Abstract
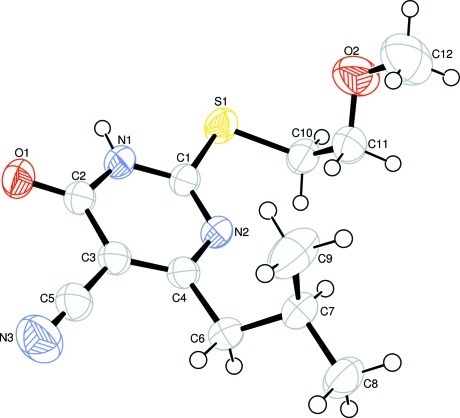
In the title compound, C12H17N3O2S, the 4-methyl-2-methylsulfanyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile part of the molecule is almost planar (r.m.s deviation = 0.062 Å). In the crystal, molecules form centrosymmetric dimers via pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For related pyrimidine structures, see: Yan et al. (2011 ▶); El-Brollosy et al. (2011 ▶); Nasir et al. (2010 ▶); Tiekink (1989 ▶); Al-Deeb et al. (2012 ▶); Durkaya et al. (2011 ▶).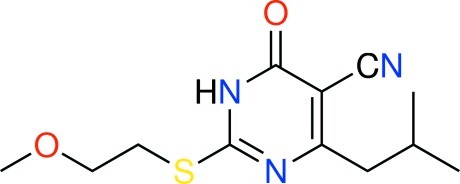
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H17N3O2S
M r = 267.35
Triclinic,
a = 5.0379 (5) Å
b = 10.5453 (10) Å
c = 13.3936 (13) Å
α = 85.274 (8)°
β = 82.170 (8)°
γ = 83.034 (8)°
V = 698.14 (12) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.23 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.68 × 0.47 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer
Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.859, T max = 0.966
6663 measured reflections
2725 independent reflections
2090 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.062
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.126
S = 1.02
2725 reflections
164 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction: X-RED32 (Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: WinGX (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812013372/bt5854sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812013372/bt5854Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812013372/bt5854Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.86 | 1.89 | 2.747 (2) | 175 |
Symmetry code: (i) 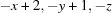 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Orhan Büyükgüngör for his help with the data collection and acknowledge the Ondokuz Mayıs University Research Fund for financial support. The financial support of the Deanship of Scientific Research and the Research Center of the College of Pharmacy, King Saud University is greatly appreciated.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In continuation to our work on the chemical and pharmacological properties of pyrimidine derivatives, we synthesized the title compound as a potential chemotherapeutic agent. The 4-methyl-2-(methylthio)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile part of the molecule is almost planar. Some pyrimidine structures have been described in the literature (Yan et al., 2011; El-Brollosy et al., 2011; Nasir et al., 2010; Tiekink 1989; Al-Deeb et al., 2012; Durkaya et al., 2011) and the bond distances of our crystal structure is comparable with these structures.
In the crystal, the molecules form centrosymmetric dimers via intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen bonds.
Experimental
To a solution of 6-(2-methylpropyl)-4-oxo-2-sulfanylidene-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile (2.09 g, 0.01 mol) in DMF (10 ml), 1-bromo-2-methoxyethane (1.4 g, 0.01 mol) and anhydrous potassium carbonate (1.38 g, 0.01 mol) were added and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Water (15 ml) was then added and the mixture was stirred for further 30 min. The separated solid was filtered, washed with cold water, dried and crystallized from water to yield 1.15 g (43%) of the title compound (C12H17N3O2S) as colorless crystals. M.P.: 113–115 oC. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution of the title compound in EtOH at room temperature. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 500.13 MHz): δ 0.93 (d, 6H, CH3, J = 7.0 Hz), 2.12–2.15 (m, 1H, CH), 2.53 (d, 2H, CH2CH, J = 7.0 Hz), 3.27 (s, 3H, CH3O), 3.53 (t, 2H, CH2S, J = 6.5 Hz), 3.56 (t, 2H, OCH2CH2, J = 6.5 Hz), 13.55 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 125.76 MHz): δ 22.55 (CH3), 27.94 (CH), 30.19 (CH2S), 45.30 (CH2CH), 58.36 (CH3O), 70.25 (OCH2), 95.97 (C-5), 115.55 (CN), 162.05 (C-6), 166.19 (C=O), 174.50 (C-2).
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically [N—H = 0.860 Å and C—H = 0.960 Å, 0.970 Å or 0.980 Å] and treated as riding with Uiso(H)=1.2Ueq(C,N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, showing the atomic numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C12H17N3O2S | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 267.35 | F(000) = 284 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.272 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.0379 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 9417 reflections |
| b = 10.5453 (10) Å | θ = 3.1–27.9° |
| c = 13.3936 (13) Å | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| α = 85.274 (8)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 82.170 (8)° | Prism, colorless |
| γ = 83.034 (8)° | 0.68 × 0.47 × 0.15 mm |
| V = 698.14 (12) Å3 |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer | 2725 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2090 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.062 |
| rotation method scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.859, Tmax = 0.966 | k = −12→12 |
| 6663 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.126 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0743P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2725 reflections | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 164 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.059 (9) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.6121 (4) | 0.32542 (17) | 0.13412 (14) | 0.0433 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.9074 (4) | 0.48214 (16) | 0.15109 (15) | 0.0450 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.8266 (4) | 0.46228 (16) | 0.25758 (15) | 0.0442 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.6474 (4) | 0.37554 (16) | 0.29360 (14) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.9463 (4) | 0.53342 (18) | 0.32209 (16) | 0.0520 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.5689 (4) | 0.34539 (18) | 0.40400 (14) | 0.0495 (5) | |
| H6A | 0.3788 | 0.3735 | 0.4212 | 0.059* | |
| H6B | 0.6694 | 0.3929 | 0.4421 | 0.059* | |
| C7 | 0.6216 (4) | 0.20252 (19) | 0.43492 (15) | 0.0479 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.5092 | 0.1569 | 0.3991 | 0.057* | |
| C8 | 0.5377 (5) | 0.1782 (2) | 0.54676 (17) | 0.0632 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.3491 | 0.2060 | 0.5625 | 0.076* | |
| H8B | 0.6398 | 0.2249 | 0.5837 | 0.076* | |
| H8C | 0.5710 | 0.0883 | 0.5652 | 0.076* | |
| C9 | 0.9103 (5) | 0.1502 (3) | 0.4063 (2) | 0.0851 (9) | |
| H9A | 1.0253 | 0.1946 | 0.4393 | 0.102* | |
| H9B | 0.9561 | 0.1620 | 0.3344 | 0.102* | |
| H9C | 0.9339 | 0.0606 | 0.4267 | 0.102* | |
| C10 | 0.3129 (4) | 0.1261 (2) | 0.12329 (17) | 0.0566 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.1835 | 0.1737 | 0.1707 | 0.068* | |
| H10B | 0.2118 | 0.0853 | 0.0808 | 0.068* | |
| C11 | 0.4729 (5) | 0.0231 (2) | 0.18197 (18) | 0.0646 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.5673 | 0.0621 | 0.2278 | 0.078* | |
| H11B | 0.3517 | −0.0319 | 0.2218 | 0.078* | |
| C12 | 0.7991 (8) | −0.1519 (3) | 0.1697 (3) | 0.1020 (10) | |
| H12A | 0.6742 | −0.2072 | 0.2050 | 0.122* | |
| H12B | 0.8951 | −0.1190 | 0.2173 | 0.122* | |
| H12C | 0.9246 | −0.1993 | 0.1222 | 0.122* | |
| N1 | 0.7874 (3) | 0.40967 (14) | 0.09326 (12) | 0.0468 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.8246 | 0.4179 | 0.0286 | 0.056* | |
| N2 | 0.5378 (3) | 0.30759 (14) | 0.23047 (12) | 0.0452 (4) | |
| N3 | 1.0420 (5) | 0.5910 (2) | 0.37314 (18) | 0.0761 (6) | |
| O1 | 1.0717 (3) | 0.55469 (13) | 0.11167 (11) | 0.0575 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.6562 (4) | −0.04885 (17) | 0.11760 (15) | 0.0855 (6) | |
| S1 | 0.50676 (11) | 0.23771 (5) | 0.04486 (4) | 0.0547 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0492 (9) | 0.0408 (9) | 0.0385 (10) | −0.0040 (7) | −0.0042 (8) | 0.0019 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0564 (10) | 0.0373 (9) | 0.0396 (10) | −0.0048 (7) | −0.0018 (8) | 0.0007 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0553 (10) | 0.0365 (9) | 0.0393 (10) | −0.0011 (7) | −0.0048 (8) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0518 (10) | 0.0375 (8) | 0.0388 (10) | 0.0004 (7) | −0.0015 (8) | −0.0005 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0637 (12) | 0.0444 (10) | 0.0473 (11) | −0.0056 (8) | −0.0067 (9) | −0.0014 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0616 (11) | 0.0483 (10) | 0.0365 (10) | −0.0073 (8) | 0.0017 (8) | −0.0027 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0479 (10) | 0.0544 (10) | 0.0402 (10) | −0.0077 (8) | −0.0033 (8) | 0.0033 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0734 (14) | 0.0715 (14) | 0.0423 (12) | −0.0143 (11) | 0.0004 (10) | 0.0074 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0608 (14) | 0.103 (2) | 0.0744 (18) | 0.0151 (13) | 0.0095 (12) | 0.0300 (16) |
| C10 | 0.0606 (12) | 0.0580 (12) | 0.0512 (12) | −0.0167 (9) | 0.0002 (9) | −0.0007 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0896 (16) | 0.0523 (11) | 0.0507 (13) | −0.0130 (11) | −0.0013 (11) | −0.0013 (10) |
| C12 | 0.127 (3) | 0.0788 (18) | 0.096 (3) | 0.0192 (17) | −0.029 (2) | −0.0031 (17) |
| N1 | 0.0598 (9) | 0.0449 (8) | 0.0347 (8) | −0.0099 (7) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0027 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0537 (8) | 0.0448 (8) | 0.0357 (8) | −0.0073 (6) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0007 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0948 (15) | 0.0671 (12) | 0.0729 (15) | −0.0169 (11) | −0.0209 (12) | −0.0147 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0751 (9) | 0.0526 (8) | 0.0456 (8) | −0.0238 (7) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0019 (6) |
| O2 | 0.1202 (15) | 0.0712 (11) | 0.0588 (11) | 0.0131 (10) | −0.0080 (10) | −0.0074 (9) |
| S1 | 0.0701 (4) | 0.0594 (3) | 0.0368 (3) | −0.0201 (2) | −0.0053 (2) | −0.0007 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N2 | 1.299 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| C1—N1 | 1.359 (2) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| C1—S1 | 1.744 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| C2—O1 | 1.232 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| C2—N1 | 1.374 (2) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.434 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.505 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.376 (3) | C10—S1 | 1.800 (2) |
| C3—C5 | 1.425 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| C4—N2 | 1.363 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C6 | 1.496 (3) | C11—O2 | 1.376 (3) |
| C5—N3 | 1.139 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.530 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C12—O2 | 1.417 (3) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C9 | 1.502 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.510 (3) | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9800 | N1—H1 | 0.8600 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9600 | ||
| N2—C1—N1 | 123.67 (18) | C7—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—S1 | 122.84 (14) | C7—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—S1 | 113.43 (14) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—N1 | 120.88 (18) | C7—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 125.26 (18) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 113.85 (16) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C5 | 122.88 (18) | C11—C10—S1 | 115.59 (16) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.35 (18) | C11—C10—H10A | 108.4 |
| C5—C3—C2 | 116.75 (17) | S1—C10—H10A | 108.4 |
| N2—C4—C3 | 121.83 (17) | C11—C10—H10B | 108.4 |
| N2—C4—C6 | 115.56 (15) | S1—C10—H10B | 108.4 |
| C3—C4—C6 | 122.56 (18) | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.4 |
| N3—C5—C3 | 179.5 (2) | O2—C11—C10 | 110.6 (2) |
| C4—C6—C7 | 112.75 (16) | O2—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C4—C6—H6A | 109.0 | C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 109.0 | O2—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C4—C6—H6B | 109.0 | C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6B | 109.0 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.1 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 107.8 | O2—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C9—C7—C8 | 110.84 (19) | O2—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C9—C7—C6 | 112.29 (18) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 110.23 (18) | O2—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C9—C7—H7 | 107.8 | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 107.8 | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 107.8 | C1—N1—C2 | 122.62 (16) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C1—N1—H1 | 118.7 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C2—N1—H1 | 118.7 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C1—N2—C4 | 117.66 (16) |
| C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C11—O2—C12 | 112.2 (2) |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C1—S1—C10 | 102.06 (10) |
| H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 | ||
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −177.90 (18) | N2—C1—N1—C2 | 1.5 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.9 (3) | S1—C1—N1—C2 | −175.81 (14) |
| O1—C2—C3—C5 | 0.4 (3) | O1—C2—N1—C1 | 177.75 (17) |
| N1—C2—C3—C5 | 179.25 (15) | C3—C2—N1—C1 | −1.1 (3) |
| C5—C3—C4—N2 | −179.28 (17) | N1—C1—N2—C4 | −1.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | −1.1 (3) | S1—C1—N2—C4 | 175.58 (13) |
| C5—C3—C4—C6 | −1.9 (3) | C3—C4—N2—C1 | 1.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C6 | 176.28 (17) | C6—C4—N2—C1 | −176.22 (16) |
| N2—C4—C6—C7 | 53.7 (2) | C10—C11—O2—C12 | −176.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—C6—C7 | −123.80 (19) | N2—C1—S1—C10 | −3.49 (19) |
| C4—C6—C7—C9 | 56.1 (3) | N1—C1—S1—C10 | 173.88 (14) |
| C4—C6—C7—C8 | −179.82 (18) | C11—C10—S1—C1 | −70.78 (19) |
| S1—C10—C11—O2 | −59.3 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.86 | 1.89 | 2.747 (2) | 175 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5854).
References
- Al-Deeb, O. A., El-Emam, A. A., Al-Turkistani, A. A., Ng, S. W. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o676–o677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Durkaya, F., Dege, N., Demirtaş, G. & Uçar, I. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, m687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- El-Brollosy, N. R., El-Emam, A. A., Al-Deeb, O. A. & Ng, S. W. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Nasir, S. B., Abdullah, Z., Fairuz, Z. A., Ng, S. W. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2002). X-AREA and X-RED32 Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Tiekink, E. R. T. (1989). Z. Kristallogr. 187, 79–84.
- Yan, W.-L., Guo, Q., Li, C., Ji, X.-Y. & He, Y.-P. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812013372/bt5854sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812013372/bt5854Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812013372/bt5854Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report