Abstract
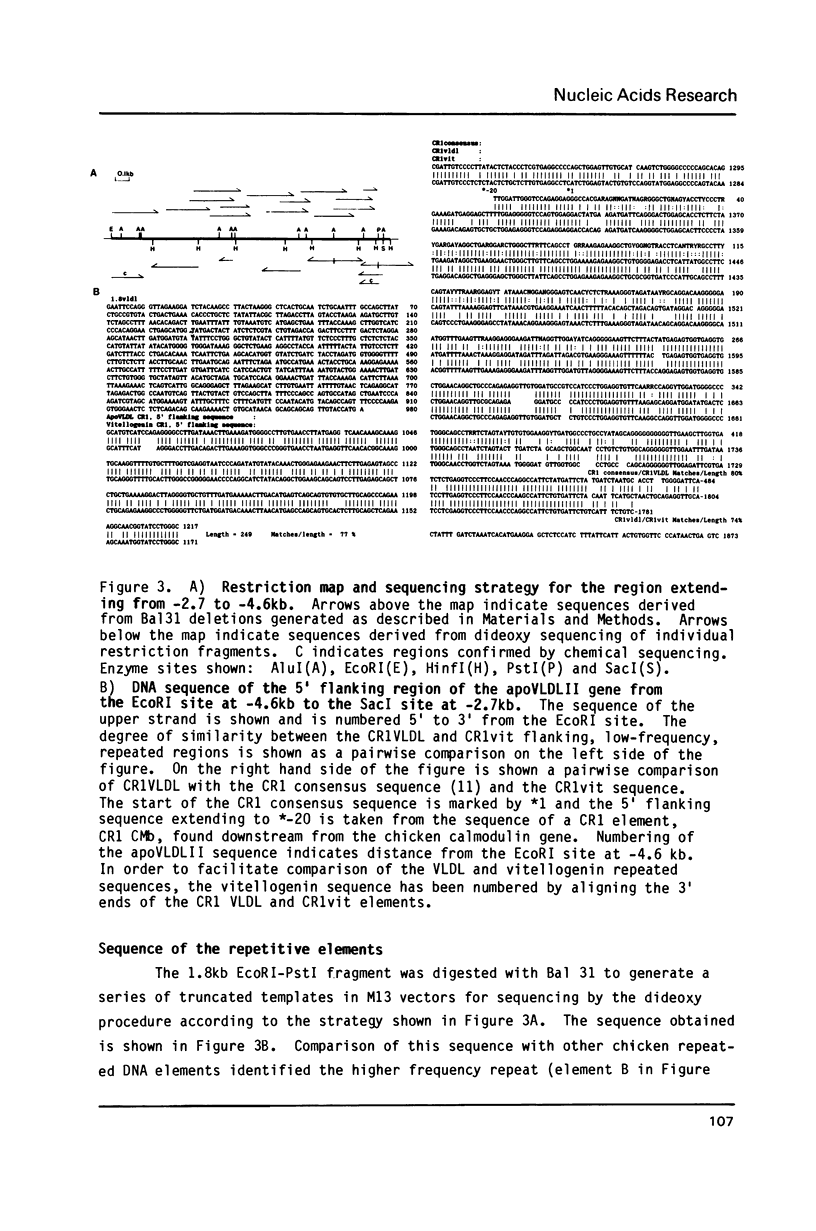
Analysis of nuclease hypersensitivity of regions flanking the estrogen-dependent, chicken apoVLDLII gene has revealed an hepatic, DNaseI hypersensitive site whose sensitivity is influenced by both the developmental stage and sex of the bird. The site is located 3.0kb upstream from the gene, in a block of middle repetitive elements. Contact hybridization studies indicate that the block consists of contiguous copies of two elements with reiteration frequencies of 500-1000 and 10,000-30,000 copies per haploid genome. Sequencing of 1.8kb spanning the repeats has revealed that the higher frequency element is a member of the CR1 family. The adjacent lower frequency repeat can also be found next to another member of the CR1 family located in the 3' flanking region of the vitellogenin gene. The hypersensitive site has been mapped to one of the two most highly conserved regions of the CR1 element. This region displays homology with a silencer sequence recently identified in a CR1 element flanking the chicken lysozyme gene.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Gait M. J., Mayol L., Young I. G. A short primer for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded phage vector M13mp2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1731–1743. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Muller M., Steiner C., Renkawitz R. Activity of two different silencer elements of the chicken lysozyme gene can be compensated by enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J. The folding of chromatin. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;15(1):57–91. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilloni G., Della Seta F., Negri R., Di Mauro E. Structure of RNA polymerase II promoters. Coordinate conformational alteration of the upstream activator of the TATA- and RNA-initiation sequences under moderate torsional stress. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6145–6148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., Jackson R. L., O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Synthesis of very low density lipoproteins in the cockerel. Effects of estrogen. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):368–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI108481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan V., Elbrecht A., Goldman P., Lazier C. B., Deeley R. The avian apoprotein II very low density lipoprotein gene. Methylation patterns of 5' and 3' flanking regions during development and following induction by estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14453–14460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Weber J. L., Gorski J. Chromatin structure, transcription, and methylation of the prolactin gene domain in pituitary tumors of Fischer 344 rats. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7086–7093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Tora L., Kelemen G., Hidvégi E. J. Supercoil induced S1 hypersensitive sites in the rat and human ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3263–3277. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haché R. J., Wiskocil R., Vasa M., Roy R. N., Lau P. C., Deeley R. G. The 5' noncoding and flanking regions of the avian very low density apolipoprotein II and serum albumin genes. Homologies with the egg white protein genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4556–4564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Human U1 RNA genes contain an unusually sensitive nuclease S1 cleavage site within the conserved 3' flanking region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7288–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Lin H. Y., Chan L., Means A. R. Amino acid sequence of a major apoprotein from hen plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):250–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen K., Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T. The DNase I sensitive domain of the chicken lysozyme gene spans 24 kb. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6085–6099. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Torri A., Kang D. S., Engler J. A., Wells R. D. Unusual DNA structures in the adenovirus genome. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11350–11354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok K., Snippe L., Ab G., Gruber M. Nuclease-hypersensitive sites in chromatin of the estrogen-inducible apoVLDL II gene of chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5189–5202. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L., Holmgren-König M., Khoury G. Transcriptional "silencer" element in rat repetitive sequences associated with the rat insulin 1 gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3151–3155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau P. C., Spencer J. H. An efficient synthetic primer for the M13 cloning dideoxy sequencing system. Biosci Rep. 1982 Sep;2(9):687–696. doi: 10.1007/BF01114830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margot J. B., Hardison R. C. DNase I and nuclease S1 sensitivity of the rabbit beta 1 globin gene in nuclei and in supercoiled plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 20;184(2):195–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon C., Schmidt A., de Crombrugghe B. A sequence conserved in both the chicken and mouse alpha 2(I) collagen promoter contains sites sensitive to S1 nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6636–6640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijlink F. C., van het Schip A. D., Arnberg A. C., Wieringa B., Ab G., Gruber M. Structure of the chicken apo very low density lipoprotein II gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9668–9671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. DNA conformation at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Transcriptionally active chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 10;782(4):343–393. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. C. Phosphorylation of nucleic acid by an enzyme from T4 bacteriophage-infected Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):158–165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanzo M., Stevens B., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Isolation of a protein fraction that binds preferentially to chicken middle repetitive DNA. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6491–6498. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selleck S. B., Elgin S. C., Cartwright I. L. Supercoil-dependent features of DNA structure at Drosophila locus 67B1. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 5;178(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senear A. W., Palmiter R. D. Expression of the mouse metallothionein-I gene alters the nuclease hypersensitivity of its 5' regulatory region. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):539–547. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strijker R., Blom van Assendelft G., Dikkeschei B. D., Gruber M., Ab G. Estradiol-dependent transcription initiation upstream from the chicken apoVLDLII gene coding for the very-low-density apolipoprotein II. Gene. 1986;45(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumph W. E., Baez M., Beattie W. G., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Characterization of deoxyribonucleic acid sequences at the 5' and 3' borders of the 100 kilobase pair ovalbumin gene domain. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):306–315. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumph W. E., Hodgson C. P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Genomic structure and possible retroviral origin of the chicken CR1 repetitive DNA sequence family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6667–6671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumph W. E., Kristo P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. A chicken middle-repetitive DNA sequence which shares homology with mammalian ubiquitous repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5383–5397. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. Active chromatin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):289–295. doi: 10.1038/297289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Bensky P., Dower W., Goldberger R. F., Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G. Coordinate regulation of two estrogen-dependent genes in avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Goldman P., Deeley R. G. Cloning and structural characterization of an estrogen-dependent apolipoprotein gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9662–9667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Nickol J., Felsenfeld G. Repeated sequence organization and RNA transcription map of the chicken adult beta-globin gene region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1502–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Cereghini S. Structure of transcriptionally active chromatin. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):1–26. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Manley J. L. Structure and function of the S1 nuclease-sensitive site in the adenovirus late promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):743–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90788-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Santos T. Reiteration frequency mapping: analysis of repetitive sequence organization within cloned DNA fragments containing the human initiator methionine tRNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5668–5672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Allan M., Paul J. The chromatin structure of the human epsilon globin gene: nuclease hypersensitive sites correlate with multiple initiation sites of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):9191–9204. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.9191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van het Schip F., Samallo J., Meijlink F., Gruber M., AB G. A new repetitive element of the CR1 family downstream of the chicken vitellogenin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4193–4202. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]