Abstract
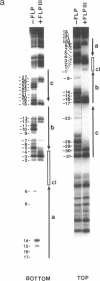
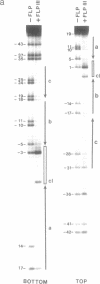
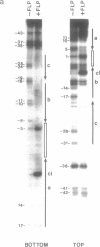
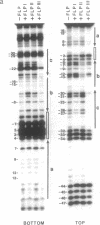
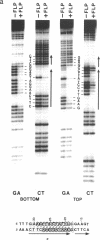
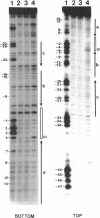
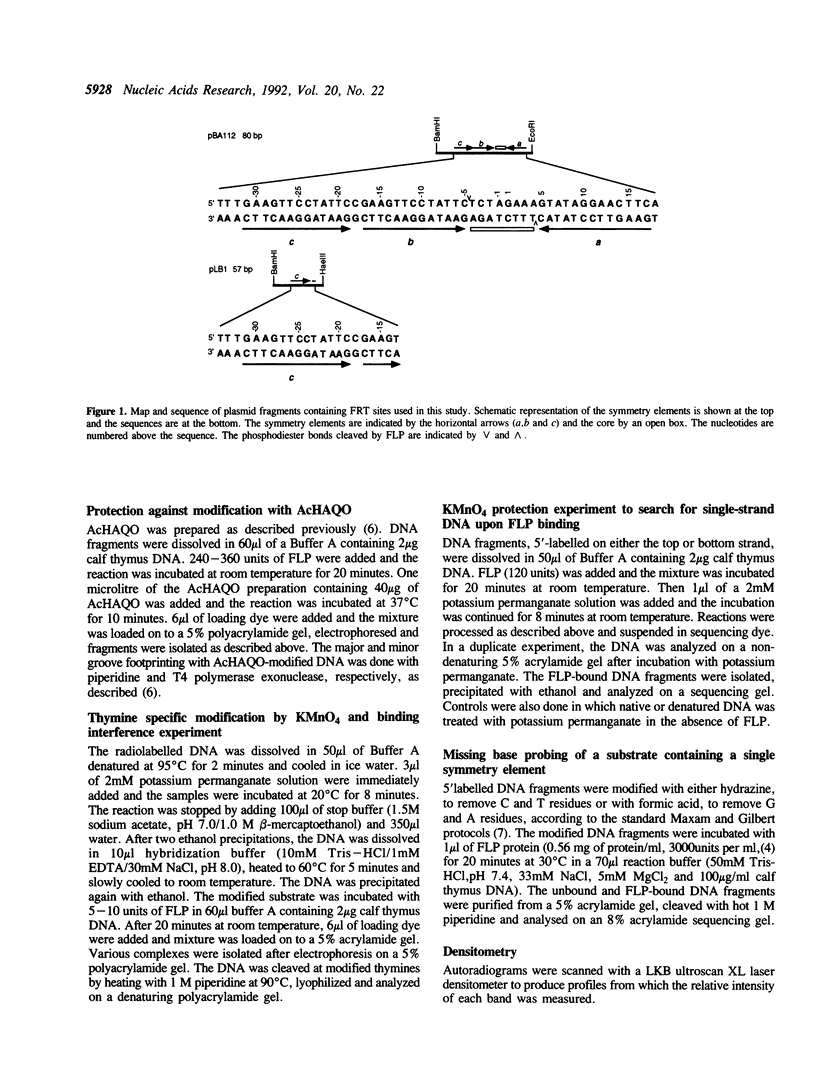
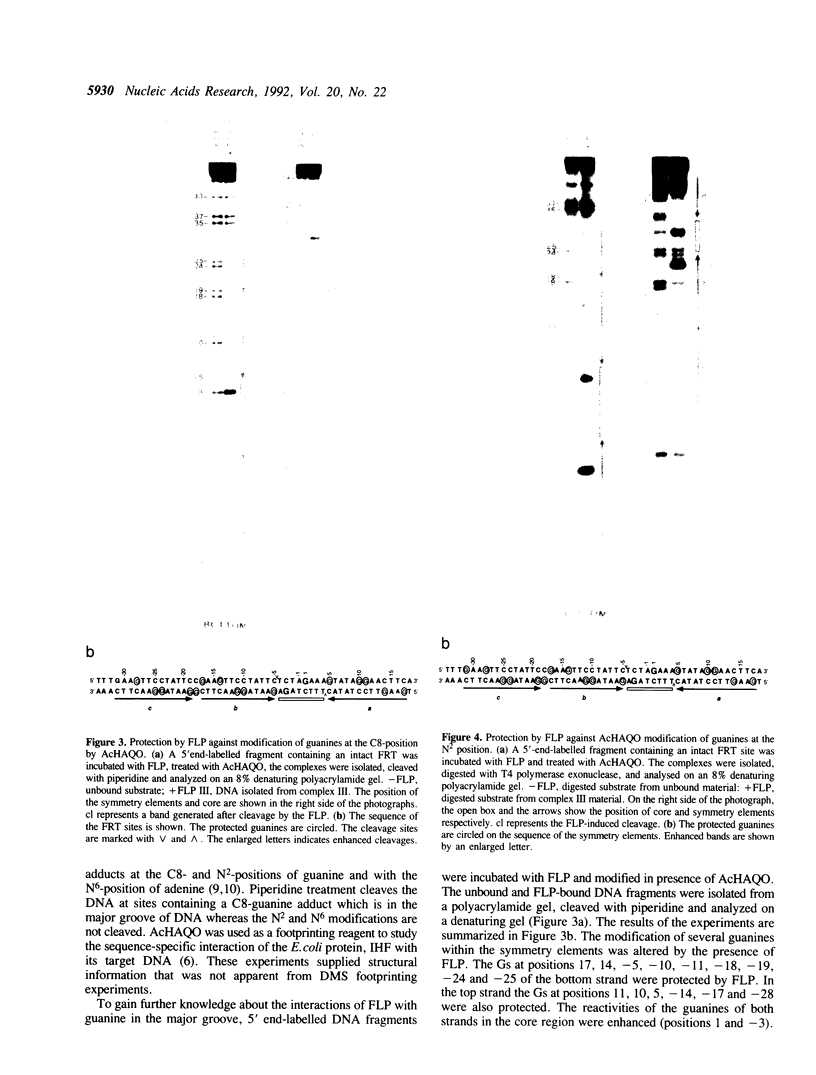
The FLP protein of the 2 microns plasmid of Saccharomyces cerevisiae promotes conservative site-specific recombination between DNA sequences that contain the FLP recognition target (FRT). FLP binds to each of the three 13 base pair symmetry elements in the FRT site in a site-specific manner. We have probed both major and minor groove contacts of FLP using dimethyl sulphate, monoacetyl-4-hydroxyaminoquinoline 1-oxide and potassium permanganate and find that the protein displays extensive interactions with residues of both the major and minor grooves of 10 base pairs of each symmetry element. We find no evidence that the FRT site assumes a single-stranded conformation upon FLP binding.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin A. A., Sadowski P. D. Synthesis of an enzymatically active FLP recombinase in vitro: search for a DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. J., Beatty L. G., Sadowski P. D. Isolation of intermediates in the binding of the FLP recombinase of the yeast plasmid 2-micron circle to its target sequence. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):345–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. J., Proteau G. A., Beatty L. G., Sadowski P. D. The FLP recombinase of the 2 micron circle DNA of yeast: interaction with its target sequences. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty L. G., Sadowski P. D. The mechanism of loading of the FLP recombinase onto its DNA target sequence. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle A., Schleif R. F. Missing contact probing of DNA-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6673–6676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Sussman J. L., Kim S. H. Secondary structural complementarity between DNA and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1458–1462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galiègue-Zouitina S., Bailleul B., Ginot Y. M., Perly B., Vigny P., Loucheux-Lefebvre M. H. N2-guanyl and N6-adenyl arylation of chicken erythrocyte DNA by the ultimate carcinogen of 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 1):1858–1863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galiègue-Zouitina S., Bailleul B., Loucheux-Lefebvre M. H. Adducts from in vivo action of the carcinogen 4-hydroxyaminoquinoline 1-oxide in rats and from in vitro reaction of 4-acetoxyaminoquinoline 1-oxide with DNA and polynucleotides. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):520–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galiègue-Zouitina S., Bailleul B., Loucheux-Lefebvre M. H. Guanyl-C8-arylamination of DNA by the ultimate carcinogen of 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide: a spectrophotometric titration. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):454–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90839-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayatsu H., Ukita T. The selective degradation of pyrimidines in nucleic acids by permanganate oxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide H., Kow Y. W., Wallace S. S. Thymine glycols and urea residues in M13 DNA constitute replicative blocks in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8035–8052. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi G. B., Walker I. G. The N2-guanine adduct but not the C8-guanine or N6-adenine adducts formed by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide blocks the 3'-5' exonuclease action of T4 DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 27;29(8):2122–2126. doi: 10.1021/bi00460a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi G. B., Walker I. G. Use of monoacetyl-4-hydroxyaminoquinoline 1-oxide to probe contacts between guanines and protein in the minor and major grooves of DNA. Interaction of Escherichia coli integration host factor with its recognition site in the early promoter and transposition enhancer of bacteriophage Mu. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9761–9767. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Evans B. R., Zheng L., Jayaram M. Functional analysis of Arg-308 mutants of Flp recombinase. Possible role of Arg-308 in coupling substrate binding to catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4527–4533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad P. V., Horensky D., Young L. J., Jayaram M. Substrate recognition by the 2 micron circle site-specific recombinase: effect of mutations within the symmetry elements of the minimal substrate. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4329–4334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. J., Sadowski P. D. FLP protein of 2 mu circle plasmid of yeast induces multiple bends in the FLP recognition target site. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):289–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senecoff J. F., Rossmeissl P. J., Cox M. M. DNA recognition by the FLP recombinase of the yeast 2 mu plasmid. A mutational analysis of the FLP binding site. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):405–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Clayton D. A. Altered mobility of polydeoxyribonucleotides in high resolution polyacrylamide gels due to removal of terminal phosphates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6787–6794. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]