Abstract
Sialic or nonulosonic acids are nine-carbon alpha ketosugars that are present in all vertebrate mucous membranes. Among bacteria, the ability to catabolize sialic acid as a carbon source is present mainly in pathogenic and commensal species of animals. Previously, it was shown that several Vibrio species carry homologues of the genes required for sialic acid transport and catabolism, which are genetically linked. In Vibrio cholerae on chromosome I, these genes are carried on the Vibrio pathogenicity island-2 region, which is confined to pathogenic isolates. We found that among the three sequenced Vibrio vulnificus clinical strains, these genes are present on chromosome II and are not associated with a pathogenicity island. To determine whether the sialic acid transport (SAT) and catabolism (SAC) region is universally present within V. vulnificus, we examined 67 natural isolates whose phylogenetic relationships are known. We found that the region was present predominantly among lineage I of V. vulnificus, which is comprised mainly of clinical isolates. We demonstrate that the isolates that contain this region can catabolize sialic acid as a sole carbon source. Two putative transporters are genetically linked to the region in V. vulnificus, the tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporter SiaPQM and a component of an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter. We constructed an in-frame deletion mutation in siaM, a component of the TRAP transporter, and demonstrate that this transporter is essential for sialic acid uptake in this species. Expression analysis of the SAT and SAC genes indicates that sialic acid is an inducer of expression. Overall, our study demonstrates that the ability to catabolize and transport sialic acid is predominately lineage specific in V. vulnificus and that the TRAP transporter is essential for sialic acid uptake.
INTRODUCTION
Sialic acids, also known as neuraminic or nonulosonic acids, are a family of nine-carbon alpha ketosugars. Sialic acids are widely distributed in deuterostomes, where they perform a number of functions such as cell-cell interactions, stabilizing glycoconjugates and cell membranes and acting as chemical messengers (46, 47). Sialic acids are utilized by commensal and pathogenic bacteria in a number of ways; for example, several pathogenic species of bacteria have been shown to decorate their cell surfaces with sialic acid to avoid recognition by the host immune system (46, 47, 49, 50). Bacteria can also utilize sialic acid as a sole carbon source, which was first shown in Clostridium perfringens (29). The enzymatic pathway to catabolize N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), the most common sialic acid, was shown by Vimr and colleagues in Escherichia coli to require three key enzymes (50, 51). First, Neu5Ac is broken down into N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) by a lyase/aldolase (NanA). ManNAc kinase (NanK) adds a phosphate group to generate N-acetylmannosamine-6-phosphate (ManNAc-6-P), upon which ManNAc-6-P epimerase (NanE) acts to convert it to N-acetylglucosamine-6-P (GlcNAc-6-P). In bacteria, the genes for the first three enzymes (NanA, NanK, and NanE) in the catabolism pathways are usually found clustered together in the genome (2). Recently, a novel epimerase was identified in Bacteroides fragilis and Tannerella forsythia that has no requirement for a phosphorylated substrate (9, 34). Finally, GlcNAc-6-P deacetylase (encoded by nagA) and glucosamine-6-P deaminase (encoded by nagB) then converts GlcNAc-6-P into fructose-6-P (Fru-6-P), which is a substrate in the glycolysis pathway.
Of the bacteria that contain a sialic acid catabolism (SAC) gene cluster, most are species known to colonize the animal intestine as pathogens or commensals (2, 9, 29, 40, 42, 51). In Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of cholera, the SAC genes are present on chromosome I within the 57-kb Vibrio pathogenicity island-2 (VPI-2) region, which is confined to pathogenic strains (21, 22). By using an infant mouse model of infection, it was shown that the ability to catabolize sialic acid conveys a significant competitive advantage in the early stage of infection for V. cholerae (3). Genetically linked to the SAC cluster in V. cholerae are homologues of siaPQM, which encode a substrate-binding protein (SBP)-dependent secondary transporter belonging to the tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporter family (2, 3, 14, 27, 38). The homologous TRAP transporter associated with the SAC cluster in Haemophilus influenzae was shown to be highly efficient in the uptake of sialic acid (14, 27, 40). It has been more recently demonstrated in V. cholerae that the SBP of the TRAP transporter SiaPQM (VC1777 to VC1779) is a Na+-dependent high-affinity secondary transporter for sialic acid also (28, 45).
There are at least four diverse families of solute transporters that are genetically linked with the SAC cluster among bacteria (2, 14, 27, 38, 39), the above-mentioned TRAP transporter from V. cholerae and H. influenzae, the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) NanT found in Escherichia coli, an ATP-binding cassette (ABC)-type transporter from Haemophilus ducreyi, and the sodium solute symporter (SSS) first identified in Photobacterium profundum (2, 14, 27, 38, 39). Among Enterobacteriaceae, NanT is the most prevalent transporter associated with the SAC cluster, whereas in the Pasteurellaceae and the Vibrionaceae, the TRAP transporter is the predominant type found (2, 14, 38, 39). Among the Firmicutes, the predominant transporters associated with the SAC cluster belong to the SSS, ABC, or sodium/proline (Sym) family of transporters (2, 14, 38, 39). Recent in silico and in vitro analyses of sialic acid transporters revealed the presence of two functional systems in Salmonella enterica, an MFS type and an SSS type (39).
Vibrio vulnificus is an inhabitant of the marine ecosystem and an opportunistic pathogen of humans, in whom it can cause severe and rapid septicemia (8, 15, 23, 31, 52). Vibrio vulnificus is commonly isolated from the water column and is also isolated in high numbers from oysters and other filter-feeding shellfish, and infections occur after the consumption of raw or improperly cooked shellfish (13) (15, 17, 23). Mortality associated with V. vulnificus infection is very high (>50%), making this bacterium the leading cause of death in the United States associated with the consumption of seafood (15, 17, 23, 43). A number of different typing schemes have been developed to separate V. vulnificus isolates into groups based on whether they are pathogenic or nonpathogenic by using biochemical, serological, or genetic methods (5–7, 10, 12, 13, 18, 26, 30, 33, 35, 36, 48). Thus, 3 biotypes are recognized among isolates based on phenotypic characteristics and host range criteria (7, 12, 25, 37). Based on 16S rRNA genotyping, Nilsson and workers found most environmental isolates had a distinct 16S rRNA genotype named genotype A and most clinical isolates had a distinct genotype designated genotype B (30). Phylogenetic analysis divides V. vulnificus strains into two major groupings designated lineage I and lineage II (7, 12, 25, 37). Lineage I is comprised almost entirely of strains that cause disease in humans and encompasses predominantly biotype 1 strains and are designated C-type strains in some typing schemes (33). Lineage II is comprised mainly of environmental or fish isolates encompassing biotypes 1 and 2 and are designated E-type strains (33). A third lineage is comprised of strains that are biotype 3 human pathogens (7, 12, 37). A recent in vivo study using a subcutaneously inoculated iron dextran-treated mouse model indicates that genotype is correlated with virulence of V. vulnificus biotype 1 strains (44).
Bioinformatic analysis demonstrated the presence of sialic acid catabolism and transporter gene clusters in the genome sequence of two V. vulnificus clinical isolates, YJ016 and CMCP6 (2). Using SOLiD sequencing analysis of four V. vulnificus strains, Gulig and colleagues demonstrated that three of these strains possessed genetically linked sialic acid catabolism and transport genes (16). In another study, it was demonstrated that a clinical strain of V. vulnificus had the ability to catabolize sialic acid, which was shown to be important for in vivo survival using a mouse model (20). Jeong and coworkers speculated that unlike V. cholerae, V. vulnificus has a NanT homologue for sialic acid transport (20).
In this study, we examined the genome arrangement of the SAC gene cluster within V. vulnificus and Vibrio species in general to determine the type of transporter associated with the cluster. Next, we examined a collection of V. vulnificus isolates, whose phylogenetic relationships are known, for the presence of the SAC gene cluster. To determine whether the presence of the SAC region is lineage specific, we mapped the distribution of nanA, which encodes aldolase, required in the first step of sialic acid catabolism, onto the phylogeny of the V. vulnificus isolates. Then, we investigated whether V. vulnificus isolates that encode the SAC region can catabolize sialic acid as a sole carbon source. Although sequenced V. vulnificus isolates appear to have two transporters associated with the SAC genes, the predominant transporter system found among Vibrio species is the TRAP system. We created a deletion mutation in TRAP system to examine whether it is essential for sialic acid transport in this species.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains.
Strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. A total of 67 V. vulnificus natural isolates whose phylogenetic relationships are known were examined in this study (12). These isolates represent all three biotypes found in V. vulnificus. The isolates were collected between 1980 and 2005, from Asia, the United States, Europe, and India, with 27 isolates recovered from clinical sources and 40 from environmental (clams, mussels, fish, oysters, seawater, sediment) (12). All strains were grown aerobically (250 rpm) at 37°C in Luria-Bertani broth (Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ) with a final NaCl concentration of 2% (Fisher Scientific) and stored at −80°C in LB broth with 20% (vol/vol) glycerol.
Table 1.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Descriptiona | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| Vibrio vulnificus | ||
| YJ016 | SAC+ SAT+; clinical isolate | 11 |
| CMCP6 | SAC+ SAT+; clinical isolate | |
| JJK0731 | CMCP6 ΔsiaM (VV2_0731) | This study |
| Escherichia coli | ||
| DH5α λ-pir | pir80dlacZΔM15 δ(lacZYA-argF)U169 recA1 hsdR17 deoR thi-1 supE44 gyrA96 relA1 | |
| β2155 DAP | Donor for bacterial conjugation; thr1004 pro thi strA hsdS lacZΔM15 (F lacZΔM15 lacTRQJ36proAB) dapA ErmrpirRP4 (Kmr from SM10) | |
| DH5α λ-pir ΔsiaM | DH5α λ-pir containing pDS132ΔsiaM | This study |
| β2155 DAP-ΔsiaM | β2155 harboring pDS132ΔsiaM | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pDS132 | Suicide plasmid, Cmr, SacB | 32 |
| pDS132ΔsiaM | pDS132 harboring truncated siaM | This study |
SAC, sialic acid catabolism; SAT, sialic acid transport.
Molecular analysis.
Chromosomal DNA was extracted from the 67 V. vulnificus isolates using the DNA isolation kit from Bio101 following the manufacturer's protocol (MP Biomedicals, Solon, OH). PCR primers for nanA were designed based on the sequence of V. vulnificus strain YJ016, VVA1199F-TTATCGCCGCTCCCCATACA and VVA1199R-GCAACGCCACCGTATTCAAC. PCR assays were performed in 25-μl reaction mixtures with a 2.5 μM concentration of each primer, 2.5 mM deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) mix, 10× PCR buffer, and 1 U of Choice Taq DNA polymerase (Denville Scientific, Metuchen, NJ). The PCR cycle program consisted of an initial denaturation step at 94°C for 1 min followed by 94°C for 30 s, 55°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min for 30 cycles. PCR products were visualized on 1.0% agarose gels. A long-range PCR primer pair, VVA1194F and VVA1212R, was designed from V. vulnificus strain YJ016 to encompass an 18-kb region spanning the SAC and SAT gene clusters from open reading frames (ORFs) VVA1194 to VVA1212. Primer VVA1194F (TTG GTG TGC TAT CGG GTA CA) was designed within the napC gene, which encodes a periplasmic nitrate reductase, cytochrome c-type protein, and primer VVA1212R (AAA GGC ATC GCT CAC AAA CT), which encodes a preprotein translocase subunit, was designed within secF. The PCR assay was conducted using DyNAzyme EXT DNA polymerase (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA) in 50-μl reaction mixtures. The program of an initial denaturation step at 94°C for 1 min followed by 94°C for 30 s, 60°C for 30 s, and 68°C for 12 min for 10 cycles, followed by 94°C for 30 s, 60°C for 30 s, 68°C for 18 min for 15 cycles, and then a final extension at 70°C for 5 min was used. The PCR products were visualized on 0.6% agarose gels. In addition, we performed four additional PCR assays encompassing nanA to nanE, rpiR to nanA, nanA to siaQ, and siaQ to nanE to test for the presence of the region within nanA-negative strains. PCR primer pairs were designed based on the sequence of V. vulnificus strain YJ016 and are shown in Table 2.
Table 2.
Primers used in this study
| Primer name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Tm (°C) | Product size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOE PCR primers | |||
| SOEAsiaQF | GCtctagaGTGTTGTCCTTGGAAGCTGCG | 57 | 527 |
| SOEBsiaMR | ATGGCCAACCATGGATTTGGCA | 57 | |
| SOECsiaMF | TGCCAAATCCATGGTTGGCCAT | 59 | 573 |
| GCATCGGCGGTCGGGATTGA | |||
| SOEDnanAR | CgagctcAACGATACTCAGAGCCCCCGT | 57 | |
| SOEFLsiaQF | CTCATTGGCTGTGCCATCGCT | 58 | 1,998 |
| SOEFLnanAR | CAAGGCCCGATCGCGGAAGT | 60 | 1,224 |
| RT-PCR primers | |||
| nanA-QF | TTGGCTACTCTCAGCGCGCG | 62 | 250 |
| nanA-QR | TTGCCACTTCCGCGATCGGG | 62 | |
| nanE-QF | TCTTGCTTCGCGGATGGGCA | 62 | 236 |
| nanE-QR | CGTGTGATGGCCGAGCCCAC | 63 | |
| siaQ-QF | AGCCCGCCAAGGGGTAAACTG | 62 | 247 |
| siaQ-QR | TGTCGCTCATTGGCTGTGCCA | 62 | |
| mdh-QF | CCCGTTTCGATCAAAGGTTA | 52 | 229 |
| mdh-QR | CAATTGGCACAGTGGTGTTC | 54 | |
| PCR assay primers | |||
| nanAF | TCGCGCATTTTCGCCACGAC | ||
| nanER | GCGGCGAGTTGAGGCGTGTT | 65 | 4,562 |
| rpiRF | TACGCAAGCCCAGCGGCATG | ||
| nanAR | TTGCCACTTCCGCGATCGGG | 65 | 1,299 |
| nanAF | TTGGCTACTCTCAGCGCGCG | ||
| siaQR | TGTCGCTCATTGGCTGTGCCA | 65 | 2,233 |
| siaQF | AGCCCGCCAAGGGGTAAACTG | ||
| nanER | CGTGTGATGGCCGAGCCCAC | 65 | 2,309 |
Bioinformatic analysis of sialic acid catabolism and transporter genes among Vibrionaceae.
We performed BLAST searches (BLASTP) against the sequenced genome database (4). We used as probes the sequences of proteins encoded by nanA (aldolase), nanE (epimerase), and siaP (periplasmic binding component of the TRAP transporter) from V. vulnificus YJ016. In addition, we examined the genes immediately upstream and downstream of the region containing siaPQM and nanA, nanEK, and nagA among all sequenced Vibrionaceae to investigate whether additional transporter genes were present.
Growth analysis in minimal medium supplemented with sialic acid.
Two strains positive for the presence of nanA, YJ016 and CMCP6, and three strains negative for the presence of nanA, C7184, ss108A-3A, and 98-640 DP B9, were examined for their ability to grow in sialic acid as a sole carbon source. Precultures of each strain were grown to stationary phase at 37°C in LB, and a 100-μl aliquot of these cultures was added to 5 ml of fresh M9 minimal medium supplemented with N-acetylneuraminic acid (1 mg/ml) or d-glucose (1 mg/ml) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), of which a 200-μl aliquot per well was added to a 96-well microtiter plate and incubated at 37°C with shaking. Optical density at 595 nm (OD595) was measured hourly for 24 h using a Genios microplate reader and Magellan plate reader software (Tecan US, Durham, NC). Graphpad Prism software was used to construct graphs based on the data obtained. Growth assays were performed in triplicate at least two times.
Mutant construction.
An in-frame nonpolar deletion mutant was constructed using the splicing by overlap extension (SOE) PCR and allelic exchange procedure (19). We used the V. vulnificus CMCP6 genome sequence as a template to design primers, which were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, IA), to perform SOE PCR and obtain an in-frame single knockout mutation for VV2_0731, which contains the siaM gene (Table 2). A 774-bp deletion was created in VV2_0731, resulting in a 510-bp nonpolar truncated version of the siaM gene (1,284 bp), thus creating a nonfunctioning TRAP transporter. Briefly, the siaM AD PCR fragment was cloned into the suicide vector pDS132 (32), which was designated pDSΔsiaMAD and electroporated into Escherichia coli strain DH5α λ-pir. pDSΔsiaMAD was then plasmid purified and transformed into the E. coli strain β2155, a diaminopimelic acid (DAP) auxotroph, and pDSΔsiaMAD was then conjugated into V. vulnificus CMCP6 via cross-streaking on LB plates containing 0.3 mM DAP (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). Growth from these plates was then transferred to LB 2% NaCl plates containing chloramphenicol (25 μg/ml) to select for V. vulnificus pDSΔsiaMAD only. Exconjugate colonies were cultured overnight in the absence of antibiotics, and serial dilutions were plated on LB 2% NaCl containing 10% sucrose to select for cells that had lost pDSsiaMAD. Double-crossover deletion mutants were then screened by PCR using the SOEFLsiaQF and SOEFLnanAR primers and confirmed by sequencing.
cDNA synthesis and RT-PCR.
Prior to RNA isolation, V. vulnificus CMPC6 was cultured overnight in LB containing 2% NaCl at pH 7 and diluted in fresh M9 minimal medium containing 2% NaCl at pH 7 supplemented with 1 mg/ml of sialic acid or glucose and grown to an OD595 of 0.6 (log phase). Total RNA was extracted from V. vulnificus CMPC6 using RNAprotect bacterial reagent (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) and an RNeasy minikit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's protocols. RNA quantity was measured on a Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA), and samples were then treated with DNase to remove genomic DNA (Turbo DNase, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) in accordance with the manufacturer's protocol. One microgram of each sample of RNA was assessed on a 1% agarose gel in 1× Tris-borate-EDTA (TBE) buffer (Mediatech Inc., Herndon, VA) to ensure the quality of the samples. cDNA was synthesized by using SuperScript II reverse transcriptase (RT; Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's protocol, with 500 ng of RNA as the template, and primed by 200 ng of random hexamers. cDNA samples were diluted 1:25 and 1:125 and used as templates for semiquantitative reverse transcription-PCRs using gene-specific primers designed using Primer3 software and listed in Table 2.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Vibrio vulnificus SAC and SAT region is predominately lineage I specific.
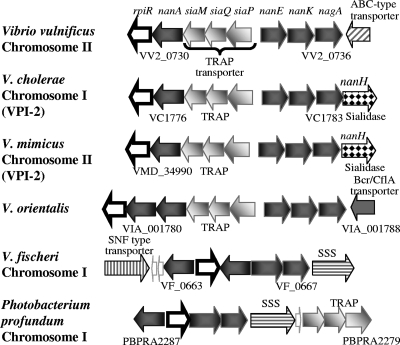
We performed a BLAST search against the three genomes of V. vulnificus strains YJ016, CMCP6, and MO6-24/O in the NCBI genome database to identify homologues of sialic acid catabolism and transport genes from V. cholerae (1–3). We identified the genes encoding enzymes in the sialic acid catabolic and transport pathways, nanA (VV2_0730), nanK (VV2_0735), nanE (VV2_0734), nagA (VV2_0736), and siaPQM (VV2_0731 to VV2_0733), in strain CMCP6 (Fig. 1). The sequences of these genes among the three V. vulnificus strains YJ016, CMCP6, and MO6-24/O were >99% identical, suggesting a highly conserved region. The order and arrangement of the sialic acid catabolism (SAC) and transport (SAT) genes in all three strains of V. vulnificus were identical to those present in V. cholerae (Fig. 1). However, in V. vulnificus, the SAC and SAT region was carried on chromosome II and was not associated with a pathogenicity island (Fig. 1). An additional difference between the two species is the absence of the nanH gene from V. vulnificus strains. In V. cholerae, the nanH gene encodes sialidase (neuraminidase), a glycohydrolase that cleaves sialic acid from high-order gangliosides, releasing free sialic acid.
Fig 1.
Genome context and arrangement of sialic acid catabolism (SAC) and transporter (SAT) gene clusters among Vibrio species. Open reading frames (ORFs) are indicated as arrows, the direction of which shows the direction of transcription. Numbers underneath ORFs represent locus tags. ORFs of similar shading represent homologous genes among the different species examined. The following annotated ORFs are shown: rpiR, transcriptional regulator; nanA, N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase/lyase; siaPQM, TRAP transporter; nanE, N-acetylmannosamine-6-P epimerase; nanK, N-acetylmannosamine kinase; nagA, N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate deacetylase; ABC, ATP-binding cassette transporter; SSS, sodium solute symporter transporter.
The SiaM protein (VV2_0731) shared an overall sequence identity of 95% with V. cholerae SiaM (VC1777) and 57% with SiaM from Haemophilus influenzae, which was shown previously to be part of a high-affinity, Na(+)-dependent unidirectional secondary TRAP transporter for sialic acid (40). No homolog of NanT, an MFS transporter present in E. coli, was identified in any of the genomes examined. Directly downstream of nagA in all three sequences was a homologue of an ABC-type transporter component (Fig. 1). However, this periplasmic ABC component has domains associated with oligopeptide binding and not amino sugar or carbohydrate binding in general. It appears that V. vulnificus is genetically capable of sialic acid transport into the bacterial cell, which can then be catabolized as a carbon source.
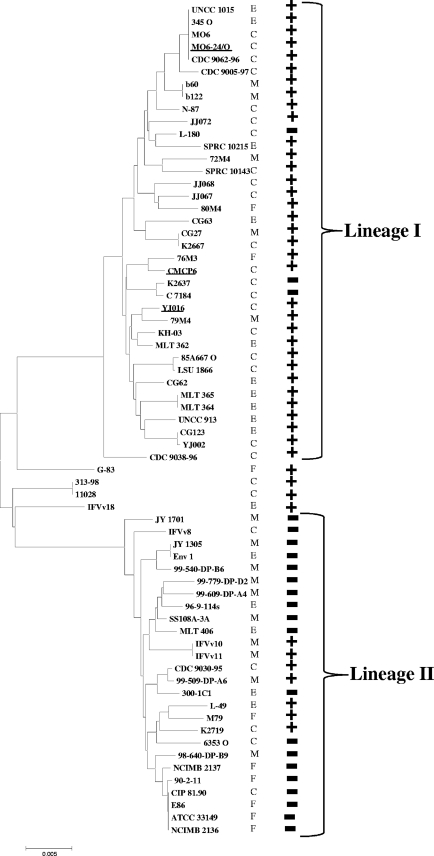
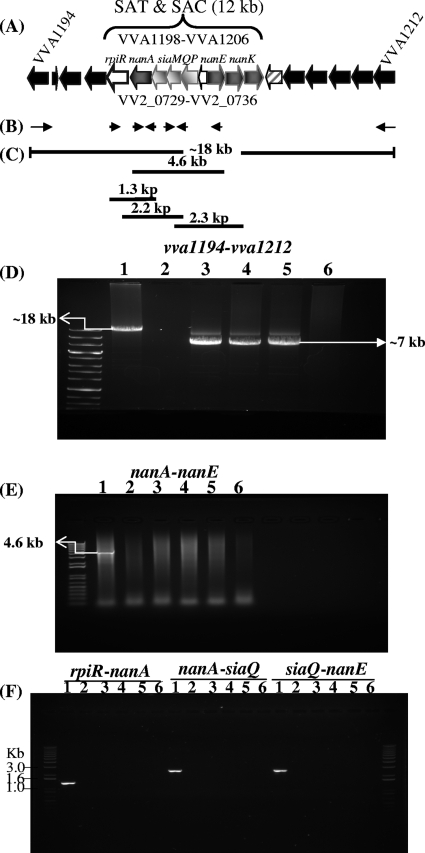
Vibrio vulnificus strains YJ016, CMCP6, and MO6-24/O are clinical isolates from Asia. We wanted to determine whether the SAC and SAT region is confined to clinical isolates of V. vulnificus, similar to V. cholerae. To accomplish this, we examined a collection of 67 natural isolates, which is comprised of both clinical and environmental isolates, for the presence of nanA. The ana gene encodes aldolase required in the first step of sialic acid catabolism. Of the 27 clinical isolates examined for the presence of nanA, 21 were positive for the gene by our PCR assay, whereas of the 40 environmental isolates examined, 17 strains gave a positive PCR band, indicating that they contained nanA. To further investigate the distribution of nanA among V. vulnificus isolates, we mapped the presence or absence of nanA onto the phylogeny of these strains (Fig. 2). The phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the analysis of six housekeeping genes as previously described (12) and contained two major lineages: lineage I was comprised primarily of clinical strains and lineage II was comprised predominately of environmental strains (12). We found that 34 out of the 37 lineage I isolates were positive for the presence of nanA, whereas only 7 of the 26 lineage II isolates were positive for the presence of nanA. These data demonstrate a strong correlation between the presence of the SAC region and lineage I strains (Fig. 2). The three strains in lineage I that lacked nanA were clinical strains isolated in Japan and the United States, and they did not cluster together on the tree, suggesting independent loss of the region. To determine whether the entire SAC and SAT region is missing in these strains and if a similar deletion event occurred in each strain, we used a long-range PCR assay with a primer pair that encompassed the SAC and SAT gene clusters (Fig. 3A). We designed the primer pair within genes that are conserved among other Vibrio species (Fig. 3B). We examined four nanA-negative strains from divergent branches of the V. vulnificus phylogenetic tree. An expected 18-kb PCR band was obtained for YJ016, which contain the SAT and SAC gene clusters. Only an ∼7-kb-sized PCR product was obtained for three of the nanA-negative strains, JY1701, E86, and L-180, which demonstrated that the SAC and SAT region was absent from these strains and that the same deletion event occurred (Fig. 3D). Since no product was obtained for K2637, we speculate that a larger deletion event that involved either vva1194 or vva1212 or both genes occurred. We performed four additional PCR assays on these strains to amplify regions within the SAT and SAC clusters encompassing nanA to nanE, rpiR to nanA, nanA to siaQ, and siaQ to nanE. Only the positive control strain YJ016 gave a positive PCR band in these assays, indicating that these regions are absent from nanA-negative strains (Fig. 3E and F).
Fig 2.
Distribution of nanA within the V. vulnificus phylogeny. The phylogenetic tree of V. vulnificus is based on the analysis of six housekeeping genes using the Kimura method and constructed using the neighbor-joining method as previously described (12). PCR assays were performed using nanA-specific primers and genomic DNA of V. vulnificus strains as templates. Positive and negative PCR results are indicated by “+”and “−,” respectively. The three sequenced V. vulnificus strains are underlined. The source of each isolate is also shown where C is for clinical, E for environmental, F for fish, and M for mollusk.
Fig 3.
PCR analysis of V. vulnificus nanA-negative strains. (A) Schematic of region examined. Solid arrows represent ORFs and black filled arrows represent ORFs outside the SAT and SAC region. Numbers above and below ORFs represent locus tags for strains YJ016 and CMCP6, respectively. (B) Line arrows indicate locations of primers used in PCR assays. (C) Black solid lines indicate regions amplified by primer pairs. (D) Long-range PCR assay. The lane to the left of lane 1 shows a 1 kb plus DNA ladder (Invitrogen). Lanes: 1, nanA-positive strain YJ016; 2 to 5, nanA-negative strains K2637, JY1701, E86, and L-180; 6, negative control, no template. A product of ∼18 kb was obtained from YJ016, whereas an ∼7-kb band was obtained from all other strains except K2637. (E) nanA-to-nanE PCR assay. Lanes 1 to 6 are as in panel D. A product of 4.6 kb was obtained from YJ016 only. (F) PCR assays for rpiR-nanA, nanA-siaQ, and siaQ-nanE. Lanes 1 to 6 are as in panel D. PCR products were obtained from YJ016 only.
Vibrio vulnificus SAC- and SAT-positive strains can utilize sialic acid as a sole carbon and energy source.
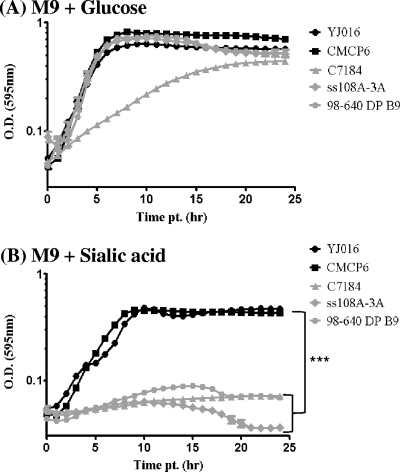
In silico analysis showed that V. vulnificus lineage I isolates carry the genes required for the transport and catabolism of sialic acid. Our next step was to determine whether V. vulnificus is capable of growth on sialic acid as a sole carbon and energy source. We examined two nanA-positive isolates and three nanA-negative isolates for their ability to grow in M9 minimal medium supplemented with glucose (M9 plus glucose) or sialic acid (M9 plus sialic acid) (Fig. 4). All V. vulnificus strains grew in M9 plus glucose, showing similar growth patterns and reaching final OD595 values of between 0.44 and 0.5 (Fig. 4A). However, only V. vulnificus nanA-positive strains grew in M9 plus sialic acid, whereas the nanA-negative strains failed to do so (Fig. 4B). This finding demonstrates that V. vulnificus nanA-positive strains are able to take up and utilize sialic acid as a sole carbon and energy source. Our data add to the growing list of bacterial species that have been shown to utilize sialic acid as a carbon and energy source (2, 3, 9, 20, 34, 38–40, 42).
Fig 4.
Growth analysis of V. vulnificus in M9 minimal medium supplemented with glucose (A) or N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid) (B) as a sole carbon source. Two V. vulnificus strains that carry the sialic acid catabolism and transporter gene clusters (YJ016 and CMCP6) and three nanA-negative strains (C7184, ss108A-3A, and 98-640 DP B9) were examined in minimal medium supplemented with glucose (A) or sialic acid (B). All cultures were grown in triplicate, and each experiment was performed at least twice using two biological replicates. Plots are represented on a natural log scale. OD, optical density. Error bars indicate standard deviations. An unpaired Student t test was used to determine statistically significant difference between cells grown in glucose and cells grown in N-acetylneuraminic acid. ***, P < 0.001.
Vibrio vulnificus SiaPQM (VV2_0731 to VV2_0733) TRAP transporter is essential for growth on sialic acid as a sole carbon source.
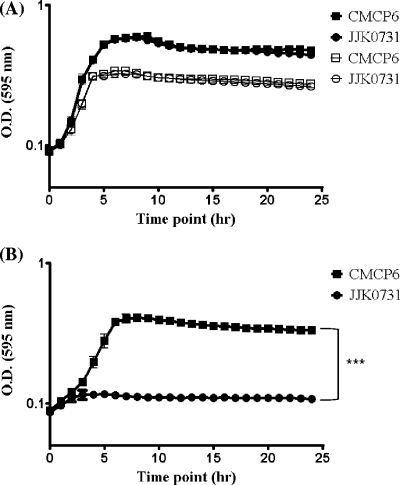
Bioinformatic analysis of sialic acid catabolism genes among Vibrionaceae indicates that the TRAP transporter system is the predominant type of transporter genetically linked to the catabolism genes within this group (Table 3). However, closer examination of the genes flanking SAC identified several species whose DNA encoded two types of transporters genetically linked to the catabolism genes (Fig. 1). In Vibrio orientalis, both a TRAP system and a Bcr/CflA transporter were adjacent to the sialic acid catabolism genes (Fig. 1 and Table 3). In P. profundum strain SS9, both a TRAP and an SSS system were genetically linked to the SAC genes. In V. vulnificus, the TRAP siaPQM operon is linked to the catabolism genes as well as an ABC transporter component. Thus, we investigated whether the TRAP system was essential for sialic acid uptake in this species. We constructed an isogenic knockout strain of V. vulnificus CMCP6 with an in-frame nonpolar truncated version of siaM. The siaM gene encodes a large permease containing 12 transmembrane helices, which is an essential component of the TRAP transporter system. The SiaPQM TRAP system was first characterized in H. influenzae and has recently been shown in V. cholerae in vitro experiments to be a high-affinity sialic acid transporter (28, 40). Wild-type CMCP6 and mutant strain JJK0731 were inoculated into LB or M9 supplemented with glucose, N-acetylglucosamine (NAG), or N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid) as the sole carbon source. Both wild-type and mutant strains demonstrated similar growth patterns in LB (data not shown), indicating that there is not a general growth defect in these strains. In addition, the wild type and the mutant strain JJK0731 grew similarly in M9 supplemented with glucose (Fig. 5A). However, strain JJK0731 did not grow in M9 supplemented with sialic acid as a sole carbon source, whereas the wild-type strain showed growth when examined under the same growth conditions (Fig. 5B). Thus, these data demonstrate that SiaPQM is essential for growth on sialic acid as the sole carbon source in V. vulnificus. As expected, both the wild-type and mutant strains grew similarly in M9 supplemented with NAG, which is one of the products of the sialic acid catabolism pathway and does not require SiaPQM for uptake into the bacterial cell (Fig. 5A).
Table 3.
Distribution of sialic acid transport and catabolism genes among the sequenced Vibrionaceae
| Species strain(s) | Genec |
|
|---|---|---|
| Transport | Catabolism | |
| Vibrio vulnificus lineage Ia | TRAP | NanAEK |
| V. vulnificus lineage IIb | X | X |
| V. cholerae pathogenic | TRAP | NanAEK |
| Vibrio cholerae nonpathogenic | X | X |
| Vibrio mimicus VM603/573/MB451 | TRAP | NanAEK |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | X | X |
| V. parahaemolyticus 16 | TRAP | NanAEK |
| Vibrio fischeri ES114/MJ1 | SSS | NanAEK |
| Vibrio shilonii AK1 | TRAP | NanAEK |
| Vibrio sinaloensis DSM21326 | TRAP | NanAEK |
| Vibrio orientalis CIP10289 | TRAP/Bcr/CflA NanAEK | |
| Vibrio sp. strain MED222 | TRAP | NanAEK |
| Vibrio anguillarum | TRAP | NanAEK |
| Photobacterium profundum SS9/3TCK | TRAP/SSS | NanAEK |
| P. damselae CIP102761 | NK | NanAEK |
| Aliivibrio salmonicida | NK | NanA only |
Three lineage I strains lacked the SAC and SAT clusters.
Seven lineage II strains contained the SAC and SAT gene clusters.
Abbreviations: SSS, sodium solute symporter; TRAP, tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic; NK, not known; X, absent.
Fig 5.
Growth analysis of V. vulnificus wild-type strain CMCP6 and its nonpolar siaM deletion mutant strain JJK0731 in M9 minimal medium supplemented with glucose or N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) (A) or N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid) (B). (A) Upper two lines with symbols of solid squares and circles indicate the growth pattern in M9 plus glucose, and the lower two are of M9 plus NAG. Plots are represented on natural log scale. OD, optical density. All cultures were grown in triplicate, and each experiment was performed at least twice using two biological replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviation. An unpaired Student t test was used to determine statistical difference between mutant strain cells and wild-type strain cells grown in N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid). ***, P < 0.001.
A recent study in V. cholerae proposed that a different TRAP transporter unrelated to SiaPQM from V. cholerae and V. vulnificus was required for sialic acid transport (41). Sharma and colleagues proposed that the VC1929 ORF, which encodes a C4-dicarboxylate-binding periplasmic protein named DctP, was part of a TRAP system (VC1927 to VC1929) involved in sialic acid transport (41). They argued that in an El Tor strain of V. cholerae, VC1929 was a mannose-sensitive hemagglutinin that was required for sialic acid utilization (41). This was an unexpected finding since VC1929 shared high sequence homology with C4-dicarboxylate permeases that are involved in the transport of malate, fumurate, or succinate (45). Recently, we investigated the role of DctP (VC1929) in V. cholerae using its nonpolar knockout mutant and demonstrated that it plays a role in C4-dicarboxylate but not sialic acid uptake (our unpublished data). A homologue of VC1929, VV1_0030, which shows 89% amino acid identity to DctP, is also present in V. vulnificus. However, like V. cholerae, DctP (VV1_0030) in V. vulnificus does not appear to be involved in sialic acid transport given that our siaM (VV2_0731) mutant is no longer able to utilize sialic acid as a sole carbon source.
Sialic acid induces expression of SAC and SAT genes.
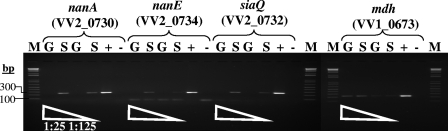
Next, we examined whether the catabolism and transporter genes are constitutively expressed or induced in the presence of sialic acid. We examined the expression of three genes: siaQ, nanA, and nanE. The siaQ gene encodes a small permease containing 4 transmembrane helices, which is a component of the TRAP transporter, nanA encodes N-acetylneuramic acid aldolase, the first enzyme in the sialic acid catabolism pathway, and nanE encodes ManNAc-6-P epimerase, which catalyzes the last step in the pathway. We isolated RNA from cultures of V. vulnificus CMCP6 grown at 37°C with aeration in M9 supplemented with glucose or sialic acid. Semiquantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) was performed, and the three genes showed no expression in M9 supplemented with glucose at 3 h postinoculation (Fig. 6). However, RT-PCR analysis of V. vulnificus strain CMCP6 cultured in M9 supplemented with sialic acid showed that all three genes were expressed (Fig. 6). Our results demonstrate that the level of expression of both the transporter and catabolism genes is induced in the presence of sialic acid in V. vulnificus. This is in agreement with what has been shown for V. cholerae, where both the catabolism and transporter genes were highly expressed in the presence of sialic acid (3). Kim and colleagues have recently demonstrated that the divergently transcribed siaP and nanE genes are under the control of the negative regulator rpiR (VV2_0730) in V. vulnificus (24). They showed that both the catabolic and transport genes are induced in the presence of sialic acid. They also found that N-acetylmannosamine-6-phosphate specifically bound to RpiR (NanR) and functioned as the inducer of the nan genes (nanEKnagA and siaPQM) (24).
Fig 6.
Expression analysis of sialic acid catabolism (e.g., nanA, nanE) and transporter (e.g., siaQ) genes, and a reference (housekeeping) gene (mdh) in V. vulnificus strain CMCP6 in the presence of glucose (G) or sialic acid (S). cDNA samples were diluted 1:25 and 1:125 and used as templates for semiquantitative RT-PCRs. Genomic DNA of CMCP6 and a PCR mixture without any DNA were used as positive (+) and negative (−) controls, respectively. The values on the left are the molecular mass (bp) standard of 1 kb plus DNA ladder (Invitrogen).
Overall, our data demonstrate that the ability to catabolize and transport sialic acid is predominately lineage specific in V. vulnificus, and clinical isolates are capable of growth in sialic acid as a sole carbon and energy source. In addition, we have demonstrated that the siaPQM genes (VV2_0731 to VV2_0733) genetically linked to the catabolism genes encode a TRAP transporter for sialic acid uptake. Vibrio vulnificus is an opportunistic pathogen and has two modes of entry, either through the gastrointestinal tract or through wound infection. It is unlikely that there is one key virulence factor that is essential for virulence at both of these sites of infection. Thus, the loss of the SAC genes in some lineage I isolates may make them less competitive in the human gut, but they may still be formidable wound pathogens. The linking of sialic acid catabolism genes with a high-affinity sialic acid transport system would certainly be advantageous to a species either in environments where nutrients are limited or in environments where competition for nutrients is high, such as the animal gut. The presence of free glucose is highly limited in the animal intestine, and gastrointestinal pathogens have evolved to take advantage of alternative carbon sources in this niche. Mucous membranes are ubiquitous within the intestinal tract and are made up of mucins, which are sialylated glycoproteins and represent a potential nutrient source. Many different pathogenic and commensal species possess sialic acid catabolism genes that enable them to utilize glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) as carbon and nitrogen sources. Sialic acids are nine-carbon amino sugars that are present at the termini of GAGs in many cell types. Commensals and pathogens can carry the gene for sialidases that cleave terminal sialic acids, releasing them for uptake into the bacterial cells. Thus, the ability to take up and utilize sialic acid as a sole carbon source should be advantageous to gastrointestinal pathogens. Indeed, it has been demonstrated that in both V. cholerae and V. vulnificus, the ability to use sialic acid as a sole carbon source increases their fitness in vivo (3, 20).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by National Science Foundation CAREER award DEB-0844409 to E.F.B. J.-B.L. was supported by the Chemistry-Biology Interface graduate program at the University of Delaware, and J.J.K. was supported by a BOYSCAST Indian government fellowship.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 17 February 2012
REFERENCES
- 1. Almagro-Moreno S, Boyd EF. 2010. Bacterial catabolism of nonulosonic (sialic) acid and fitness in the gut. Gut Microbes 1:45–50 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Almagro-Moreno S, Boyd EF. 2009. Insights into the evolution of sialic acid catabolism among bacteria. BMC Evol. Biol. 9:118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Almagro-Moreno S, Boyd EF. 2009. Sialic acid catabolism confers a competitive advantage to pathogenic Vibrio cholerae in the mouse intestine. Infect. Immun. 77:3807–3816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Altschul SF, et al. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3389–3402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Amaro C, Biosca EG. 1996. Vibrio vulnificus biotype 2, pathogenic for eels, is also an opportunistic pathogen for humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62:1454–1457 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Biosca EG, Amaro C, Larsen JL, Pedersen K. 1997. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Vibrio vulnificus: proposal for the substitution of the subspecific taxon biotype for serovar. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63:1460–1466 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Bisharat N, et al. 2005. Hybrid Vibrio vulnificus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 11:30–35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Blackwell KD, Oliver JD. 2008. The ecology of Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio cholerae, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in North Carolina estuaries. J. Microbiol. 46:146–153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Brigham C, et al. 2009. Sialic acid (N-acetyl neuraminic acid or NANA) utilization by Bacteroides fragilis requires a novel N-acetylmannosamine (manNAc) epimerase. J. Bacteriol. 191:3629–3638 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Chatzidaki-Livanis M, Jones MK, Wright AC. 2006. Genetic variation in the Vibrio vulnificus group 1 capsular polysaccharide operon. J. Bacteriol. 188:1987–1998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Chen CY, et al. 2003. Comparative genome analysis of Vibrio vulnificus, a marine pathogen. Genome Res. 13:2577–2587 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Cohen AL, Oliver JD, DePaola A, Feil E, Boyd EF. 2007. Molecular phylogeny of Vibrio vulnificus based on multilocus sequence analysis and a 33-kilobase genomic island correlates with pathogenic potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73:5553–5565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. DePaola A, et al. 2003. Analysis of Vibrio vulnificus from market oysters and septicemia cases for virulence markers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69:4006–4011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Fischer M, Zhang Q, Hubbard R, Thomas G. 2010. Caught in a TRAP: substrate-binding proteins in secondary transport. Trends Microbiol. 18:471–478 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Gulig PA, Bourdage KL, Starks AM. 2005. Molecular pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus. J. Microbiol. 43:118–131 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Gulig PA, et al. 2010. SOLiD sequencing of four Vibrio vulnificus genomes enables comparative genomic analysis and identification of candidate clade-specific virulence genes. BMC Genomics 11:512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Harwood VJ, Gandhi JP, Wright AC. 2004. Methods for isolation and confirmation of Vibrio vulnificus from oysters and environmental sources: a review. J. Microbiol. Methods 59:301–316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Hayat U, et al. 1993. Capsular types of Vibrio vulnificus: an analysis of strains from clinical and environmental sources. J. Infect. Dis. 168:758–762 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Horton RM, Hunt HD, Ho SN, Pullen JK, Pease LR. 1989. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene 77:61–68 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Jeong HG, et al. 2009. Capability of catabolic utilization of N-acetylneuraminic acid, a sialic acid, is essential for pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 77:3209–3217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Jermyn WS, Boyd EF. 2002. Characterization of a novel Vibrio pathogenicity island (VPI-2) encoding neuraminidase (nanH) among toxigenic Vibrio cholerae isolates. Microbiology 148:3681–3693 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Jermyn WS, Boyd EF. 2005. Molecular evolution of Vibrio pathogenicity island-2 (VPI-2): mosaic structure among Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus natural isolates. Microbiology 151:311–322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Jones MK, Oliver JD. 2009. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 77:1723–1733 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Kim BS, Hwang J, Kim MH, Choi SH. 2011. Cooperative regulation of the Vibrio vulnificus nan gene cluster by NanR protein, cAMP receptor protein, and N-acetylmannosamine 6-phosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 286:40889–40899 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Kwak JS, Jeong HG, Satchell KJ. 2011. Vibrio vulnificus rtxA1 gene recombination generates toxin variants with altered potency during intestinal infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108:1645–1650 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Morris JG, Jr, et al. 1987. Identification of environmental Vibrio vulnificus isolates with a DNA probe for the cytotoxin-hemolysin gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53:193–195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Mulligan C, Fischer M, Thomas GH. 2011. Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporters in bacteria and archaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 35:68–86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Mulligan C, Leech AP, Kelly DJ, Thomas GH. 2012. The membrane proteins SiaQ and SiaM form an essential stoichiometric complex in the sialic acid ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporter SiaPQM (VC1777-1779) from Vibrio cholerae. J. Biol. Chem. 287:3598–3608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Nees S, Schauer R, Mayer F. 1976. Purification and characterization of N-acetylneuraminate lyase from Clostridium perfringens. Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 357:839–853 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Nilsson W, Paranjype R, DePaola A, Strom M. 2003. Sequence polymorphism of the 16S rRNA gene of Vibrio vulnificus is a possible indicator of strain virulence. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:442–446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Oliver JD, Warner RA, Cleland DR. 1982. Distribution and ecology of Vibrio vulnificus and other lactose-fermenting marine vibrios in coastal waters of the southeastern United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 44:1404–1414 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Philippe N, Alcaraz JP, Coursange E, Geiselmann J, Schneider D. 2004. Improvement of pCVD442, a suicide plasmid for gene allele exchange in bacteria. Plasmid 51:246–255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Rosche TM, Yano Y, Oliver JD. 2005. A rapid and simple PCR analysis indicates there are two subgroups of Vibrio vulnificus which correlate with clinical or environmental isolation. Microbiol. Immunol. 49:381–389 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Roy S, Douglas CW, Stafford GP. 2010. A novel sialic acid utilization and uptake system in the periodontal pathogen Tannerella forsythia. J. Bacteriol. 192:2285–2293 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Sanjuan E, Amaro C. 2007. Multiplex PCR assay for detection of Vibrio vulnificus biotype 2 and simultaneous discrimination of serovar E strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73:2029–2032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Sanjuan E, Fouz B, Oliver JD, Amaro C. 2009. Evaluation of genotypic and phenotypic methods to distinguish clinical from environmental Vibrio vulnificus strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:1604–1613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Sanjuan E, Gonzalez-Candelas F, Amaro C. 2011. Polyphyletic origin of Vibrio vulnificus biotype 2 as revealed by sequence-based analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77:688–695 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Severi E, Hood DW, Thomas GH. 2007. Sialic acid utilization by bacterial pathogens. Microbiology 153:2817–2822 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Severi E, Hosie AH, Hawkhead JA, Thomas GH. 2010. Characterization of a novel sialic acid transporter of the sodium solute symporter (SSS) family and in vivo comparison with known bacterial sialic acid transporters. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 304:47–54 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Severi E, et al. 2005. Sialic acid transport in Haemophilus influenzae is essential for lipopolysaccharide sialylation and serum resistance and is dependent on a novel tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporter. Mol. Microbiol. 58:1173–1185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Sharma SK, Moe TS, Srivastava R, Chandra D, Srivastava BS. 2011. Functional characterization of VC1929 of Vibrio cholerae El Tor: role in mannose-sensitive haemagglutination, virulence and utilization of sialic acid. Microbiology 157:3180–3186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Steenbergen SM, et al. 2005. Sialic acid metabolism and systemic pasteurellosis. Infect. Immun. 73:1284–1294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Strom M, Paranjpye RN. 2000. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus. Microbes Infect. 2:177–188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Thiaville PC, et al. 2011. Genotype is correlated with but does not predict virulence of Vibrio vulnificus biotype 1 in subcutaneously inoculated, iron dextran-treated mice. Infect. Immun. 79:1194–1207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Thomas GH, Boyd EF. 2011. On sialic acid transport and utilization by Vibrio cholerae. Microbiology 157:3253–3254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Varki A. 1992. Diversity in the sialic acids. Glycobiology 2:25–40 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Varki A. 2008. Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 14:351–360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Vickery MC, Nilsson WB, Strom MS, Nordstrom JL, DePaola A. 2007. A real-time PCR assay for the rapid determination of 16S rRNA genotype in Vibrio vulnificus. J. Microbiol. Methods 68:376–384 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Vimr E, Lichtensteiger C. 2002. To sialylate, or not to sialylate: that is the question. Trends Microbiol. 10:254–257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Vimr ER, Kalivoda KA, Deszo EL, Steenbergen SM. 2004. Diversity of microbial sialic acid metabolism. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68:132–153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Vimr ER, Troy FA. 1985. Identification of an inducible catabolic system for sialic acids (nan) in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 164:845–853 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Wright AC, et al. 1996. Distribution of Vibrio vulnificus in the Chesapeake Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62:717–724 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]