Abstract
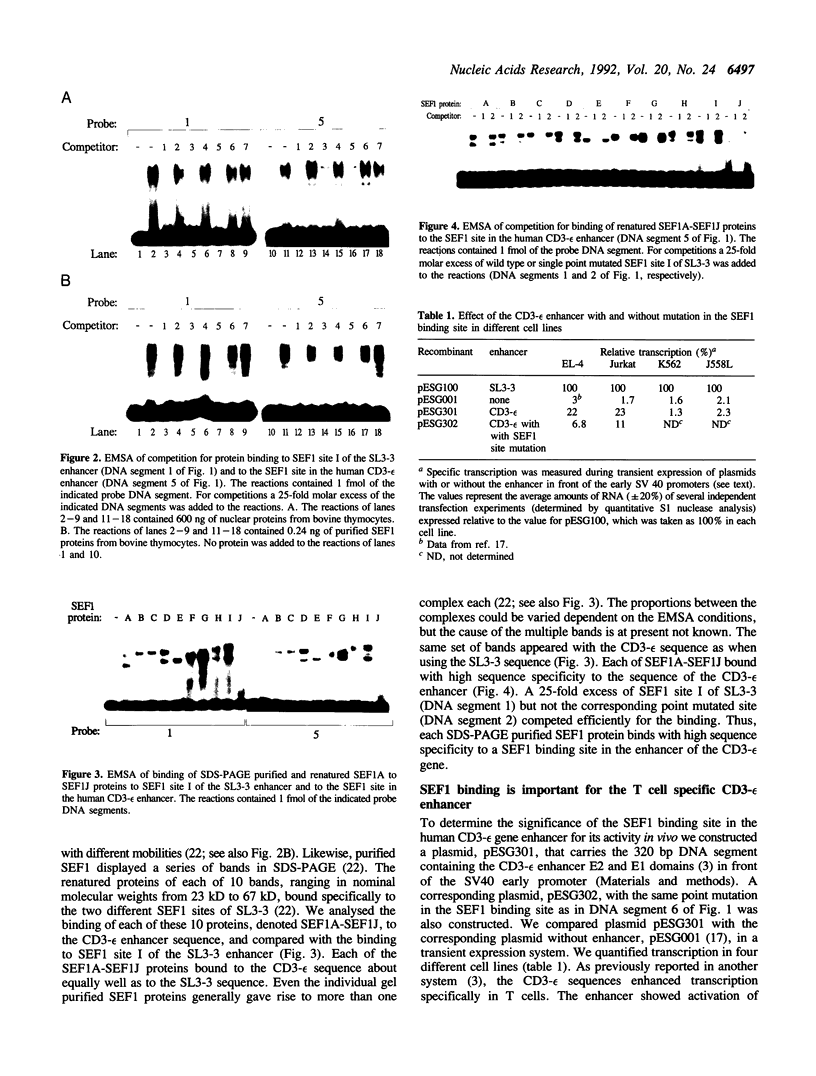
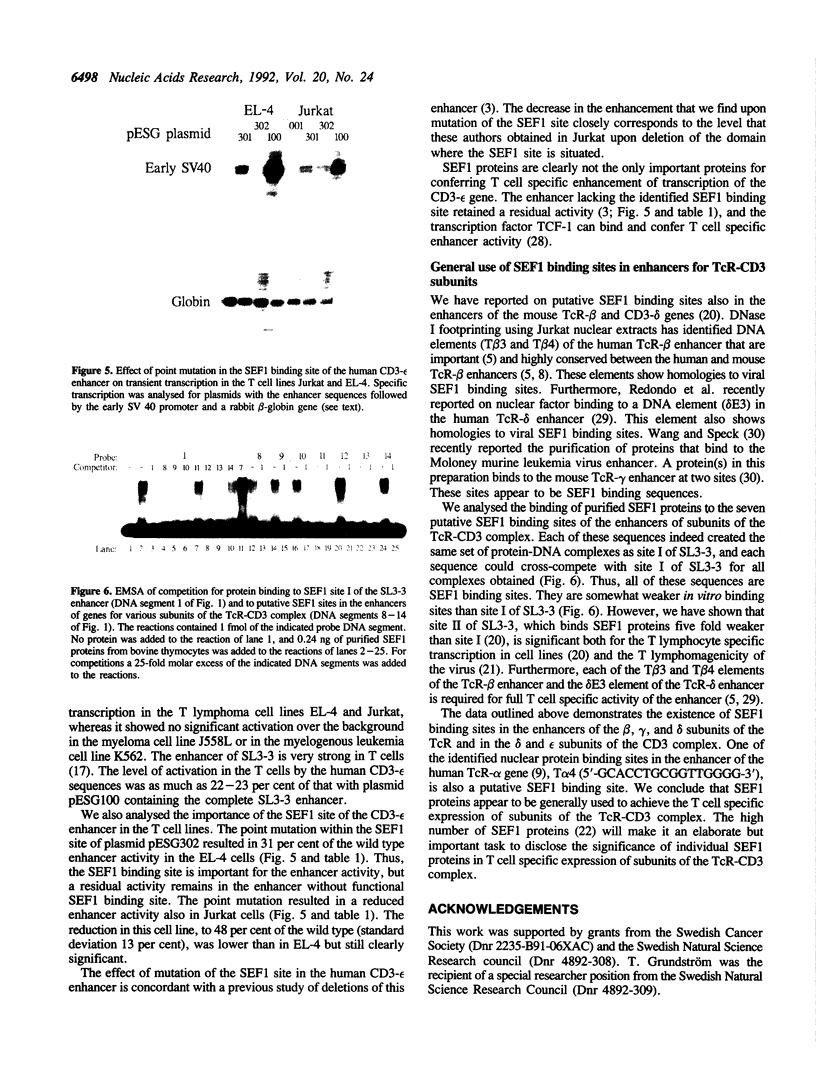
A family of proteins, denoted SL3-3 enhancer factor 1 (SEF1), interacts with DNA sequences in the T cell specific enhancer of SL3-3 murine leukemia virus and in the enhancers of several other viruses. A putative SEF1 binding site was also identified in the T cell specific enhancer of the gene encoding the human T cell antigen receptor (TcR) associated CD3-epsilon polypeptide. In this study we show that the identified sequence is a strong SEF1 binding site, and that purified SEF1 proteins bind specifically to the sequence. We report also that the SEF1 binding site is important for T cell specific activation of transcription by the CD3-epsilon enhancer. We show that SEF1 binding sites are present also in the T cell specific enhancers of other subunits of the TcR-CD3 complex, and that SEF1 proteins appear to play a central role in the T cell specific expression of this set of enhancers.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bories J. C., Loiseau P., d'Auriol L., Gontier C., Bensussan A., Degos L., Sigaux F. Regulation of transcription of the human T cell antigen receptor delta chain gene. A T lineage-specific enhancer element is located in the J delta 3-C delta intron. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):75–83. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Haseltine W. A. Tissue-specific transcription preference as a determinant of cell tropism and leukaemogenic potential of murine retroviruses. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):159–162. doi: 10.1038/312159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., Lonberg N., Dunlap S., Lacy E., Terhorst C. An enhancer located in a CpG-island 3' to the TCR/CD3-epsilon gene confers T lymphocyte-specificity to its promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2527–2535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. The tandem direct repeats within the long terminal repeat of murine leukemia viruses are the primary determinant of their leukemogenic potential. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):945–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.945-952.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORER P. A. Studies in antibody response of mice to tumour inoculation. Br J Cancer. 1950 Dec;4(4):372–379. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1950.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., van den Elsen P., Bier E., Maxam A., Terhorst C. A T cell-specific enhancer is located in a DNase I-hypersensitive area at the 3' end of the CD3-delta gene. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2401–2407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03085.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk L. R., Leiden J. M. Identification and functional characterization of the human T-cell receptor beta gene transcriptional enhancer: common nuclear proteins interact with the transcriptional regulatory elements of the T-cell receptor alpha and beta genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5486–5495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg B., Grundström T. Tissue specific sequence motifs in the enhancer of the leukaemogenic mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5927–5944. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg B., Schmidt J., Luz A., Pedersen F. S., Grundström T. SL3-3 enhancer factor 1 transcriptional activators are required for tumor formation by SL3-3 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4177–4181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4177-4181.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Yang L. H., Morle G., Leiden J. M. A T-cell-specific transcriptional enhancer element 3' of C alpha in the human T-cell receptor alpha locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6714–6718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappes D. J., Browne C. P., Tonegawa S. Identification of a T-cell-specific enhancer at the locus encoding T-cell antigen receptor gamma chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2204–2208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koning F. Lymphocyte antigen receptors: a common design? Immunol Today. 1991 Apr;12(4):100–101. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimpenfort P., de Jong R., Uematsu Y., Dembic Z., Ryser S., von Boehmer H., Steinmetz M., Berns A. Transcription of T cell receptor beta-chain genes is controlled by a downstream regulatory element. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):745–750. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M. Transcriptional regulation during T-cell development: the alpha TCR gene as a molecular model. Immunol Today. 1992 Jan;13(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90200-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. Activation of T cells by a tyrosine kinase activation domain in the cytoplasmic tail of CD3 epsilon. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1532456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohit B., Fan K. Hybrid cell line from a cloned immunoglobulin-producing mouse myeloma and a nonproducing mouse lymphoma. Science. 1971 Jan 8;171(3966):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3966.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redondo J. M., Hata S., Brocklehurst C., Krangel M. S. A T cell-specific transcriptional enhancer within the human T cell receptor delta locus. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1225–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.2156339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redondo J. M., Pfohl J. L., Krangel M. S. Identification of an essential site for transcriptional activation within the human T-cell receptor delta enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5671–5680. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Binding of SL3-3 enhancer factor 1 transcriptional activators to viral and chromosomal enhancer sequences. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.42-50.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Differential protein binding in lymphocytes to a sequence in the enhancer of the mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1625–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. W., Speck N. A. Purification of core-binding factor, a protein that binds the conserved core site in murine leukemia virus enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):89–102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. A novel, inducible and T cell-specific enhancer located at the 3' end of the T cell receptor alpha locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):729–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Oosterwegel M., Dooijes D., Clevers H. Identification and cloning of TCF-1, a T lymphocyte-specific transcription factor containing a sequence-specific HMG box. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):123–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]