Abstract
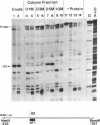
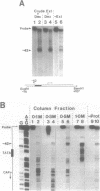
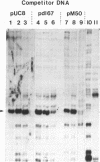
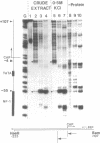
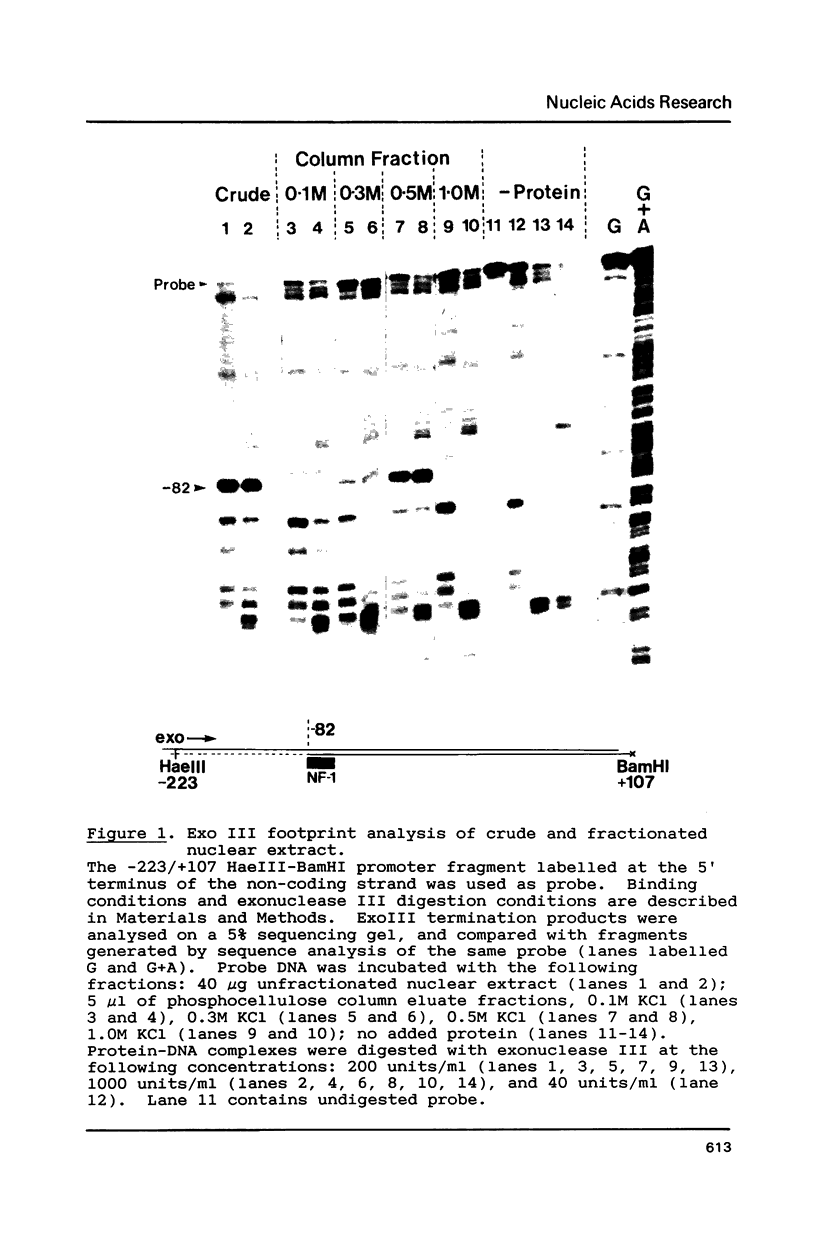
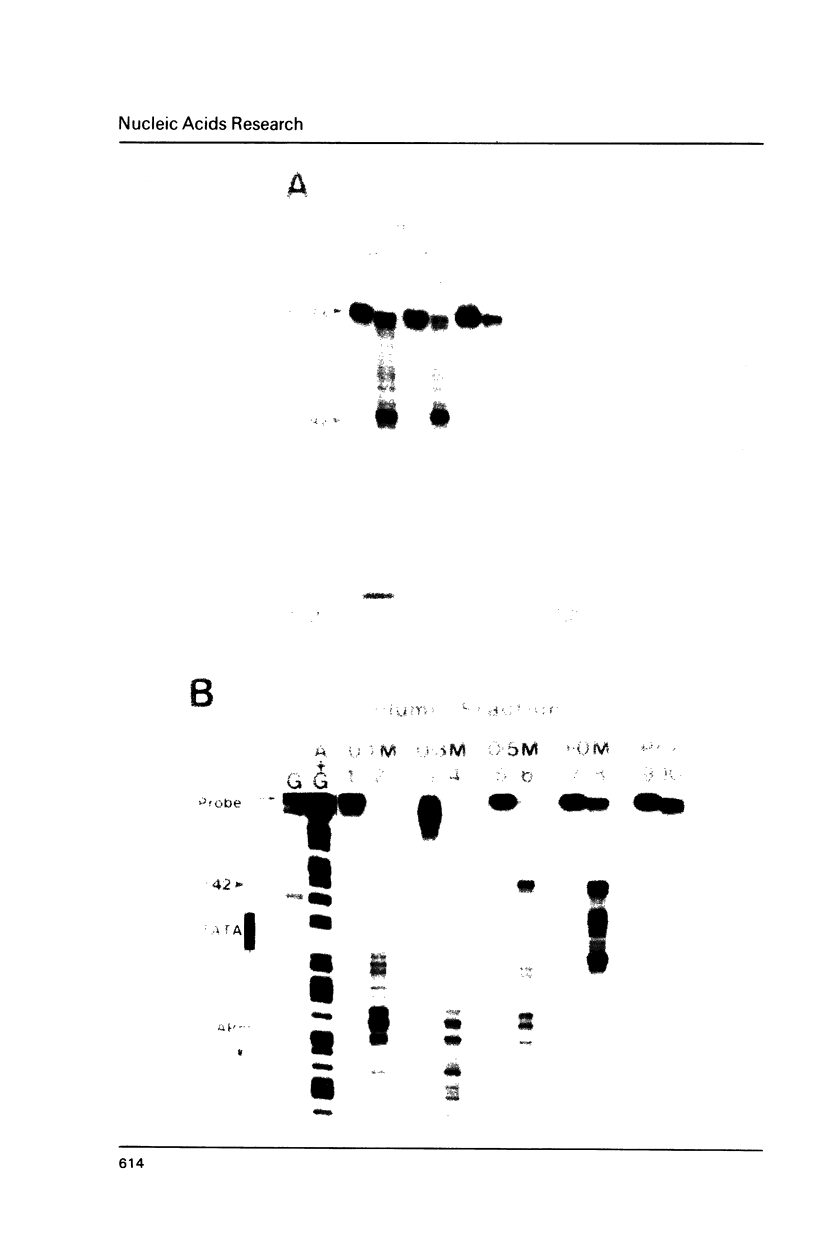
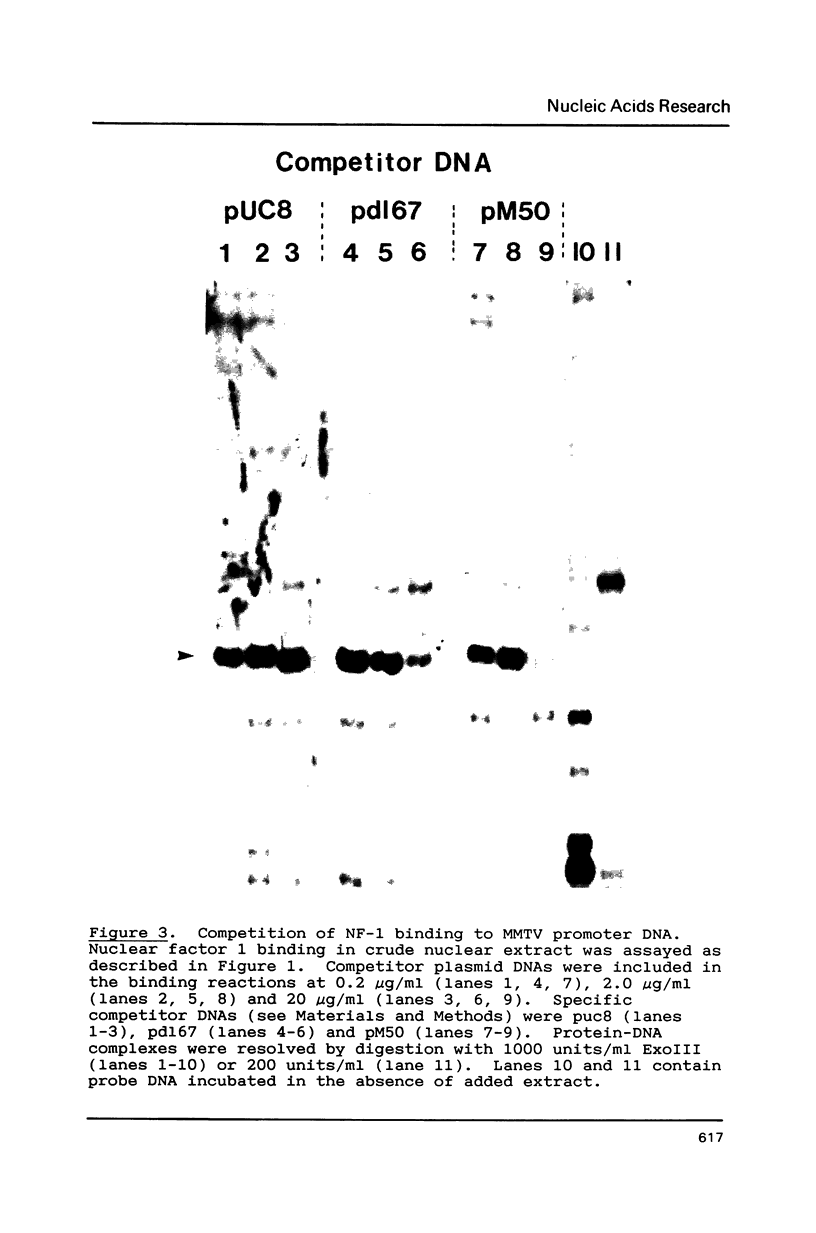
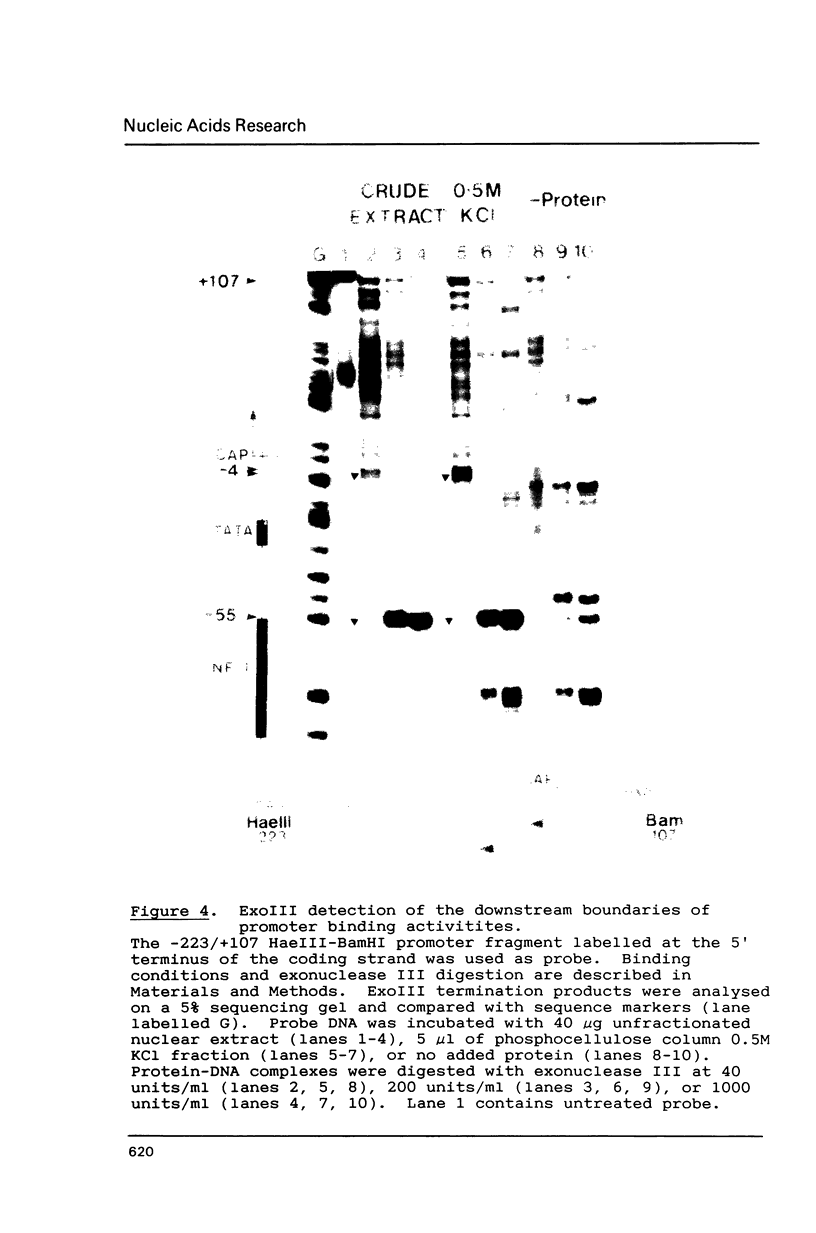
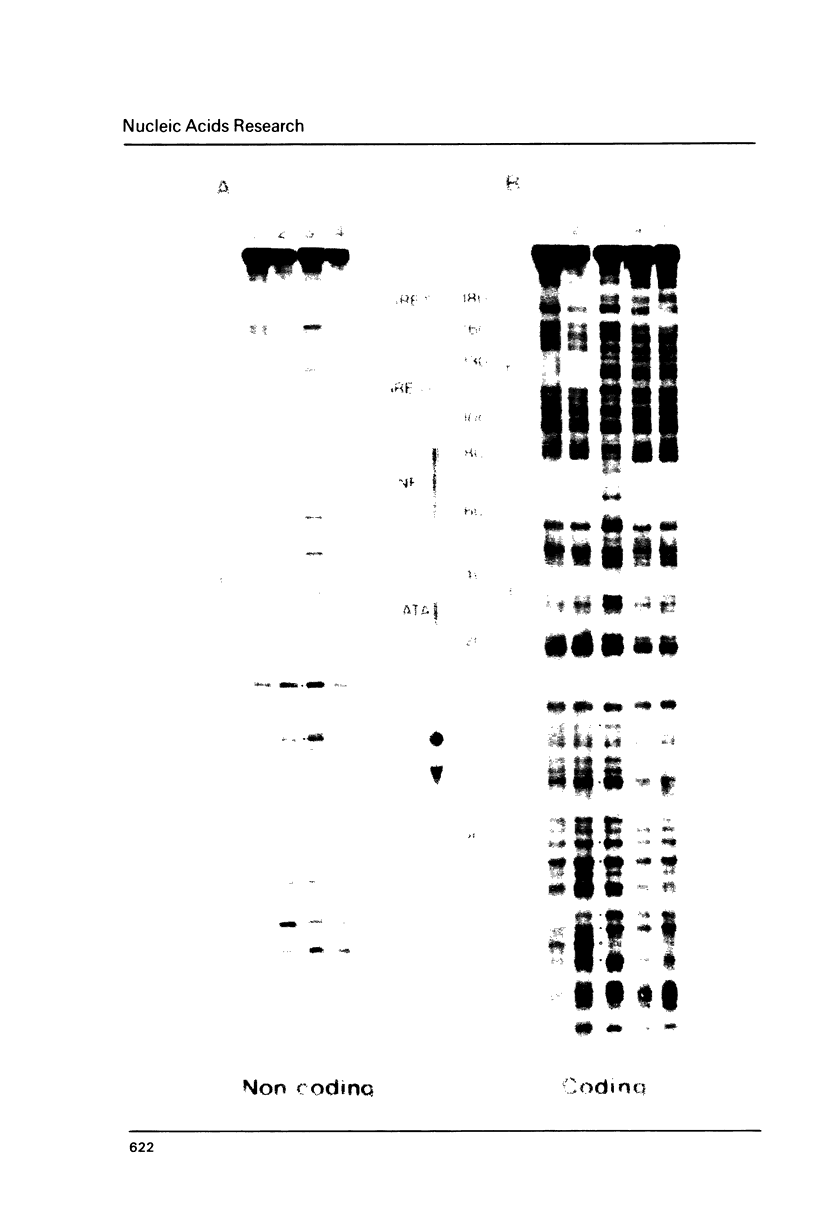
Hormone activation of MMTV transcription results in the establishment of a tightly bound transcription factor complex at the promoter (Cordingley et al., Cell 48, 261-270, 1987). We have characterized two fractionable binding activities which participate in this complex. One factor, previously identified as the mouse homologue of NF-1 (or CTF), protects sequences -82 to -56 from exonuclease III digestion in vitro. Sequences protected by a second factor (-42 to -4) span the TATA box of the promoter, suggesting that the binding activity in this fraction is equivalent to the HeLa cell transcription factor TFIID (Sawadogo and Roeder, Cell 43, 165-175, 1986). The downstream boundary of exonuclease protection by the putative TATA-binding factor is -4; DNase1 footprinting of this fraction, however, showed additional protection of discrete sites downstream of the cap site. The apparent concentration and promoter-specific binding activity of both factors is unaffected by hormone treatment of the cells.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Wides R. J., Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J., Jr Structure and function of the adenovirus origin of replication. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X. P., Lee R., Weinmann R. Protein factor(s) binding independently to two different regions of the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3729–3744. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P. Steroid induction of mouse mammary tumor virus: effect upon synthesis and degradation of viral RNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.139-146.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]