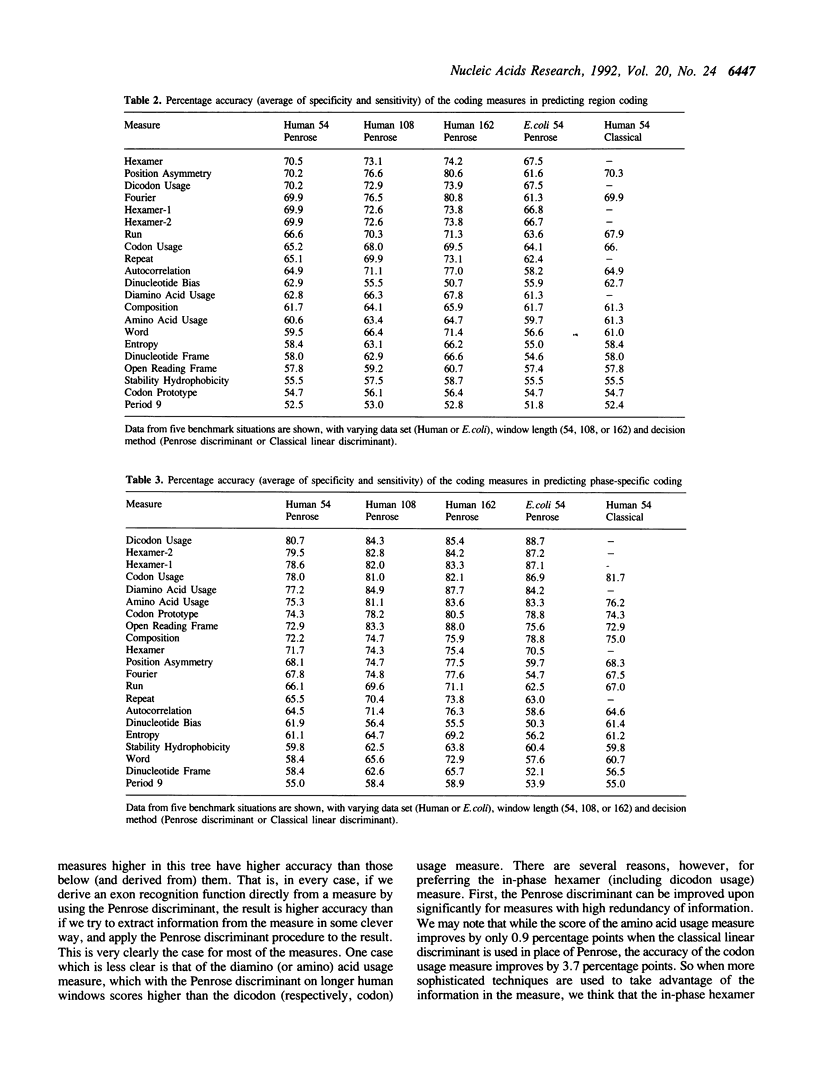
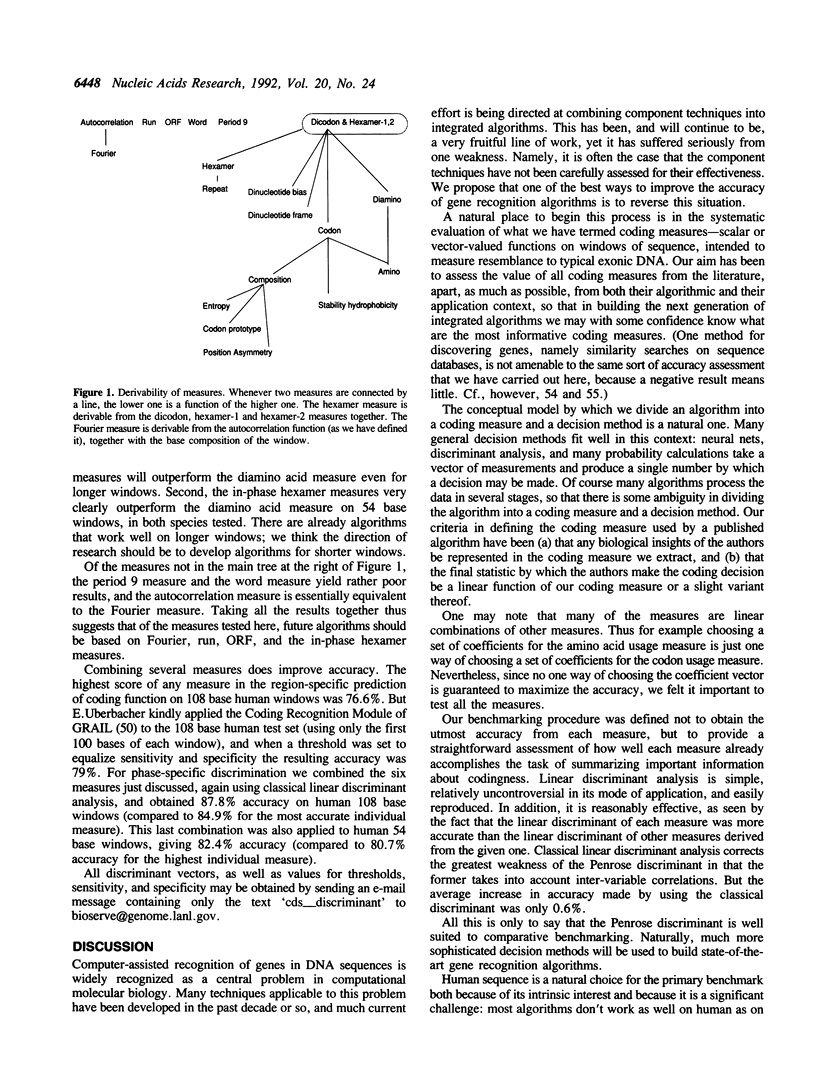
Abstract
A number of methods for recognizing protein coding genes in DNA sequence have been published over the last 13 years, and new, more comprehensive algorithms, drawing on the repertoire of existing techniques, continue to be developed. To optimize continued development, it is valuable to systematically review and evaluate published techniques. At the core of most gene recognition algorithms is one or more coding measures--functions which produce, given any sample window of sequence, a number or vector intended to measure the degree to which a sample sequence resembles a window of 'typical' exonic DNA. In this paper we review and synthesize the underlying coding measures from published algorithms. A standardized benchmark is described, and each of the measures is evaluated according to this benchmark. Our main conclusion is that a very simple and obvious measure--counting oligomers--is more effective than any of the more sophisticated measures. Different measures contain different information. However there is a great deal of redundancy in the current suite of measures. We show that in future development of gene recognition algorithms, attention can probably be limited to six of the twenty or so measures proposed to date.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almagor H. Nucleotide distribution and the recognition of coding regions in DNA sequences: an information theory approach. J Theor Biol. 1985 Nov 7;117(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(85)80168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arquès D. G., Michel C. J. Periodicities in introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7581–7592. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaisdell B. E. A prevalent persistent global nonrandomness that distinguishes coding and non-coding eucaryotic nuclear DNA sequences. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(2):122–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02300750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake R. D., Earley S. Distribution and evolution of sequence characteristics in the E. coli genome. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Oct;4(2):291–307. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10506347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borodovskii M. Iu, Sprizhitskii Iu A., Golovanov E. I., Aleksandrov A. A. Statisticheskie zakonomernosti v pervichnykh strukturakh funktsional'nykh oblastei genoma Escherichia coli. I. Chastotnye kharakteristiki. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1986 Jul-Aug;20(4):1014–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borodovskii M. Iu, Sprizhitskii Iu A., Golovanov E. I., Aleksandrov A. A. Statisticheskie zakonomernosti v pervichnykh strukturakh funktsional'nykh oblastei genoma Escherichia coli. II. Neodnorodnye markovskie modeli. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1986 Jul-Aug;20(4):1024–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borodovskii M. Iu, Sprizhitskii Iu A., Golovanov E. I., Aleksandrov A. A. Statisticheskie zakonomernosti v pervichnykh strukturakh funktsional'nykh oblastei genoma Escherichia coli. III. Komp'iuternoe raspoznavanie kodiruiushchikh oblastei. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1986 Sep-Oct;20(5):1390–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinkosky M. J., Fickett J. W., Gilna P., Burks C. Electronic data publishing and GenBank. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1273–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.1925538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M., Bougueleret L. Heuristic informational analysis of sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):179–196. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M. Identifying coding exons by similarity search: alu-derived and other potentially misleading protein sequences. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):838–841. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90321-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M., Sauvaget I., Bougueleret L. K-tuple frequency analysis: from intron/exon discrimination to T-cell epitope mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:237–252. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichant G., Gautier C. Statistical method for predicting protein coding regions in nucleic acid sequences. Comput Appl Biosci. 1987 Nov;3(4):287–295. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/3.4.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickett J. W. Recognition of protein coding regions in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5303–5318. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields C. A., Soderlund C. A. gm: a practical tool for automating DNA sequence analysis. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Jul;6(3):263–270. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Devereux J., Burgess R. R. The codon preference plot: graphic analysis of protein coding sequences and prediction of gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):539–549. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guigó R., Knudsen S., Drake N., Smith T. Prediction of gene structure. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 5;226(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90130-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Fuchs R., Stoehr P. J., Cameron G. N. The EMBL Data Library. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2071–2074. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Blake R. D. Delineation of coding areas in DNA sequences through assignment of codon probabilities. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Dec;3(3):543–549. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolaskar A. S., Reddy B. V. A method to locate protein coding sequences in DNA of prokaryotic systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):185–194. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka A. K., Smythers G. W. DISTAN--a program which detects significant distances between short oligonucleotides. Comput Appl Biosci. 1987 Sep;3(3):193–201. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/3.3.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaldon P., Argos P. Oligopeptide biases in protein sequences and their use in predicting protein coding regions in nucleotide sequences. Proteins. 1988;4(2):99–122. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel C. J. New statistical approach to discriminate between protein coding and non-coding regions in DNA sequences and its evaluation. J Theor Biol. 1986 May 21;120(2):223–236. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. E., Fristensky B. Database bias and the identification of protein coding sequences. DNA. 1987 Oct;6(5):493–495. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., van der Aart Q. J., Agostoni-Carbone M. L., Aigle M., Alberghina L., Alexandraki D., Antoine G., Anwar R., Ballesta J. P., Benit P. The complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome III. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):38–46. doi: 10.1038/357038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENROSE L. S. Distance, size and shape. Ann Eugen. 1954 Mar;18(4):337–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1952.tb02527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seely O., Jr, Feng D. F., Smith D. W., Sulzbach D., Doolittle R. F. Construction of a facsimile data set for large genome sequence analysis. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90227-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. The codon Adaptation Index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1281–1295. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C. Method to determine the reading frame of a protein from the purine/pyrimidine genome sequence and its possible evolutionary justification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1596–1600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M. J., Steinberg C. M., Westmoreland N. The coding function of nucleotide sequences can be discerned by statistical analysis. J Theor Biol. 1981 Feb 7;88(3):409–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman B. D., Linsker R. A measure of DNA periodicity. J Theor Biol. 1986 Feb 7;118(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Finding protein coding regions in genomic sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:163–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Measurements of the effects that coding for a protein has on a DNA sequence and their use for finding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):551–567. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D. Computer methods for analyzing sequence recognition of nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:241–263. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano A., Macchiato M. F. Probability of coding of a DNA sequence: an algorithm to predict translated reading frames from their thermodynamic characteristics. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):127–135. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Translation framing code and frame-monitoring mechanism as suggested by the analysis of mRNA and 16 S rRNA nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uberbacher E. C., Mural R. J. Locating protein-coding regions in human DNA sequences by a multiple sensor-neural network approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11261–11265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volinia S., Gambari R., Bernardi F., Barrai I. The frequency of oligonucleotides in mammalian genic regions. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Feb;5(1):33–40. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



