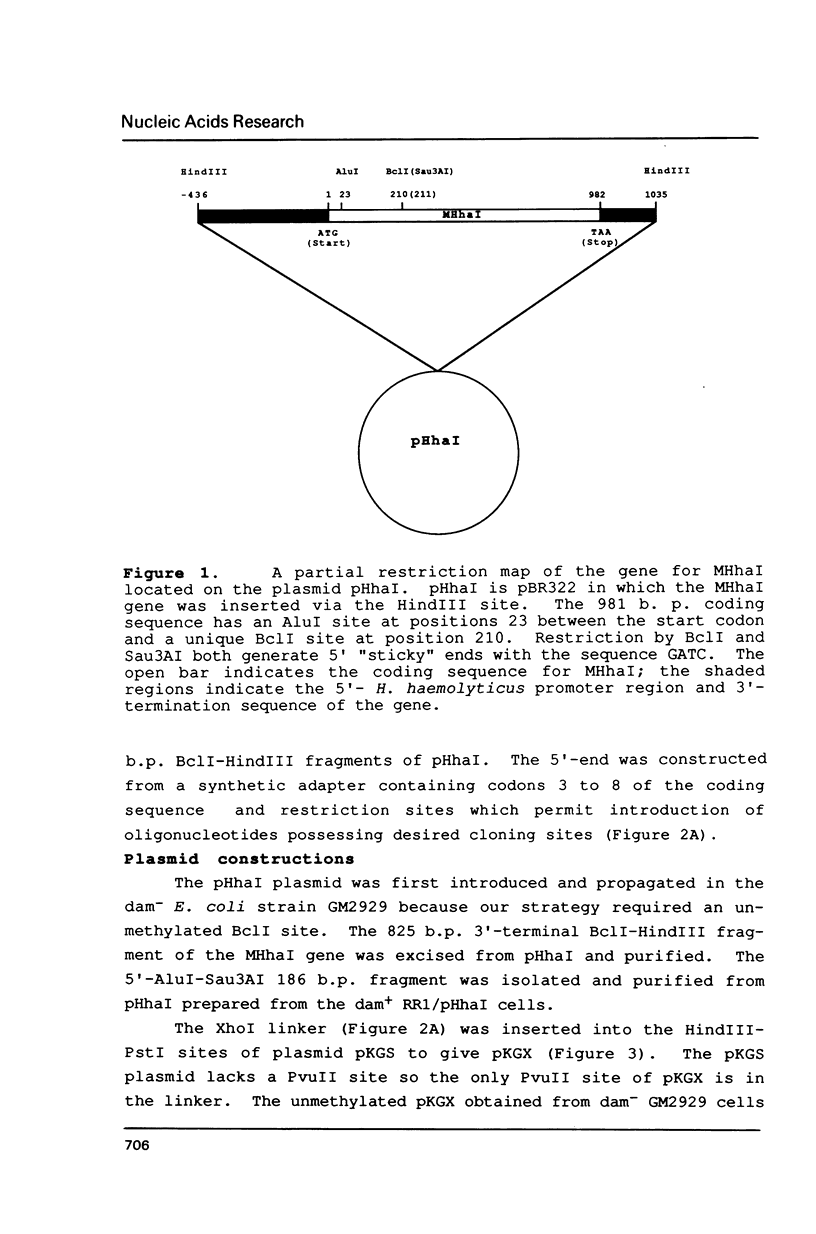
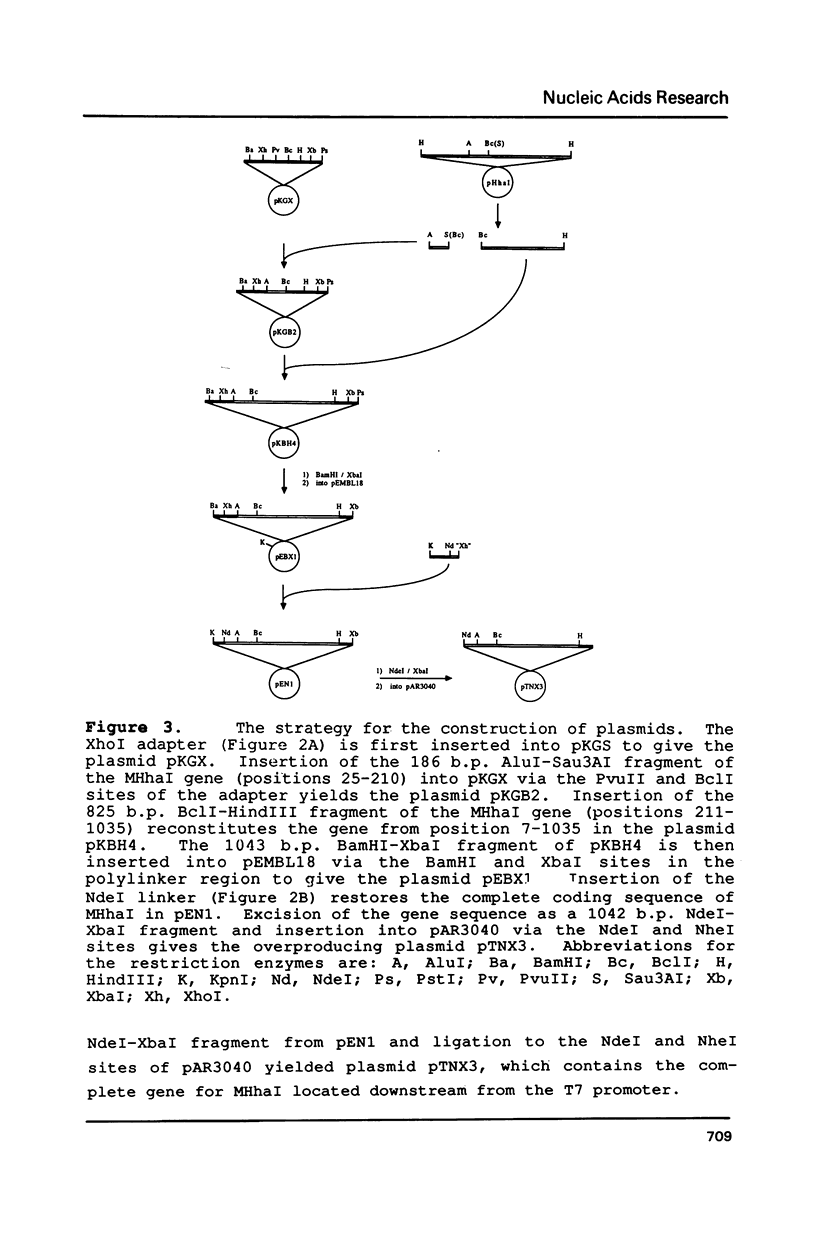
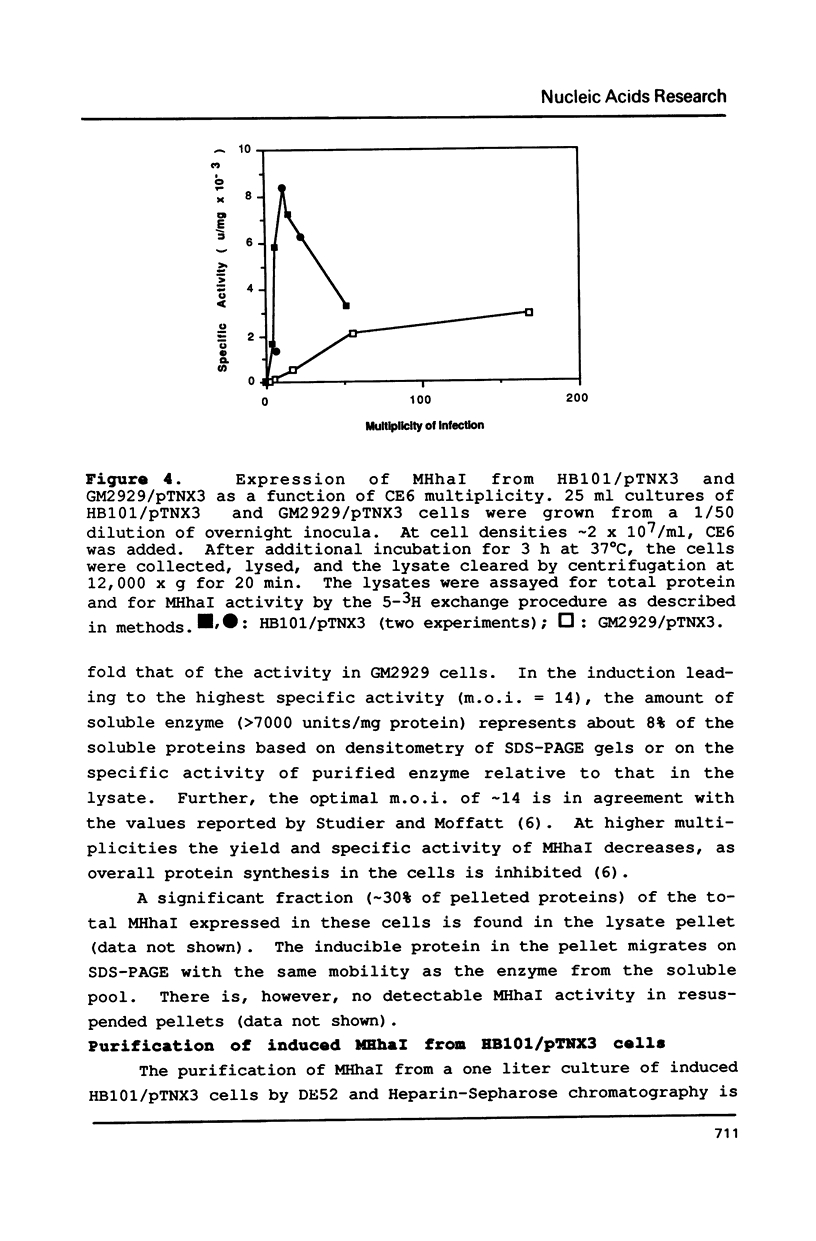
Abstract
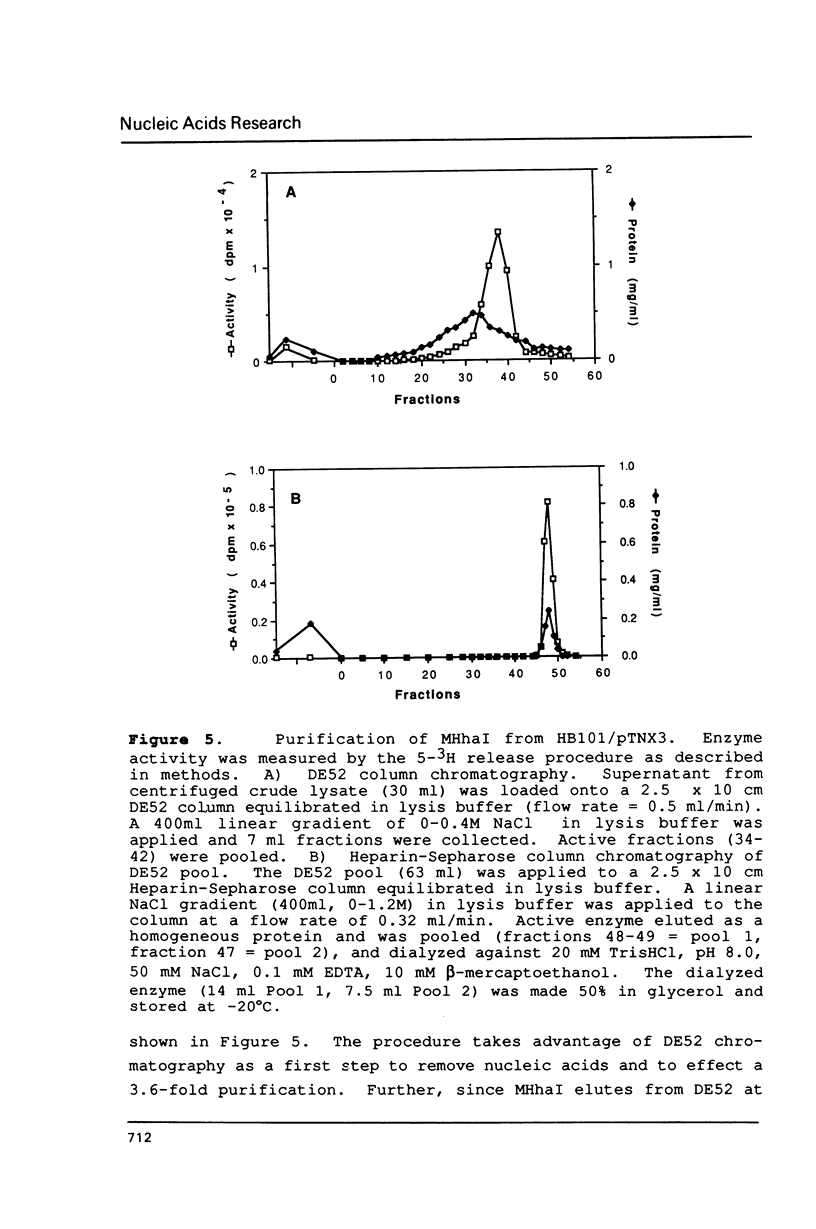
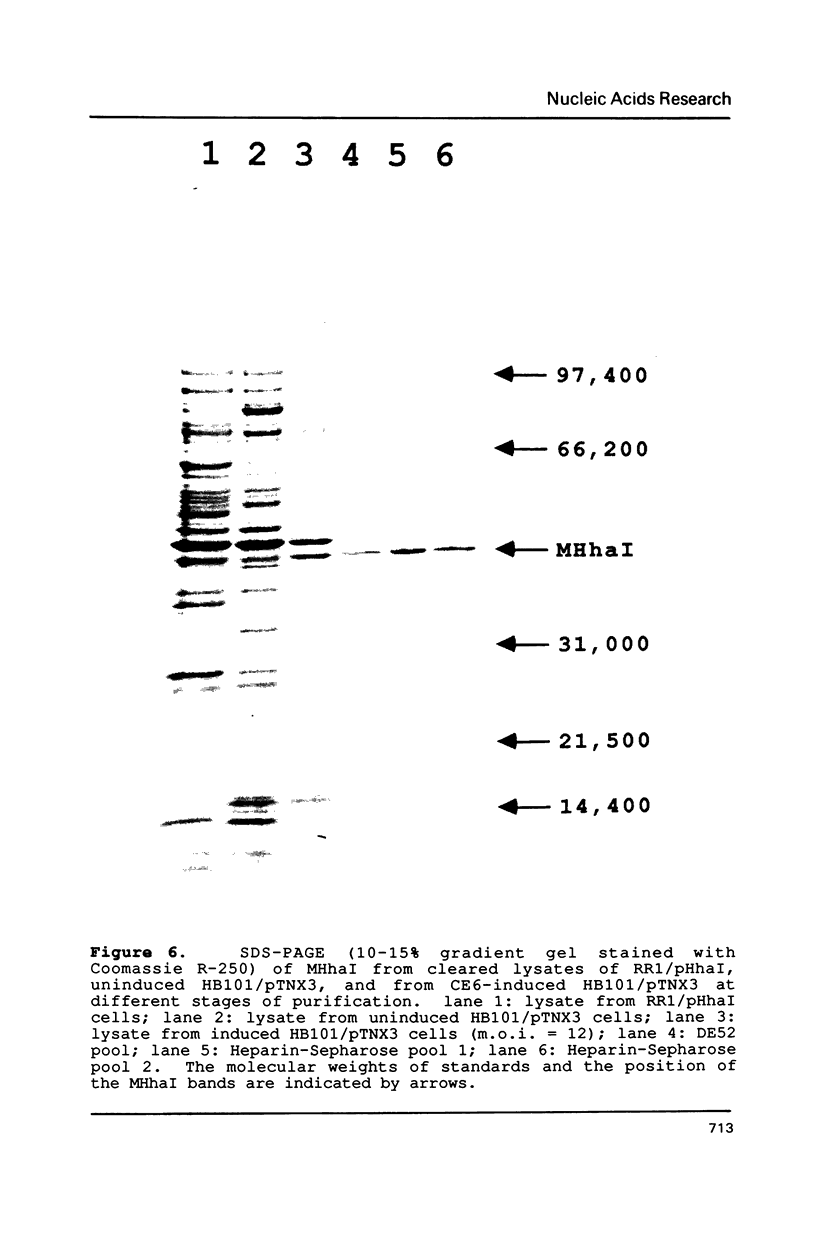
A cloning system for the DNA-(cytosine-5)-methyltransferase MHhaI and high level expression of the enzyme are described. A parent plasmid was constructed from fragments of the MHhaI gene and synthetic oligonucleotides. The construct permits introduction of various restriction sites for cloning at precise positions near the initiation codon, and beyond the termination codon. The entire MHhaI coding sequence was introduced as a 1042 b.p. NdeI-XbaI fragment into the vector pAR3040 which contains the T7 RNA polymerase promoter. The resultant plasmid pTNX3 (MHhaI-pAR3040) was introduced into McrB- E. coli strains HB101 and GM2929, and expression of MHhaI was induced by infection with the lambda phage CE6 carrying the T7 RNA polymerase gene. In induced cells, catalytically active MHhaI was produced at a level that corresponds to about 8% of the total soluble protein; an insoluble form of the protein was also formed, but could be readily removed. The expressed soluble enzyme from HB101/pTNX3 was purified to apparent homogeneity in about 50% yield by a two-step chromatographic procedure involving DEAE-cellulose and Heparin-Sepharose; a one liter culture gave about 2.5 mg of pure enzyme. The molecular weight and kinetic properties of the expressed protein are identical to those reported for the authentic MHhaI, and its amino terminal sequence agrees with that predicted from the DNA sequence.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caserta M., Zacharias W., Nwankwo D., Wilson G. G., Wells R. D. Cloning, sequencing, in vivo promoter mapping, and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for the HhaI methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4770–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss A., Posfai G., Keller C. C., Venetianer P., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the BsuRI restriction-modification system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6403–6421. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn I., Stephenson F. H., Boyer H. W., Greene P. J. Positive-selection vectors utilizing lethality of the EcoRI endonuclease. Gene. 1986;42(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Wilson G. Escherichia coli K-12 restricts DNA containing 5-methylcytosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9070–9074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., Garrett C. E., Barr P. J. On the mechanism of inhibition of DNA-cytosine methyltransferases by cytosine analogs. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., Norment A., Garrett C. E. Covalent bond formation between a DNA-cytosine methyltransferase and DNA containing 5-azacytosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6993–6997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Santi D. V. Kinetic and catalytic mechanism of HhaI methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4778–4786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]