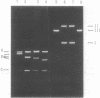
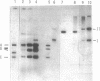
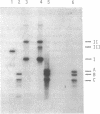
Abstract
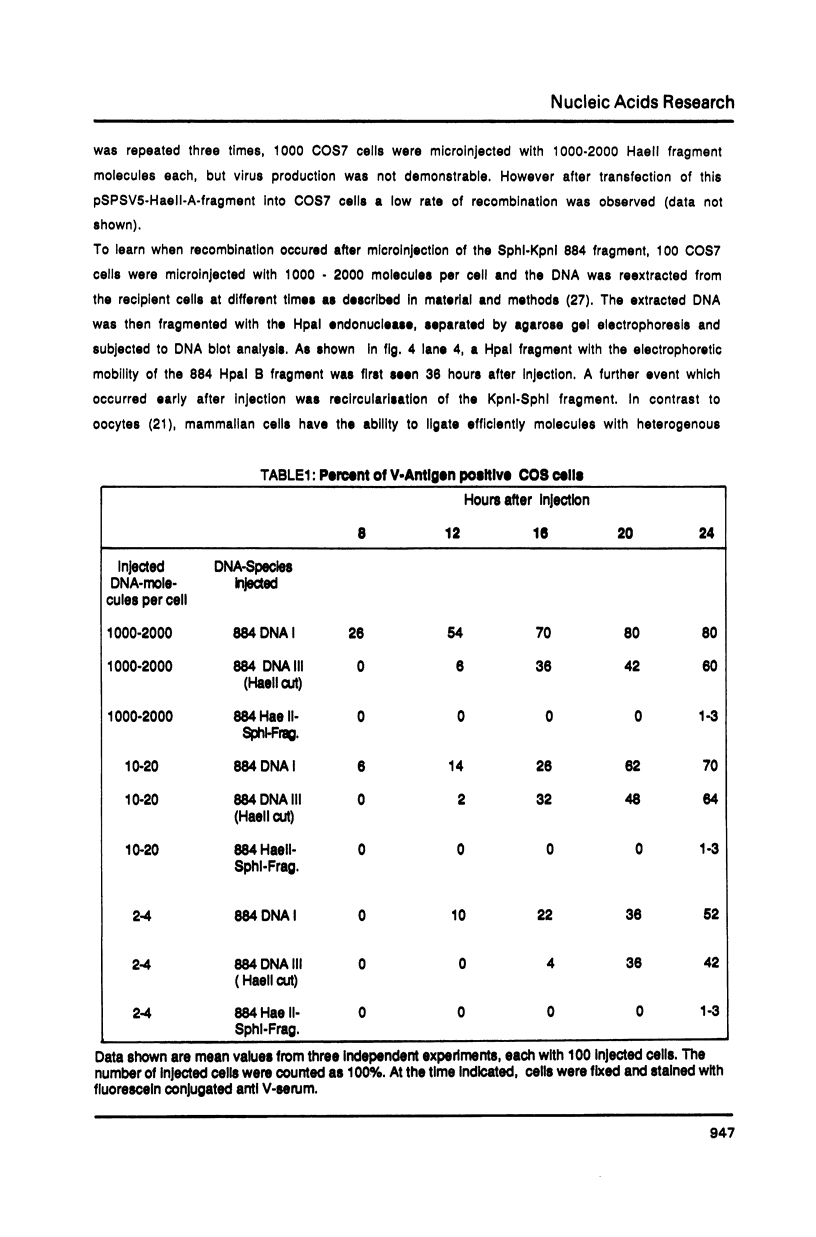
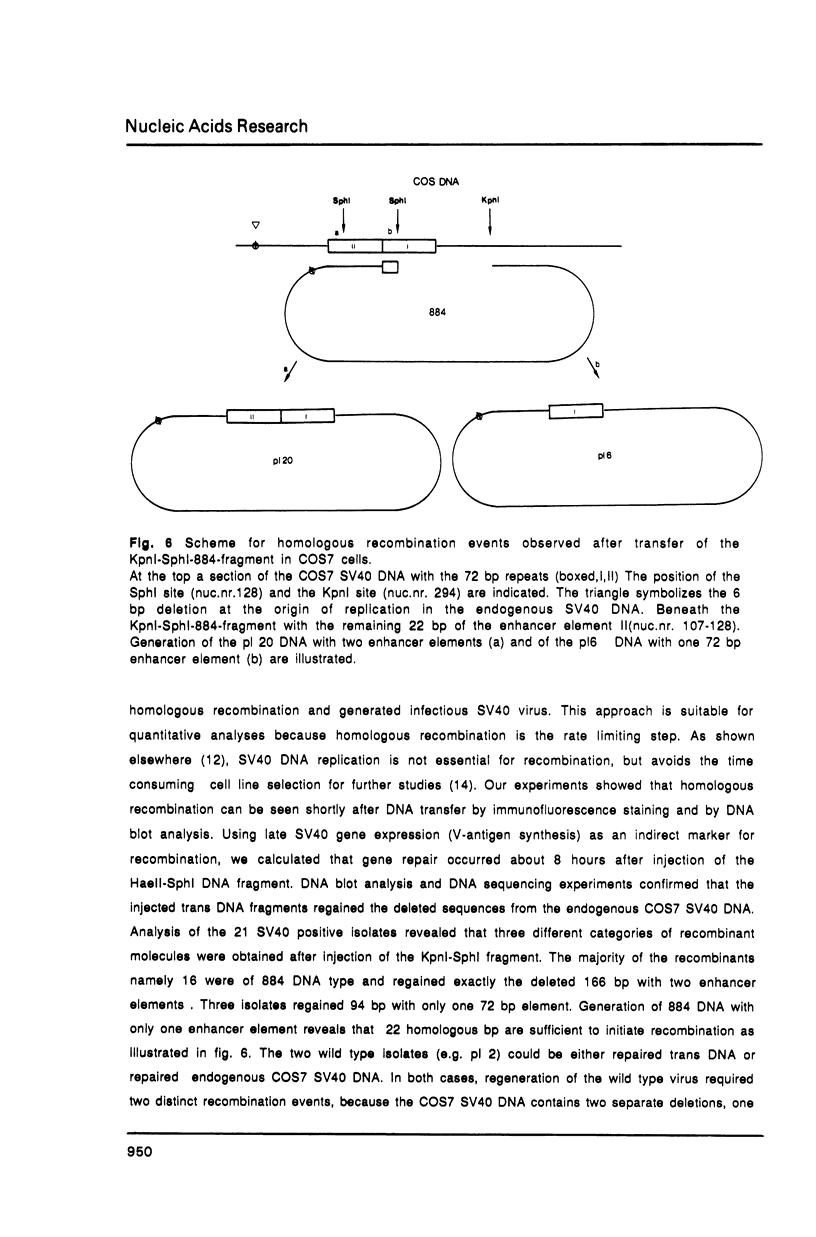
Homologous recombination between microinjected SV40 DNA fragments and endogenous SV40 DNA in COS7 cells was analysed by immunofluorescence staining and DNA blotting. Time course experiments revealed that recombination between the transferred (trans) DNA and the chromosomal DNA occurred about 8 hours after microinjection with high efficiency in a gene dose independent fashion. Deletions of up to 1018 basepairs (bp) within the early or the late SV40 region were efficiently repaired after the transfer of linear but not of circular DNA molecules. A 22 bp homology between the trans DNA and the endogenous DNA was sufficient to initiate recombination but 14 nonhomologous bp at one open end of the SV40 DNA fragments hindered gap repair.
Full text
PDF

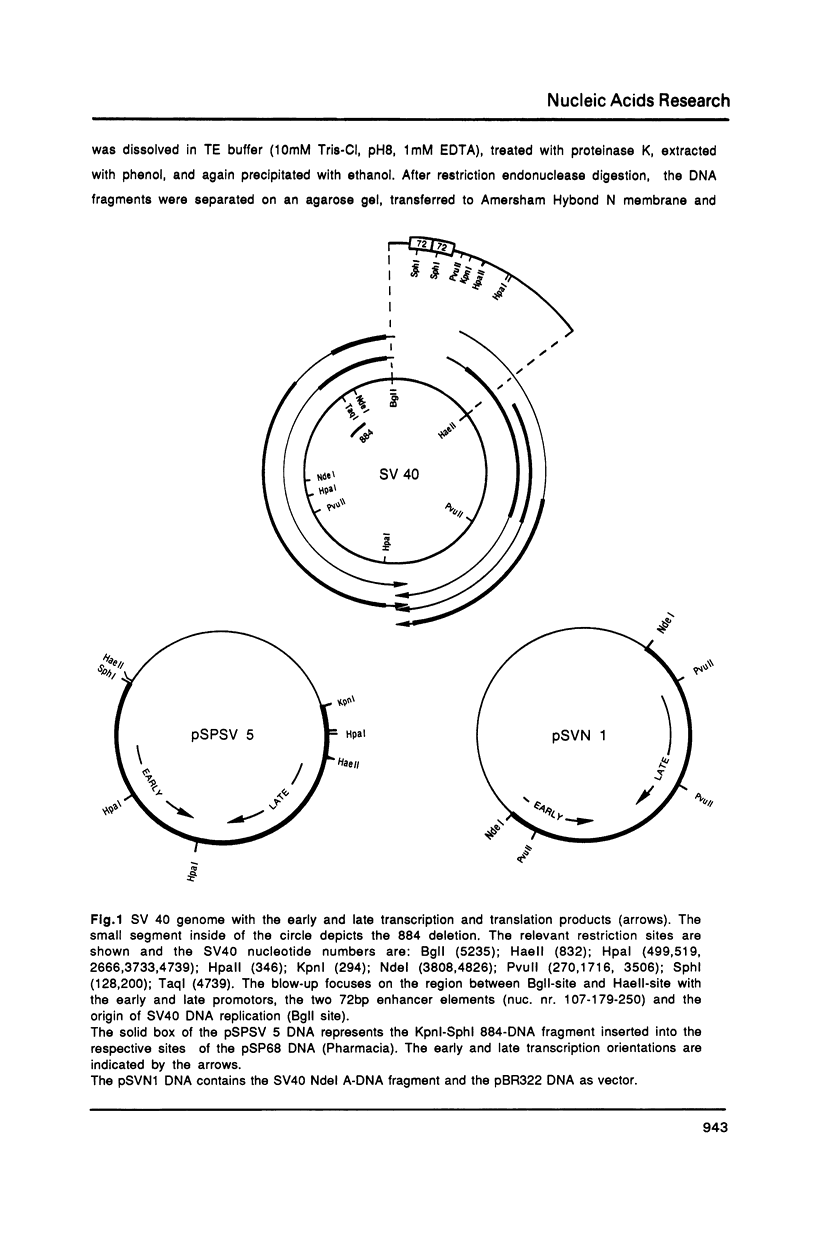







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer M., Guhl E., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Cellular mutation mediates T-antigen-positive revertant cells resistant to simian virus 40 transformation but not to retransformation by polyomavirus and adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1821–1827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1821-1827.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., Smigocki A. C., Camerini-Otero R. D. Double-strand gap repair results in homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1762–1766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschhausen G., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Inhibition of herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene expression by DNA methylation is an indirect effect. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5503–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschhausen G., Wittig B., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Chromatin structure is required to block transcription of the methylated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1177–1181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Wright S. H., Wolff R. K., Grzesiuk E., Maryon E. B. Efficient homologous recombination of linear DNA substrates after injection into Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2053–2061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Thomas K., Capecchi M. R. Nonreciprocal exchanges of information between DNA duplexes coinjected into mammalian cell nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):59–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Bumke-Vogt C., Buschhausen G., Bauer M., Graessmann M. SV40 chromatin structure is not essential for viral gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Tjian R., Topp W. C. Simian virus 40 small-t protein is required for loss of actin cable networks in rat cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1182–1191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1182-1191.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessman A. "Early" simian-virus-40-specific RNA contains information for tumor antigen formation and chromatin replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Simian virus 40 cRNA is processed into functional mRNA in microinjected monkey cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1081–1088. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessmann A., Westphal H. Microinjected simian virus 40 cRNA is spliced, as evidenced by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):296–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.296-299.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzesiuk E., Carroll D. Recombination of DNAs in Xenopus oocytes based on short homologous overlaps. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):971–985. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin M., de Villiers J., Weber F., Schaffner W. High frequency of homologous recombination in mammalian cells between endogenous and introduced SV40 genomes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:139–149. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Recombination in mouse L cells between DNA introduced into cells and homologous chromosomal sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1391–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Genetic applications of yeast transformation with linear and gapped plasmids. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:228–245. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauth S., Song K. Y., Ayares D., Wallace L., Moore P. D., Kucherlapati R. Transfection and homologous recombination involving single-stranded DNA substrates in mammalian cells and nuclear extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5587–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubnitz J., Subramani S. Rapid assay for extrachromosomal homologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):529–537. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gregg R. G., Boggs S. S., Koralewski M. A., Kucherlapati R. S. Insertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):230–234. doi: 10.1038/317230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Berg P. Homologous and nonhomologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1040–1052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S. Rescue of chromosomal T-antigen sequences onto extrachromosomally replicating, defective simian virus 40 DNA by homologous recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1320–1325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Nucleotide sequence analysis of viable deletion mutants lacking segments of the simian virus 40 genome coding for small t antigen. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):668–673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.668-673.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Folger K. R., Capecchi M. R. High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wende M., Dorbic T., Wittig B. Novel procedure of elution and concentration of nucleic acids with NACS Prepac minicolumns by electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):9043–9043. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.9043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Lemischka I. R., Nathan D. G., Mulligan R. C. Introduction of new genetic material into pluripotent haematopoietic stem cells of the mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):476–480. doi: 10.1038/310476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]