Abstract
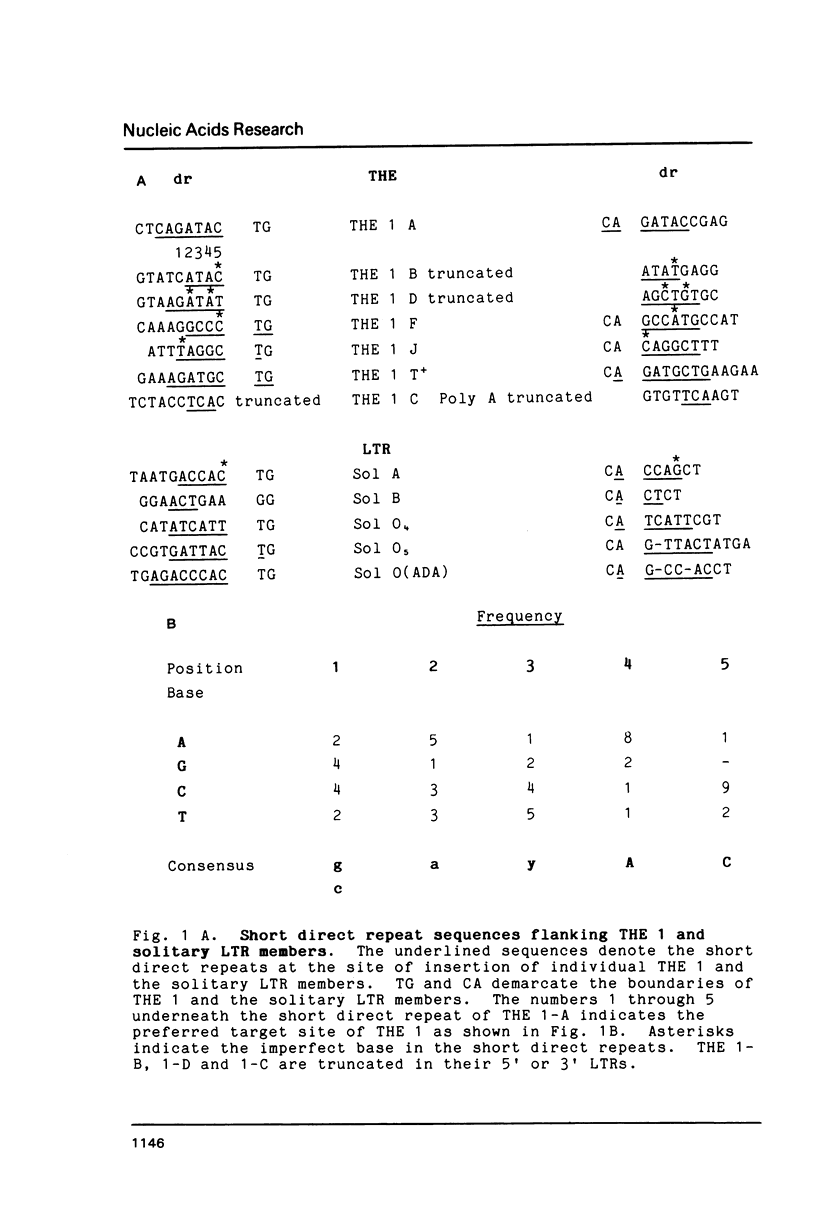
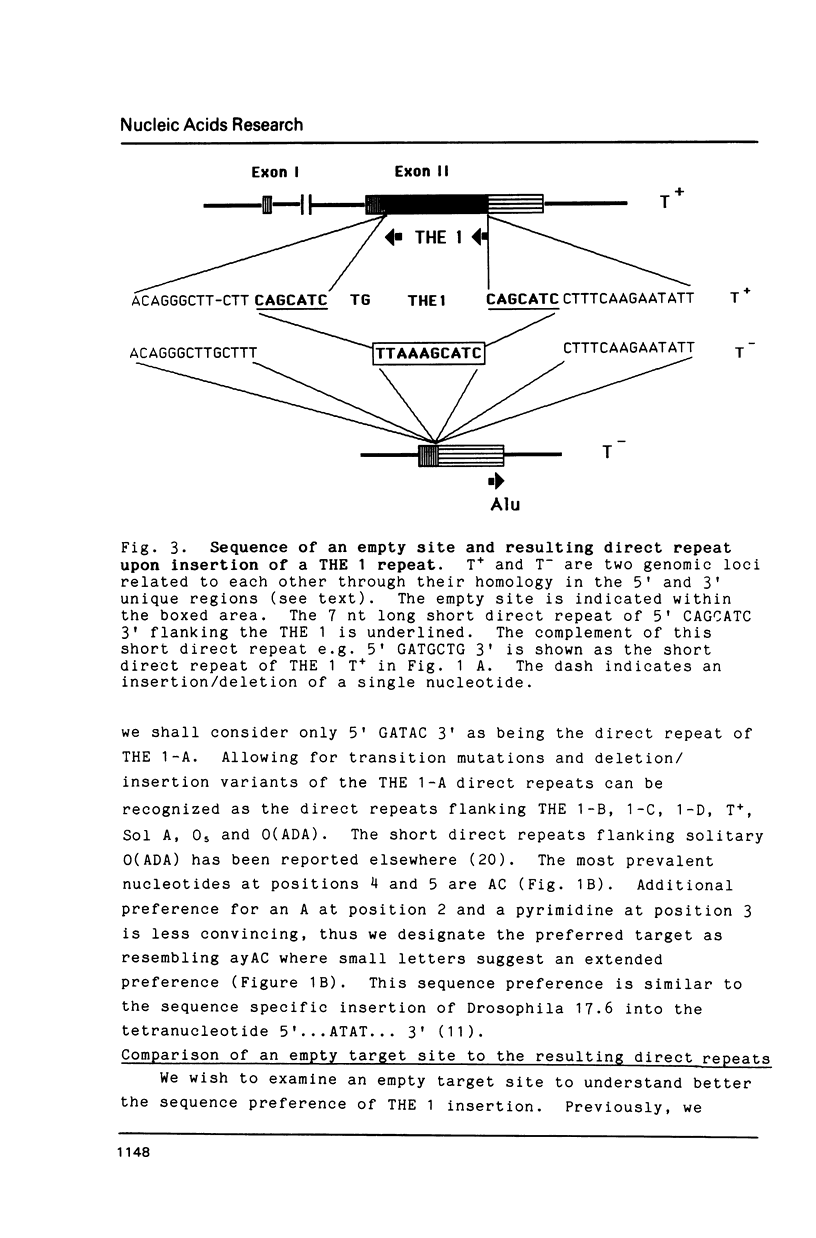
Members of the human transposon-like family of repetitive sequences (called THE 1 repeats) like many other repetitive DNA sequences are flanked by short direct repeats. Comparison of the base sequences of twelve examples of these flanking direct repeats indicates that THE 1 repeats insert into a preferred genomic target site. In one case, we have identified the sequence of an empty site into which a THE 1 element inserted. The sequence of this empty site and sequences of truncated THE 1 LTRs are consistent with a retroviral mechanism for the insertion of THE 1 elements. Truncated transposon structures illustrate for the first time that intermediate structures of retrotransposition may also be integrated into the genome.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arkhipova I. R., Mazo A. M., Cherkasova V. A., Gorelova T. V., Schuppe N. G., Llyin Y. V. The steps of reverse transcription of Drosophila mobile dispersed genetic elements and U3-R-U5 structure of their LTRs. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Mutants and pseudorevertants of Moloney murine leukemia virus with alterations at the integration site. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90114-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibel H., Philippsen P. Preferential integration of yeast transposable element Ty into a promoter region. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):386–388. doi: 10.1038/307386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. RNA from the yeast transposable element Ty1 has both ends in the direct repeats, a structure similar to retrovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Levis R., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. The 5' termini of RNAs encoded by the transposable element copia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6279–6291. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furano A. V., Somerville C. C., Tsichlis P. N., D'Ambrosio E. Target sites for the transposition of rat long interspersed repeated DNA elements (LINEs) are not random. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3717–3727. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C. Site-specific nicking at the avian retrovirus LTR circle junction by the viral pp32 DNA endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6205–6221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Sequence-specific insertion of the Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):332–333. doi: 10.1038/310332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Smith L., Hawley R., Hozumi N., Shulman M. Intracisternal A-particle genes as movable elements in the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1992–1996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Creation of a processed pseudogene by retroviral infection. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90759-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R., Shih A., Rush M., Wong E., Schmid C. W. Cloned extrachromosomal circular DNA copies of the human transposable element THE-1 are related predominantly to a single type of family member. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90687-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. Circles with two tandem LTRs are precursors to integrated retrovirus DNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Deka N., Schmid C. W., Misra R., Schindler C. W., Rush M. G., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. A transposon-like element in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):359–361. doi: 10.1038/316359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Matera A. G., Deka N., Schmid C. W. Transcription of a human transposon-like sequence is usually directed by other promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5199–5215. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Paulson K. E., Schmid C. W., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. Non-Alu family interspersed repeats in human DNA and their transcriptional activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2669–2690. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Structure, variation and synthesis of retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90353-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Form and function of retroviral proviruses. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):812–820. doi: 10.1126/science.6177038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiginton D. A., Kaplan D. J., States J. C., Akeson A. L., Perme C. M., Bilyk I. J., Vaughn A. J., Lattier D. L., Hutton J. J. Complete sequence and structure of the gene for human adenosine deaminase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8234–8244. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


