Abstract
The PdII ion in the title complex, [PdBr2(C18H12N2)], is four-coordinated in a distorted square-planar environment by the two N atoms from the chelating 2,2′-biquinoline (Biqu) ligand and two mutually cis Br− anions. The Biqu ligand is not planar, the dihedral angle between the quinoline systems being 17.2 (2)°. In the crystal, the complex molecules are connected by C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds, forming chains along the c axis. When viewed down the b axis, successive chains are stacked in opposite directions. Intramolecular C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds are also observed.
Related literature
For the crystal structure of the related chlorido PdII complex [PdCl2(Biqu)], see: Muranishi et al. (2005 ▶).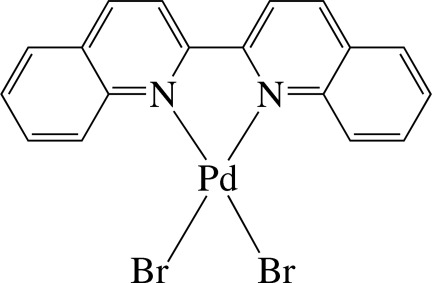
Experimental
Crystal data
[PdBr2(C18H12N2)]
M r = 522.50
Triclinic,

a = 8.9390 (5) Å
b = 9.2187 (5) Å
c = 11.1486 (6) Å
α = 72.398 (1)°
β = 69.318 (1)°
γ = 87.258 (1)°
V = 817.47 (8) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 6.02 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.17 × 0.12 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART 1000 CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.813, T max = 1.000
5100 measured reflections
3126 independent reflections
2612 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.018
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.028
wR(F 2) = 0.070
S = 1.12
3126 reflections
208 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.67 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.65 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812015425/rk2351sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812015425/rk2351Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2⋯Br1 | 0.95 | 2.73 | 3.252 (5) | 116 |
| C14—H14⋯Br1i | 0.95 | 2.90 | 3.754 (5) | 150 |
| C17—H17⋯Br2 | 0.95 | 2.85 | 3.261 (5) | 107 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2011-0030747).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title complex, [PdBr2(C18H12N2)], crystallized in the triclinic space group P1, whereas the analogous chlorido PdII complex [PdCl2(C18H12N2)] crystallized in the monoclinic space group P21/c (Muranishi et al., 2005).
The central PdII ion is four-coordinated in a distorted square-planar environment by the two N atoms from the chelating 2,2'-biquinoline (Biqu) ligand and two mutually cis Br- anions (Fig. 1). The main contribution to the distortion is the tight N1-Pd1-N2 chelate angle of 78.90 (15)°, which results in non-linear trans axes [angle Br1–Pd1-N2 = 169.85 (10)° and angle Br2–Pd1-N1 = 167.99 (11)°]. The pairs of Pd-N and Pd–Br bond lengths are nearly equivalent [Pd-N = 2.064 (4)Å and 2.073 (4)Å; Pd–Br = 2.4113 (6)Å and 2.4151 (6)Å]. In the crystal structure, the Biqu ligand is not planar. The dihedral angle between the least-squares planes of the quinoline rings is 17.2 (2)°. The quinoline rings are inclined considerably to the least-squares plane of the PdBr2N2 unit [maximum deviation = 0.162 (1)Å], making dihedral angles of 41.46 (8)° and 44.33 (8)°. In the crystal, the complex molecules are connected by intermolecular C–H···Br hydrogen bonds, forming chains along the c axis (Fig. 2 and Table 1). When viewed down the b axis, successive chains are stacked in opposite directions. Intramolecular C–H···Br hydrogen bonds are also observed (Table 1). In addition, intermolecular π···π interactions between the six-membered rings are present, the shortest ring centroid-centroid distance being 3.753 (3)Å between pyridine rings.
Experimental
To a solution of K2PdBr4 (0.1507 g, 0.299 mmol) in MeOH (20 ml) was added 2,2'-biquinoline (0.0772 g, 0.301 mmol) and stirred for 3 h at room temperature. After addition of H2O (30 ml) to the reaction mixture, the formed precipitate was separated by filtration and washed with H2O and acetone, and dried at 323 K, to give a pale red powder (0.1305 g). Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation from an acetone solution.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and allowed to ride on their respective parent atoms: C–H = 0.95Å with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The highest peak (0.67eÅ-3) and the deepest hole (-0.65eÅ-3) in the difference Fourier map are located 0.86Å and 0.84Å, respectively, from the atoms H14 and Pd1.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A molecular structure of the title complex with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are presented as a small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
A view of the unit-cell contents of the title complex. Intermolecular C–H···Br H-bond interactions are drawn with dashed lines.
Crystal data
| [PdBr2(C18H12N2)] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 522.50 | F(000) = 500 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 2.123 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.9390 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 3201 reflections |
| b = 9.2187 (5) Å | θ = 2.6–26.0° |
| c = 11.1486 (6) Å | µ = 6.02 mm−1 |
| α = 72.398 (1)° | T = 200 K |
| β = 69.318 (1)° | Block, red |
| γ = 87.258 (1)° | 0.17 × 0.12 × 0.11 mm |
| V = 817.47 (8) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART 1000 CCD diffractometer | 3126 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2612 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.018 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000) | h = −10→11 |
| Tmin = 0.813, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −11→10 |
| 5100 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.028 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.070 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.12 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0152P)2 + 2.2618P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3126 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 208 parameters | Δρmax = 0.67 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.65 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Pd1 | 0.18588 (4) | 0.23543 (4) | 0.12682 (3) | 0.02511 (10) | |
| Br1 | 0.27983 (6) | 0.30923 (6) | 0.27917 (5) | 0.03917 (15) | |
| Br2 | 0.46432 (6) | 0.24992 (6) | −0.01469 (5) | 0.03636 (14) | |
| N1 | −0.0535 (4) | 0.2651 (4) | 0.2177 (4) | 0.0272 (8) | |
| N2 | 0.0935 (4) | 0.2114 (4) | −0.0130 (4) | 0.0262 (8) | |
| C1 | −0.1396 (6) | 0.2604 (5) | 0.3488 (5) | 0.0298 (11) | |
| C2 | −0.0886 (6) | 0.1742 (6) | 0.4531 (5) | 0.0355 (11) | |
| H2 | 0.0083 | 0.1239 | 0.4333 | 0.043* | |
| C3 | −0.1800 (7) | 0.1634 (6) | 0.5841 (5) | 0.0429 (13) | |
| H3 | −0.1471 | 0.1023 | 0.6546 | 0.051* | |
| C4 | −0.3222 (7) | 0.2412 (7) | 0.6164 (6) | 0.0492 (15) | |
| H4 | −0.3821 | 0.2355 | 0.7073 | 0.059* | |
| C5 | −0.3710 (7) | 0.3236 (7) | 0.5160 (6) | 0.0488 (15) | |
| H5 | −0.4661 | 0.3762 | 0.5375 | 0.059* | |
| C6 | −0.2853 (6) | 0.3342 (6) | 0.3796 (5) | 0.0340 (11) | |
| C7 | −0.3393 (6) | 0.4086 (6) | 0.2740 (6) | 0.0428 (13) | |
| H7 | −0.4315 | 0.4659 | 0.2909 | 0.051* | |
| C8 | −0.2613 (6) | 0.3996 (5) | 0.1484 (6) | 0.0350 (12) | |
| H8 | −0.3032 | 0.4427 | 0.0789 | 0.042* | |
| C9 | −0.1173 (6) | 0.3254 (5) | 0.1219 (5) | 0.0297 (11) | |
| C10 | −0.0315 (5) | 0.2984 (5) | −0.0078 (5) | 0.0267 (10) | |
| C11 | −0.0841 (6) | 0.3520 (5) | −0.1181 (5) | 0.0358 (12) | |
| H11 | −0.1739 | 0.4125 | −0.1125 | 0.043* | |
| C12 | −0.0034 (6) | 0.3152 (6) | −0.2328 (5) | 0.0386 (13) | |
| H12 | −0.0303 | 0.3588 | −0.3108 | 0.046* | |
| C13 | 0.1192 (6) | 0.2134 (6) | −0.2371 (5) | 0.0367 (12) | |
| C14 | 0.1985 (7) | 0.1614 (7) | −0.3494 (5) | 0.0426 (14) | |
| H14 | 0.1746 | 0.2013 | −0.4292 | 0.051* | |
| C15 | 0.3082 (7) | 0.0553 (6) | −0.3442 (6) | 0.0432 (13) | |
| H15 | 0.3597 | 0.0206 | −0.4200 | 0.052* | |
| C16 | 0.3463 (6) | −0.0038 (6) | −0.2269 (5) | 0.0390 (12) | |
| H16 | 0.4214 | −0.0800 | −0.2235 | 0.047* | |
| C17 | 0.2771 (6) | 0.0469 (5) | −0.1187 (5) | 0.0327 (11) | |
| H17 | 0.3049 | 0.0066 | −0.0408 | 0.039* | |
| C18 | 0.1640 (6) | 0.1591 (5) | −0.1213 (5) | 0.0293 (10) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Pd1 | 0.02232 (19) | 0.03082 (19) | 0.02356 (19) | 0.00450 (14) | −0.01142 (15) | −0.00677 (15) |
| Br1 | 0.0325 (3) | 0.0603 (3) | 0.0312 (3) | 0.0010 (2) | −0.0168 (2) | −0.0163 (3) |
| Br2 | 0.0241 (3) | 0.0522 (3) | 0.0343 (3) | 0.0056 (2) | −0.0098 (2) | −0.0166 (2) |
| N1 | 0.021 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.0009 (16) | −0.0103 (17) | −0.0085 (17) |
| N2 | 0.023 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.0006 (16) | −0.0107 (16) | −0.0026 (17) |
| C1 | 0.024 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.037 (3) | −0.003 (2) | −0.011 (2) | −0.012 (2) |
| C2 | 0.034 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.031 (3) | −0.001 (2) | −0.011 (2) | −0.008 (2) |
| C3 | 0.041 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.009 (3) | −0.007 (2) | −0.008 (3) |
| C4 | 0.042 (3) | 0.061 (4) | 0.035 (3) | −0.009 (3) | 0.006 (3) | −0.021 (3) |
| C5 | 0.028 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.062 (4) | −0.002 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.032 (3) |
| C6 | 0.021 (2) | 0.035 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.002 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.015 (2) |
| C7 | 0.029 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.067 (4) | 0.010 (2) | −0.017 (3) | −0.026 (3) |
| C8 | 0.028 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.004 (2) | −0.021 (2) | −0.012 (2) |
| C9 | 0.028 (3) | 0.026 (2) | 0.041 (3) | 0.002 (2) | −0.020 (2) | −0.010 (2) |
| C10 | 0.026 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.033 (3) | −0.0025 (19) | −0.015 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C11 | 0.033 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.048 (3) | 0.001 (2) | −0.027 (3) | −0.008 (2) |
| C12 | 0.046 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.008 (3) | −0.026 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| C13 | 0.037 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.030 (3) | −0.006 (2) | −0.015 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| C14 | 0.046 (3) | 0.058 (4) | 0.023 (3) | −0.018 (3) | −0.013 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| C15 | 0.040 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.037 (3) | −0.007 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.025 (3) |
| C16 | 0.035 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.045 (3) | −0.005 (2) | −0.009 (2) | −0.018 (3) |
| C17 | 0.033 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.000 (2) | −0.010 (2) | −0.011 (2) |
| C18 | 0.031 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.027 (3) | −0.005 (2) | −0.013 (2) | −0.009 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Pd1—N1 | 2.064 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| Pd1—N2 | 2.073 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.407 (7) |
| Pd1—Br1 | 2.4113 (6) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| Pd1—Br2 | 2.4151 (6) | C9—C10 | 1.468 (7) |
| N1—C9 | 1.349 (6) | C10—C11 | 1.413 (6) |
| N1—C1 | 1.378 (6) | C11—C12 | 1.363 (7) |
| N2—C10 | 1.339 (6) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C18 | 1.369 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.405 (7) |
| C1—C2 | 1.405 (7) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.421 (7) | C13—C14 | 1.415 (7) |
| C2—C3 | 1.373 (7) | C13—C18 | 1.425 (6) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C14—C15 | 1.355 (8) |
| C3—C4 | 1.416 (8) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C15—C16 | 1.411 (8) |
| C4—C5 | 1.350 (8) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C16—C17 | 1.357 (7) |
| C5—C6 | 1.415 (7) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C17—C18 | 1.413 (7) |
| C6—C7 | 1.404 (7) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.352 (7) | ||
| N1—Pd1—N2 | 78.90 (15) | C7—C8—C9 | 119.2 (5) |
| N1—Pd1—Br1 | 96.71 (11) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.4 |
| N2—Pd1—Br1 | 169.85 (10) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.4 |
| N1—Pd1—Br2 | 167.99 (11) | N1—C9—C8 | 121.8 (5) |
| N2—Pd1—Br2 | 96.02 (11) | N1—C9—C10 | 114.9 (4) |
| Br1—Pd1—Br2 | 86.49 (2) | C8—C9—C10 | 123.1 (4) |
| C9—N1—C1 | 119.3 (4) | N2—C10—C11 | 121.6 (4) |
| C9—N1—Pd1 | 109.1 (3) | N2—C10—C9 | 116.2 (4) |
| C1—N1—Pd1 | 130.2 (3) | C11—C10—C9 | 122.1 (4) |
| C10—N2—C18 | 120.3 (4) | C12—C11—C10 | 118.7 (5) |
| C10—N2—Pd1 | 107.9 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.7 |
| C18—N2—Pd1 | 129.2 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.7 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 119.9 (4) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.8 (5) |
| N1—C1—C6 | 120.1 (4) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.9 (5) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.4 (5) | C12—C13—C14 | 123.4 (5) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.3 | C12—C13—C18 | 117.9 (5) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.3 | C14—C13—C18 | 118.7 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.6 (5) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.7 (5) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.2 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.2 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.8 (5) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.3 (5) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.2 (5) | C17—C16—C15 | 120.9 (5) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.9 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 118.9 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 123.6 (5) | C16—C17—C18 | 120.4 (5) |
| C7—C6—C1 | 118.3 (5) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.0 (5) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.6 (5) | N2—C18—C17 | 121.0 (4) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.7 | N2—C18—C13 | 120.1 (4) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.7 | C17—C18—C13 | 118.9 (4) |
| N2—Pd1—N1—C9 | −29.4 (3) | C1—N1—C9—C10 | −168.6 (4) |
| Br1—Pd1—N1—C9 | 141.3 (3) | Pd1—N1—C9—C10 | 23.2 (5) |
| Br2—Pd1—N1—C9 | 36.4 (7) | C7—C8—C9—N1 | −1.0 (7) |
| N2—Pd1—N1—C1 | 164.1 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 174.6 (5) |
| Br1—Pd1—N1—C1 | −25.1 (4) | C18—N2—C10—C11 | −6.7 (7) |
| Br2—Pd1—N1—C1 | −130.0 (5) | Pd1—N2—C10—C11 | 156.5 (4) |
| N1—Pd1—N2—C10 | 30.8 (3) | C18—N2—C10—C9 | 169.1 (4) |
| Br1—Pd1—N2—C10 | −34.3 (8) | Pd1—N2—C10—C9 | −27.7 (4) |
| Br2—Pd1—N2—C10 | −138.2 (3) | N1—C9—C10—N2 | 3.3 (6) |
| N1—Pd1—N2—C18 | −168.0 (4) | C8—C9—C10—N2 | −172.6 (4) |
| Br1—Pd1—N2—C18 | 126.9 (5) | N1—C9—C10—C11 | 179.1 (4) |
| Br2—Pd1—N2—C18 | 23.0 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 3.1 (7) |
| C9—N1—C1—C2 | 168.6 (4) | N2—C10—C11—C12 | −0.9 (7) |
| Pd1—N1—C1—C2 | −26.1 (6) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −176.4 (4) |
| C9—N1—C1—C6 | −7.3 (6) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 6.4 (7) |
| Pd1—N1—C1—C6 | 158.0 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 174.8 (5) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −176.4 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C18 | −4.5 (7) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.5 (7) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −175.5 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −2.1 (8) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 3.8 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 2.2 (8) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.7 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.3 (9) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −1.6 (8) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 174.7 (5) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.6 (7) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −2.8 (8) | C10—N2—C18—C17 | −169.1 (4) |
| N1—C1—C6—C7 | 1.1 (7) | Pd1—N2—C18—C17 | 31.7 (6) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −174.7 (4) | C10—N2—C18—C13 | 8.5 (6) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.7 (4) | Pd1—N2—C18—C13 | −150.7 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 2.9 (7) | C16—C17—C18—N2 | −179.9 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −172.2 (5) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | 2.5 (7) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | 5.3 (7) | C12—C13—C18—N2 | −3.0 (7) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −5.3 (8) | C14—C13—C18—N2 | 177.7 (4) |
| C1—N1—C9—C8 | 7.4 (7) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | 174.7 (4) |
| Pd1—N1—C9—C8 | −160.8 (4) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | −4.7 (7) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···Br1 | 0.95 | 2.73 | 3.252 (5) | 116 |
| C14—H14···Br1i | 0.95 | 2.90 | 3.754 (5) | 150 |
| C17—H17···Br2 | 0.95 | 2.85 | 3.261 (5) | 107 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y, z−1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RK2351).
References
- Bruker (2000). SADABS, SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Muranishi, Y., Wang, Y., Odoko, M. & Okabe, N. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, m307–m310. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812015425/rk2351sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812015425/rk2351Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




