Abstract
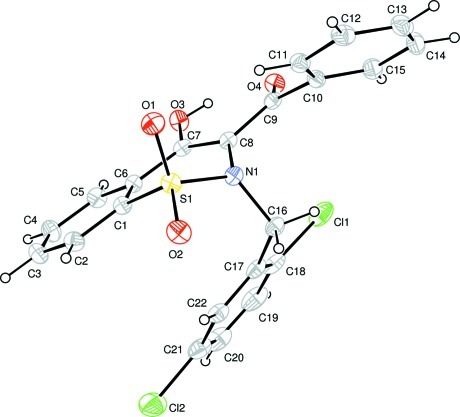
In the title molecule, C22H15Cl2NO4S, the heterocyclic thiazine ring adopts a half-chair conformation, with the S and N atoms displaced by 0.343 (5) and 0.402 (5) Å, respectively, on opposite sides of the mean plane formed by the remaining ring atoms. The molecular structure is consolidated by an intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond, which generates an S(?) ring. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by C—H⋯O interactions into [010] chains.
Related literature
For background information on the activity of anti-inflammatory and analgesic oxicams, see: Lombardino et al. (1971 ▶); Soler (1985 ▶); Carty et al. (1993 ▶); Turck et al. (1995 ▶); Blackham & Owen (1975 ▶). For the biological activity of benzothiazine derivatives, see: Zia-ur-Rehman et al. (2005 ▶); Ahmad et al. (2010 ▶). For the syntheses and crystal stuctures of related benzothiazine derivatives, see: Ahmad et al. (2011 ▶); Aslam et al. (2012 ▶).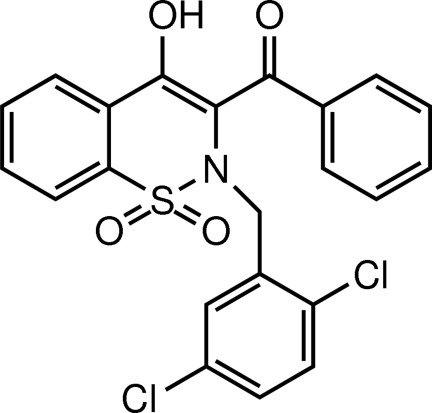
Experimental
Crystal data
C22H15Cl2NO4S
M r = 460.32
Monoclinic,
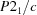
a = 12.8172 (5) Å
b = 9.9215 (4) Å
c = 16.7155 (5) Å
β = 110.511 (2)°
V = 1990.89 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.46 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.20 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SORTAV; Blessing, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.913, T max = 0.930
16108 measured reflections
4592 independent reflections
3598 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.055
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.057
wR(F 2) = 0.118
S = 1.11
4592 reflections
272 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Hooft, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681201481X/rk2344sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681201481X/rk2344Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681201481X/rk2344Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3—H3⋯O4i | 0.95 | 2.60 | 3.310 (4) | 132 |
| O3—H3O⋯O4 | 0.84 | 1.80 | 2.539 (3) | 146 |
Symmetry code: (i) 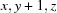 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Higher Education Commission, Pakistan, and the Institute of Chemistry, University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan, for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Oxicam is the most recent class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and includes molecules that are derived from 1,2-benzothiazine-1,1-dioxide nuclei which are found to be potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents, e.g., piroxicam (Lombardino et al., 1971), droxicam (Soler, 1985), ampiroxicam (Carty et al., 1993), meloxicam (Turck et al., 1995) and sudoxicam (Blackham & Owen, 1975), etc. Besides oxicam, a large number of benzothiazine derivatives are found to possess anti-microbial (Zia-ur-Rehman et al., 2005) and anti-oxidant activities (Ahmad et al., 2010). As part of our ongoing research we are interested in the synthesis and characterization of novel benzothiazine derivatives (Aslam et al., 2012; Ahmad et al., 2011). In this paper we report the synthesis, molecular and crystal structure of the title compound.
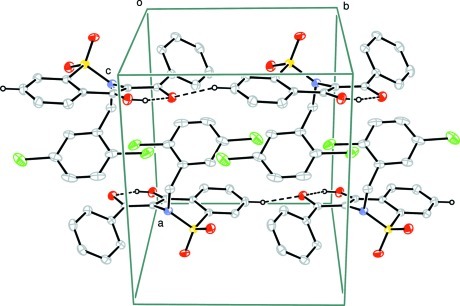
The bond distances and angles in the title compound (Fig. 1) agree well with the corresponding bond distances and angles reported for structures of closely related compounds (Ahmad et al., 2011; Aslam et al., 2012). The heterocyclic thiazine ring adopts a half chair conformation with atoms N1 and S1 displaced by 0.402 (5)Å and 0.343 (5)Å, respectively, on the opposite sides from the mean plane formed by the remaining ring atoms. The dihedral angle between the mean planes of benzene rings C1-C6 and C17-C22 is 31.17 (7)° while the mean planes of the benzene rings C1-C6 and C10-C15 are oriented at 35.09 (9)° with respect to each other. The molecular structure of the title compound is stabilized by intramolecular interactions O3–H3O···O4, C11–H11···N1 and C16–H16A···O2, etc, while the crystal packing is consolidated by C3–H3···O4i intermolecular nonclassical hydrogen bonds resulting in chains of molecules lying along the b-axis (Fig. 2 and Table 1). Symmetry code: (i) x, y+1, z.
Experimental
A mixture of 3-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2H-1,2-benzothiazine 1,1-dioxide (1.0 g, 3.32 mmol), aqueous sodium hydroxide (0.26 g, 6.6 mmol) and 2-(bromomethyl)-1,4-dichlorobenzene (0.80 g, 3.32 mmol) in acetone (10 ml) was subjected to ultrasonic irradiation for 20 minutes at 318 K. The reaction mixture was then acidified to pH = 3 by using dilute hydrochloric acid. The precipitates were filtered, washed with excess of distilled water and dried at room temperature to get chrome yellow powder of the title compound (1.38 g, 90.3%). The crystals suitable for X-ray crystallographic analysis were grown from methanol by slow evaporation at room temperature.
Refinement
The H atoms bonded to C and O atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with O–H = 0.84Å and C–H = 0.95Å and 0.99Å, respectively, for aryl and methylene type H-atoms. The Uiso(H) were allowed at 1.2Ueq(parent atom).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 25% probability level. The H atoms are presented as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
A part of the unit cell showing intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) in the crystal structure of the title compound. H atoms non-participating in hydrogen-bonding were omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C22H15Cl2NO4S | F(000) = 944 |
| Mr = 460.32 | Dx = 1.536 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 8696 reflections |
| a = 12.8172 (5) Å | θ = 1.0–27.5° |
| b = 9.9215 (4) Å | µ = 0.46 mm−1 |
| c = 16.7155 (5) Å | T = 173 K |
| β = 110.511 (2)° | Prism, yellow |
| V = 1990.89 (13) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 4592 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3598 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.055 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SORTAV; Blessing, 1997) | h = −16→16 |
| Tmin = 0.913, Tmax = 0.930 | k = −12→12 |
| 16108 measured reflections | l = −21→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.057 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.118 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.11 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0232P)2 + 2.3517P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4592 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 272 parameters | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.52481 (7) | −0.04749 (10) | 0.39033 (6) | 0.0658 (3) | |
| Cl2 | 0.50174 (9) | 0.57915 (12) | 0.37257 (7) | 0.0804 (3) | |
| S1 | 0.87675 (5) | 0.25684 (7) | 0.53887 (4) | 0.03478 (16) | |
| O1 | 0.98780 (15) | 0.2067 (2) | 0.56375 (12) | 0.0457 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.84712 (17) | 0.3467 (2) | 0.59407 (11) | 0.0465 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.79566 (17) | 0.0186 (2) | 0.31269 (11) | 0.0418 (5) | |
| H3O | 0.7866 | −0.0624 | 0.3235 | 0.050* | |
| O4 | 0.77251 (15) | −0.18006 (19) | 0.40080 (11) | 0.0408 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.79342 (17) | 0.1262 (2) | 0.52149 (12) | 0.0331 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.8421 (2) | 0.3280 (3) | 0.43643 (16) | 0.0339 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.8521 (2) | 0.4653 (3) | 0.42629 (18) | 0.0406 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.8739 | 0.5236 | 0.4744 | 0.049* | |
| C3 | 0.8297 (2) | 0.5165 (3) | 0.34482 (19) | 0.0465 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.8365 | 0.6104 | 0.3369 | 0.056* | |
| C4 | 0.7977 (3) | 0.4316 (3) | 0.27565 (18) | 0.0483 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.7830 | 0.4676 | 0.2201 | 0.058* | |
| C5 | 0.7866 (2) | 0.2949 (3) | 0.28534 (17) | 0.0421 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.7638 | 0.2378 | 0.2366 | 0.050* | |
| C6 | 0.8089 (2) | 0.2404 (3) | 0.36662 (15) | 0.0318 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.7989 (2) | 0.0952 (3) | 0.37903 (15) | 0.0326 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.7978 (2) | 0.0396 (3) | 0.45361 (14) | 0.0307 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.7971 (2) | −0.1051 (3) | 0.46462 (16) | 0.0334 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.8276 (2) | −0.1656 (3) | 0.55114 (16) | 0.0357 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.9160 (2) | −0.1140 (3) | 0.61913 (17) | 0.0403 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.9531 | −0.0345 | 0.6119 | 0.048* | |
| C12 | 0.9498 (2) | −0.1792 (3) | 0.69745 (18) | 0.0463 (7) | |
| H12 | 1.0107 | −0.1448 | 0.7438 | 0.056* | |
| C13 | 0.8954 (3) | −0.2934 (3) | 0.70810 (19) | 0.0498 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.9190 | −0.3376 | 0.7619 | 0.060* | |
| C14 | 0.8066 (3) | −0.3445 (3) | 0.6410 (2) | 0.0505 (8) | |
| H14 | 0.7685 | −0.4226 | 0.6491 | 0.061* | |
| C15 | 0.7735 (3) | −0.2815 (3) | 0.56220 (19) | 0.0448 (7) | |
| H15 | 0.7137 | −0.3175 | 0.5157 | 0.054* | |
| C16 | 0.6823 (2) | 0.1408 (3) | 0.53043 (16) | 0.0376 (6) | |
| H16A | 0.6906 | 0.1968 | 0.5813 | 0.045* | |
| H16B | 0.6560 | 0.0507 | 0.5403 | 0.045* | |
| C17 | 0.5954 (2) | 0.2036 (3) | 0.45391 (16) | 0.0396 (6) | |
| C18 | 0.5232 (2) | 0.1274 (4) | 0.38632 (19) | 0.0502 (8) | |
| C19 | 0.4486 (3) | 0.1900 (5) | 0.3150 (2) | 0.0661 (11) | |
| H19 | 0.4009 | 0.1372 | 0.2695 | 0.079* | |
| C20 | 0.4435 (3) | 0.3273 (5) | 0.3101 (2) | 0.0685 (11) | |
| H20 | 0.3933 | 0.3699 | 0.2606 | 0.082* | |
| C21 | 0.5114 (3) | 0.4044 (4) | 0.37701 (19) | 0.0564 (9) | |
| C22 | 0.5870 (2) | 0.3432 (3) | 0.44836 (17) | 0.0437 (7) | |
| H22 | 0.6336 | 0.3972 | 0.4938 | 0.052* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0454 (4) | 0.0807 (7) | 0.0762 (6) | −0.0194 (4) | 0.0274 (4) | −0.0311 (5) |
| Cl2 | 0.0780 (7) | 0.0882 (8) | 0.0780 (6) | 0.0331 (6) | 0.0310 (5) | 0.0324 (6) |
| S1 | 0.0355 (3) | 0.0382 (4) | 0.0259 (3) | −0.0025 (3) | 0.0048 (2) | −0.0050 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0316 (10) | 0.0547 (13) | 0.0402 (10) | −0.0033 (9) | −0.0006 (8) | −0.0019 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0582 (13) | 0.0452 (12) | 0.0332 (10) | −0.0025 (10) | 0.0124 (9) | −0.0114 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0569 (12) | 0.0388 (11) | 0.0303 (9) | −0.0066 (10) | 0.0160 (9) | −0.0086 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0440 (11) | 0.0395 (11) | 0.0358 (10) | −0.0041 (9) | 0.0102 (8) | −0.0087 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0342 (11) | 0.0379 (12) | 0.0265 (10) | −0.0022 (10) | 0.0100 (9) | −0.0041 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0311 (13) | 0.0375 (15) | 0.0310 (13) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0082 (10) | −0.0024 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0414 (15) | 0.0378 (15) | 0.0399 (15) | −0.0015 (12) | 0.0108 (12) | −0.0062 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0529 (18) | 0.0349 (16) | 0.0515 (17) | 0.0000 (13) | 0.0178 (14) | 0.0047 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0578 (19) | 0.0464 (18) | 0.0389 (15) | −0.0002 (15) | 0.0146 (14) | 0.0081 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0469 (16) | 0.0474 (17) | 0.0304 (13) | −0.0005 (13) | 0.0117 (12) | −0.0024 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0305 (12) | 0.0366 (14) | 0.0276 (11) | −0.0021 (11) | 0.0092 (10) | −0.0020 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0281 (12) | 0.0398 (15) | 0.0290 (12) | −0.0016 (11) | 0.0088 (10) | −0.0074 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0276 (12) | 0.0380 (14) | 0.0246 (11) | −0.0008 (11) | 0.0066 (9) | −0.0035 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0274 (12) | 0.0388 (15) | 0.0337 (13) | −0.0021 (11) | 0.0103 (10) | −0.0028 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0379 (14) | 0.0354 (14) | 0.0349 (13) | 0.0042 (12) | 0.0140 (11) | 0.0028 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0391 (15) | 0.0417 (16) | 0.0387 (14) | 0.0041 (12) | 0.0119 (12) | 0.0034 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0454 (16) | 0.0536 (19) | 0.0365 (15) | 0.0096 (14) | 0.0102 (13) | 0.0026 (13) |
| C13 | 0.062 (2) | 0.0496 (19) | 0.0413 (16) | 0.0147 (16) | 0.0226 (15) | 0.0116 (14) |
| C14 | 0.067 (2) | 0.0375 (17) | 0.0579 (19) | 0.0017 (15) | 0.0351 (17) | 0.0071 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0504 (17) | 0.0423 (17) | 0.0449 (16) | −0.0002 (13) | 0.0206 (14) | −0.0016 (13) |
| C16 | 0.0365 (14) | 0.0490 (17) | 0.0306 (13) | −0.0006 (12) | 0.0156 (11) | −0.0037 (12) |
| C17 | 0.0292 (13) | 0.0628 (19) | 0.0296 (13) | 0.0001 (13) | 0.0138 (11) | −0.0029 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0313 (14) | 0.079 (2) | 0.0444 (16) | −0.0037 (15) | 0.0190 (13) | −0.0138 (16) |
| C19 | 0.0351 (17) | 0.119 (4) | 0.0399 (18) | −0.002 (2) | 0.0073 (14) | −0.013 (2) |
| C20 | 0.0389 (18) | 0.124 (4) | 0.0366 (17) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0057 (14) | 0.015 (2) |
| C21 | 0.0395 (16) | 0.088 (3) | 0.0434 (17) | 0.0170 (17) | 0.0171 (14) | 0.0127 (17) |
| C22 | 0.0343 (14) | 0.065 (2) | 0.0340 (14) | 0.0068 (14) | 0.0142 (12) | 0.0029 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C18 | 1.736 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.486 (3) |
| Cl2—C21 | 1.738 (4) | C10—C15 | 1.389 (4) |
| S1—O1 | 1.425 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.391 (4) |
| S1—O2 | 1.4268 (19) | C11—C12 | 1.386 (4) |
| S1—N1 | 1.640 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| S1—C1 | 1.759 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.375 (4) |
| O3—C7 | 1.333 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| O3—H3O | 0.8400 | C13—C14 | 1.384 (4) |
| O4—C9 | 1.247 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C8 | 1.440 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.384 (4) |
| N1—C16 | 1.491 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.384 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.397 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.506 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.372 (4) | C17—C22 | 1.389 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C17—C18 | 1.404 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.379 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.387 (5) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C19—C20 | 1.365 (6) |
| C5—C6 | 1.396 (4) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C20—C21 | 1.383 (5) |
| C6—C7 | 1.467 (4) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.368 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.386 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.448 (4) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| O1—S1—O2 | 119.62 (12) | C12—C11—C10 | 119.7 (3) |
| O1—S1—N1 | 107.33 (12) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| O2—S1—N1 | 107.70 (12) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| O1—S1—C1 | 108.03 (12) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.1 (3) |
| O2—S1—C1 | 110.19 (12) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| N1—S1—C1 | 102.62 (11) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C7—O3—H3O | 109.5 | C12—C13—C14 | 120.5 (3) |
| C8—N1—C16 | 116.06 (19) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C8—N1—S1 | 114.13 (16) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C16—N1—S1 | 119.42 (18) | C13—C14—C15 | 119.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.6 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 120.8 (2) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C6—C1—S1 | 117.5 (2) | C14—C15—C10 | 120.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.0 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C10—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.5 | N1—C16—C17 | 113.8 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.1 (3) | N1—C16—H16A | 108.8 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C17—C16—H16A | 108.8 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | N1—C16—H16B | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.2 (3) | C17—C16—H16B | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.4 | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.7 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C22—C17—C18 | 118.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.1 (3) | C22—C17—C16 | 119.1 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C18—C17—C16 | 122.9 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C19—C18—C17 | 120.7 (3) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.1 (2) | C19—C18—Cl1 | 118.4 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.3 (2) | C17—C18—Cl1 | 120.8 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.6 (2) | C20—C19—C18 | 120.3 (3) |
| O3—C7—C8 | 121.4 (2) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.9 |
| O3—C7—C6 | 114.9 (2) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.9 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 123.7 (2) | C19—C20—C21 | 119.9 (3) |
| C7—C8—N1 | 119.5 (2) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.0 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 121.2 (2) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.0 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 119.2 (2) | C20—C21—C22 | 120.4 (4) |
| O4—C9—C8 | 119.6 (2) | C20—C21—Cl2 | 120.1 (3) |
| O4—C9—C10 | 119.6 (2) | C22—C21—Cl2 | 119.4 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 120.8 (2) | C21—C22—C17 | 120.5 (3) |
| C15—C10—C11 | 119.9 (3) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.7 |
| C15—C10—C9 | 119.4 (2) | C17—C22—H22 | 119.7 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.5 (2) | ||
| O1—S1—N1—C8 | −61.89 (19) | S1—N1—C8—C9 | 138.3 (2) |
| O2—S1—N1—C8 | 168.09 (17) | C7—C8—C9—O4 | −16.1 (4) |
| C1—S1—N1—C8 | 51.8 (2) | N1—C8—C9—O4 | 161.9 (2) |
| O1—S1—N1—C16 | 154.46 (18) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 162.6 (2) |
| O2—S1—N1—C16 | 24.5 (2) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | −19.5 (3) |
| C1—S1—N1—C16 | −91.83 (19) | O4—C9—C10—C15 | −36.4 (4) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | −96.7 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C15 | 144.9 (3) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | 35.6 (3) | O4—C9—C10—C11 | 138.0 (3) |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | 150.1 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −40.7 (4) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | 80.8 (2) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.3 (4) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | −146.9 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −174.1 (3) |
| N1—S1—C1—C6 | −32.4 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.7 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.8 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.0 (4) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | 176.6 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.1 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.3 (4) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −1.5 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.3 (5) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.8 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.5 (5) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | 175.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.0 (4) | C8—N1—C16—C17 | −62.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −179.3 (3) | S1—N1—C16—C17 | 80.4 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.7 (4) | N1—C16—C17—C22 | −86.3 (3) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | −176.8 (2) | N1—C16—C17—C18 | 92.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −180.0 (2) | C22—C17—C18—C19 | 2.1 (4) |
| S1—C1—C6—C7 | 2.5 (3) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −176.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O3 | 16.2 (4) | C22—C17—C18—Cl1 | −177.5 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—O3 | −163.1 (2) | C16—C17—C18—Cl1 | 3.9 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −166.5 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.7 (5) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | 14.2 (4) | Cl1—C18—C19—C20 | 178.9 (3) |
| O3—C7—C8—N1 | −175.6 (2) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | −1.2 (5) |
| C6—C7—C8—N1 | 7.3 (4) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 1.8 (5) |
| O3—C7—C8—C9 | 2.3 (4) | C19—C20—C21—Cl2 | −177.8 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −174.8 (2) | C20—C21—C22—C17 | −0.4 (4) |
| C16—N1—C8—C7 | 101.2 (3) | Cl2—C21—C22—C17 | 179.2 (2) |
| S1—N1—C8—C7 | −43.8 (3) | C18—C17—C22—C21 | −1.5 (4) |
| C16—N1—C8—C9 | −76.8 (3) | C16—C17—C22—C21 | 177.1 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C3—H3···O4i | 0.95 | 2.60 | 3.310 (4) | 132 |
| O3—H3O···O4 | 0.84 | 1.80 | 2.539 (3) | 146 |
| C11—H11···N1 | 0.95 | 2.62 | 3.003 (3) | 105 |
| C16—H16A···O2 | 0.99 | 2.45 | 2.862 (3) | 105 |
| C16—H16B···Cl1 | 0.99 | 2.67 | 3.120 (3) | 108 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RK2344).
References
- Ahmad, M., Siddiqui, H. L., Zia-ur-Rehman, M. & Parvez, M. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 698–704. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N., Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Siddiqui, H. L., Arshad, M. N. & Asiri, A. M. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Aslam, S., Siddiqui, H. L., Ahmad, M., Bukhari, I. H. & Parvez, M. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Blackham, A. & Owen, R. T. (1975). J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 27, 201–203. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Blessing, R. H. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 421–426.
- Carty, T. J., Marfat, A., Moore, P. F., Falkner, F. C., Twomey, T. M. & Weissmen, A. (1993). Agents Actions, 39, 157–165. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Hooft, R. W. W. (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Lombardino, J. G., Wiseman, E. H. & Chiaini, J. (1971). J. Med. Chem. 14, 1171–1175. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Soler, J. E. (1985). US Patent No. 4 563 452.
- Turck, D., Busch, U., Heinzel, G., Narjes, H. & Nehmiz, G. (1995). Clin. Drug Invest. 9, 270–276.
- Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Choudhary, J. A. & Ahmad, S. (2005). Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 54, 1171–1175.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681201481X/rk2344sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681201481X/rk2344Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681201481X/rk2344Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report