. Chem. Bull. Int. Ed 58, 1837–1840.
- Scott, F. L., Crowley, K. M. & Reilly, J. (1952). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74, 3444–3445.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wang, S. (2001). Coord. Chem. Rev. 215, 79–98.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014390/hg5206sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014390/hg5206Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report