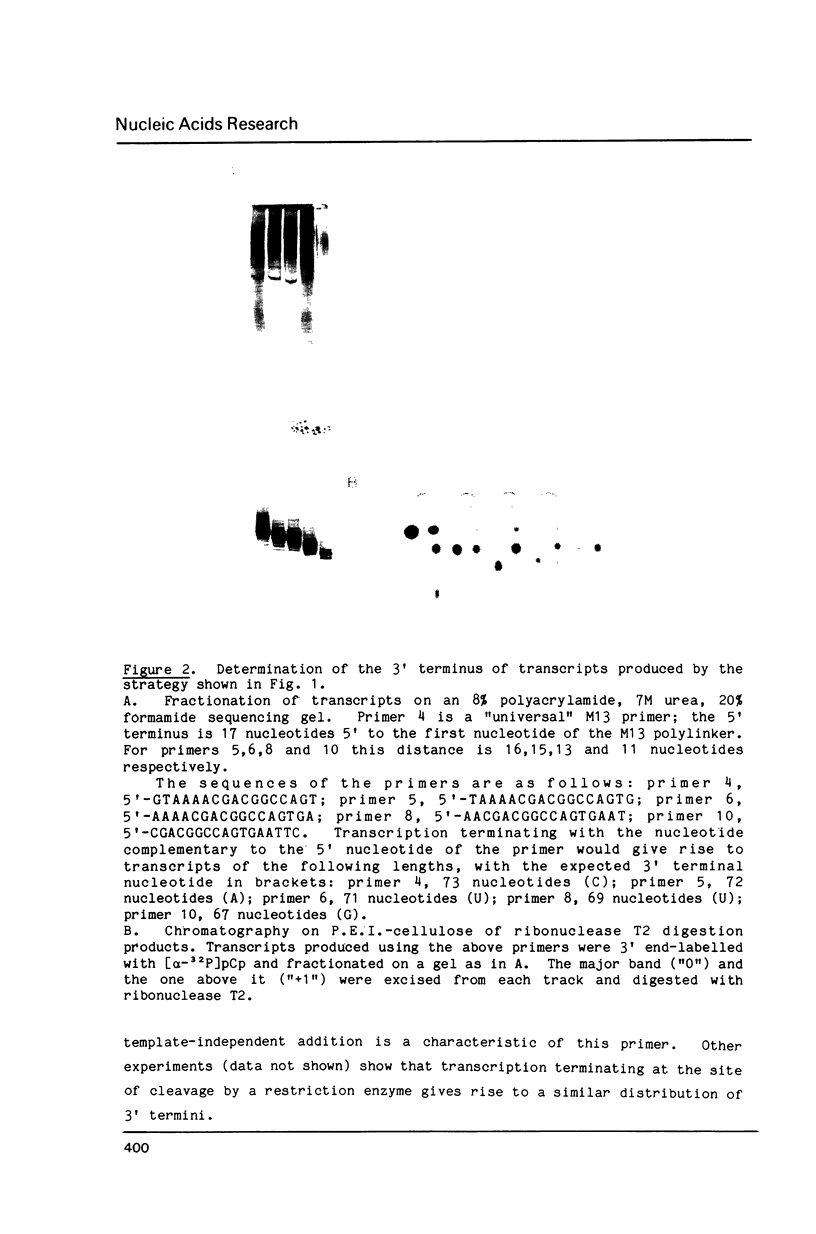
Abstract
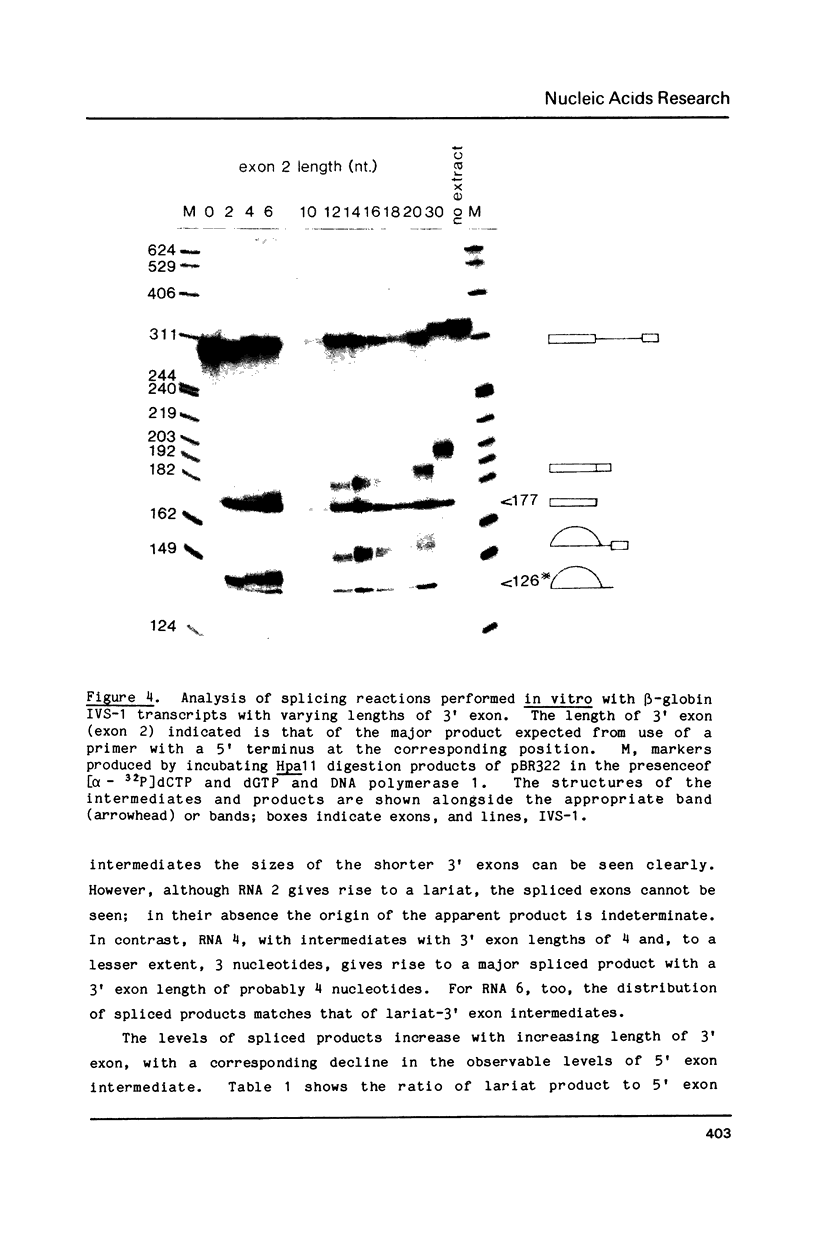
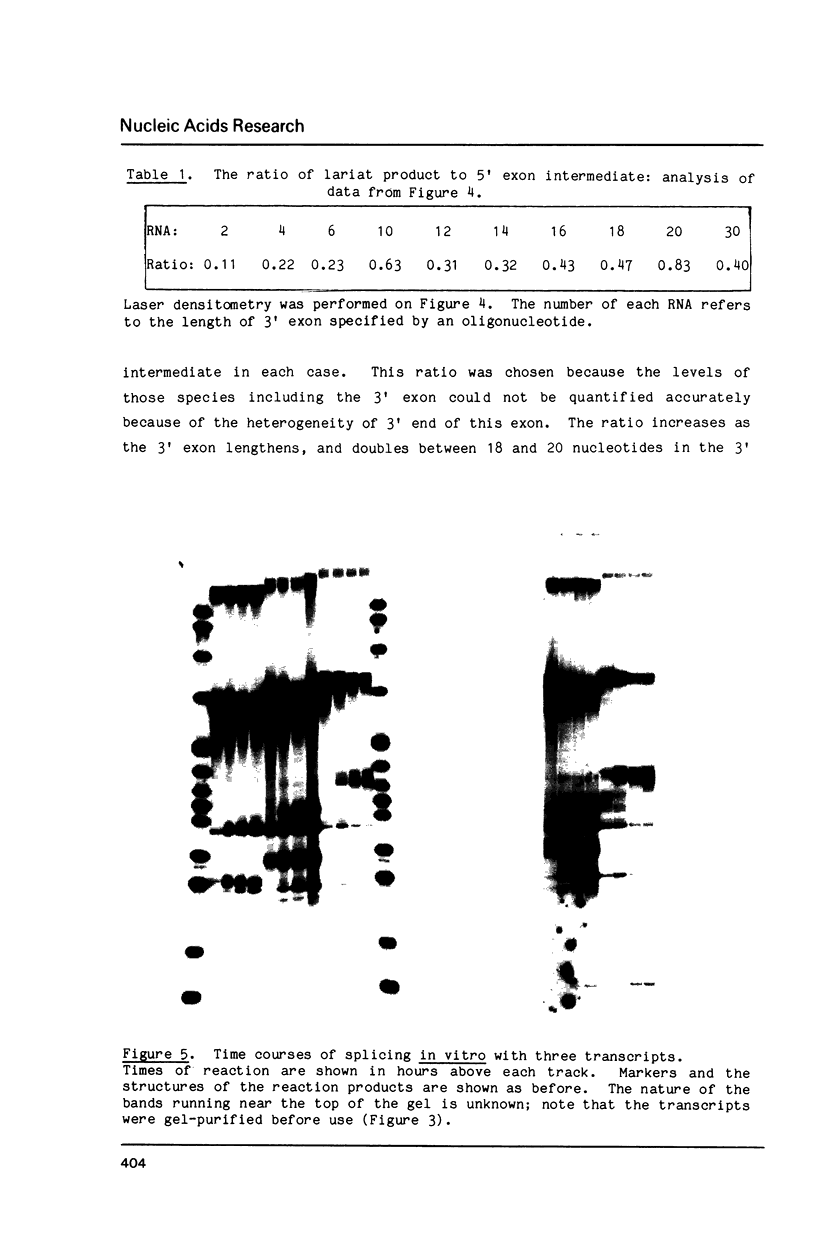
Oligonucleotide-limited transcription has been used to prepare a series of transcripts which allowed the positions of termination by T7 RNA polymerase to be characterized. The same technique was used to prepare a set of transcripts from a rabbit beta-globin gene that extend in intervals of two nucleotides from the 3' splice site of IVS-1 into the second exon. Splicing efficiency in a HeLa cell nuclear extract decreased with decreasing length of the 3' exon, although both steps of the splicing reaction could still be detected with as few as four nucleotides in this exon. No evidence was found for a lower limit to the length of the 3' exon below which splicing would not take place. With longer substrates, the rate of the second step of splicing was increased substantially.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Weissmann C. 5' cleavage site in eukaryotic pre-mRNA splicing is determined by the overall 5' splice region, not by the conserved 5' GU. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. An ordered pathway of snRNP binding during mammalian pre-mRNA splicing complex assembly. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Black D. L., LeMaster D. M., Steitz J. A. The 3' splice site of pre-messenger RNA is recognized by a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1344–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2933810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Steitz J. A. Multiple interactions between the splicing substrate and small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in spliceosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):281–293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C. M13 vectors with T7 polymerase promoters: transcription limited by oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2830–2830. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C. Rapid preparation of bacteriophage DNA for sequence analysis in sets of 96 clones, using filtration. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):406–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furdon P. J., Kole R. Inhibition of splicing but not cleavage at the 5' splice site by truncating human beta-globin pre-mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):927–931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg C. J., Hauser S. D. Accurate and efficient in vitro splicing of purified precursor RNAs specified by early region 2 of the adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1337–1348. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. F., Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Cofactor requirements of splicing of purified messenger RNA precursors. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):375–377. doi: 10.1038/308375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Transcription of human histone genes in extracts from synchronized HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2713–2717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornig H., Aebi M., Weissmann C. Effect of mutations at the lariat branch acceptor site on beta-globin pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):589–591. doi: 10.1038/324589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Characterization of the branch site in lariat RNAs produced by splicing of mRNA precursors. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):552–557. doi: 10.1038/313552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes H. W., Zenke W. M., Grundström T., Staub A., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Simultaneous rapid chemical synthesis of over one hundred oligonucleotides on a microscale. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):801–805. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A., Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. Minimal exon sequence requirements for efficient in vitro splicing of mono-intronic nuclear pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11284–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Furneaux H. M., Hurwitz J. RNA splicing products formed with isolated fractions from HeLa cells are associated with fast-sedimenting complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):887–891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. R., Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. In vivo characterization of yeast mRNA processing intermediates. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Role of the 3' splice site consensus sequence in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):732–734. doi: 10.1038/317732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. A., Eperon I. C. Misincorporation by AMV reverse transcriptase shows strong dependence on the combination of template and substrate nucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6945–6964. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volckaert G., Fiers W. A micromethod for base analysis of 32P-labeled oligoribonulcleotides. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90530-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]